Abstract
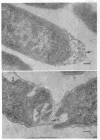
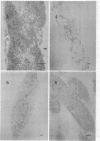
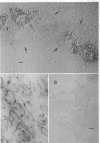
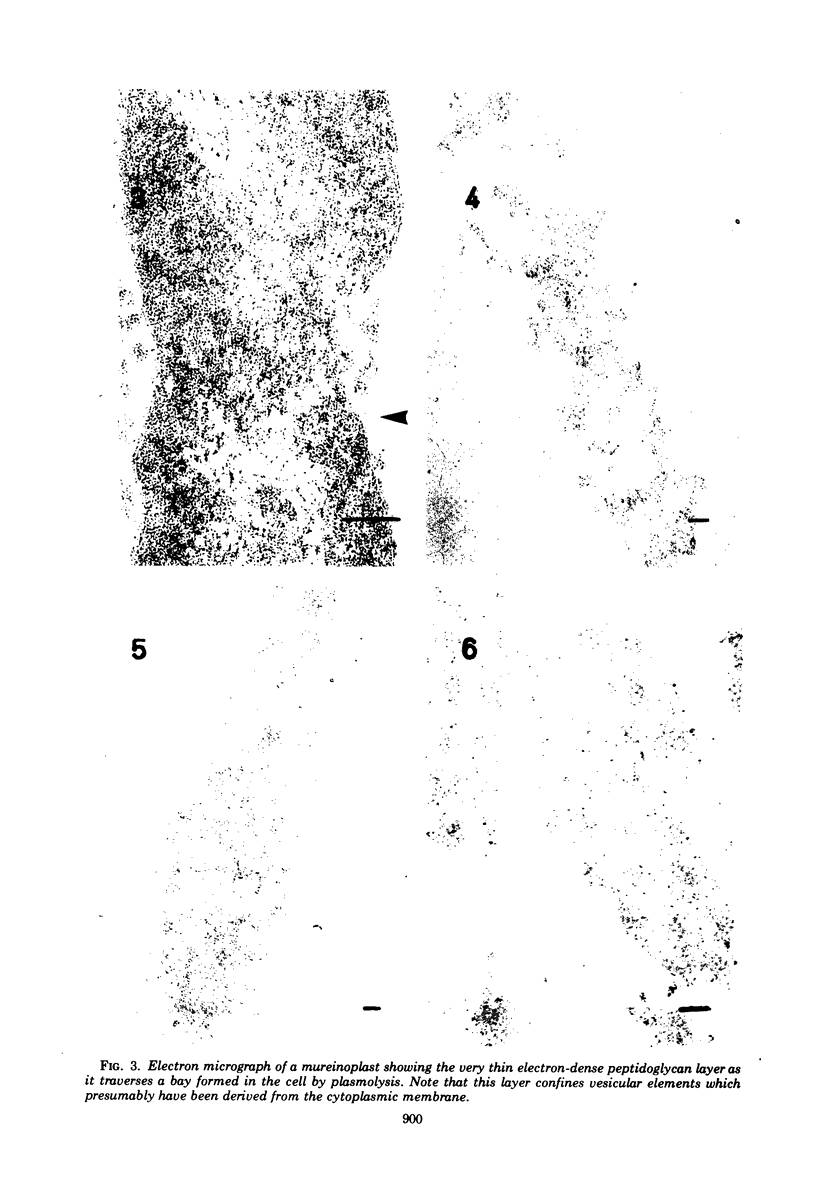
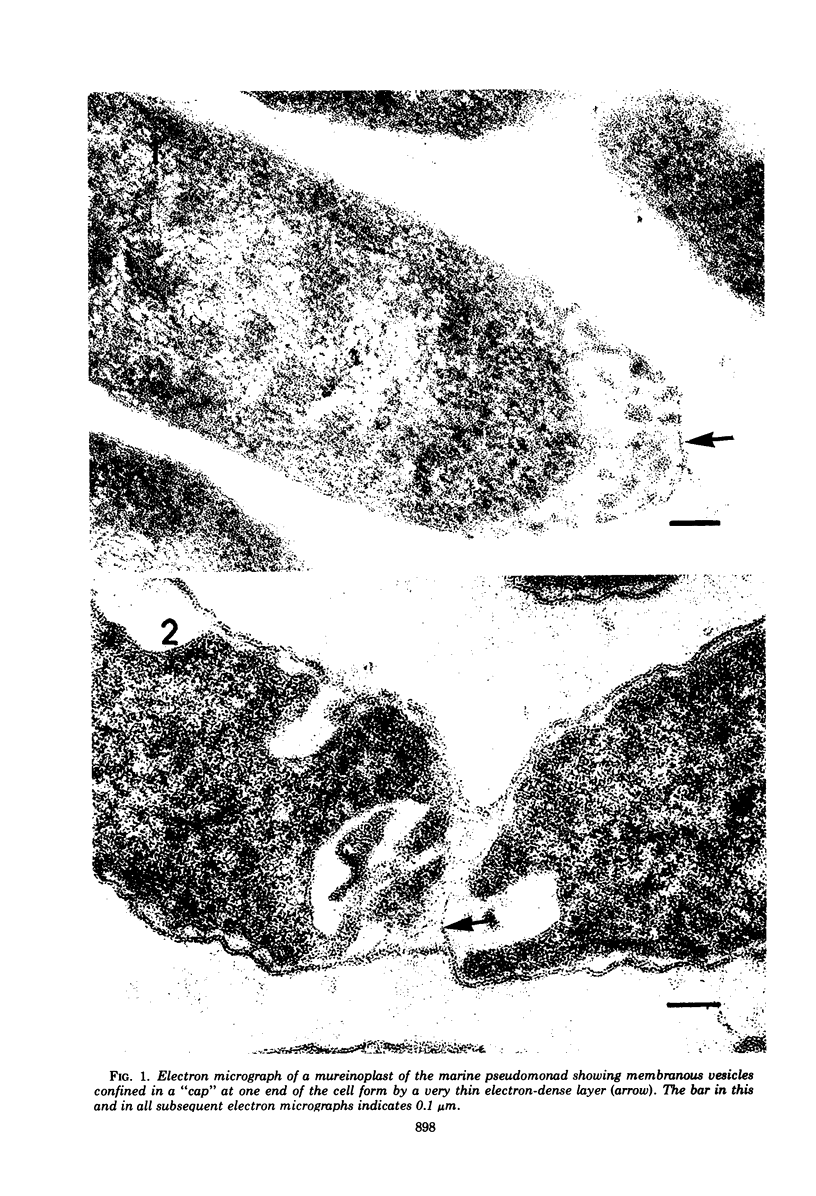
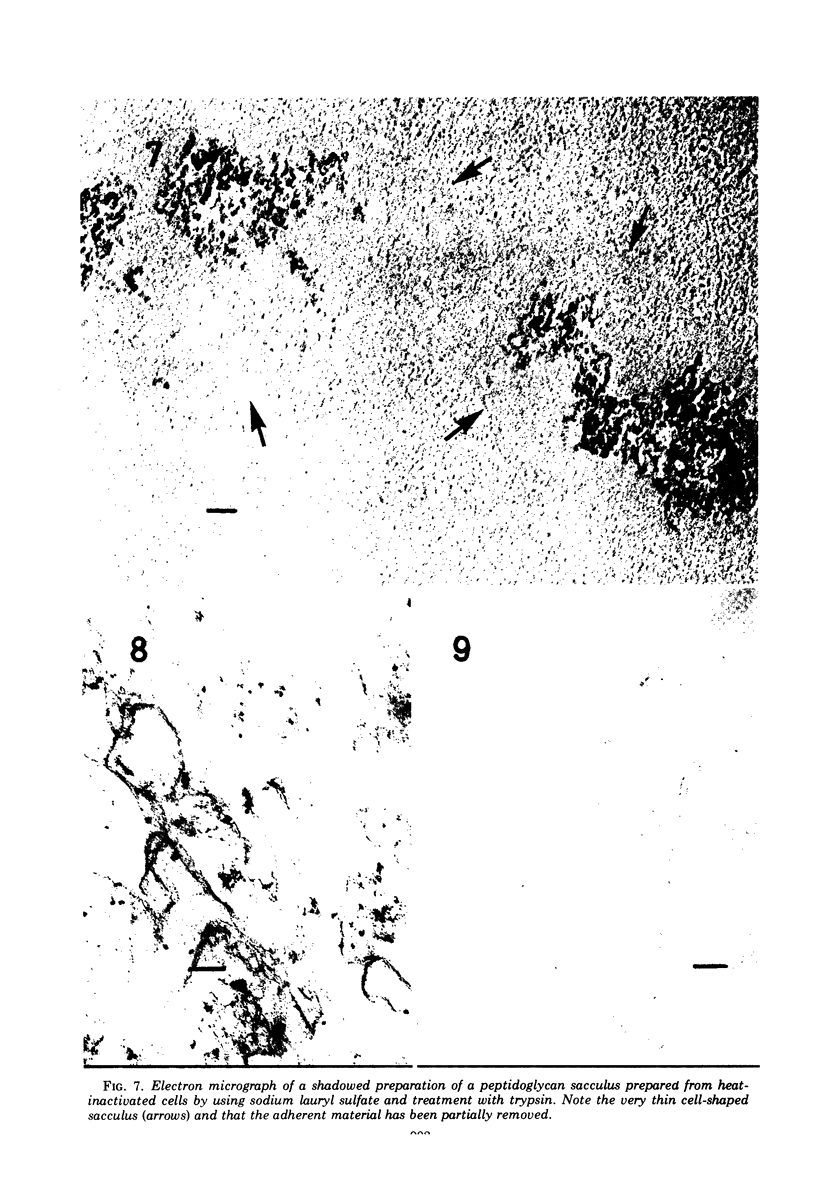
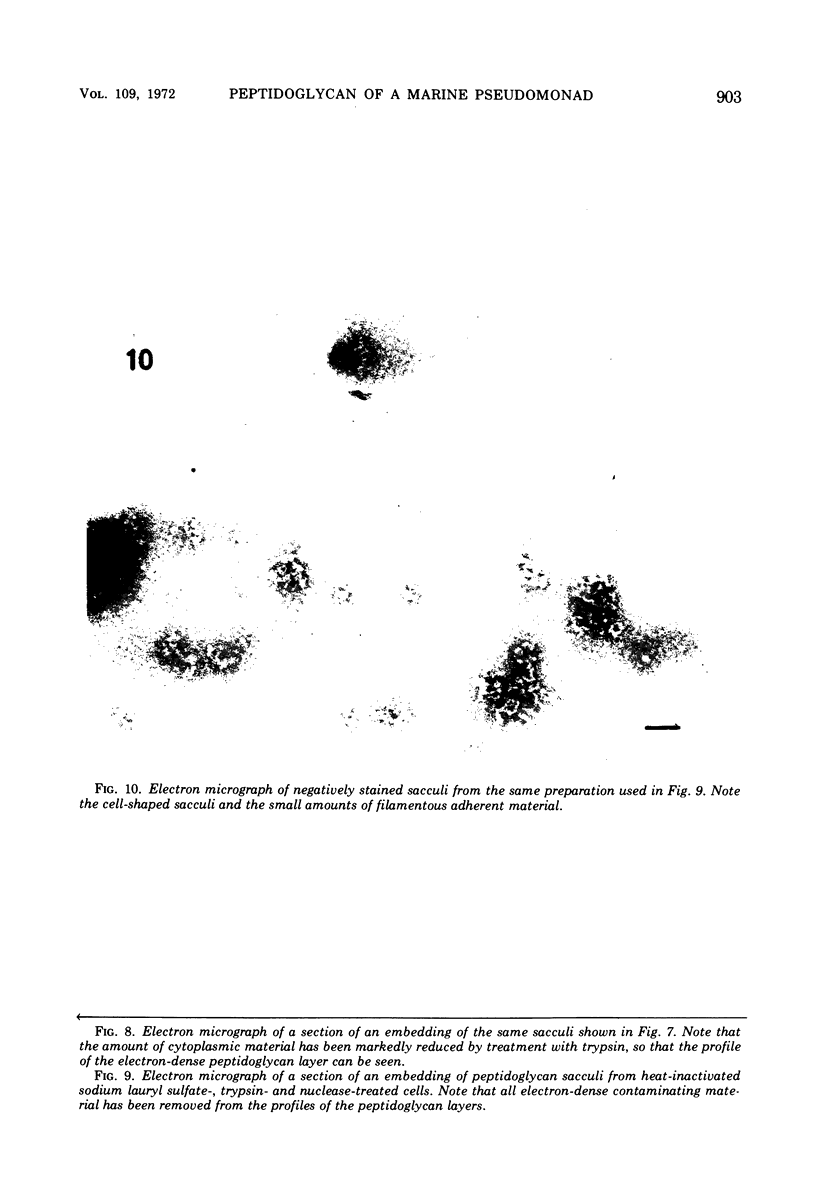
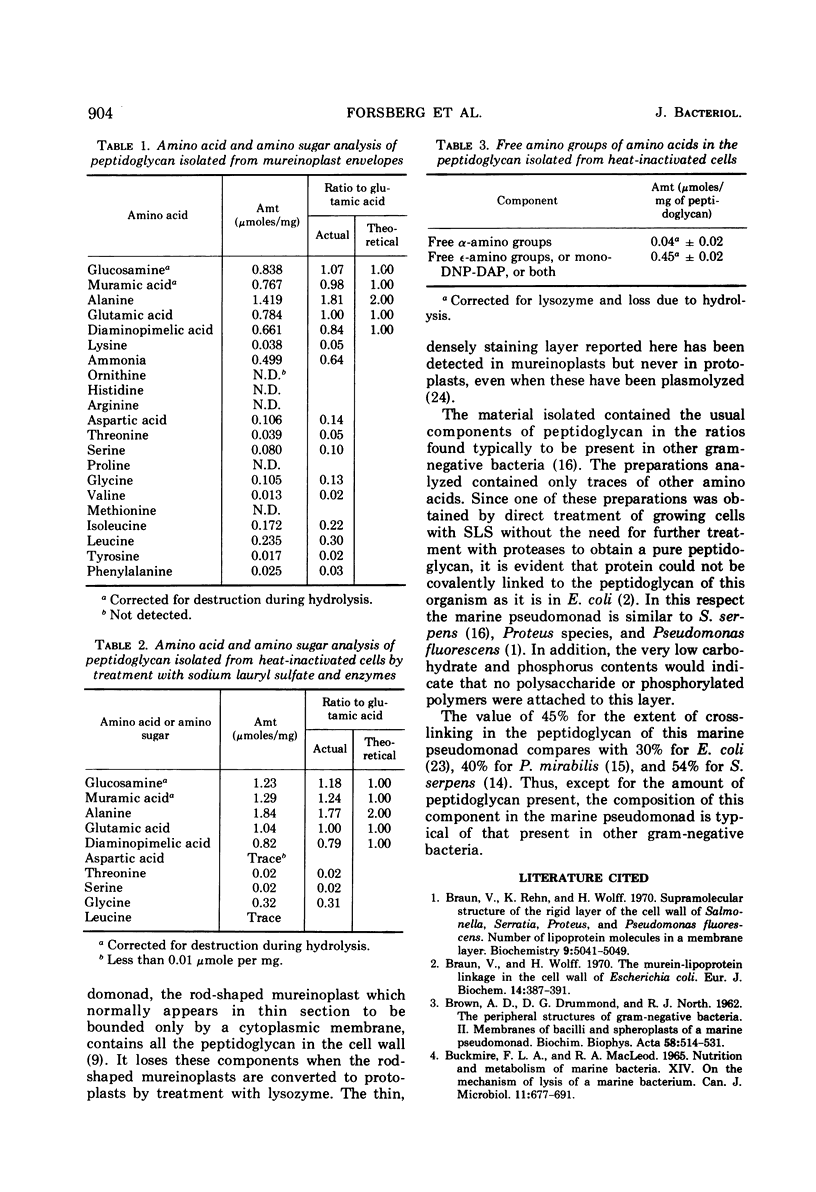
The peptidoglycan layer of a marine pseudomonad was observed by electron microscopy in thin sections of plasmolyzed intact cells and mureinoplasts but not in untreated intact cells. Only fragments of this layer could be isolated by sodium lauryl sulfate (SLS) treatment of mureinoplast envelopes. Sacculus-like peptidoglycan structures were obtained from growing cells by immediate heat inactivation of cellular autolytic enzymes and subsequent SLS, trypsin, and nuclease treatments. Recently, similar peptidoglycan sacculus-like structures have been obtained by adding SLS to the growing culture and treating the isolated particulate material with nucleases. Thin-sectioned and negatively stained preparations of whole cell peptidoglycan showed compressed profiles of cell-shaped sacculi. Peptidoglycan prepared by SLS treatment of mureinoplast envelopes had a similar composition to that prepared