Abstract
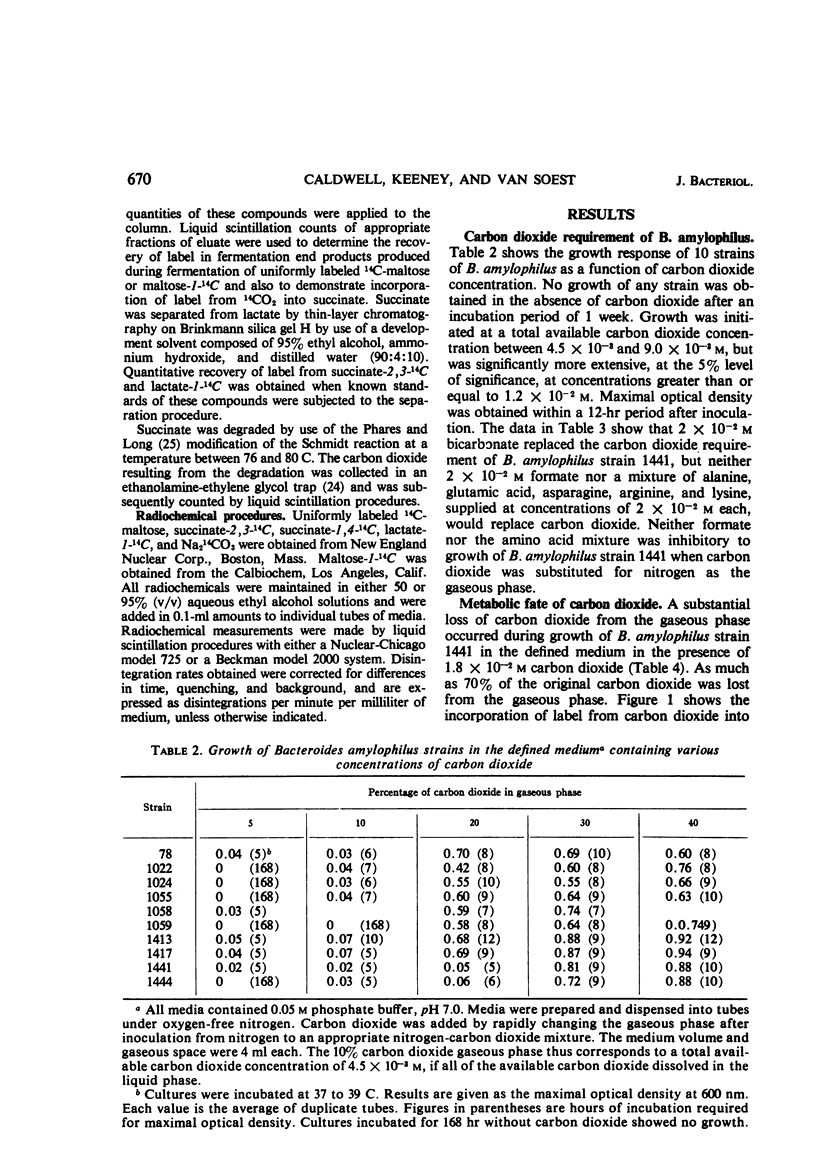
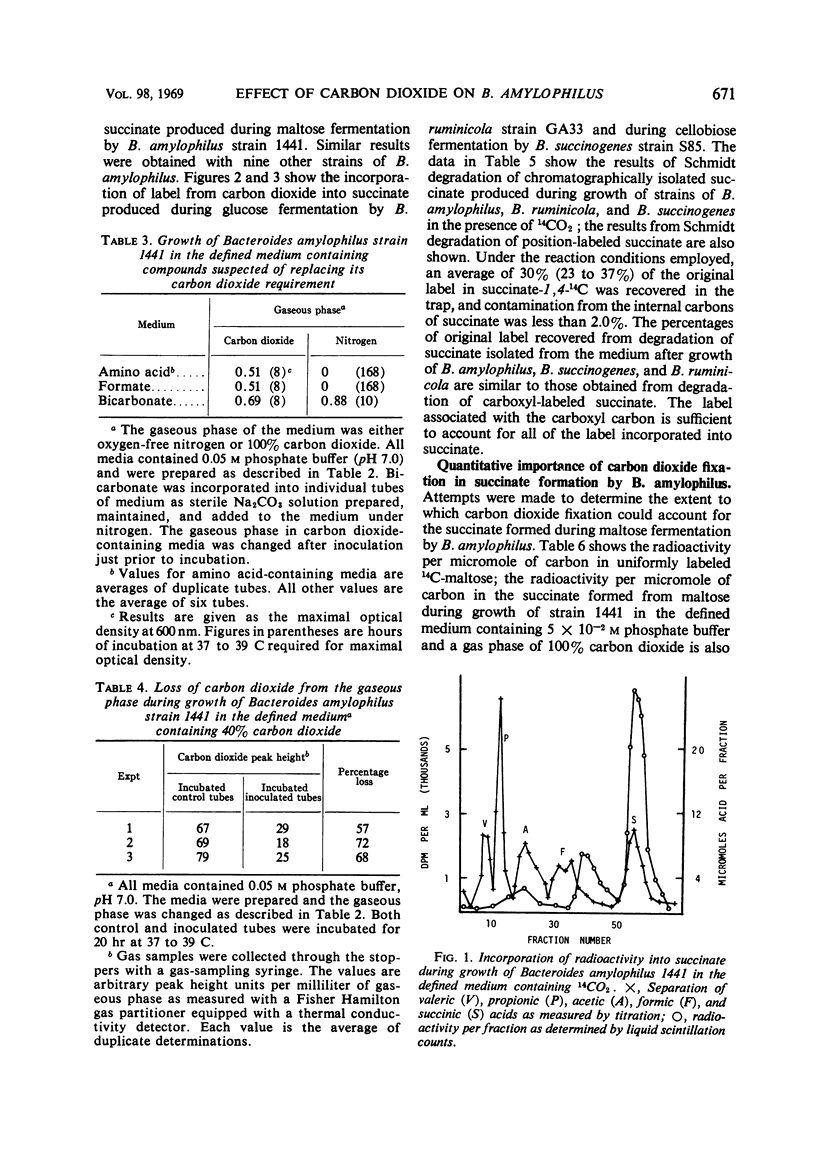
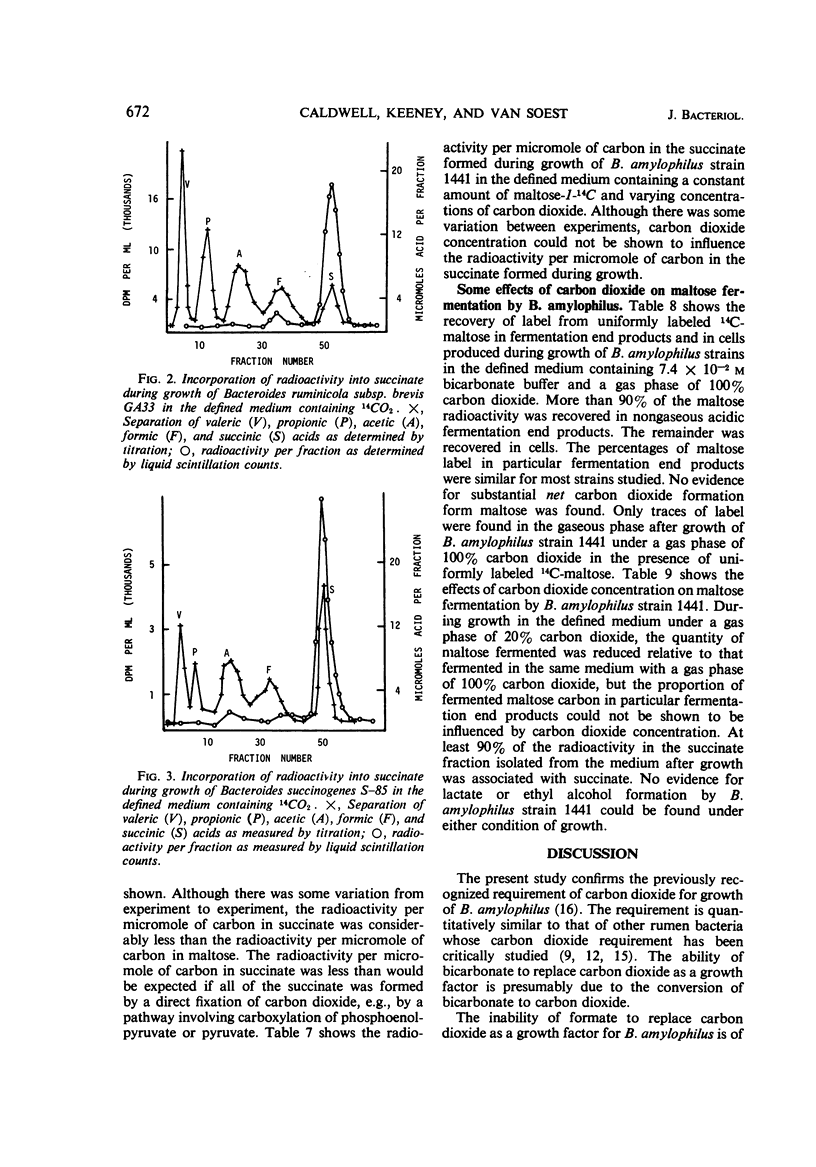
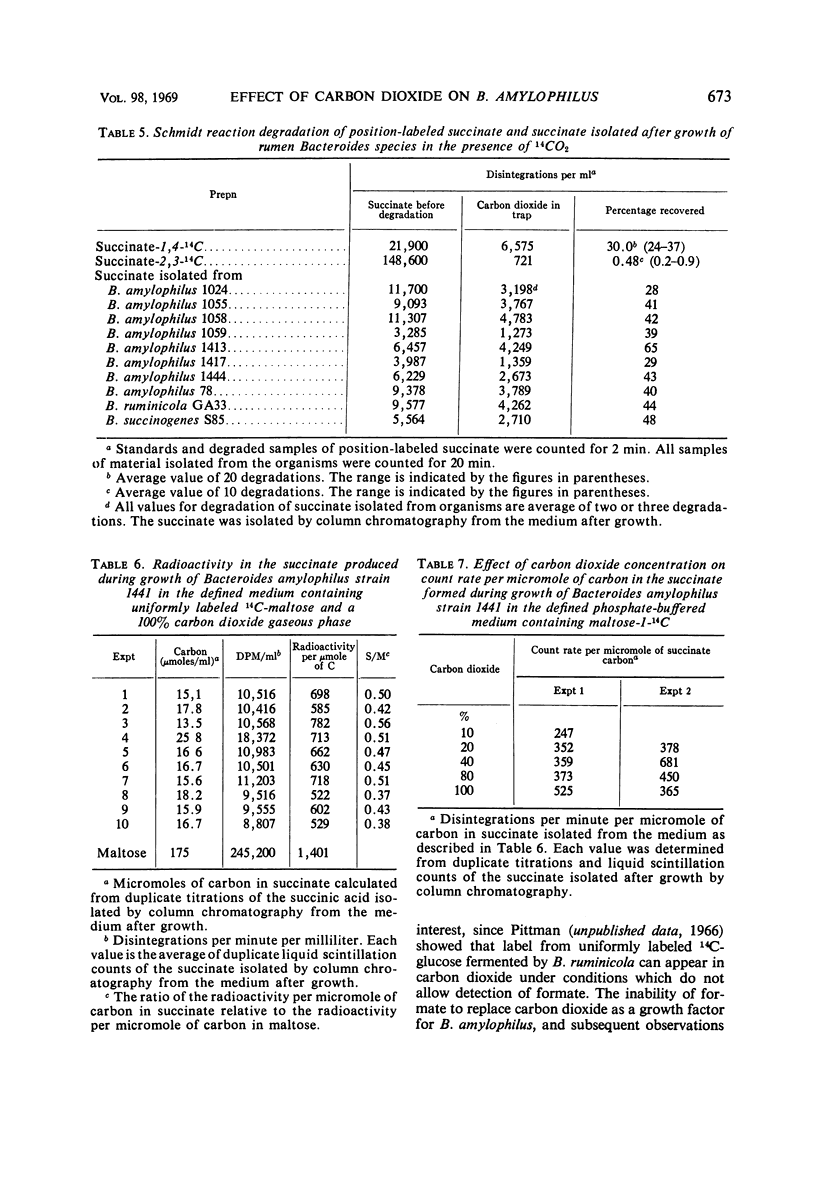
The requirement of carbon dioxide for growth of Bacteroides amylophilus is quantitatively similar to that of certain other rumen bacteria. Carbon dioxide could be replaced by bicarbonate, but not by formate or certain amino acids. Label from 14CO2 was incorporated into the succinate produced during maltose fermentation by B. amylophilus, and during glucose fermentation by B. ruminicola, and during cellobiose fermentation by B. succinogenes. All of the incorporated label could be associated with the carboxyl function of the molecule. The depression in radioactivity per micromole of carbon in the succinate formed from the fermentation of uniformly labeled 14C-maltose by B. amylophilus was greater than would be expected if all of the succinate formed was produced via a direct CO2 fixation pathway(s) involving phosphoenolpyruvate or pyruvate; the radioactivity per micromole of carbon suggests that as much as 60% of the total succinate results from a pathway(s) involving direct CO2 fixation. Maltose fermentation by B. amylophilus was dependent upon CO2 concentration, but CO2 concentration could not be shown to influence either the fermentation end-product ratios or the proportion of total succinate formed attributable to CO2 fixation.
