Abstract
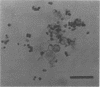
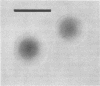
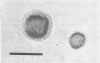
Defined conditions are described which allowed luxuriant growth over continuous subculture of strains of Neisseria gonorrhoeae in broth and on agar. Growth was equal to or surpassed that observed in Mueller-Hinton broth or on Mueller-Hinton blood agar. The final medium adopted consisted of medium 199 and a supplemental mixture of cysteine, glucose, and various salts. Addition of sodium bicarbonate or CO2 enrichment was not required. For solidification, only agarose allowed growth of all strains; glutamic acid stimulated growth of two strains but was inhibitory for a third. The addition of 8% polyvinylpyrrolidone (PVP), 2% purified albumin, and penicillin resulted in induction of all three strains to the L-form with frequencies up to 0.3%. At present no induction to the L-form has been achieved in the absence of albumin. Various lots of PVP proved toxic in the defined medium, and extensive dialysis was required for good growth and L-form induction. Substitution of PVP with sucrose indicated a sucrose toxicity for the parental gonococcus even on the addition of albumin. L-form induction did occur on sucrose L-medium but at significantly lower frequencies. The colonies appeared 1 week later than those on PVP L-medium but at significantly lower frequencies. The colonies appeared 1 week later than those on PVP L-medium and remained very small and poorly developed.
Full text
PDF

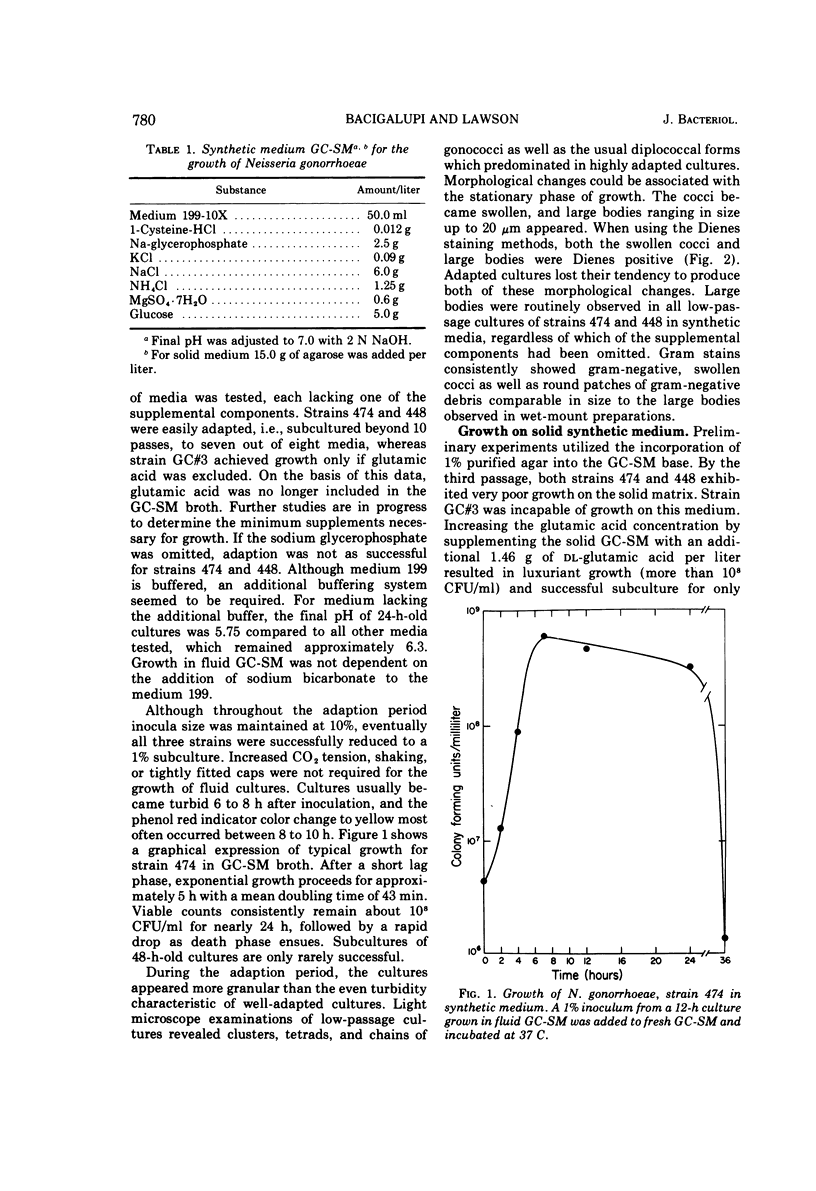
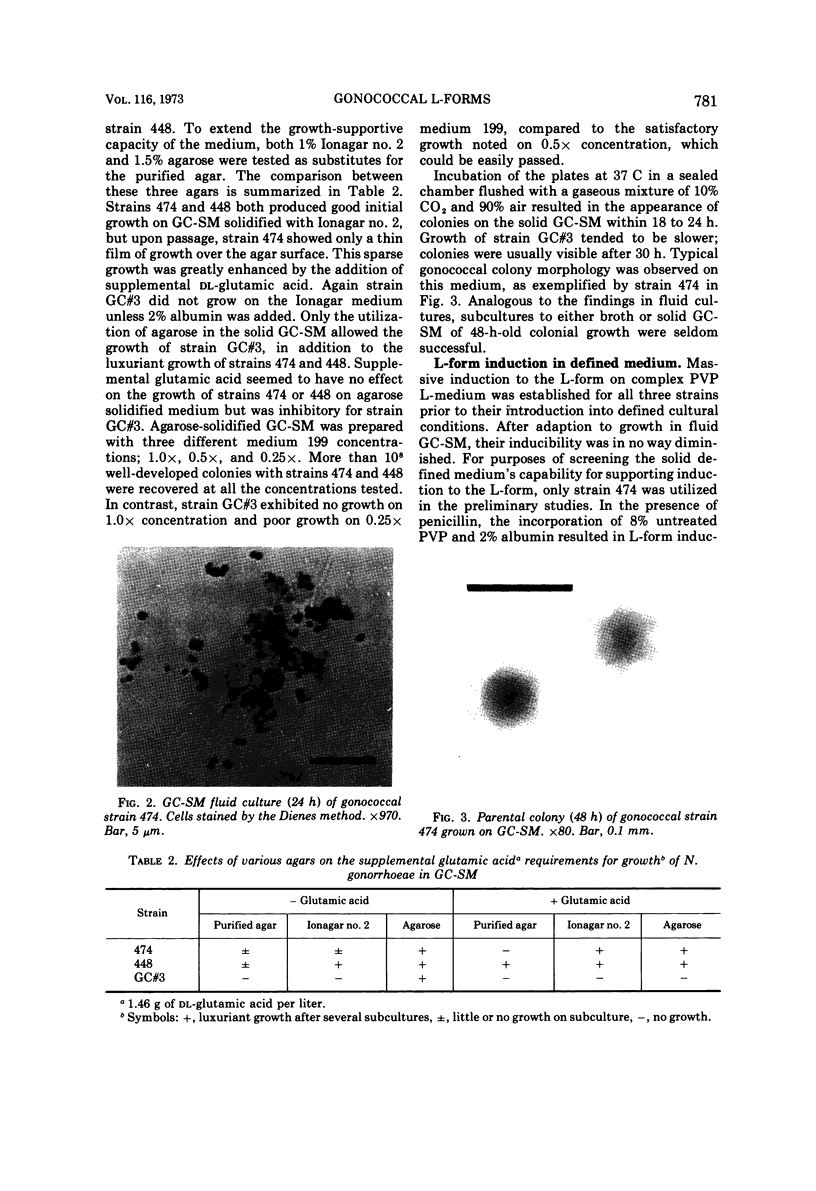



Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Ashwood-Smith M. J., Warby C. Studies on the molecular weight and cryoprotective properties of polyvinylpyrrolidone and dextran with bacteria and erythrocytes. Cryobiology. 1971 Oct;8(5):453–464. doi: 10.1016/0011-2240(71)90036-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- BARILE M. F., VAN ZEE G. K., YAGUCHI R. The occurrence of failures in penicillin-treated gonorrheal urethritis. I. The significance of L-form transformation of Neisseria gonorrhoeae to penicillin resistance. Antibiotic Med Clin Ther (New York) 1959 Aug;6:470–479. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brookes R., Hedén C. G. Dense cultures of Neisseria gonorrhoeae in liquid medium. Appl Microbiol. 