Abstract
Bone marrow stromal cells [BMSCs; also known as mesenchymal stem cells (MSCs)] effectively suppress inflammatory responses in acute graft-versus-host disease in humans and in a number of disease models in mice. Many of the studies concluded that BMSC-driven immunomodulation is mediated by the suppression of proinflammatory Th1 responses while rebalancing the Th1/Th2 ratio toward Th2. In this study, using a ragweed induced mouse asthma model, we studied if BMSCs could be beneficial in an allergic, Th2-dominant environment. When BMSCs were injected i.v. at the time of the antigen challenge, they protected the animals from the majority of asthma-specific pathological changes, including inhibition of eosinophil infiltration and excess mucus production in the lung, decreased levels of Th2 cytokines (IL-4, IL-5, and IL-13) in bronchial lavage, and lowered serum levels of Th2 immunoglobulins (IgG1 and IgE). To explore the mechanism of the effect we used BMSCs isolated from a variety of knockout mice, performed in vivo blocking of cytokines and studied the effect of asthmatic serum and bronchoalveolar lavage from ragweed challenged animals on the BMSCs in vitro. Our results suggest that IL-4 and/or IL-13 activate the STAT6 pathway in the BMSCs resulting in an increase of their TGF-β production, which seems to mediate the beneficial effect, either alone, or together with regulatory T cells, some of which might be recruited by the BMSCs. These data suggest that, in addition to focusing on graft-versus-host disease and autoimmune diseases, allergic conditions—specifically therapy resistant asthma—might also be a likely target of the recently discovered cellular therapy approach using BMSCs.
Keywords: allergy, cellular therapy, immunomodulation, mesenchymal stem cell
Asthma is a chronic inflammatory airway disease affecting 16 million people in the United States alone and more than 300 million worldwide (1). It can range from a mild, intermittent disease to one that is severe, persistent, and difficult to treat (i.e., therapy-resistant) (2). Asthma-related deaths are uncommon, but they appear to be increasing; currently there are approximately 5,000 deaths per year in the United States and 100,000 throughout the world (3). New treatments are needed for therapy-resistant, severe cases.
Bone marrow stromal cells (BMSCs) have recently been shown to suppress harmful immune responses in patients with acute graft-versus-host disease (4, 5) and in several animal models of allogeneic rejection (6–8), a variety of autoimmune diseases (9–11), and lung injury (12–15). The authors of many of these studies concluded that BMSC-driven immunosuppression results from a shift in Th1/Th2 balance (8, 16, 17). During BMSC treatment, Th1 responses appear to be decreasing while Th2 responses begin to dominate. In animals with established allergies, Th2 responses are already dominant, and we wondered how BMSCs would react to such an environment. In this study we thus examined the effect of BMSCs on Th2-driven allergic reactions in a mouse model of asthma (18, 19).
Results
Lung Pathology.
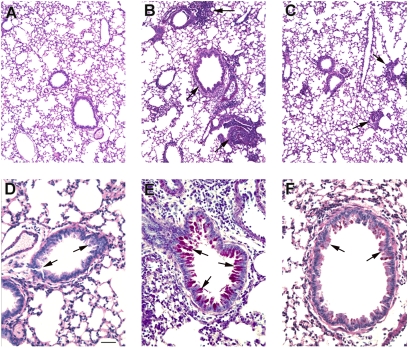
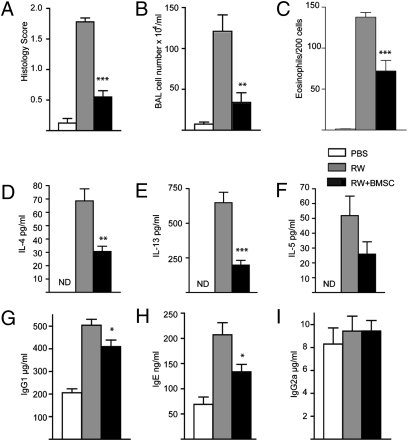
Following ragweed (RW) challenge (for timing of the events see Fig. 1), microscopic examination of the lungs showed minimal or no inflammation in mice sensitized with PBS solution and alum but no RW (Fig. 2A). Conversely, RW-sensitized mice showed extensive inflammation with eosinophil and lymphocyte invasion and severe perivascular and peribronchial cuffing (Fig. 2B). Mice that were challenged with RW but treated with i.v. injections of BMSCs had significantly less lung pathology: few inflammatory cell infiltrates were observed (Fig. 2C). Although no abnormal mucus-filled cells were observed in controls as defined by histological staining using PAS (Fig. 2D), the amount of stainable mucus in the airways was visibly increased following RW challenge (Fig. 2E). BMSC treatment reduced the amount of mucus to near control levels (Fig. 2F). In addition to improved lung scores (Fig. 3A), we also observed a significant decrease in both total inflammatory cell numbers and eosinophils in the bronchoalveolar lavage (BAL) fluid (Fig. 3 B and C).
