Abstract
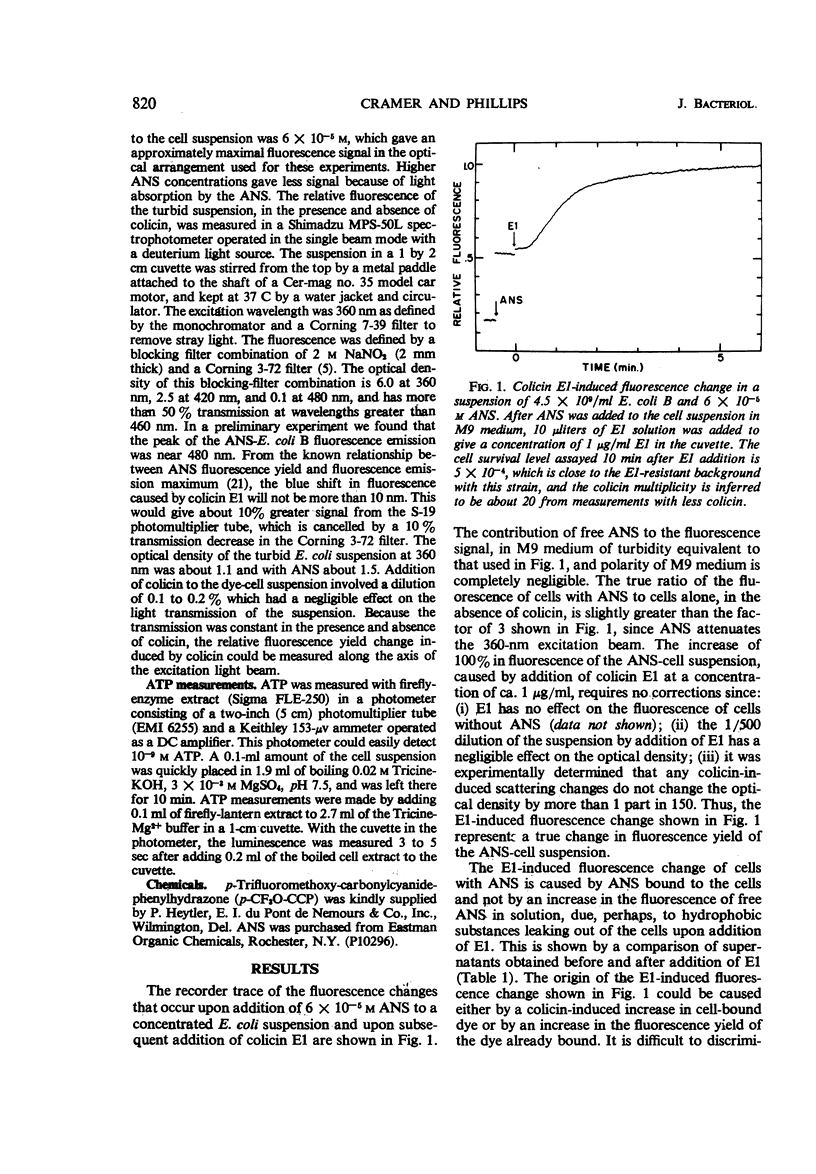
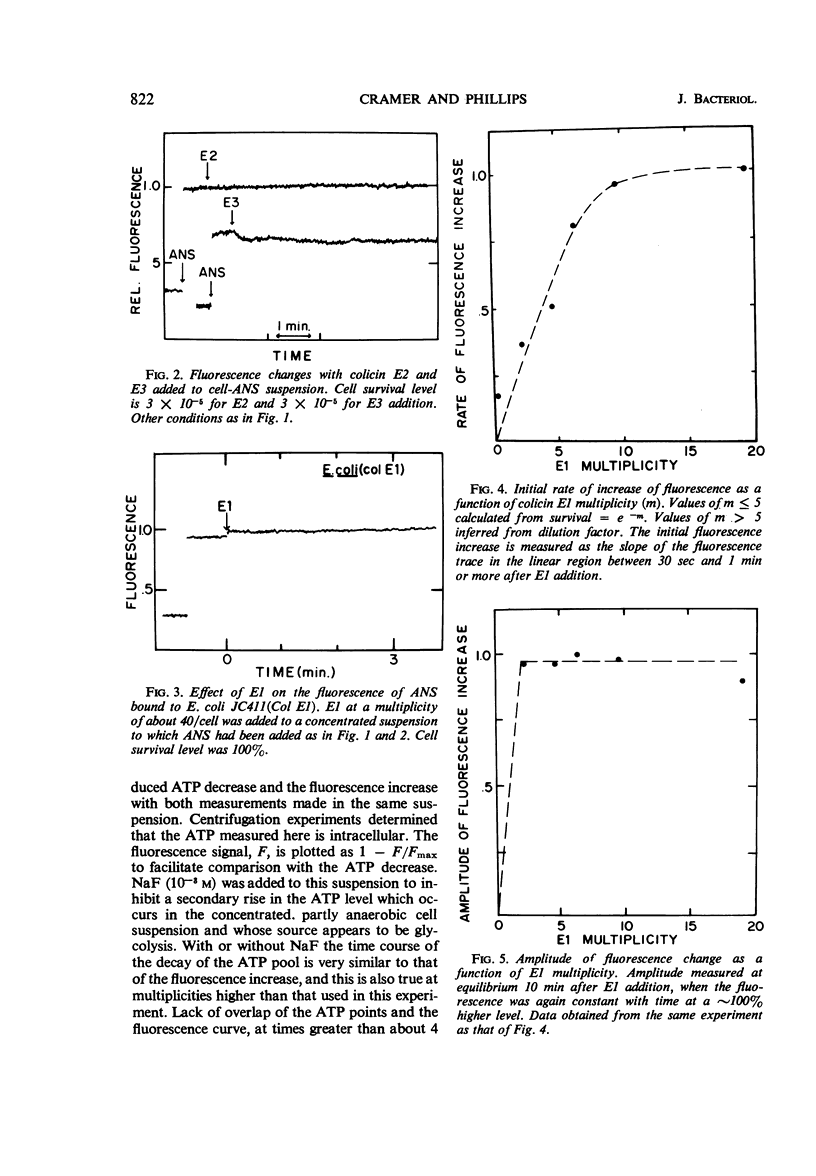
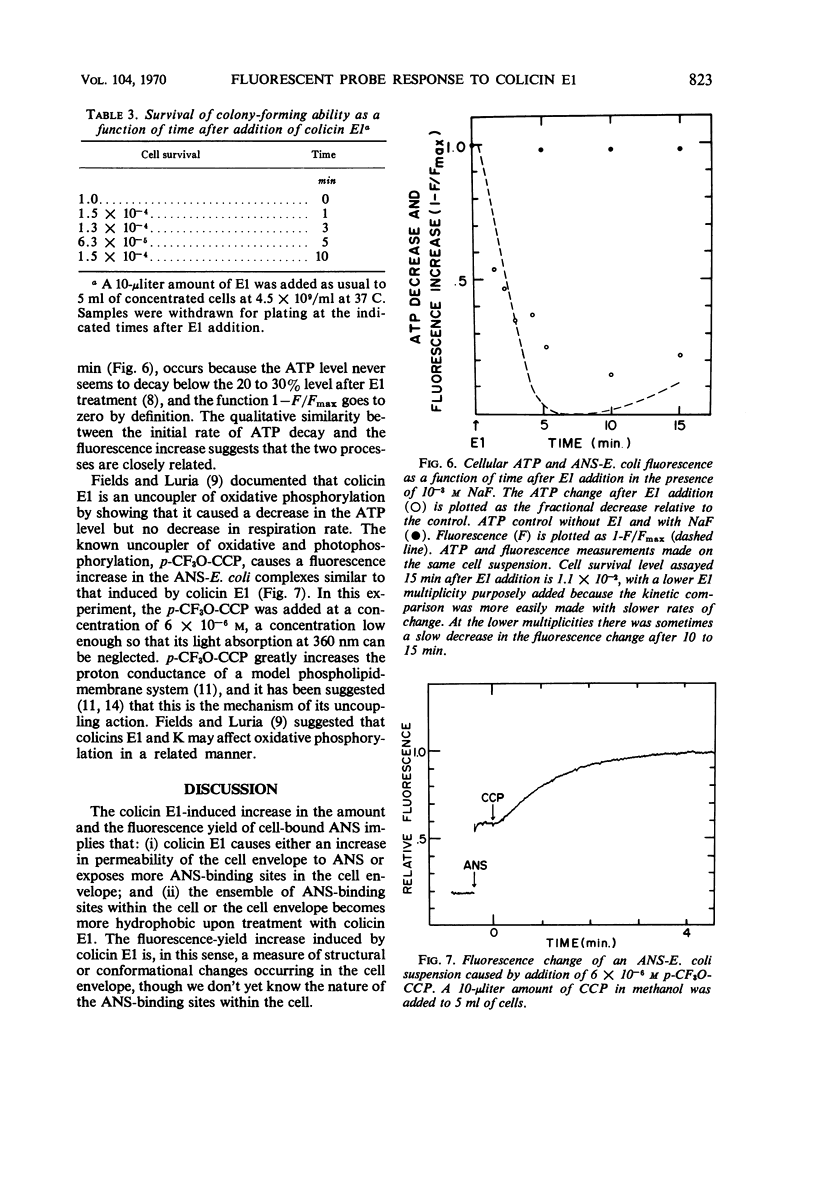
The fluorescent probe, 8-anilino-1-napthalenesulfonate (ANS) binds to Escherichia coli, showing an enhanced fluorescence. The interaction of colicin E1 with sensitive cells causes an increase of about 100% in the fluorescence of the bound ANS, and this change at equilibrium has an apparent “all-or-none” nature as a function of E1 multiplicity. Approximately 6 to 8% of the ANS is bound to the cells at equilibrium. The colicin E1-induced fluorescence increase can be attributed partly to an increase in ANS binding and partly to an increase in the fluorescence yield of the bound ANS. The kinetics of the E1-induced fluorescence increase in sensitive cells are very similar to those of the adenosine triphosphate decrease. The phosphorylation uncoupler p-trifluoromethoxy-carbonylcyanidephenylhydrazone also causes a large change in the fluorescence of bound ANS. Colicin E2 or E3 does not cause any fluorescence change, nor does colicin E1 cause fluorescence change with a colicinogenic strain. ANS appears to be a probe of structural or conformational change in the cell envelope that is closely associated with the colicin E1-induced adenosine triphosphate decrease.