Full text
PDF



Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- ALLISON M. J., BRYANT M. P. Biosynthesis of branched-chain amino acids from branched-chain fatty acids by rumen bacteria. Arch Biochem Biophys. 1963 May;101:269–277. doi: 10.1016/s0003-9861(63)80012-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- BARNES I. J., SEELEY H. W., VANDEMARK P. J. Nutrition of Streptococcus bovis in relation to dextran formation. J Bacteriol. 1961 Jul;82:85–93. doi: 10.1128/jb.82.1.85-93.1961. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- BRYANT M. P. Bacterial species of the rumen. Bacteriol Rev. 1959 Sep;23(3):125–153. doi: 10.1128/br.23.3.125-153.1959. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- BRYANT M. P., ROBINSON I. M., LINDAHL I. L. A note on the flora and fauna in the rumen of steers fed a feedlot bloat-provoking ration and the effect of penicillin. Appl Microbiol. 1961 Nov;9:511–515. doi: 10.1128/am.9.6.511-515.1961. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- BRYANT M. P., ROBINSON I. M. Some nutritional characteristics of predominant culturable ruminal bacteria. J Bacteriol. 1962 Oct;84:605–614. doi: 10.1128/jb.84.4.605-614.1962. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- BRYANT M. P., SMALL N., BOUMA C., CHU H. Bacteroides ruminicola n. sp. and Succinimonas amylolytica; the new genus and species; species of succinic acid-producing anaerobic bacteria of the bovine rumen. J Bacteriol. 1958 Jul;76(1):15–23. doi: 10.1128/jb.76.1.15-23.1958. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- CARROLL E. J., HUNGATE R. E. Formate dissimilation and methane production in bovine rumen contents. Arch Biochem Biophys. 1955 Jun;56(2):525–536. doi: 10.1016/0003-9861(55)90272-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- GILL J. W., KING K. W. Nutritional characteristics of a Butyrivibrio. J Bacteriol. 1958 Jun;75(6):666–673. doi: 10.1128/jb.75.6.666-673.1958. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- HAMLIN L. J., HUNGATE R. E. Culture and physiology of a starch-digesting bacterium (Bacteroides amylophilus n. sp.) from the bovine rumen. J Bacteriol. 1956 Oct;72(4):548–554. doi: 10.1128/jb.72.4.548-554.1956. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- HUHTANEN C. N., CARLETON F. J., ROBERTS H. R. Carbon dioxide utilization by rumen microorganisms. J Bacteriol. 1954 Dec;68(6):749–751. doi: 10.1128/jb.68.6.749-751.1954. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- HUNGATE R. E., BRYANT M. P., MAH R. A. THE RUMEN BACTERIA AND PROTOZOA. Annu Rev Microbiol. 1964;18:131–166. doi: 10.1146/annurev.mi.18.100164.001023. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- HUNGATE R. E. The anaerobic mesophilic cellulolytic bacteria. Bacteriol Rev. 1950 Mar;14(1):1–49. doi: 10.1128/br.14.1.1-49.1950. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hobson P. N., McDougall E. I., Summers R. The nitrogen sources of Bacteroides amylophilus. J Gen Microbiol. 1968 Mar;50(3 Suppl):i–i. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hobson P. N., Summers R. The continuous culture of anaerobic bacteria. J Gen Microbiol. 1967 Apr;47(1):53–65. doi: 10.1099/00221287-47-1-53. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hopgood M. F., Walker D. J. Succinic acid production by rumen bacteria. I. Isolation and metabolism of Ruminococcus flavefaciens. Aust J Biol Sci. 1967 Feb;20(1):165–182. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hopgood M. F., Walker D. J. Succinic acid production by rumen bacteria. II. Radioisotope studies on succinate production by Ruminococcus flavefaciens. Aust J Biol Sci. 1967 Feb;20(1):183–192. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- PRESCOTT J. M., STUTTS A. L. Effects of carbon dioxide on the growth and amino acid metabolism of Streptococcus bovis. J Bacteriol. 1955 Sep;70(3):285–288. doi: 10.1128/jb.70.3.285-288.1955. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- SMITH P. H., HUNGATE R. E. Isolation and characterization of Methanobacterium ruminantium n. sp. J Bacteriol. 1958 Jun;75(6):713–718. doi: 10.1128/jb.75.6.713-718.1958. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- WHITE D. C., BRYANT M. P., CALDWELL D. R. Cytochromelinked fermentation in Bacteroides ruminicola. J Bacteriol. 1962 Oct;84:822–828. doi: 10.1128/jb.84.4.822-828.1962. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- WRIGHT D. E. The metabolism of carbon dioxide by Streptococcus bovis. J Gen Microbiol. 1960 Jun;22:713–725. doi: 10.1099/00221287-22-3-713. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]