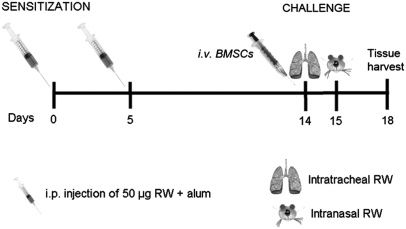
Fig. 1.
Timeline of the experiments showing the days of the interventions.
Fig. 2.
Histological images of airways stained with PAS to show the mucin-producing goblet cells (dark red in the lumen). Low-magnification images depict a control lung (A), a lung following RW challenge with no treatment (B), and a lung with BMSC treatment (C). Note the significant increase in lymphocytic infiltrates (arrows) in B and their decrease in C. The high magnification images of the airways show a normal bronchus in D, a bronchus from RW-challenged mouse with mucus buildup (arrows) in the luminal surface (E), and a treated mouse with less mucus in F. (Scale bar, 250 μm in A–C and 50 μm in D–F.)
Fig. 3.
Evaluation of the effect of BMSC treatment on the different parameters of RW-induced asthma. Mice treated with BMSCs showed a significant reduction in lung histology scores (A), total number of BAL cells (B), relative ratio of BAL eosinophils (C), and levels of allergy-specific Th2 cytokines IL-4 (D), IL-13 (E), and IL5 (F) in BAL. From the sera of challenged mice we measured Ig concentrations, and in the BMSC-treated group we found a significant decrease in the level of Th2-specific Ig concentrations IgG1 (G) and IgE (H), whereas there was no change in the level of IgG2a (I). There were four to eight mice per group. *P < 0.05, **P < 0.01, and ***P < 0.001 in all graphs.
Cytokine Response.
RW-challenged mice showed increased levels of IL-4, IL-13, and IL-5 in BAL, all characteristic Th2 cytokines that highlight allergic inflammation. IL-4 and IL-13 levels were significantly reduced when the animals were treated with i.v. BMSCs (Fig. 3 D–F).
Ig Response.
RW sensitization and subsequent antigen challenge is known to affect Th2-specific Ig concentrations in blood (19). Indeed, we found that both IgG1 and IgE serum levels were significantly increased following RW application, whereas IgG2a did not change. BMSC treatment resulted in a significant decrease of RW induced elevation of IgG1 and IgE concentrations (Fig. 3 G–I).
Use of Allogeneic BMSCs or Skin Fibroblasts Instead of Syngeneic BMSCs.
In a few groups of mice, we determined whether there was a difference in effect when we use allogeneic BMSCs prepared from Balb/C mice or syngeneic C57BL/6J dermal fibroblasts instead of syngeneic (C57/BL6) BMSCs. We measured total cell numbers and the number of eosinophils (Fig. 4 A and B) as well as IL-4 and IL-13 levels (Fig. 4 C and D) from BAL and immunoglobulins from serum (Fig. 4 E–G). We found that there was no significant difference between syngeneic versus allogeneic BMSCs (i.e., both were equally effective), and skin fibroblasts had only partial effect. Although the number of total cells in BAL was reduced following fibroblast treatment, the number of eosinophils was not different from the untreated group. Fibroblasts behaved similarly to BMSCs in regulating cytokine levels, but they had no effect on serum IgE concentrations. Interestingly, IgG2a levels were highly increased following fibroblast administration—an effect that we never observed using BMSCs.
Fig. 4.
Assessing the effect of allogeneic BMSCs or syngeneic skin fibroblasts on RW-induced asthma. Allogeneic BMSCs exhibit a similar inhibitory effect as syngeneic BMSCs on the total number of BAL cells (A), relative ratio of eosinophils (B), BAL inflammatory cytokines IL-4 (C) and IL-13 (D), and serum immunoglobulins IgG1 (E), IgE (F), and IgG2a (G). There were four to eight mice per group. Skin fibroblasts had a partial effect on the aforementioned parameters (see same graphs).
Searching for Mechanism of Action.
