Abstract
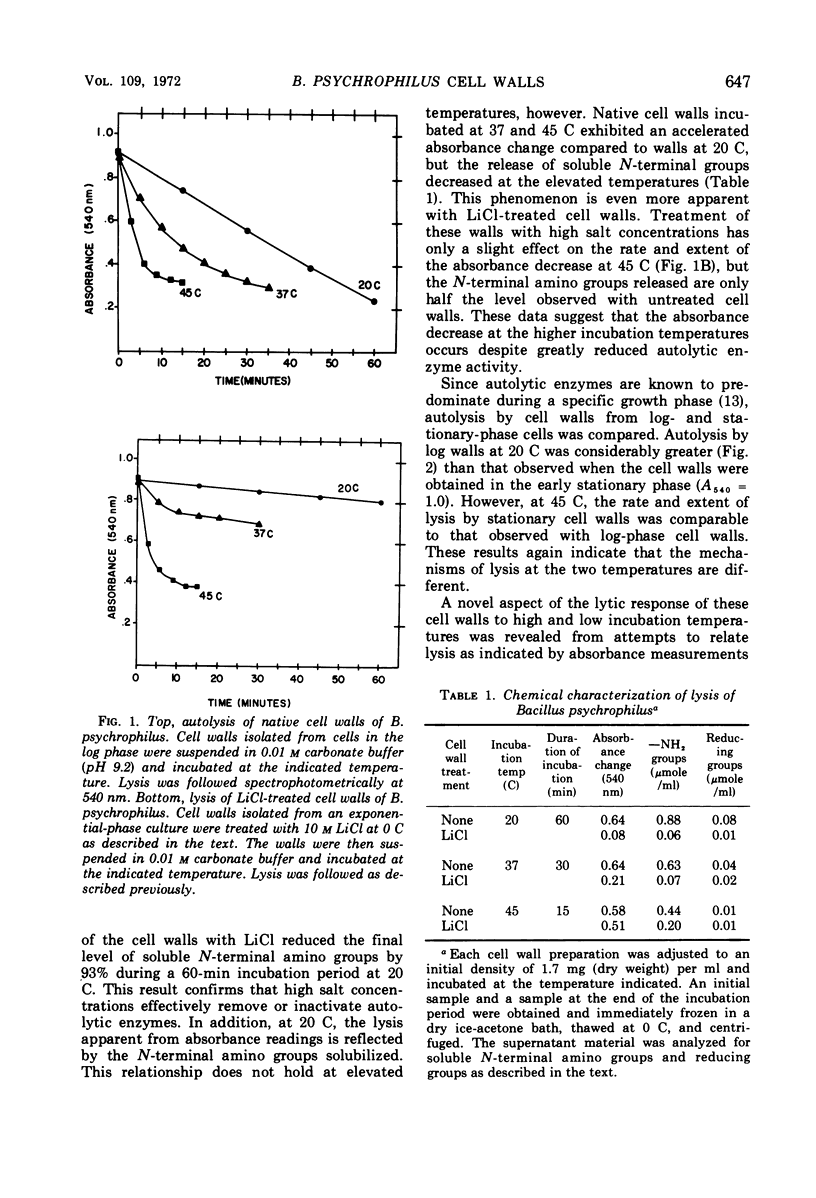
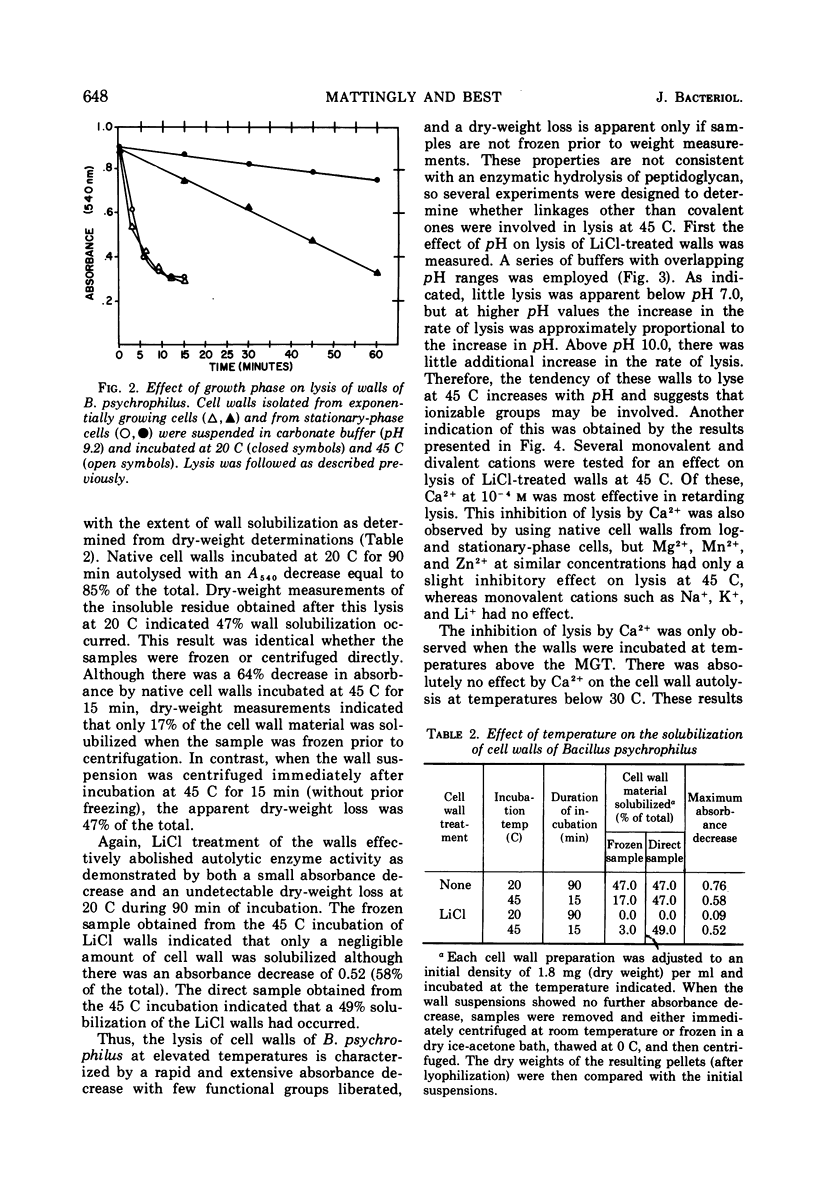
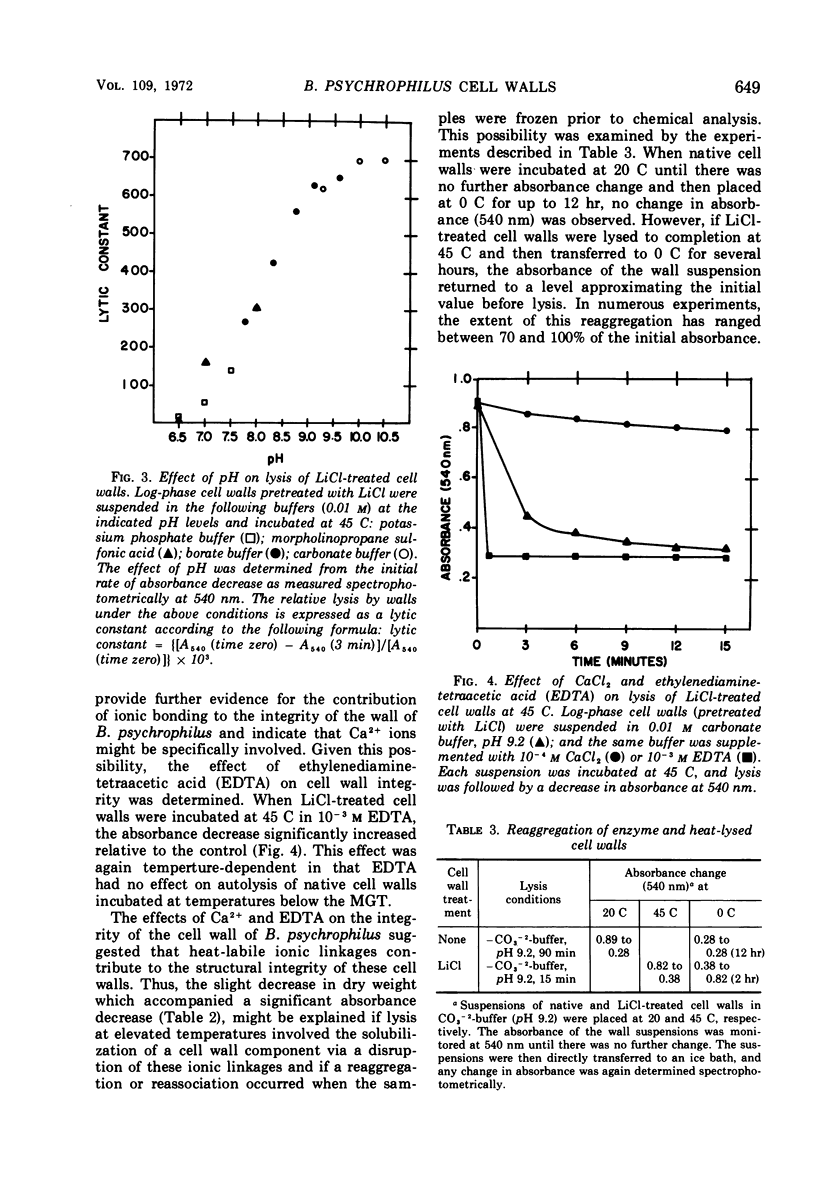
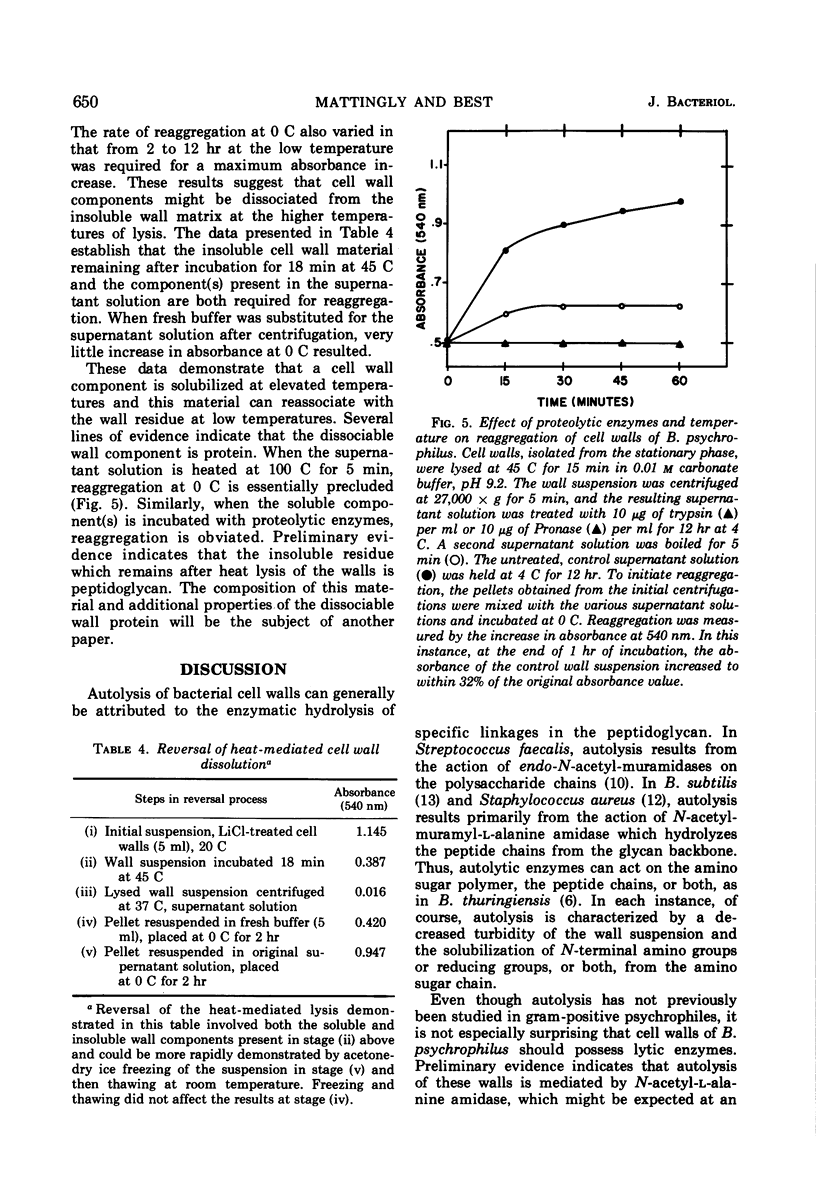
Cell walls isolated from Bacillus psychrophilus autolyse at temperatures which support growth. At temperatures above the maximum growth temperature (28 C), a nonenzymatic lysis occurs. Removal of autolytic enzyme activity with 10 m LiCl had little effect on the rate or extent of lysis at elevated temperatures (37 and 45 C). Nonenzymatic lysis was characterized chemically by a decrease in the liberation of N-terminal groups, and the effects of pH, Ca2+, and ethylenediaminetetraacetic acid suggest that ionic linkages are involved in much of the integrity of the cell wall of this psychrophile. The nonenzymatic absorbance decrease at 45 C can be reversed to the extent of 70 to 100% at 0 C. Centrifugation of a heat-lysed wall suspension separated a soluble protein component which is required for low-temperature reaggregation. Preliminary evidence indicates the insoluble residue which remains after temperature-mediated lysis is primarily peptidoglycan.
