Abstract
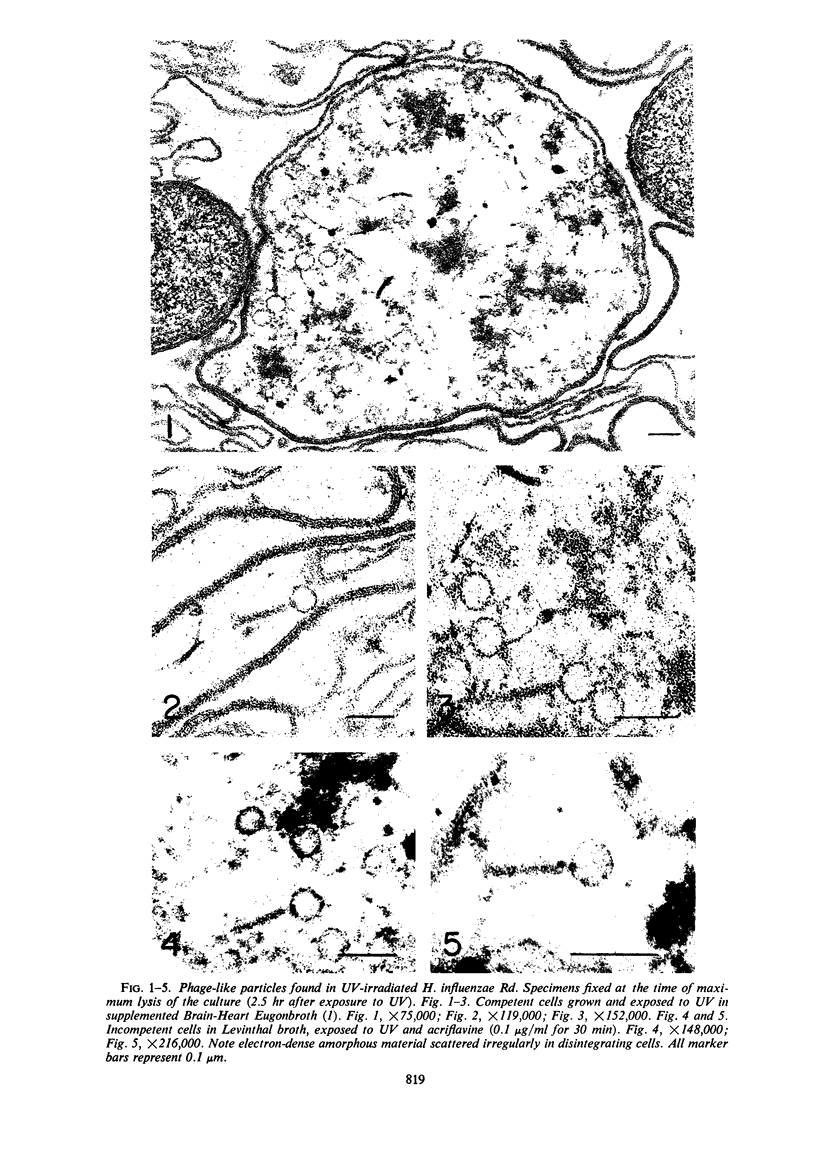
Incomplete phagelike particles were found in competent and incompetent cells of Haemophilus influenzae Rd (transformable) lysed after exposure to ultraviolet radiation.
Full text
PDF

Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- ALEXANDER H. E., HAHN E., LEIDY G. On the specificity of the desoxyribonucleic acid which induces streptomycin resistance in Hemophilus. J Exp Med. 1956 Sep 1;104(3):305–320. doi: 10.1084/jem.104.3.305. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- BARNHART B. J., HERRIOTT R. M. PENETRATION OF DEOXYRIBONUCLEIC ACID INTO HEMOPHILUS INFLUENZAE. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1963 Sep 17;76:25–39. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bradley D. E. Ultrastructure of bacteriophage and bacteriocins. Bacteriol Rev. 1967 Dec;31(4):230–314. doi: 10.1128/br.31.4.230-314.1967. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- LEIDY G., HAHN E., ALEXANDER H. E. Interspecific transformation in Hemophilus: a possible index of relationship between H. influenzae and H. aegyptius. Proc Soc Exp Biol Med. 1959 Oct;102:86–88. doi: 10.3181/00379727-102-25151. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- LIEB M. DARK REPAIR OF UV INDUCTION IN K12 (LAMBDA). Virology. 1964 Jul;23:381–388. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(64)90260-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- STUY J. H. Studies on the radiation inactivation of microorganisms. V. Deoxyribonucleic acid metabolism in ultraviolet-irradiated Haemophilus influenzae. J Bacteriol. 1959 Jul;78(1):49–58. doi: 10.1128/jb.78.1.49-58.1959. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]