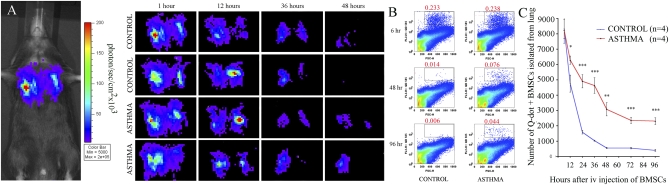
One hour after i.v. injection of BMSCs on d 14, the cells were found exclusively in the lung whereas virtually no cells were seen in other organs as demonstrated by bioluminescence measurements using luciferase expressing stromal cells (Fig. 5A). To determine if the inflammatory environment seen in asthma could influence homing to and/or survival of BMSCs in the lung, we injected luciferase-expressing cells into animals on d 14, immediately after intraairway application of PBS solution or RW. Comparing emitted luminescence at different time points we assessed the number of stromal cells still present in the lungs. At 1, 12, and 24 h, the number of BMSCs in control and asthmatic animals were comparable, whereas at 36 h—and more evidently after 48 h—we detected considerably more BMSCs in the asthmatic lungs (Fig. 5A). To follow up on this observation, we injected Q-dot–labeled BMSCs into control and RW-challenged animals and isolated the Q-dot–positive BMSCs from the protease-digested lung cell suspensions using FACS. At 6, 12, and 24 h after injection, the number of Q-dot–positive cells did not differ between the two groups. After 36 h, however, we detected a significant increase in the number of BMSCs retained in the asthmatic lungs, and this difference remained detectable at 48, 72, and 96 h after BMSC injection (Fig. 5 B and C). These observations suggest that the developing allergic environment is capable to attract and retain more BMSCs than unaffected lungs, indicating that asthmatic lungs are likely to secrete factors that affect BMSC homing and survival. We next continued to explore the nature of such factors.
Fig. 5.
After i.v. delivery of BMSCs at the time of the first challenge, stromal cells are concentrated in the lung. Asthmatic lungs seem to retain more BMSCs than control unchallenged lungs at 48 h after administration, demonstrated by bioluminescence detection of luciferase-expressing stromal cells. Two representative mice of three used are shown (A). To confirm this observation, Q-dot–labeled BMSCs were injected at the time of the first challenge, and lung cell suspensions were analyzed using FACS at several time points after injection. After 6 h, the number of Q-dot–positive cells (BMSCs) are still comparable in the two groups (each had four mice), but starting at 12 h there are significantly more BMSCs retained in the asthmatic lungs compared with the controls at all time points examined (B and C).
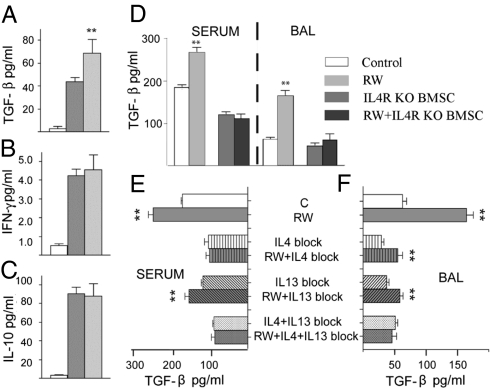
Among the number of cytokines known to suppress allergic responses the antiinflammatory actions of IL-10, TGFβ, and IFN-γ are especially well established. To determine whether any of these factors contributes to the beneficial effect of BMSCs, we first examined their levels in BAL fluid. There was a significant increase in the level of TGF-β in BAL fluid collected from BMSC-treated versus untreated mice, but no change in IFN-γ or IL-10 levels (Fig. 6 A–C). As TGF-β was increased in BAL fluid, and BMSCs are reported to be able to secrete TGF-β (20), we next asked whether serum or BAL fluid from RW-challenged mice could affect TGF-β production by BMSCs in vitro. TGF-β increased in the medium when BMSCs were cultured in the presence of RW-challenged serum or BAL, suggesting that allergy-specific microenvironment (i.e., serum or BAL) is capable of modulating immunoregulatory functions of BMSCs. It has been reported that stimulation of certain immune cells through the IL-4R pathway results in up-regulated TGF-β expression (32). To find out if enhanced TGF-β production by BMSCs in the presence of allergic serum or BAL could be triggered by activation through the IL-4R, we repeated the aforementioned experiments using IL-4R–deficient BMSCs. We found that RW-challenged serum or BAL could not enhance TGF-β production in IL-4R–KO BMSCs, suggesting an important role for IL-4 (Fig. 6D).
Fig. 6.
Studying the mechanism of BMSC effect. In BAL BMSC treatment resulted in elevated TGF-β levels (A). IFN-γ (B) and IL-10 (C) did not change. Serum or BAL from RW challenged mice induced BMSCs to producemore TGF-β in vitro, but this effect was eliminated when BMSCs lacked IL-4Ra (D). Using neutralizing antibodies for IL-4 or IL-13 suggested both cytokines are involved in stimulating BMSC's TGF-β production when cocultured with serum (E) or BAL (F) from RW challenged mice.
