Abstract
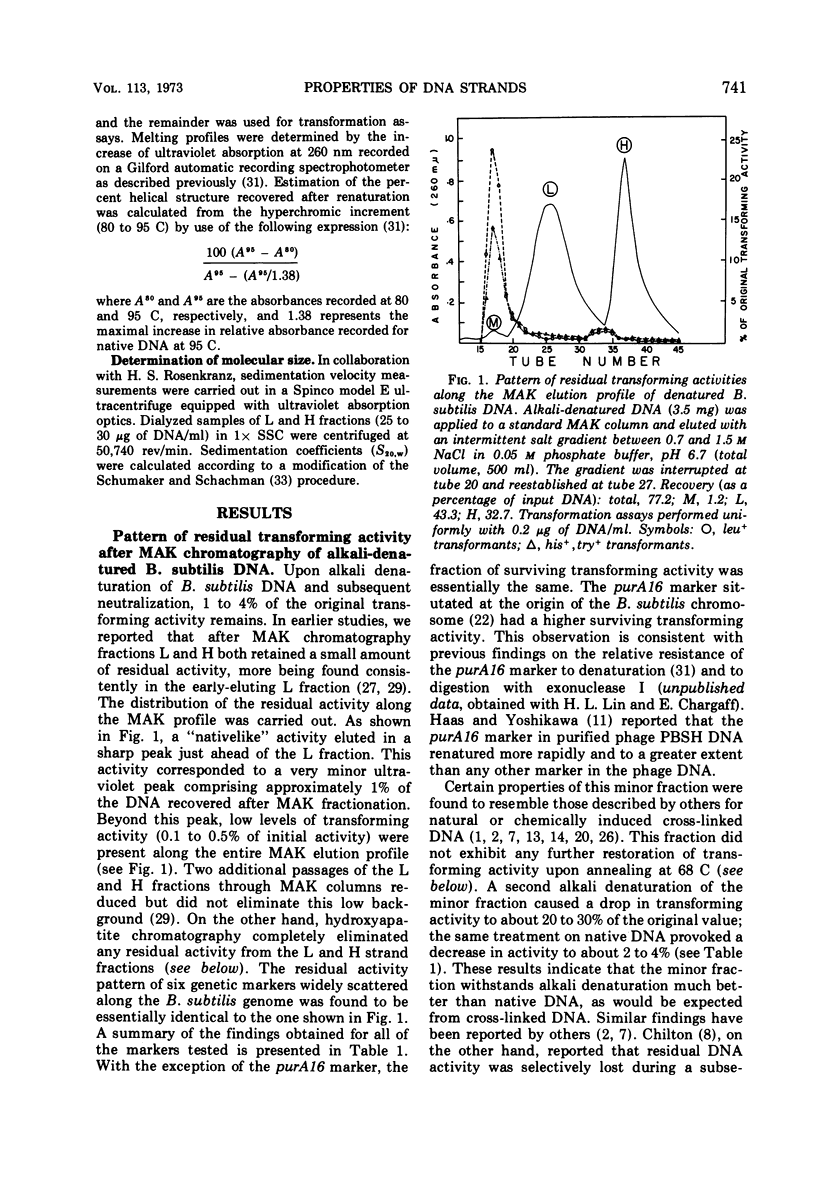
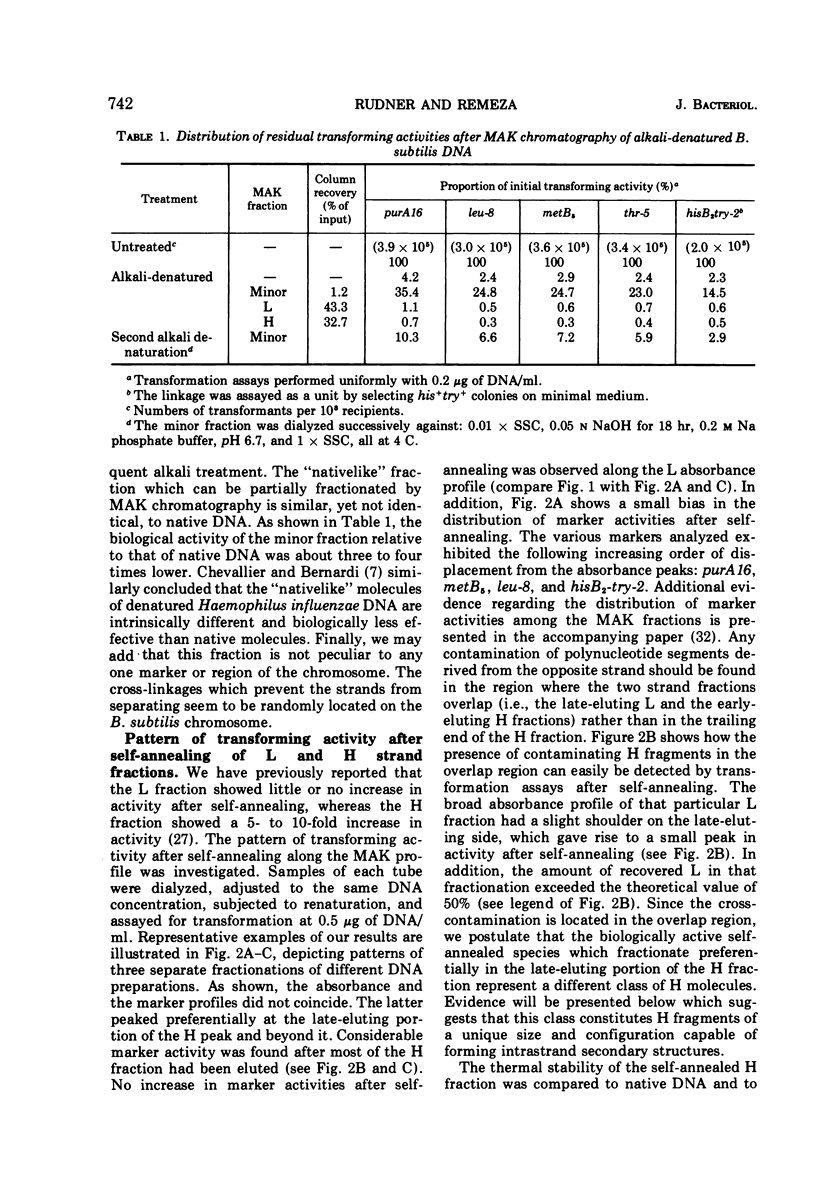
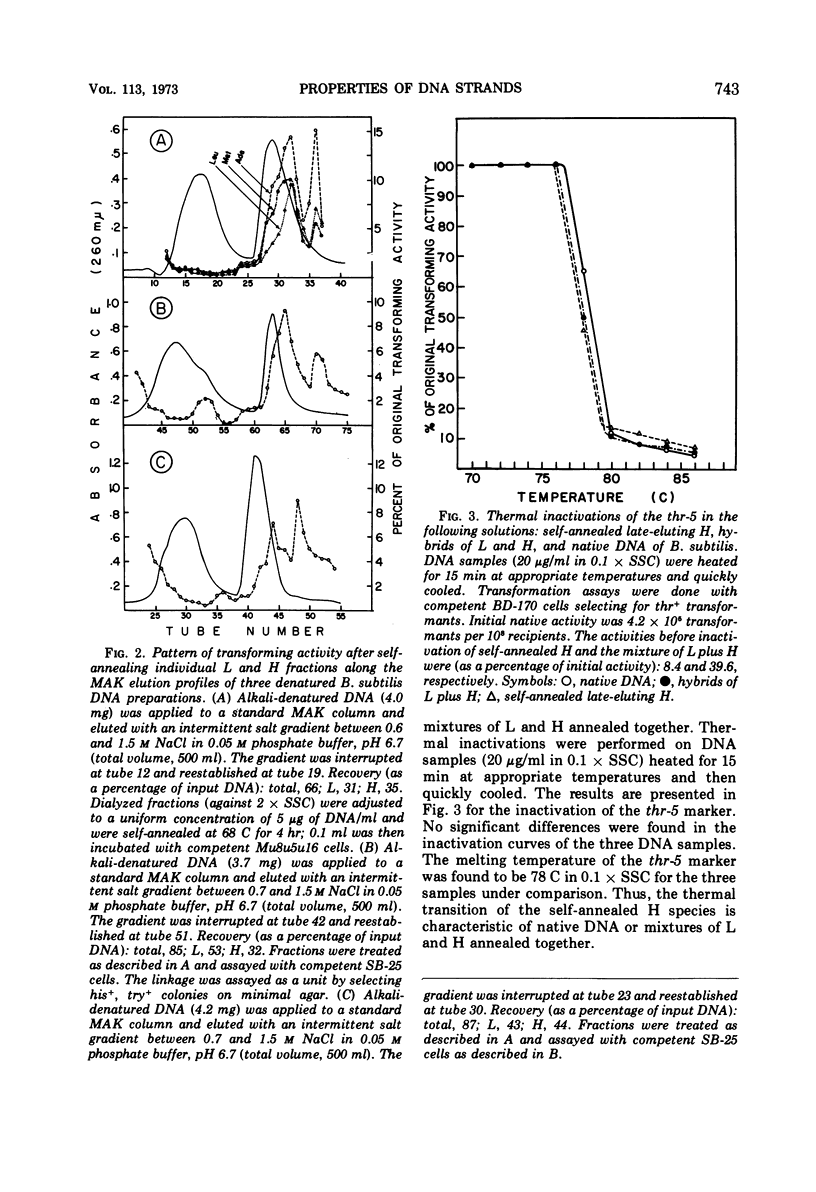
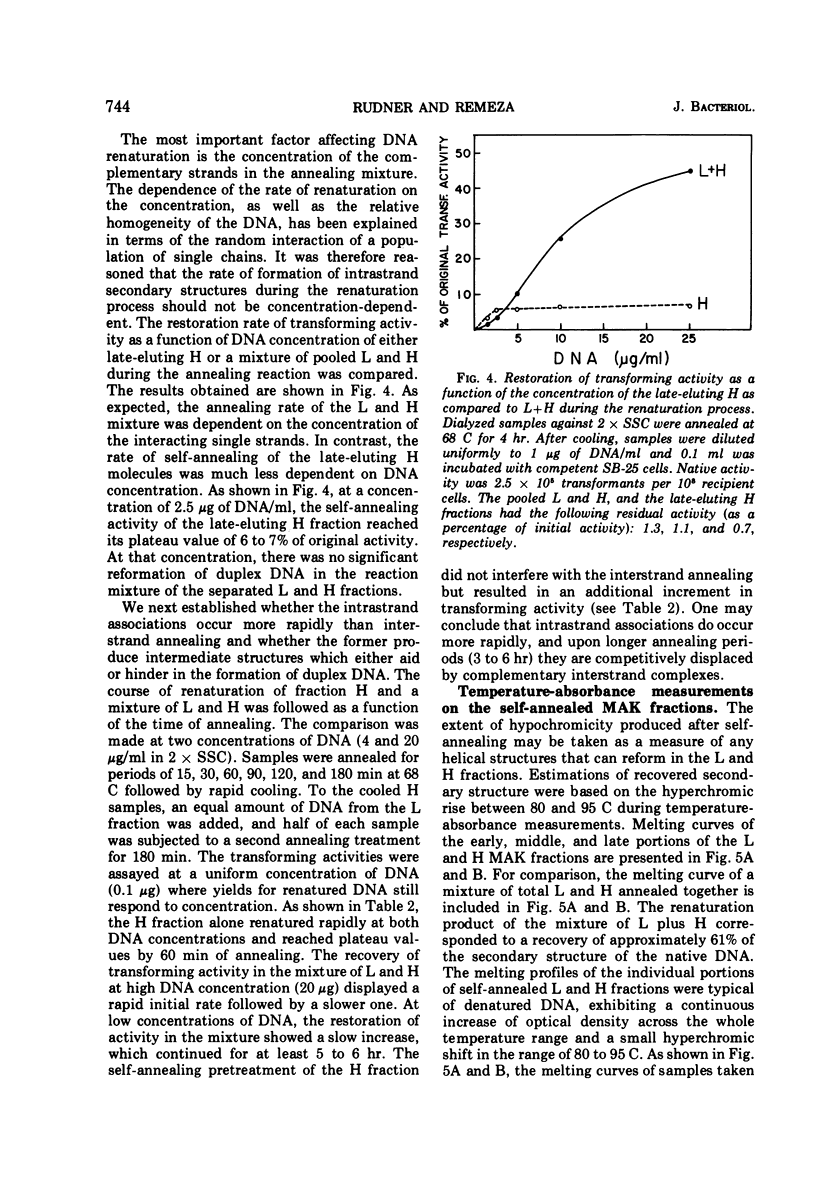
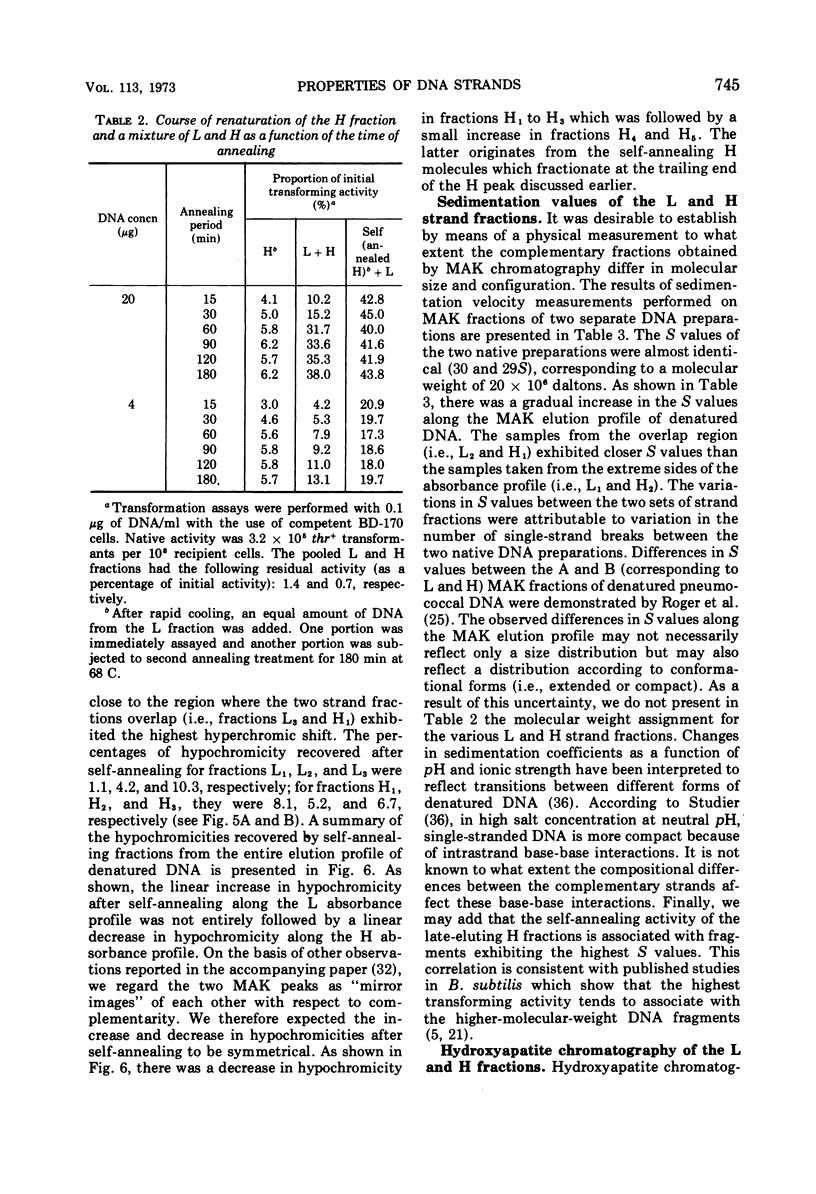
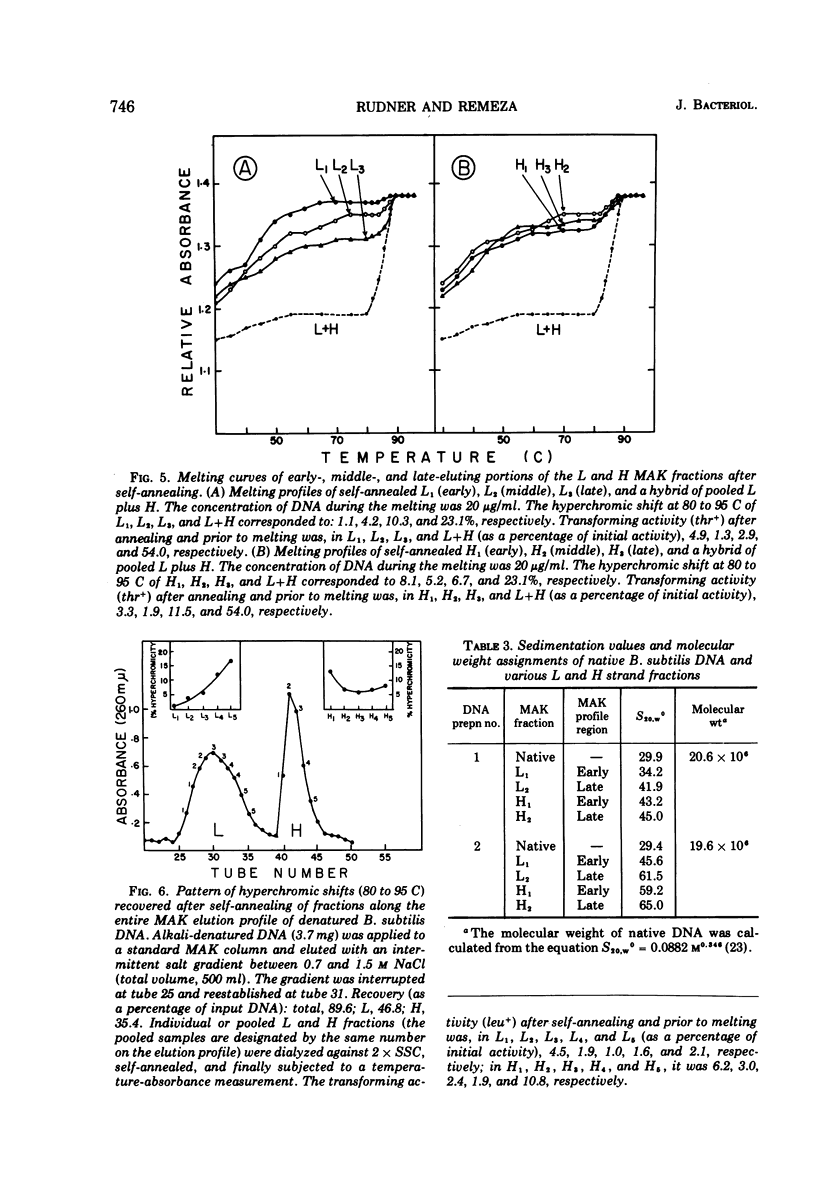