Full text
PDF


Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Asbell M. A., Eagon R. G. Role of Multivalent Cations in the Organization, Structure, and Assembly of the Cell Wall of Pseudomonas aeruginosa. J Bacteriol. 1966 Aug;92(2):380–387. doi: 10.1128/jb.92.2.380-387.1966. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fan D. P. Cell wall binding properties of the Bacillus subtilis autolysin(s). J Bacteriol. 1970 Aug;103(2):488–493. doi: 10.1128/jb.103.2.488-493.1970. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- HAGEN P. O., KUSHNER D. J., GIBBONS N. E. TEMPERATURE-INDUCED DEATH AND LYSIS IN A PSYCHROPHILIC BACTERIUM. Can J Microbiol. 1964 Dec;10:813–822. doi: 10.1139/m64-106. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hughes R. C., Tanner P. J., Stokes E. Cell-wall thickening in Bacillus subtilis. Comparison of thickened and normal walls. Biochem J. 1970 Nov;120(1):159–170. doi: 10.1042/bj1200159. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kingan S. L., Ensign J. C. Isolation and characterization of three autolytic enzymes associated with sporulation of Bacillus thuringiensis var. thuringiensis. J Bacteriol. 1968 Sep;96(3):629–638. doi: 10.1128/jb.96.3.629-638.1968. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mattingly S. J., Best G. K. The effect of temperature on lysis of cells and cell walls of Bacillus psychrophilus. Can J Microbiol. 1971 Sep;17(9):1161–1168. doi: 10.1139/m71-185. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nermut M. V., Murray R. G. Ultrastructure of the cell wall of Bacillus polymyxa. J Bacteriol. 1967 Jun;93(6):1949–1965. doi: 10.1128/jb.93.6.1949-1965.1967. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pooley H. M., Porres-Juan J. M., Shockman G. D. Dissociation of an autolytic enzyme-cell wall complex by treatment with unusually high concentrations of salt. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1970 Mar 27;38(6):1134–1140. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(70)90357-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shockman G. D., Thompson J. S., Conover M. J. The autolytic enzyme system of Streptococcus faecalis. II. Partial characterization of the autolysin and its substrate. Biochemistry. 1967 Apr;6(4):1054–1065. doi: 10.1021/bi00856a014. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stokes J. L., Larkin J. M. Comparative effect of temperature on the oxidative metabolism of whole and disrupted cells of a psychrophilic and a mesophilic species of Bacillus. J Bacteriol. 1968 Jan;95(1):95–98. doi: 10.1128/jb.95.1.95-98.1968. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tipper D. J. Mechanism of autolysis of isolated cell walls of Staphylococcus aureus. J Bacteriol. 1969 Feb;97(2):837–847. doi: 10.1128/jb.97.2.837-847.1969. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Young F. E. Autolytic enzyme associated with cell walls of Bacillus subtilis. J Biol Chem. 1966 Aug 10;241(15):3462–3467. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]