As both IL-4 and IL-13 are able to bind to IL-4R, in another series of experiments we examined the effect of blocking (using specific antibodies) IL-4, IL-13, or both on the TGF-β production by BMSCs when they came in contact with RW-sensitized serum or BAL (Fig. 6 E and F). When serum from RW challenged mice was added to the media, IL4 neutralization alone eliminated the increased TGF-β production but blocking IL-13 did not have this effect (Fig. 6E). Interestingly, when BAL from RW challenged mice was added, the BMSCs increased their TGF-β production even when either IL-4 or IL-13 was blocked; however, blocking both cytokines simultaneously eliminated the effect (Fig. 6F). On the other hand, neither recombinant IL-4 or IL-13 alone or in combination increased TGF-β production (Fig. S1), suggesting a possible role for other factors.
When treating mice with TGF-β– and IL-10–specific neutralizing antibodies before BMSC injection, we observed that blocking TGF-β—but not IL-10—eliminated the beneficial effect of BMSCs demonstrated by the lack of reduction in BAL total cell numbers and eosinophil counts (Fig. 7 A and B). Furthermore, in mice injected with TGF-β1–KO BMSCs, the beneficial effect was no longer seen: treated animals showed no reduction in BAL cell numbers, asthma-specific BAL cytokines, or serum Th2 immunoglobulins. Importantly TGF-β1–KO cells were unable to elicit increase in BAL TGF-β concentrations, suggesting that BMSC-derived TGF-β1 is responsible for the effect (Fig. 7C).
Fig. 7.
In vivo demonstration of mechanism of action. The beneficial effect of BMSCs on inflammatory changes is eliminated in the presence of TGF-β neutralizing antibodies, but spared when animals are treated with anti-IL-10 antibodies (A and B). BMSCs from TGF-β or STAT6 deficient animals did not induce TGF-β production (C) or decrease BAL total cell numbers (D), eosinophil numbers (E), cytokine levels (F and G), or serum immunoglobulin concentrations (H–J).
The IL-4 receptor is known to activate the STAT6 signaling pathway (21). To see if the IL4Ra/STAT6 pathway is indeed necessary for the BMSCs to act beneficially in an allergic environment—as suggested by the in vitro studies just described—we injected STAT6-deficient BMSCs instead of WT cells and observed no TGF-β elevation in the BAL samples (Fig. 7C). In accordance with this result the elimination of STAT6 also reversed the BMSC-derived attenuation of RW-induced asthma, pointing to the importance of the IL4R/STAT6 pathway (Fig. 7 D–J).
As regulatory T cells (T-regs) are known to play a role in alleviating asthma symptoms and TGF-β has been suggested to play a role in T-reg differentiation, we wondered if the number of T-regs in the lung tissue could also be affected by the BMSC treatment in our model. Analyzing lung single cell suspensions using FACS, we detected a steady increase in the number of T-regs in challenged animals over time. Importantly, as early as after 48 h, as well as after 72 and 96 h after challenge, we found significantly more T-regs in the BMSC-treated lungs than the ones collected from challenged but untreated animals (Fig. 8).
Fig. 8.
Quantification of regulatory T cells in asthmatic lungs. With time there is a gradual increase in the number of regulatory T cells in lungs challenged with RW. BMSC-treated asthmatic lungs show a greater influx of T-regs starting at 36 h after challenge and further increasing up to 96 h.
Discussion
Asthma is an inflammatory disease of the airways. In asthma, the lungs are invaded by a variety of inflammatory cells, including eosinophils and lymphocytes. These cells, in addition to resident mast cells, secrete cytokines and chemokines that trigger constriction of the bronchi and secretion of mucus.
The current working hypothesis is that asthma is caused by an abnormal shift in the Th1/Th2 balance in favor of Th2 cells and the production of IL-4, IL-5, and IL-13. Through these mediators, Th2 lymphocytes are thought to recruit additional effector cells to the lungs, and the cells recruited promote allergic inflammatory events (22). BMSCs have been shown to have useful effects in a number of diseases and disease models. In the majority of these disorders, however, the T cell balance is shifted toward Th1 dominance. As BMSCs seem to “normalize” immune responses and reestablish the physiological balance in a variety of autoimmune and infectious diseases (23–27), we wondered whether these cells might also be able to tip the balance back to normal in an allergic environment with already-established Th2 dominance. The rebalancing act would require that the cells detect an imbalance and then take appropriate measures to correct it.
Our initial experiments showed that injecting BMSCs on d 14, when first challenging the sensitized animals significantly improved lung pathology, such as total cell number in BAL; number of eosinophils in BAL and lung scores. Using luciferase-expressing or Q-dot–labeled BMSCs, we demonstrated that lungs are the primary site of BMSC accumulation following i.v. injection, confirming the known phenomenon of cell trapping in the pulmonary microvasculature that is partially related to cell size (28, 29). However, using Q-dot–labeled BMSCs we found significantly more BMSCs retained in the lungs when RW-induced allergic inflammation was present compared with the unchallenged state—a tendency also suggested by the bioluminescent measurements. As in our model, the primary site of pathologic processes is the lung itself, and the enhanced presence of BMSCs could deliver a concentrated effort to modulate pathological immune responses.
