Abstract
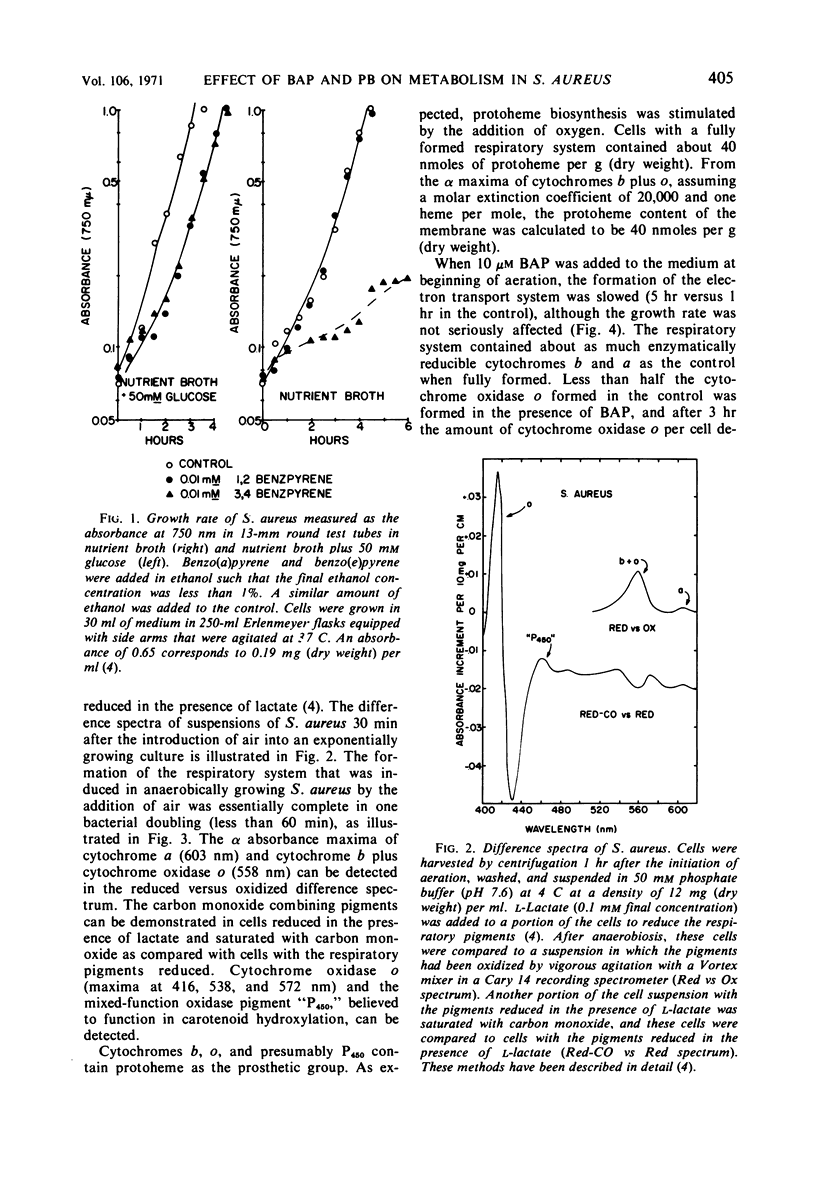
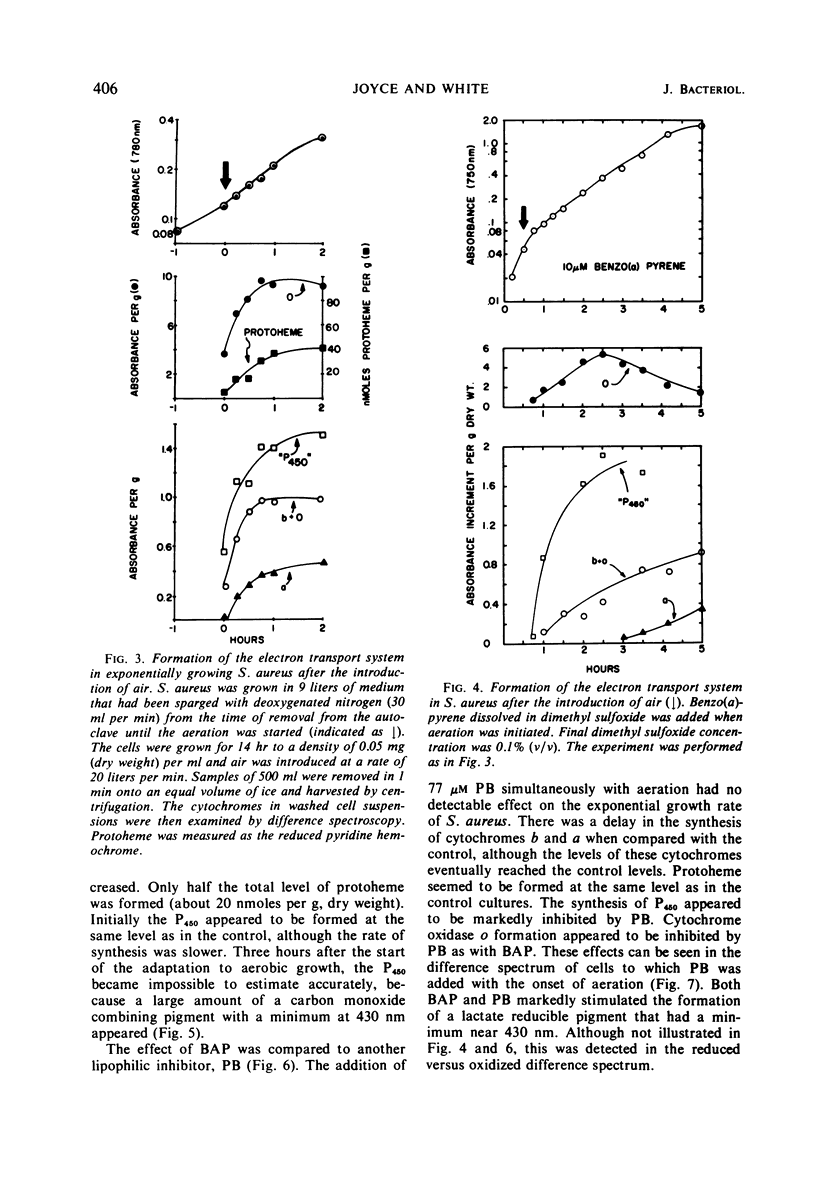
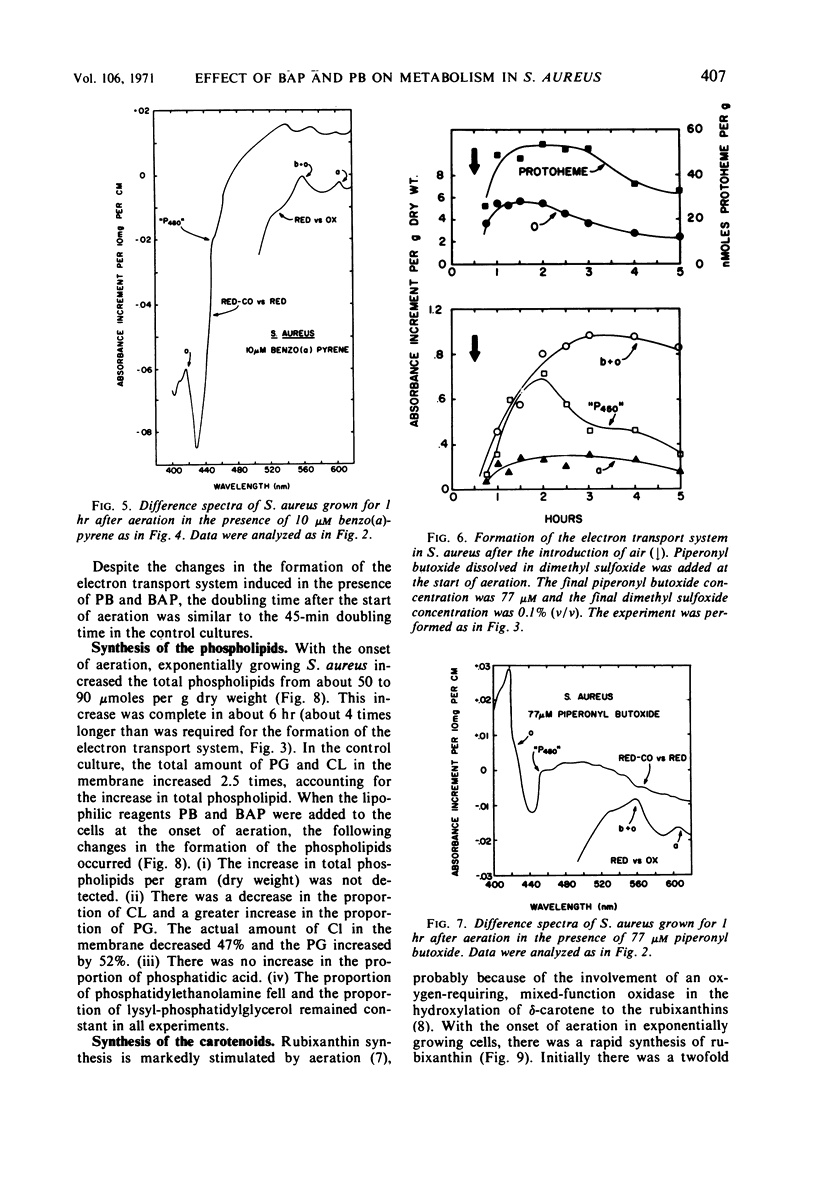
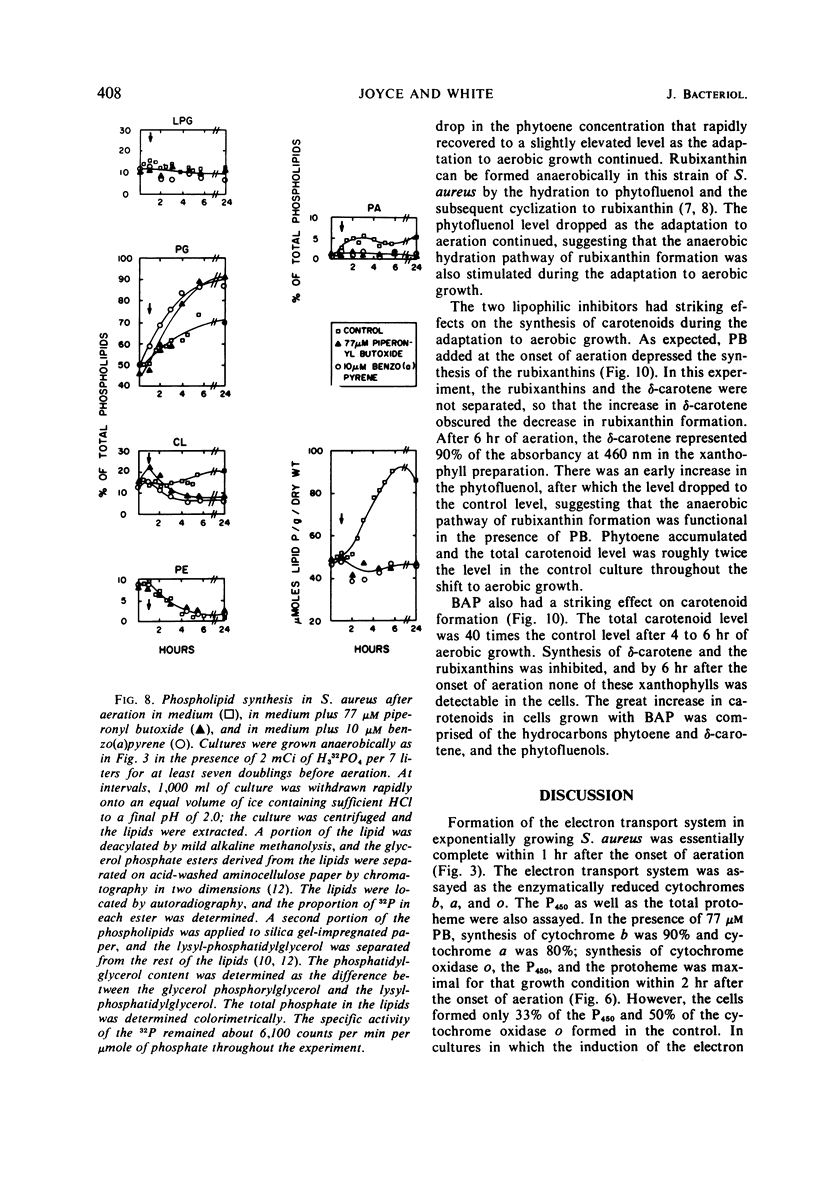
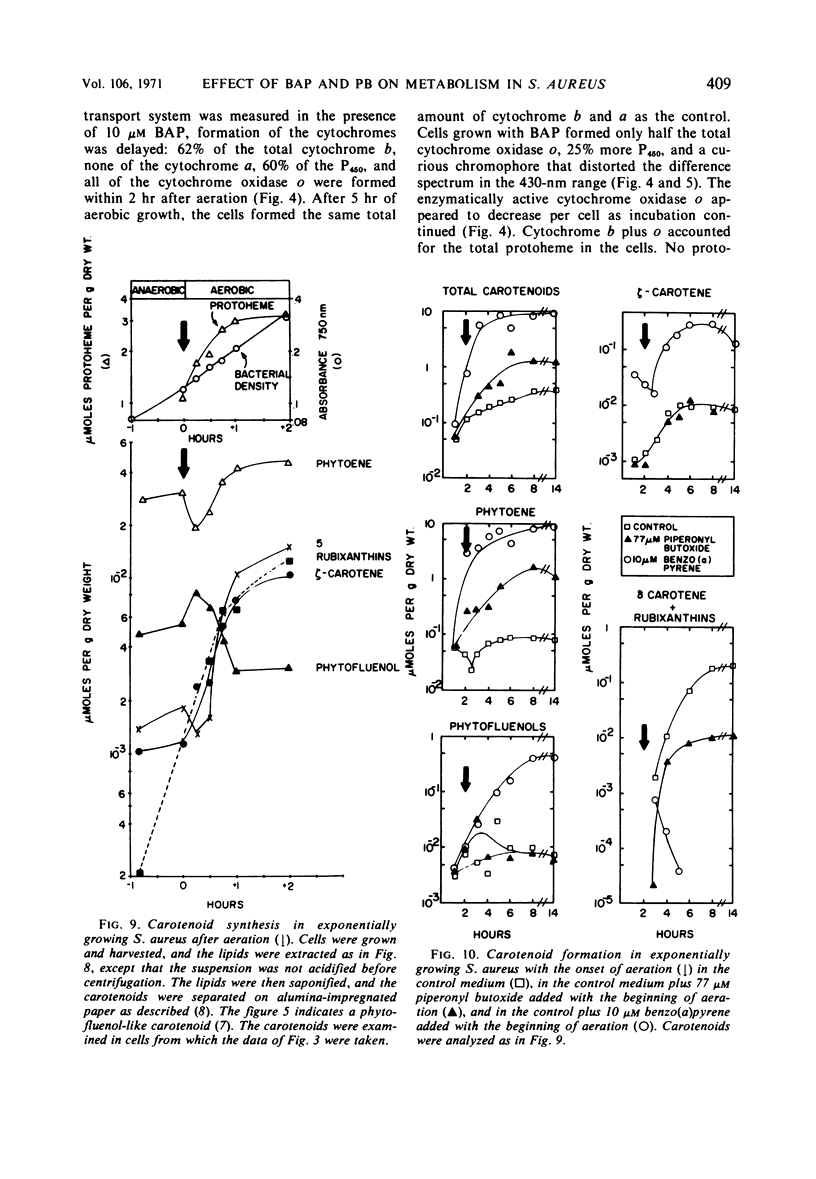
Staphylococcus aureus formed an electron transport system when exponentially growing cells were aerated. Formation of the electron transport system occurred concomitantly with increases in the phospholipids and the carotenoids. The addition of piperonyl butoxide or benzo(a)pyrene at the onset of aeration (i) slowed the formation of the electron transport system, (ii) both inhibited cytochrome oxidase o synthesis and decreased its stability, (iii) simultaneously depressed the increase in total phospholipid (especially cardiolipin), and (iv) depressed the synthesis of the carotenoid rubixanthin. Benzo(a)pyrene was the more inhibitory of the two, both on the rate of synthesis of the electron transport system and on rubixanthin formation. Evidence obtained with the inhibitors suggested that inhibition of the lipid synthesis was related to the formation of the electron transport system.