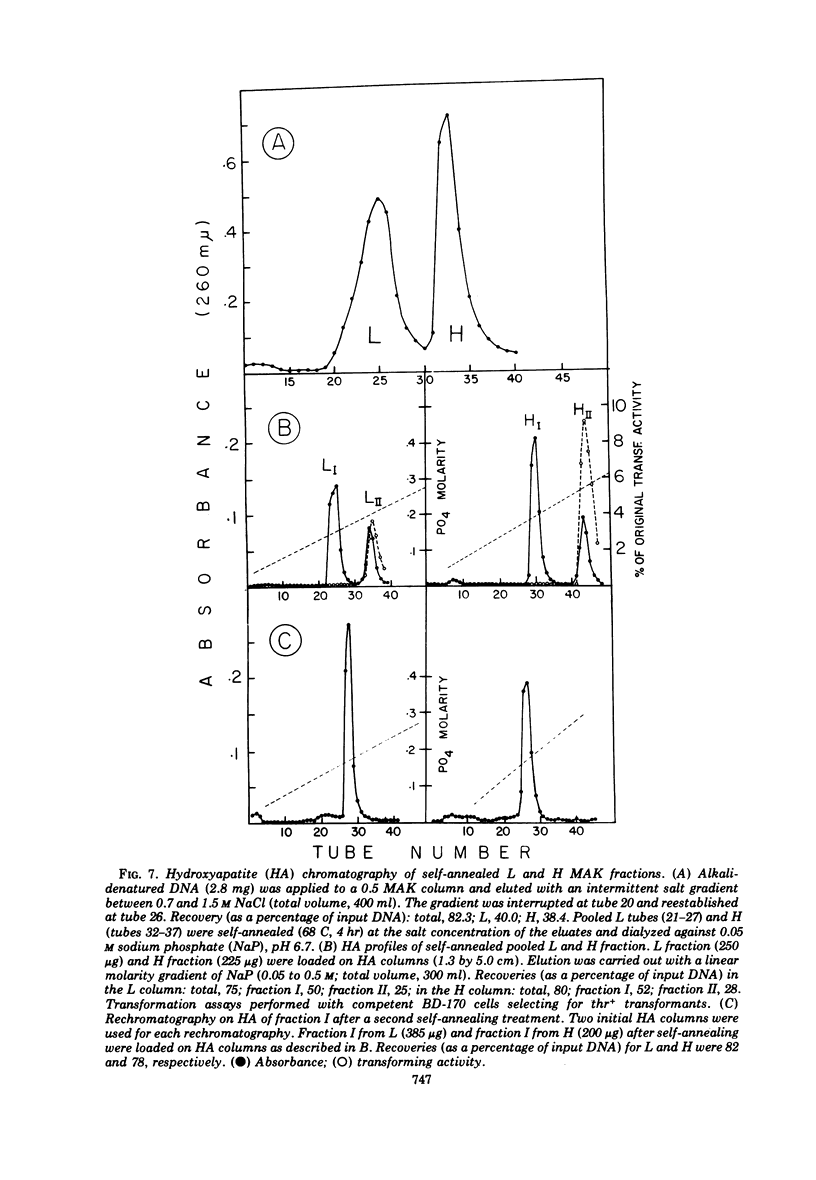
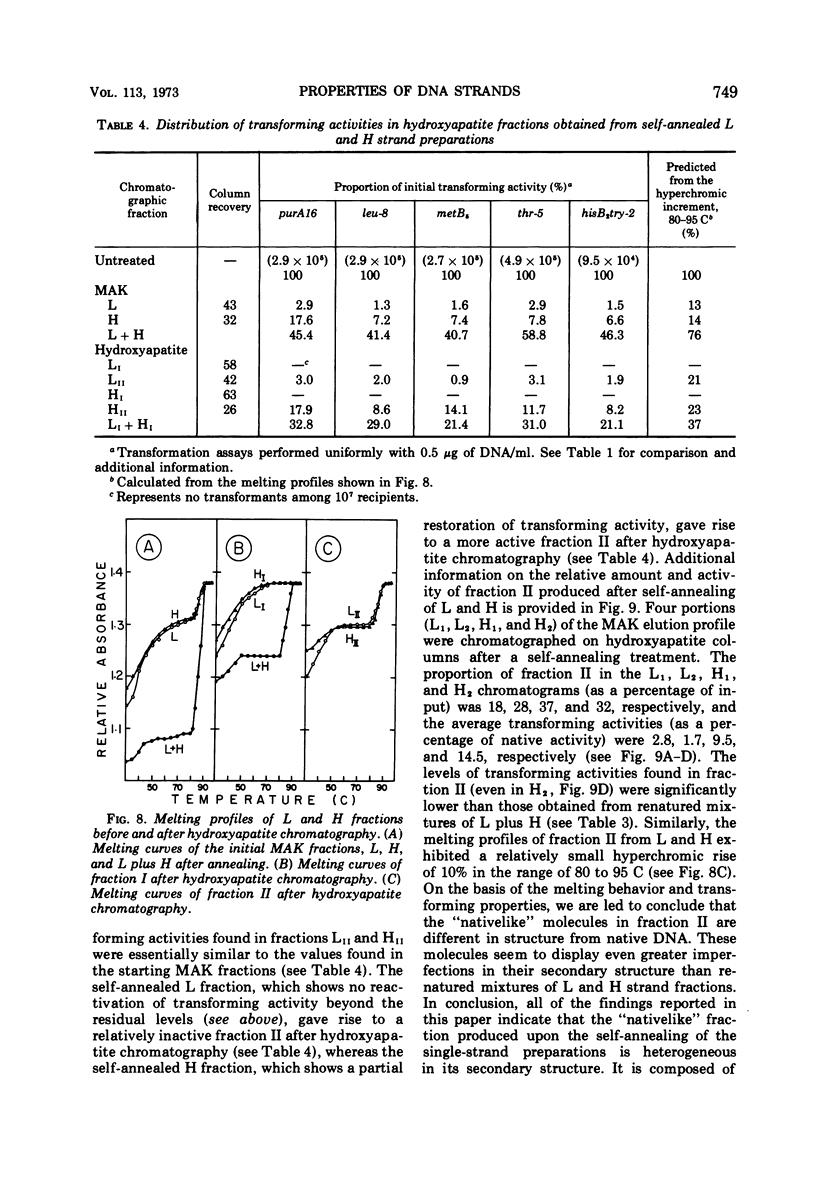
Biological, physical, and chromatographic properties of methylated albuminkieselguhr (MAK)-fractionated complementary strands, designated as light (L) and heavy (H), of Bacillus subtilis deoxyribonucleic acid (DNA) are presented. The pattern of transforming activity along the MAK elution profile of alkilidenatured DNA shows that the residually active molecules selectively fractionated ahead of the L strand fraction, whereas the most active self-annealed molecules fractionated preferentially at the trailing end of the H strand fraction. The restoration rate of transforming activity in the late-eluting H molecules was rapid and independent of concentration during the annealing reaction. The data suggest that the self-annealing activity in the H strand is due in part to the formation of intrastrand secondary structures. Hydroxyapatite chromatography of self-annealed L and H strands yielded a major fraction (I) of highly purified strand preparations devoid of transforming activity and hypochromicity, and a minor “nativelike” fraction (II). Sedimentation velocity measurements show that, in addition to the mutual complementary nature of the L and H fractions, they differ in molecular size and possibly configuration.