IL-10 and TGF-β, two well characterized antiinflammatory cytokines, and IFN-γ, a key Th1 cytokine capable of down-regulating Th2-mediated pathological responses, are all thought to be capable of suppressing asthma (22, 30). As IL-10 has been shown to play a significant role in the beneficial effect of BMSCs in sepsis (27), we first measured cytokines in serum and BAL in the treated versus untreated RW-challenged mice. We found no change in IL-10 or IFN-γ levels, but there was a significant increase in the level of TGF-β, suggesting a different mechanism of action than what was found in a septic environment. We then demonstrated the importance of TGF-β in vivo by treating the mice with TGF-β–specific neutralizing antibodies before BMSC injection. Blocking TGF-β—but not IL-10—eliminated the beneficial effect of BMSC treatment. Next we looked for a possible source of TGF-β. BMSCs themselves are capable of secreting TGF-β (31), which has been implicated as one of the possible mediators of the BMSCs’ immunosuppressive effect. We thus repeated the experiment injecting BMSCs derived from TGF-β1–KO mice and found no beneficial effect, suggesting that the BMSC-derived TGF-β is critical in suppressing the allergic responses. As TGF-β synthesis can be enhanced through IL-4R in some immune cells (32), we wondered if it is the IL-4 and IL-13 that “turns on” the BMSCs to make TGF-β. We first used BMSCs from mice lacking the IL-4R (which is used by both IL-4 and IL-13) and found that RW-challenged serum or BAL could no longer elicit increased TGF-β production in these cells in vitro. In another set of experiments using neutralizing antibodies against IL-4 or IL-13, we could further demonstrate the importance of the IL4R. As the IL-4R is known to activate the STAT6 pathway (21), we wanted to confirm our results by using BMSCs that genetically lacked STAT6. As expected, STAT6-KO BMSCs were ineffective in alleviating asthma pathology and could not trigger TGF-β elevation in the BAL fluids either. Based on these data, we suggest that IL-4 and/or IL-13 bind to IL-4R receptors on BMSCs activating the STAT6 pathway. This, in turn, drives the cells to produce increased amounts of TGF-β. When this TGF-β is released from the BMSCs in the allergic (i.e., Th2-dominant) environment, TGF-β receptor activation on immune cells could result in a decrease in IL-4 production (33) and ultimately leads to a shift back toward immunological equilibrium (Fig. 9). Surprisingly, neither recombinant IL-4 nor IL-13 alone or in combination was able to elicit the elevation of TGF-β by BMSCs seen with RW-conditioned BAL fluid or blood serum in vitro. This indicates that activation of the IL-4R/STAT6 pathway is necessary but not sufficient to cause TGF-β up-regulation in BMSCs. In addition to IL-4 or IL-13, there must be other important factors in vivo (present in BAL fluid or serum) that contribute to the production and subsequent release of TGF-β by BMSCs.
Fig. 9.
Schematic drawing shows the mechanism of effect based on data of the present study. BMSCs “sense” the allergic environment, and as a result of the increased levels of IL-4/IL-13, they respond by producing higher amounts of TGF-β that, either alone or by recruiting regulatory T cells, will ultimately lead to a decrease of lung eosinophil infiltration, as well as allergy-specific cytokine and Ig production.
We also demonstrated that BMSC-treated asthmatic animals recruit significantly more regulatory T cells to the lungs than untreated mice. In animal models of allergic airways disease, T-regs can suppress established airway inflammation and airway hyperresponsiveness (34). Regulatory T cells are thought to suppress infection/inflammation by secreting antiinflammatory molecules (e.g., IL-10, TGF-β) (35, 36). It is possible that BMSCs work together with regulatory T cells to suppress harmful allergic responses in our model. BMSCs could initiate the suppressive process by secreting TGF-β to block the proinflammatory Th2 responses and at the same time induce the differentiation and help the survival of regulatory T cells (30) that will then continue to improve asthma pathology after the BMSCs disappear.
It is worth mentioning that dermal fibroblasts—cells frequently used as control cells in studies of BMSCs—had beneficial effects in the model that we used when injected intravenously. The effect of the fibroblasts was not as strong as that of BMSCs. This suggests, however, that fibroblast-like cells, whether derived from the bone marrow or other organs (including skin dermis), may also have some immunomodulatory properties (37).
In the present study we demonstrated that i.v. injected BMSCs are capable of suppressing Th2-driven allergic responses. It appears that IL-4 and/or IL-13 induce production and secretion of TGF-β by the BMSCs, which in turn effectively suppresses allergy specific pathological changes in the asthma model we studied. These data provide another example of the ability of BMSCs to “sense” their immunological environment and respond accordingly. It is hard to imagine a drug or combination of drugs that could act this way, and further work should be done to determine whether the cells could be used to treat patients with therapy-resistant asthma.