from whole cells. The major amino sugars and amino acids in the peptidoglycan component were glucosamine, muramic acid, alanine, glutamic acid and diaminopimelic acid in the molar ratios 1.18:1.24:1.77:1.00:0.79. Forty-five per cent of the ε-amino groups of diaminopimelic acid were cross-linked. The peptidoglycan was estimated to account for about 1% of the cell dry weight.
Full text
PDF






Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Braun V., Rehn K., Wolff H. Supramolecular structure of the rigid layer of the cell wall of Salmonella, Serratia, Proteus, and Pseudomonas fluorescens. Number of lipoprotein molecules in a membrane layer. Biochemistry. 1970 Dec 22;9(26):5041–5049. doi: 10.1021/bi00828a001. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Braun V., Wolff H. The murein-lipoprotein linkage in the cell wall of Escherichia coli. Eur J Biochem. 1970 Jun;14(2):387–391. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1970.tb00301.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Buckmire F. L., MacLeod R. A. Nutrition and metabolism of marine bacteria. XIV. On the mechanism of lysis of a marine bacterium. Can J Microbiol. 1965 Aug;11(4):677–691. doi: 10.1139/m65-091. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- CESSI C., PILIEGO F. The determination of amino sugars in the presence of amino acids and glucose. Biochem J. 1960 Dec;77:508–510. doi: 10.1042/bj0770508. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Costerton J. W., Forsberg C., Matula T. I., Buckmire F. L., MacLeod R. A. Nutrition and metabolism of marine bacteria. XVI. Formation of protoplasts, spheroplasts, and related forms from a gram-negative marine bacterium. J Bacteriol. 1967 Nov;94(5):1764–1777. doi: 10.1128/jb.94.5.1764-1777.1967. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- De Petris S. Ultrastructure of the cell wall of Escherichia coli and chemical nature of its constituent layers. J Ultrastruct Res. 1967 Jul;19(1):45–83. doi: 10.1016/s0022-5320(67)80059-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- De Voe I. W., Thompson J., Costerton J. W., MacLeod R. A. Stability and comparative transport capacity of cells, mureinoplasts, and true protoplasts of a gram-negative bacterium. J Bacteriol. 1970 Mar;101(3):1014–1026. doi: 10.1128/jb.101.3.1014-1026.1970. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Forsberg C. W., Costerton J. W., Macleod R. A. Quantitation, chemical characteristics, and ultrastructure of the three outer cell wall layers of a gram-negative bacterium. J Bacteriol. 