Full text
PDF



Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- CONNEY A. H., MILLER E. C., MILLER J. A. Substrate-induced synthesis and other properties of benzpyrene hydroxylase in rat liver. J Biol Chem. 1957 Oct;228(2):753–766. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Epstein S. S., Andrea J., Clapp P., Mackintosh D. Enhancement by piperonyl butoxide of acute toxicity due to Freons, benzo[alpha]pyrene, and griseofulvin in infant mice. Toxicol Appl Pharmacol. 1967 Nov;11(3):442–448. doi: 10.1016/0041-008x(67)90045-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Frerman F. E., White D. C. Membrane lipid changes during formation of a functional electron transport system in Staphylococcus aureus. J Bacteriol. 1967 Dec;94(6):1868–1874. doi: 10.1128/jb.94.6.1868-1874.1967. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hammond R. K., White D. C. Carotenoid formation by Staphylococcus aureus. J Bacteriol. 1970 Jul;103(1):191–198. doi: 10.1128/jb.103.1.191-198.1970. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hammond R. K., White D. C. Formation of vitamin K2 isoprenologues by Staphylococcus aureus. J Bacteriol. 1969 Nov;100(2):573–578. doi: 10.1128/jb.100.2.573-578.1969. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hammond R. K., White D. C. Inhibition of carotenoid hydroxylation in Staphylococcus aureus by mixed-function oxidase inhibitors. J Bacteriol. 1970 Sep;103(3):607–610. doi: 10.1128/jb.103.3.607-610.1970. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hammond R. K., White D. C. Inhibition of vitamin K2 and carotenoid synthesis in Staphylococcus aureus by diphenylamine. J Bacteriol. 1970 Sep;103(3):611–615. doi: 10.1128/jb.103.3.611-615.1970. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hammond R. K., White D. C. Separation of vitamin K2 isoprenologues by reversed-phase thin-layer chromatography. J Chromatogr. 1969 Dec 23;45(3):446–452. doi: 10.1016/s0021-9673(01)86242-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Joyce G. H., Hammond R. K., White D. C. Changes in membrane lipid composition in exponentially growing Staphylococcus aureus during the shift from 37 to 25 C. J Bacteriol. 1970 Oct;104(1):323–330. doi: 10.1128/jb.104.1.323-330.1970. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kuntzman R., Mark L. C., Brand L. C., Jacobson B. M., Levin W., Conney A. H. Metabolism of drugs and carcinogens by human liver enzymes. J Pharmacol Exp Ther. 1966 Apr;152(1):151–156. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Short S. A., White D. C. Metabolism of the glycosyl diglycerides and phosphatidylglucose of Staphylococcus aureus. J Bacteriol. 1970 Oct;104(1):126–132. doi: 10.1128/jb.104.1.126-132.1970. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tucker A. N., White D. C. Heterogeneity of phospholipid composition in the bacterial membrane. J Bacteriol. 1970 May;102(2):508–513. doi: 10.1128/jb.102.2.508-513.1970. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tucker A. N., White D. C. Metabolism of phospholipid 2-linked fatty acids during the release of membrane fragments from Haemophilus parainfluenzae by ethylenediaminetetraacetic acid-tris(hydroxymethyl)-aminomethane. J Bacteriol. 1970 Aug;103(2):329–334. doi: 10.1128/jb.103.2.329-334.1970. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- White D. C., Frerman F. E. Extraction, characterization, and cellular localization of the lipids of Staphylococcus aureus. J Bacteriol. 1967 Dec;94(6):1854–1867. doi: 10.1128/jb.94.6.1854-1867.1967. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- White D. C., Frerman F. E. Fatty acid composition of the complex lipids of Staphylococcus aureus during the formation of the membrane-bound electron transport system. J Bacteriol. 1968 Jun;95(6):2198–2209. doi: 10.1128/jb.95.6.2198-2209.1968. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- White D. C. Lipid composition of the electron transport membrane of Haemophilus parainfluenzae. J Bacteriol. 1968 Oct;96(4):1159–1170. doi: 10.1128/jb.96.4.1159-1170.1968. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- White D. C., Tucker A. N. Phospholipid metabolism during bacterial growth. J Lipid Res. 1969 Mar;10(2):220–233. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- White D. C., Tucker A. N. Phospholipid metabolism during changes in the proportions of membrane-bound respiratory pigments in Haemophilus parainfluenzae. J Bacteriol. 1969 Jan;97(1):199–209. doi: 10.1128/jb.97.1.199-209.1969. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


