Abstract
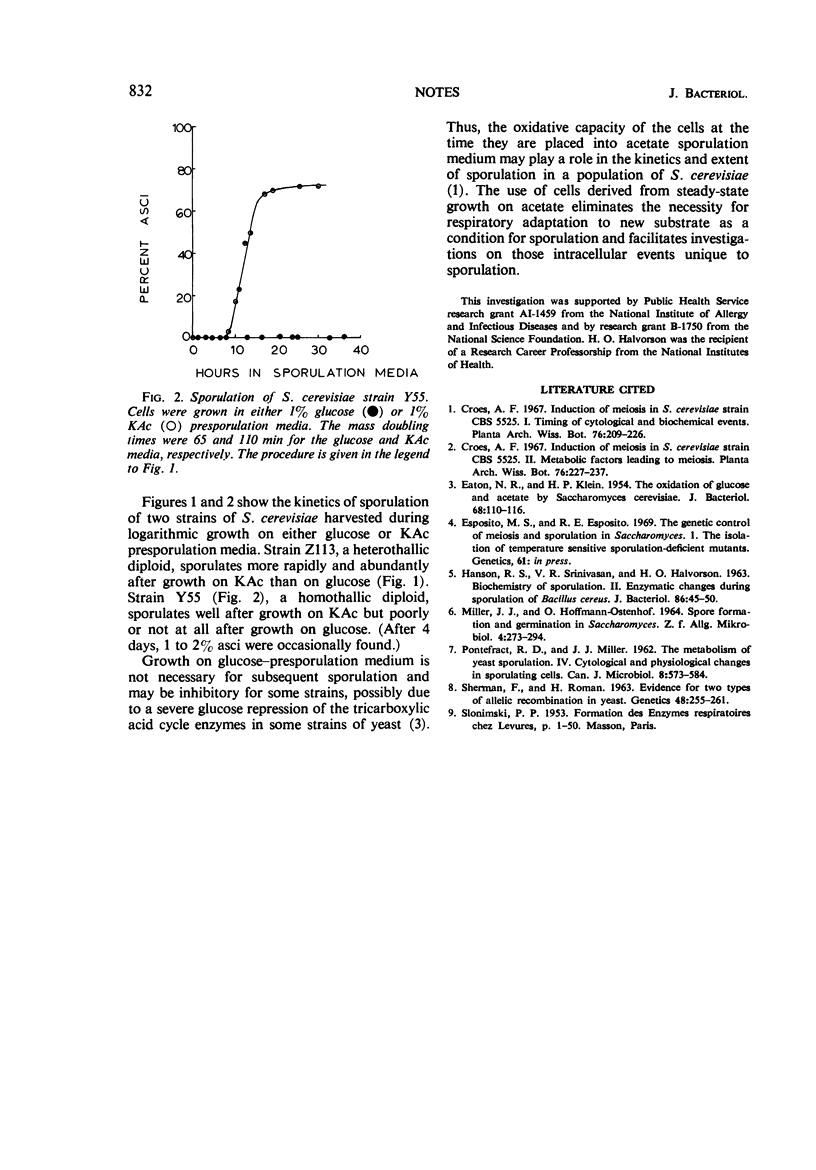
Rapid and abundant sporulation of yeast can be obtained, with cells harvested during logarithmic growth, by employing potassium acetate rather than glucose as a carbon source.
Full text
PDF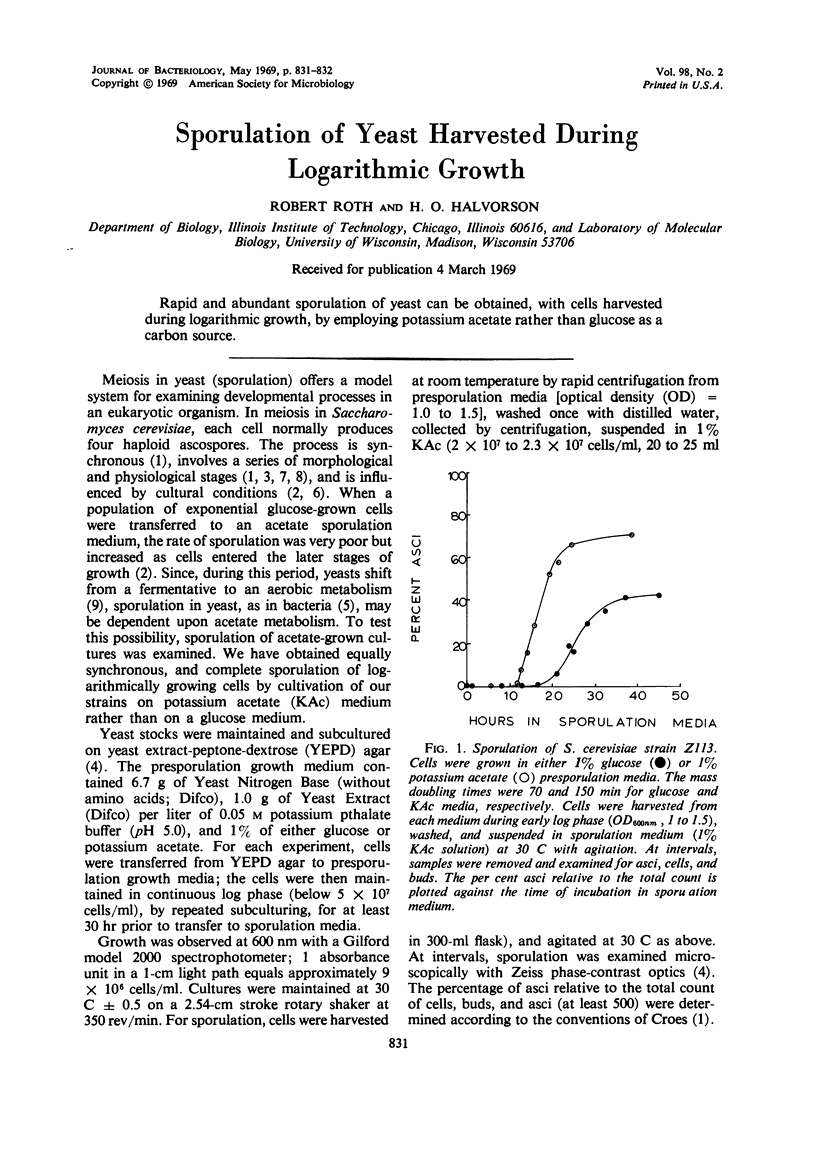
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- EATON N. R., KLEIN H. P. The oxidation of glucose and acetate by Saccharomyces cerevisiae. J Bacteriol. 1954 Jul;68(1):110–116. doi: 10.1128/jb.68.1.110-116.1954. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- HANSON R. S., SRINIVASAN V. R., HALVORSON H. O. BIOCHEMISTRY OF SPORULATION. II. ENZYMATIC CHANGES DURING SPORULATION OF BACILLUS CEREUS. J Bacteriol. 1963 Jul;86:45–50. doi: 10.1128/jb.86.1.45-50.1963. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- MILLER J. J., HOFFMANN-OSTENHOF C. SPORE FORMATION AND GERMINATION IN SACCHAROMYCES. Z Allg Mikrobiol. 1964;4:273–294. doi: 10.1002/jobm.3630040404. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- SHERMAN F., ROMAN H. Evidence for two types of allelic recombination in yeast. Genetics. 1963 Feb;48:255–261. doi: 10.1093/genetics/48.2.255. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]