Methods
Mice.
C57BL/6J or Balb/C mice (6 to 8 weeks old) were obtained from Taconic Farms. IL-4Rα–KO and STAT6-KO animals were purchased from Jackson Laboratories. TGF-β1–KO mice have previously been produced and characterized (38). The animals were housed and maintained in the National Institute of Allergy and Infectious Diseases or National Institute of Dental and Craniofacial Research animal facilities. All studies conformed to the principles for laboratory animal research outlined by the Animal Welfare Act, and were approved by the National Institute of Dental and Craniofacial Research and/or National Institute of Allergy and Infectious Diseases Animal Care and Use Committee. The groups for in vivo studies contained four to 10 mice, and each experiment was repeated two to three times.
Antigen Challenge.
To elicit a bronchial allergic response, RW sensitization and challenge were used (18, 19). C57BL/6J mice were sensitized on d 0 and 5 with 200 μL i.p. injections of 50 μg RW extract (Greer Laboratories), emulsified in an equal volume (100 μL/antigen injection) of alum (Pierce) as described earlier (39). Control animals were injected i.p. with the same amount of alum mixed with PBS solution. Subsequently, as shown in Fig. 1, the mice were challenged on d 14 and 15 with 50 μg RW extract in PBS solution by intratracheal and intranasal inoculation (30 μL), respectively. Control mice received an equal volume of PBS solution administered via the same routes. In all cases, mice were killed by anesthetizing them with ketamine (Fort Dodge Animal Health) and xylazine (Phoenix Pharmaceuticals) 100 mg/kg and 10 mg/kg, respectively, followed by exsanguination.
Histology.
To assess pulmonary inflammation, BAL was performed 72 h after the final allergen challenge (as described later). Lungs were then immediately placed in 10% neutral buffered formalin and sent to Histoserv (Germantown, MD), where they were embedded in paraffin and stained. H&E was used to evaluate cellular inflammation and periodic acid–Schiff (PAS) stain was used to visualize mucus-containing goblet cells. Slides were coded and read “blind”; a minimum of four lungs per group were given scores ranging from 0 to 2 based on the level of peribronchial cuffing, perivascular cuffing, goblet cell hyperplasia, and interstitial inflammation (40).
BAL.
Immediately after the mice were exsanguinated, the lungs were cannulated with a 20-gauge i.v. catheter and gently washed once with 500 μL 1% FBS (HyClone) in PBS solution (for cytokine analysis) or twice with 750 μL 1% FBS in PBS solution (for analysis of cellular infiltration). Samples for cytokine analysis were stored at −80°C. Samples for cellular analysis were spun onto glass slides in a cytospin instrument (Thermo-Shandon) and stained with Kwik-Diff for differential cell analysis (Thermo-Shandon). A fraction was used to determine total cell counts.
In Vivo Neutralization of Cytokines.
IL-10– or TGF-β–neutralizing antibodies (Clone 2A5 from Pierce Endogen or Clone 1D11 from R&D Systems, respectively) were injected intraperitoneally (10 μg/g body weight in 200 μL PBS) on two consecutive days at the approximate time of BMSC injection (d 14 and 15).
Measurement of Serum Antibody Isotypes.
Antibody isotypes (IgG1, IgG2a, and IgE) were assayed in sera collected 72 h after last RW challenge using ELISA kits according to the manufacturer's instructions (Immunology Consultants Laboratory). All samples, including standards, were assayed in duplicate.
Preparation of Lung Cell Suspension.
Lungs were removed, minced into small pieces, and incubated in RPMI medium 1640 with 1% penicillin–streptomycin and 1% glutamine for 30 min at 37 °C 5% CO2 in the presence of collagenase type 1 (300 U mL−1) and DNase I (50 U mL−1; Worthington Biochemicals). After the incubation, the cell suspension was filtered through a 70-μm cell strainer and then washed with complete RPMI medium.
Data Analysis.
Data are summarized as mean ± SE. Student t test or two-way ANOVA were performed using GraphPad Prism version 4.00 for Macintosh (GraphPad Software). The statistical significance value was set at P < 0.05.
Supplementary Material
Acknowledgments
We thank Dr. William Paul for his continuing support and suggestions during the preparation of the study. We also thank Dr. Natasha Chairman for her help with the differentiation assays, Dr. Silvio Gutkind for providing the luciferase expressing lentiviral vectors, and Dr. Daniel Martin for his help with the bioluminescence measurements. This research was supported by the Division of Intramural Research Program of the National Institute of Dental and Craniofacial Research and National Institute of Allergy and Infectious Diseases.
