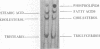Abstract
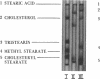
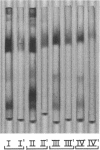
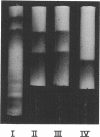
An improved apparatus and a procedure are described by which the migration of sample components in column chromatography is accelerated by centrifugal force, thereby making it possible to use beds of densely packed gel prepared with ultrafine silica. This technique was used to resolve components of certain lipid mixtures where other methods have failed, and it has been found generally useful as an adjunct to other methods for the fractionation of lipids. Biologically active phosphoglycolipids from Mycobacterium tuberculosis and a phosphatidylglycerol-like substance from Mycoplasma pneumoniae which formed single spots on thin-layer chromatographic plates were each found to contain a major and several minor components by centrifugal chromatography. The method enabled us to isolate individual components of Wax D from M. tuberculosis rather than a spectrum of components. Minor components were resolved which, although present in insufficient quantity to influence results of chemical analyses, may be responsible for biological activity. The apparatus provides an essentially closed system which reduces highly volatile solvents to minimal evaporation during the chromatographic process. Samples are applied in solution and are not allowed to dry on the columns until after separation has been achieved. Consequently, polar, labile microbial lipids can be resolved without the use of harsh reagents which destroy some of their properties. Single components may be harvested by cutting and removing appropriate segments of the larger chromatograms or by eluting them from the columns.
Full text
PDF










Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- AEBI A., ASSELINEAU J., LEDERER E. Sur les lipides de la souche humaine Brevannes. de Mycobacterium tuberculosis. Bull Soc Chim Biol (Paris) 1953;35(7):661–684. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Deyl Z., Rosmus J., Pavlícek M. Centrifugal chromatography. Chromatogr Rev. 1964;6:19–52. doi: 10.1016/0009-5907(64)80004-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- HAMILTON J. G., SWARTWOUT J. R., MILLER O. N., MULDREY J. E. A silica gel impregnated glass fiber filter paper and its use for the separation of cholesterol, triglycerides and the cholesteryl and methyl esters of fatty acids. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1961 Jun 28;5:226–230. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(61)90115-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Louis-Ferdinand R. T., Therriault D. G., Blatt W. F., Mager M. Application of thin-layer chromatography to the quantitation of plasma neutral lipids and free fatty acids. Clin Chem. 1967 Sep;13(9):773–787. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Milner K. C., Finkelstein R. A. Bioassay of endotoxin: correlation between pyrogenicity for rabbits and lethality for chick embryos. J Infect Dis. 1966 Dec;116(5):529–536. doi: 10.1093/infdis/116.5.529. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pangborn M. C., McKinney J. A. Purification of serologically active phosphoinositides of Mycobacterium tuberculosis. J Lipid Res. 1966 Sep;7(5):627–633. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Raff R. A., Wheat R. W. Carbohydrate composition of the phenol-soluble lipopolysaccharides of Citrobacter freundii. J Bacteriol. 1968 Jun;95(6):2035–2043. doi: 10.1128/jb.95.6.2035-2043.1968. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- STAHL E. Dünnschicht-Chromatographie; Methode, Einflussfaktoren und einige Anwendungsbeispiele. Pharmazie. 1956 Oct;11(10):633–637. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]