1970 Dec;104(3):1354–1368. doi: 10.1128/jb.104.3.1354-1368.1970. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Forsberg C. W., Costerton J. W., Macleod R. A. Separation and localization of cell wall layers of a gram-negative bacterium. J Bacteriol. 1970 Dec;104(3):1338–1353. doi: 10.1128/jb.104.3.1338-1353.1970. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Glauert A. M., Thornley M. J. The topography of the bacterial cell wall. Annu Rev Microbiol. 1969;23:159–198. doi: 10.1146/annurev.mi.23.100169.001111. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hofschneider P. H., Martin H. H. Diversity of surface layers in L-forms of Proteus mirabilis. J Gen Microbiol. 1968 Apr;51(1):23–33. doi: 10.1099/00221287-51-1-23. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kolenbrander P. E., Ensign J. C. Isolation and chemical structure of the peptidoglycan of Spirillum serpens cell walls. J Bacteriol. 1968 Jan;95(1):201–210. doi: 10.1128/jb.95.1.201-210.1968. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- MURRAY R. G., STEED P., ELSON H. E. THE LOCATION OF THE MUCOPEPTIDE IN SECTIONS OF THE CELL WALL OF ESCHERICHIA COLI AND OTHER GRAM-NEGATIVE BACTERIA. Can J Microbiol. 