1967 Mar;15(2):219–223. doi: 10.1128/am.15.2.219-223.1967. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Clasener H. Pathogenicity of the L-phase of bacteria. Annu Rev Microbiol. 1972;26:55–84. doi: 10.1146/annurev.mi.26.100172.000415. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- DIENES L., BANDUR B. M., MADOFF S. DEVELOPMENT OF L-TYPE GROWTH IN NEISSERIA GONORRHOEAE CULTURES. J Bacteriol. 1964 Jun;87:1471–1476. doi: 10.1128/jb.87.6.1471-1476.1964. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Frantz I. D. Growth Requirements of the Meningococcus. J Bacteriol. 1942 Jun;43(6):757–761. doi: 10.1128/jb.43.6.757-761.1942. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gnarpe H., Wallin J., Forsgren A. Studies in venereal disease. I. Isolation of L-phase organisms of N. gonorrhoeae from patients with gonorrhoea. Br J Vener Dis. 1972 Dec;48(6):496–499. doi: 10.1136/sti.48.6.496. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hunter K. M., McVeigh I. Development of a chemically defined medium for growth of Neisseria gonorrhoeae. Antonie Van Leeuwenhoek. 1970;36(2):305–316. doi: 10.1007/BF02069032. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kenny C. P., Ashton F. E., Diena B. B., Greenberg L. A chemically defined protein-free liquid medium for the cultivation of some species of Neisseria. Bull World Health Organ. 1967;37(4):569–573. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kenny C. P., Diena B. B., Wallace R., Greenberg L. Cultivation and properties of Neisseria sp. grown in chemically defined media. Can J Microbiol. 1972 Jul;18(7):1087–1090. doi: 10.1139/m72-168. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Roberts R. B. L form of Neisseria gonorrhoeae. J Bacteriol. 1966 Dec;92(6):1609–1614. doi: 10.1128/jb.92.6.1609-1614.1966. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Swanson J., Kraus S. J., Gotschlich E. C. Studies on gonococcus infection. I. Pili and zones of adhesion: their relation to gonococcal growth patterns. J Exp Med. 1971 Oct 1;134(4):886–906. doi: 10.1084/jem.134.4.886. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Welton J. P., Stokinger H. E., Carpenter C. M. A CHEMICALLY DEFINED MEDIUM FOR THE CULTIVATION OF THE GONOCOCCUS. Science. 1944 May 5;99(2575):372–372. doi: 10.1126/science.99.2575.372. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]