Full text
PDF



Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Azzi A., Chance B., Radda G. K., Lee C. P. A fluorescence probe of energy-dependent structure changes in fragmented membranes. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1969 Feb;62(2):612–619. doi: 10.1073/pnas.62.2.612. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brand L., Gohlke J. R., Rao D. S. Evidence for binding of rose bengal and anilinonaphthalenesulfonates at the active site regions of liver alcohol dehydrogenase. Biochemistry. 1967 Nov;6(11):3510–3518. doi: 10.1021/bi00863a024. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- CONWAY E. J., DOWNEY M. An outer metabolic region of the yeast cell. Biochem J. 1950 Sep;47(3):347–355. doi: 10.1042/bj0470347. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Changeux J. P., Thiéry J., Tung Y., Kittel C. On the cooperativity of biological membranes. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1967 Feb;57(2):335–341. doi: 10.1073/pnas.57.2.335. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Daniel E., Weber G. Cooperative effects in binding by bovine serum albumin. I. The binding of 1-anilino-8-naphthalenesulfonate. Fluorimetric titrations. Biochemistry. 1966 Jun;5(6):1893–1900. doi: 10.1021/bi00870a016. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Datta A., Penefsky H. S. Interaction of fluorescent probes with submitochondrial particles during oxidative phosphorylation. J Biol Chem. 1970 Apr 10;245(7):1537–1544. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fields K. L., Luria S. E. Effects of colicins E1 and K on cellular metabolism. J Bacteriol. 1969 Jan;97(1):64–77. doi: 10.1128/jb.97.1.64-77.1969. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fields K. L., Luria S. E. Effects of colicins E1 and K on transport systems. J Bacteriol. 1969 Jan;97(1):57–63. doi: 10.1128/jb.97.1.57-63.1969. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Herschman H. R., Helinski D. R. Purification and characterization of colicin E2 and colicin E3. J Biol Chem. 1967 Nov 25;242(22):5360–5368. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hopfer U., Lehninger A. L., Thompson T. E. Protonic conductance across phospholipid bilayer membranes induced by uncoupling agents for oxidative phosphorylation. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1968 Feb;59(2):484–490. doi: 10.1073/pnas.59.2.484. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kasai M., Changeux J. P., Monnerie L. In vitro interaction of 1-anilino 8 naphthalene sulfonate with excitable membranes isolated from the electric organ of Electrophorus electricus. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1969 Aug 7;36(3):420–427. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(69)90581-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- LURIA S. E. ON THE MECHANISMS OF ACTION OF COLICINS. Ann Inst Pasteur (Paris) 1964 Nov;107:SUPPL–SUPPL:73. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mitchell P. Chemiosmotic coupling in oxidative and photosynthetic phosphorylation. Biol Rev Camb Philos Soc. 1966 Aug;41(3):445–502. doi: 10.1111/j.1469-185x.1966.tb01501.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- NOMURA M. MECHANISM OF ACTION OF COLICINES. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1964 Dec;52:1514–1521. doi: 10.1073/pnas.52.6.1514. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nagel de Zwaig R., Luria S. E. Genetics and physiology of colicin-tolerant mutants of Escherichia coli. J Bacteriol. 1967 Oct;94(4):1112–1123. doi: 10.1128/jb.94.4.1112-1123.1967. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nomura M., Witten C. Interaction of colicins with bacterial cells. 3. Colicin-tolerant mutations in Escherichia coli. J Bacteriol. 1967 Oct;94(4):1093–1111. doi: 10.1128/jb.94.4.1093-1111.1967. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rubalcava B., Martínez de Muñoz D., Gitler C. Interaction of fluorescent probes with membranes. I. Effect of ions on erythrocyte membranes. Biochemistry. 1969 Jul;8(7):2742–2747. doi: 10.1021/bi00835a008. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- SILVER S. ACRIFLAVINE RESISTANCE: A BACTERIOPHAGE MUTATION AFFECTING THE UPTAKE OF DYE BY THE INFECTED BACTERIAL CELLS. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1965 Jan;53:24–30. doi: 10.1073/pnas.53.1.24. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stryer L. Fluorescence spectroscopy of proteins. Science. 1968 Nov 1;162(3853):526–533. doi: 10.1126/science.162.3853.526. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tasaki I., Watanabe A., Sandlin R., Carnay L. Changes in fluorescence, turbidity, and birefringence associated with nerve excitation. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1968 Nov;61(3):883–888. doi: 10.1073/pnas.61.3.883. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vanderkooi J., Martonosi A. Sarcoplasmic reticulum. 8. Use of 8-anilino-1-naphthalene sulfonate as conformational probe on biological membranes. Arch Biochem Biophys. 1969 Aug;133(1):153–163. doi: 10.1016/0003-9861(69)90499-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]