1965 Jun;11:547–560. doi: 10.1139/m65-072. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Martin H. H. Biochemistry of bacterial cell walls. Annu Rev Biochem. 1966;35:457–484. doi: 10.1146/annurev.bi.35.070166.002325. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Osborn M. J. Structure and biosynthesis of the bacterial cell wall. Annu Rev Biochem. 1969;38:501–538. doi: 10.1146/annurev.bi.38.070169.002441. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- REYNOLDS E. S. The use of lead citrate at high pH as an electron-opaque stain in electron microscopy. J Cell Biol. 1963 Apr;17:208–212. doi: 10.1083/jcb.17.1.208. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- SALTON M. R. Studies of the bacterial cell wall. VIII. Reaction of walls with hydrazine and with fluorodinitrobenzene. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1961 Sep 16;52:329–342. doi: 10.1016/0006-3002(61)90682-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Steed P., Murray R. G. The cell wall and cell division of gram-negative bacteria. Can J Microbiol. 1966 Apr;12(2):263–270. doi: 10.1139/m66-036. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- TAKEBE I. EXTENT OF CROSS LINKAGE IN THE MUREIN SACCULUS OF ESCHERICHIA COLI B CELL WALL. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1965 Mar 1;101:124–126. doi: 10.1016/0926-6534(65)90038-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Thompson J., Costerton J. W., MacLeon R. A. K plus-dependent deplasmolysis of a marine pseudomonad plasmolyzed in a hypotonic solution. J Bacteriol. 1970 Jun;102(3):843–854. doi: 10.1128/jb.102.3.843-854.1970. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- WEIDEL W., FRANK H., LEUTGEB W. Autolytic enzymes as a source of error in the preparation and study of gram-negative cell walls. J Gen Microbiol. 1963 Jan;30:127–130. doi: 10.1099/00221287-30-1-127. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- WEIDEL W., PELZER H. BAGSHAPED MACROMOLECULES--A NEW OUTLOOK ON BACTERIAL CELL WALLS. Adv Enzymol Relat Areas Mol Biol. 1964;26:193–232. doi: 10.1002/9780470122716.ch5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- White D., Dworkin M., Tipper D. J. Peptidoglycan of Myxococcus xanthus: structure and relation to morphogenesis. J Bacteriol. 1968 Jun;95(6):2186–2197. doi: 10.1128/jb.95.6.2186-2197.1968. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]