Footnotes
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
*This Direct Submission article had a prearranged editor.
This article contains supporting information online at www.pnas.org/cgi/content/full/0910720107/DCSupplemental.
References
- 1.Urbano FL. Review of the NAEPP 2007 Expert Panel Report (EPR-3) on asthma diagnosis and treatment guidelines. J Manag Care Pharm. 2008;14:41–49. doi: 10.18553/jmcp.2008.14.1.41. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 2.Chung KF, et al. European Respiratory Society. Difficult/therapy-resistant asthma: the need for an integrated approach to define clinical phenotypes, evaluate risk factors, understand pathophysiology and find novel therapies. ERS Task Force on Difficult/Therapy-Resistant Asthma. Eur Respir J. 1999;13:1198–1208. doi: 10.1034/j.1399-3003.1999.13e43.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 3.Papiris S, Kotanidou A, Malagari K, Roussos C. Clinical review: severe asthma. Crit Care. 2002;6:30–44. doi: 10.1186/cc1451. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 4.Le Blanc K, et al. Treatment of severe acute graft-versus-host disease with third party haploidentical mesenchymal stem cells. Lancet. 2004;363:1439–1441. doi: 10.1016/S0140-6736(04)16104-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 5.Le Blanc K, Ringdén O. Use of mesenchymal stem cells for the prevention of immune complications of hematopoietic stem cell transplantation. Haematologica. 2005;90:438. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 6.Aggarwal S, Pittenger MF. Human mesenchymal stem cells modulate allogeneic immune cell responses. Blood. 2005;105:1815–1822. doi: 10.1182/blood-2004-04-1559. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 7.Kuo YR, et al. Mesenchymal stem cells prolong composite tissue allotransplant survival in a swine model. Transplantation. 2009;87:1769–1777. doi: 10.1097/TP.0b013e3181a664f1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 8.Zhou HP, et al. Administration of donor-derived mesenchymal stem cells can prolong the survival of rat cardiac allograft. Transplant Proc. 2006;38:3046–3051. doi: 10.1016/j.transproceed.2006.10.002. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 9.Rafei M, Birman E, Forner K, Galipeau J. Allogeneic mesenchymal stem cells for treatment of experimental autoimmune encephalomyelitis. Mol Ther. 2009;17:1799–1803. doi: 10.1038/mt.2009.157. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 10.Rafei M, et al. Mesenchymal stromal cells ameliorate experimental autoimmune encephalomyelitis by inhibiting CD4 Th17 T cells in a CC chemokine ligand 2-dependent manner. J Immunol. 2009;182:5994–6002. doi: 10.4049/jimmunol.0803962. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 11.Zappia E, et al. Mesenchymal stem cells ameliorate experimental autoimmune encephalomyelitis inducing T-cell anergy. Blood. 2005;106:1755–1761. doi: 10.1182/blood-2005-04-1496. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 12.Gupta N, et al. Intrapulmonary delivery of bone marrow-derived mesenchymal stem cells improves survival and attenuates endotoxin-induced acute lung injury in mice. J Immunol. 2007;179:1855–1863. doi: 10.4049/jimmunol.179.3.1855. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 13.Kumamoto M, Nishiwaki T, Matsuo N, Kimura H, Matsushima K. Minimally-cultured bone marrow mesenchymal stem cells ameliorate fibrotic lung injury. Eur Respir J. 2009;34:740–748. doi: 10.1183/09031936.00128508. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 14.Mei SH, et al. Prevention of LPS-induced acute lung injury in mice by mesenchymal stem cells overexpressing angiopoietin 1. PLoS Med. 2007;4:e269. doi: 10.1371/journal.pmed.0040269. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 15.Ortiz LA, et al. Interleukin 1 receptor antagonist mediates the antiinflammatory and antifibrotic effect of mesenchymal stem cells during lung injury. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA. 2007;104:11002–11007. doi: 10.1073/pnas.0704421104. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 16.Bai L, et al. Human bone marrow-derived mesenchymal stem cells induce Th2-polarized immune response and promote endogenous repair in animal models of multiple sclerosis. Glia. 2009;57:1192–1203. doi: 10.1002/glia.20841. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 17.Wang Q, et al. Murine bone marrow mesenchymal stem cells cause mature dendritic cells to promote T-cell tolerance. Scand J Immunol. 2008;68:607–615. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-3083.2008.02180.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 18.McConchie BW, et al. Ascaris suum-derived products suppress mucosal allergic inflammation in an interleukin-10-independent manner via interference with dendritic cell function. Infect Immun. 2006;74:6632–6641. doi: 10.1128/IAI.00720-06. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 19.Norris HH, et al. Inhibitory receptor gp49B regulates eosinophil infiltration during allergic inflammation. J Leukoc Biol. 2007;82:1531–1541. doi: 10.1189/jlb.1106667. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 20.Nasef A, et al. Identification of IL-10 and TGF-beta transcripts involved in the inhibition of T-lymphocyte proliferation during cell contact with human mesenchymal stem cells. Gene Expr. 2007;13:217–226. doi: 10.3727/000000006780666957. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 21.Takeda K, et al. Essential role of Stat6 in IL-4 signalling. Nature. 1996;380:627–630. doi: 10.1038/380627a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 22.Hamid Q, Tulic M. Immunobiology of asthma. Annu Rev Physiol. 2009;71:489–507. doi: 10.1146/annurev.physiol.010908.163200. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 23.Rasmusson I. Immune modulation by mesenchymal stem cells. Exp Cell Res. 2006;312:2169–2179. doi: 10.1016/j.yexcr.2006.03.019. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 24.Tyndall A, et al. Immunomodulatory properties of mesenchymal stem cells: a review based on an interdisciplinary meeting held at the Kennedy Institute of Rheumatology Division, London, UK, 31 October 2005. Arthritis Res Ther. 2007;9:301. doi: 10.1186/ar2103. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 25.Uccelli A, Moretta L, Pistoia V. Immunoregulatory function of mesenchymal stem cells. Eur J Immunol. 2006;36:2566–2573. doi: 10.1002/eji.200636416. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 26.Uccelli A, Moretta L, Pistoia V. Mesenchymal stem cells in health and disease. Nat Rev Immunol. 2008;8:726–736. doi: 10.1038/nri2395. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 27.Németh K, et al. Bone marrow stromal cells attenuate sepsis via prostaglandin E(2)-dependent reprogramming of host macrophages to increase their interleukin-10 production. Nat Med. 2009;15:42–49. doi: 10.1038/nm.1905. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 28.Harting MT, et al. Intravenous mesenchymal stem cell therapy for traumatic brain injury. J Neurosurg. 2009;110:1189–1197. doi: 10.3171/2008.9.JNS08158. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 29.Schrepfer S, et al. Stem cell transplantation: the lung barrier. Transplant Proc. 2007;39:573–576. doi: 10.1016/j.transproceed.2006.12.019. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 30.Qian BF, Wahl SM. TGF-beta can leave you breathless. Curr Opin Pharmacol. 2009;9:454–461. doi: 10.1016/j.coph.2009.04.001. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 31.Di Nicola M, et al. Human bone marrow stromal cells suppress T-lymphocyte proliferation induced by cellular or nonspecific mitogenic stimuli. Blood. 2002;99:3838–3843. doi: 10.1182/blood.v99.10.3838. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 32.Elovic AE, et al. IL-4-dependent regulation of TGF-alpha and TGF-beta1 expression in human eosinophils. J Immunol. 1998;160:6121–6127. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 33.Holter W, et al. Transforming growth factor-beta inhibits IL-4 and IFN-gamma production by stimulated human T cells. Int Immunol. 1994;6:469–475. doi: 10.1093/intimm/6.3.469. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 34.Robinson DS. Regulatory T cells and asthma. Clin Exp Allergy. 2009;39:1314–1323. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2222.2009.03301.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 35.Corthay A. How do regulatory T cells work? Scand J Immunol. 2009;70:326–336. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-3083.2009.02308.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 36.Sakaguchi S, Wing K, Onishi Y, Prieto-Martin P, Yamaguchi T. Regulatory T cells: how do they suppress immune responses? Int Immunol. 2009;21:1105–1111. doi: 10.1093/intimm/dxp095. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 37.Jones S, Horwood N, Cope A, Dazzi F. The antiproliferative effect of mesenchymal stem cells is a fundamental property shared by all stromal cells. J Immunol. 2007;179:2824–2831. doi: 10.4049/jimmunol.179.5.2824. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 38.Gorham JD, Lin JT, Sung JL, Rudner LA, French MA. Genetic regulation of autoimmune disease: BALB/c background TGF-beta 1-deficient mice develop necroinflammatory IFN-gamma-dependent hepatitis. J Immunol. 2001;166:6413–6422. doi: 10.4049/jimmunol.166.10.6413. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 39.Miyazaki D, et al. Macrophage inflammatory protein-1alpha as a costimulatory signal for mast cell-mediated immediate hypersensitivity reactions. J Clin Invest. 2005;115:434–442. doi: 10.1172/JCI18452. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 40.Al-Shami A, Spolski R, Kelly J, Keane-Myers A, Leonard WJ. A role for TSLP in the development of inflammation in an asthma model. J Exp Med. 2005;202:829–839. doi: 10.1084/jem.20050199. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
Associated Data
This section collects any data citations, data availability statements, or supplementary materials included in this article.