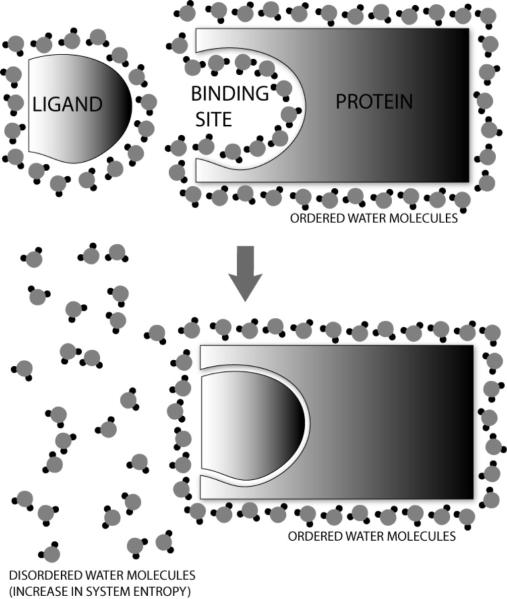
Figure 1. The Hydrophobic Effect.
Hydrophobic molecules are surrounded by an ordered cage of water molecules. When two such molecules come together, they aggregate in order to reduce their surface area in contact with the polar water molecules. This causes a number of water molecules to be removed from their ordered formation, thus increasing disorder (increased entropy) and potentially making the process energetically favorable.