Full text
PDF





Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Alberts B. M. Characterization of a naturally occurring, cross-linked fraction of DNA. II. Origin of the cross-linkage. J Mol Biol. 1968 Mar 14;32(2):405–421. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(68)90018-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Alberts B. M., Doty P. Characterization of a naturally occurring, cross-linked fraction of DNA. 1. Nature of the cross-linkage. J Mol Biol. 1968 Mar 14;32(2):379–403. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(68)90017-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Anagnostopoulos C., Spizizen J. REQUIREMENTS FOR TRANSFORMATION IN BACILLUS SUBTILIS. J Bacteriol. 1961 May;81(5):741–746. doi: 10.1128/jb.81.5.741-746.1961. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bernardi G. Chromatography of nucleic acids on hydroxyapatite. II. Chromatography of denatured DNA. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1969 Feb 18;174(2):435–448. doi: 10.1016/0005-2787(69)90274-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bodmer W. F. Integration of deoxyribonuclease-treated DNA in bacillus subtilis transformation. J Gen Physiol. 1966 Jul;49(6):233–258. doi: 10.1085/jgp.49.6.233. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chevallier M. R., Bernardi G. Residual transforming activity of denatured Haemophilus influenzae DNA. J Mol Biol. 1968 Mar 14;32(2):437–451. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(68)90020-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chilton M. D. Transforming Activity in Both Complementary Strands of Bacillus subtilis DNA. Science. 1967 Aug 18;157(3790):817–819. doi: 10.1126/science.157.3790.817. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gabor M., Hotchkiss R. D. Manifestation of linear organization in molecules of pneumococcal transforming DNA. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1966 Nov;56(5):1441–1448. doi: 10.1073/pnas.56.5.1441. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- HJERTEN S., LEVIN O., TISELIUS A. Protein chromatography on calcium phosphate columns. Arch Biochem Biophys. 1956 Nov;65(1):132–155. doi: 10.1016/0003-9861(56)90183-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Haas M., Yoshikawa H. Defective Bacteriophage PBSH in Bacillus subtilis: III. Properties of Adenine-16 Marker in Purified Bacteriophage Deoxyribonucleic Acid. J Virol. 1969 Dec;4(6):844–850. doi: 10.1128/jvi.4.6.844-850.1969. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Karkas J. D., Rudner R., Chargaff E. Seapration of B. subtilis DNA into complementary strands. II. Template functions and composition as determined by transcription with RNA polymerase. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1968 Jul;60(3):915–920. doi: 10.1073/pnas.60.3.915. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kohn K. W., Green D. M. Transforming activity of nitrogen mustard-crosslinked DNA. J Mol Biol. 1966 Aug;19(2):289–302. doi: 10.1016/s0022-2836(66)80005-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kohn K. W., Spears C. L., Doty P. Inter-strand crosslinking of DNA by nitrogen mustard. J Mol Biol. 1966 Aug;19(2):266–288. doi: 10.1016/s0022-2836(66)80004-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- MANDELL J. D., HERSHEY A. D. A fractionating column for analysis of nucleic acids. Anal Biochem. 1960 Jun;1:66–77. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(60)90020-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- MIYAZAWA Y., THOMAS C. A., Jr NUCLEOTIDE COMPOSITION OF SHORT SEGMENTS OF DNA MOLECULES. J Mol Biol. 1965 Feb;11:223–237. doi: 10.1016/s0022-2836(65)80053-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Margulies L., Remeza V., Rudner R. Asymmetric template function of microbial deoxyribonucleic acids: transcription of messenger ribonucleic acid. J Bacteriol. 1971 Sep;107(3):610–617. doi: 10.1128/jb.107.3.610-617.1971. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Margulies L., Remeza V., Rudner R. Asymmetric template function of microbial deoxyribonucleic acids: transcription of ribosomal and soluble ribonucleic acids. J Bacteriol. 1970 Sep;103(3):560–568. doi: 10.1128/jb.103.3.560-568.1970. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mulder C., Doty P. Residual activity of denatured transforming DNA of Haemophilus influenzae: a natrually occurring cross-linked DNA. J Mol Biol. 1968 Mar 14;32(2):423–435. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(68)90019-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nester E. W., Ganesan A. T., Lederberg J. EFFECTS OF MECHANICAL SHEAR ON GENETIC ACTIVITY OF BACILLUS SUBTILIS DNA. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1963 Jan;49(1):61–68. doi: 10.1073/pnas.49.1.61. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- OISHI M., YOSHIKAWA H., SUEOKA N. SYNCHRONOUS AND DICHOTOMOUS REPLICATIONS OF THE BACILLUS SUBTILIS CHROMOSOME DURING SPORE GERMINATION. Nature. 1964 Dec 12;204:1069–1073. doi: 10.1038/2041069a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Roger M., Beckmann C. O., Hotchkiss R. D. Fractionation of denatured pneumococcal DNA: evidence for resolution of complementary strands. J Mol Biol. 1966 Jun;18(1):174–194. doi: 10.1016/s0022-2836(66)80084-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Roger M., Beckmann C. O., Hotchkiss R. D. Separation of native and denatured fractions from partially denatured pneumococcal DNA. J Mol Biol. 1966 Jun;18(1):156–173. doi: 10.1016/s0022-2836(66)80083-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Roger M. Chromatographic resolution of complementary strands of denatured Pneumococcal DNA. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1968 Jan;59(1):200–207. doi: 10.1073/pnas.59.1.200. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rownd R., Green D. M., Sternglanz R., Doty P. Origin of the residual transforming activity of denatured Bacillus subtilis DNA. J Mol Biol. 1968 Mar 14;32(2):369–377. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(68)90016-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rudner R., Karkas J. D., Chargaff E. Separation of B. subtilis DNA into complementary strands, I. Biological properties. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1968 Jun;60(2):630–635. doi: 10.1073/pnas.60.2.630. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rudner R., Karkas J. D., Chargaff E. Separation of B. subtilis DNA into complementary strands. 3. Direct analysis. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1968 Jul;60(3):921–922. doi: 10.1073/pnas.60.3.921. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rudner R., Karkas J. D., Chargaff E. Separation of microbial deoxyribonucleic acids into complementary strands. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1969 May;63(1):152–159. doi: 10.1073/pnas.63.1.152. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rudner R., Ledoux M., Mazelis A. Distribution of pyrimidine oligonucleotides in strands L and H of Bacillus subtilis DNA. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1972 Sep;69(9):2745–2749. doi: 10.1073/pnas.69.9.2745. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rudner R., Lin H. J., Hoffmann E. M., Chargaff E. Studies on the loss and the restoration of the transforming activity of the deoxyribonucleic acid of Bacillus subtilis. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1967 Nov 21;149(1):199–219. doi: 10.1016/0005-2787(67)90702-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rudner R., Remeza V. Chromatographically fractionated complementary strands of Bacillus subtilis deoxyribonucleic acid: transformation of hybrids. J Bacteriol. 1973 Feb;113(2):754–762. doi: 10.1128/jb.113.2.754-762.1973. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- SCHUMAKER V. N., SCHACHMAN H. K. Ultracentrifugal analysis of dilute solutions. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1957 Mar;23(3):628–639. doi: 10.1016/0006-3002(57)90386-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- STUDIER F. W. SEDIMENTATION STUDIES OF THE SIZE AND SHAPE OF DNA. J Mol Biol. 1965 Feb;11:373–390. doi: 10.1016/s0022-2836(65)80064-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- SUEOKA N., CHENG T. Y. Fractionation of nucleic acids with the methylated albumin column. J Mol Biol. 1962 Mar;4:161–172. doi: 10.1016/s0022-2836(62)80048-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stewart C. R. Physical heterogeneity among Bacillus subtilis deoxyribonucleic acid molecules carrying particular genetic markers. J Bacteriol. 1969 Jun;98(3):1239–1247. doi: 10.1128/jb.98.3.1239-1247.1969. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Strauss N. Transformation of Bacillus subtilis using hybrid DNA molecules constructed by annealing resolved complementary strands. Genetics. 1970 Dec;66(4):583–593. doi: 10.1093/genetics/66.4.583. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


