Abstract
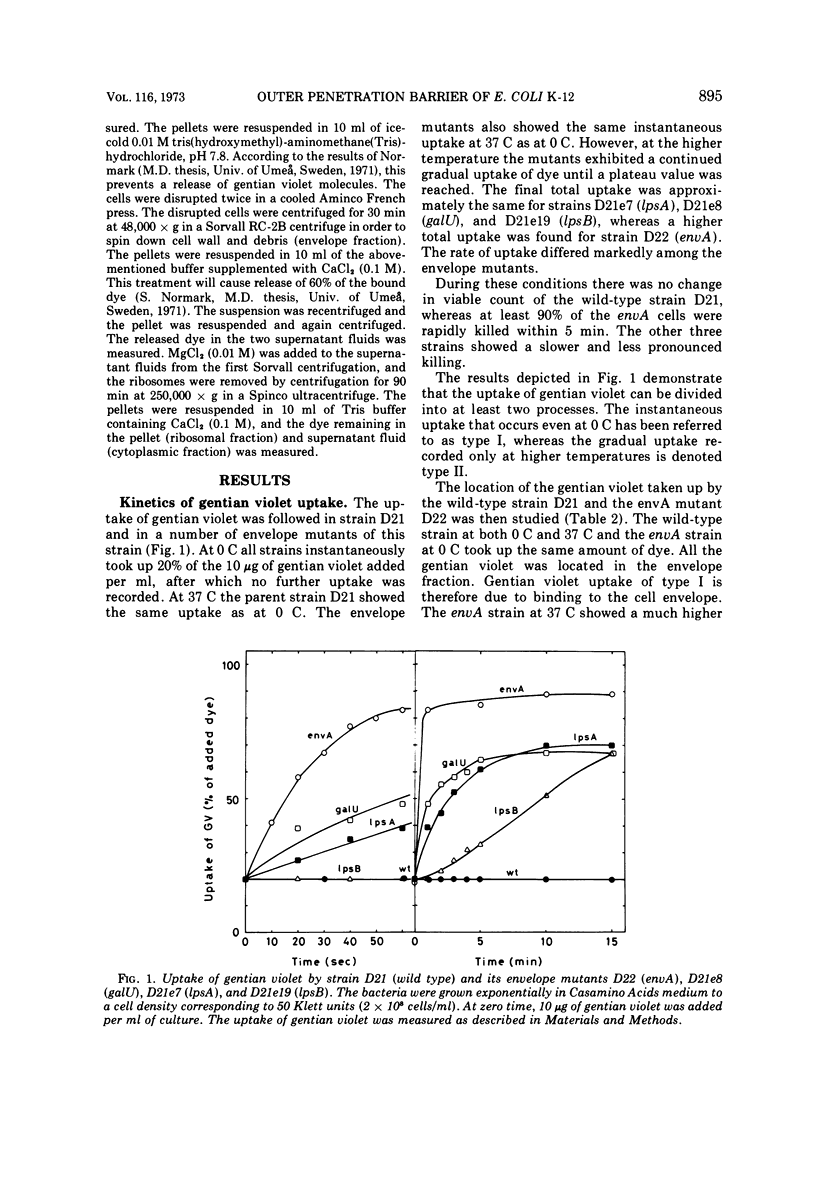
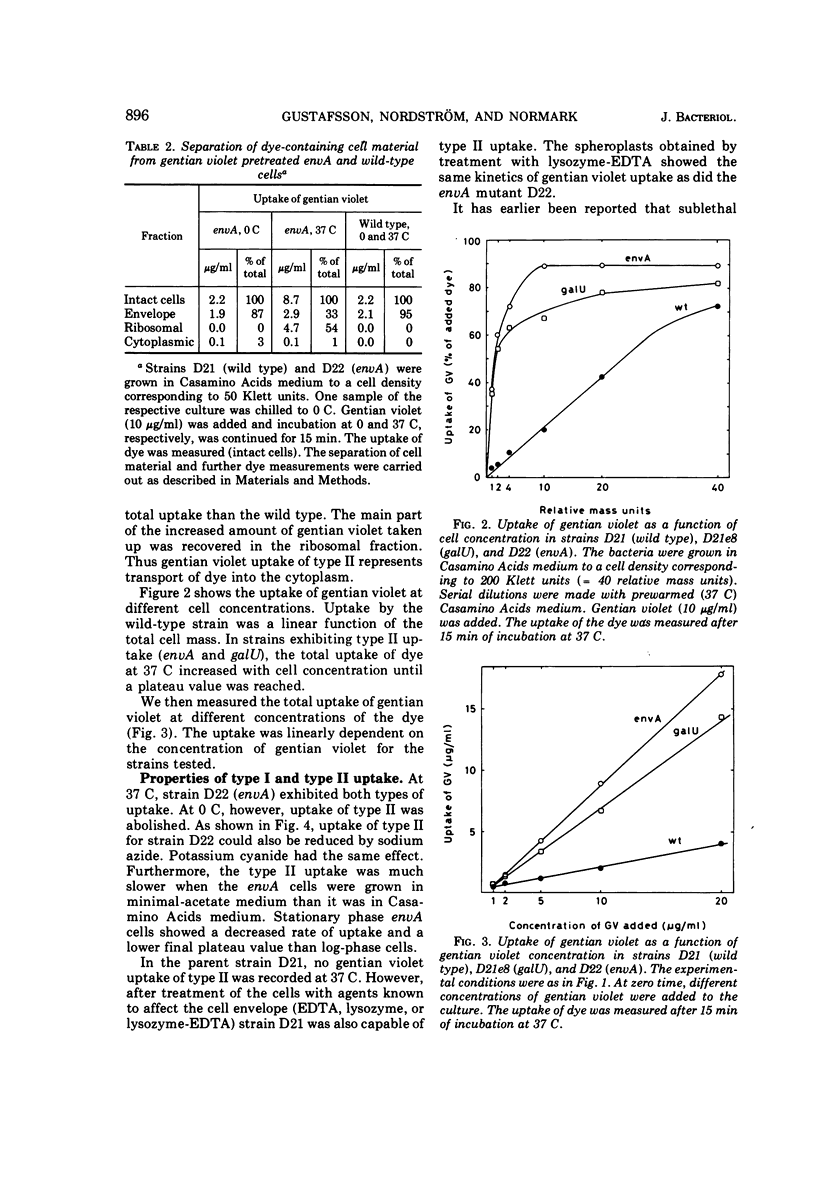
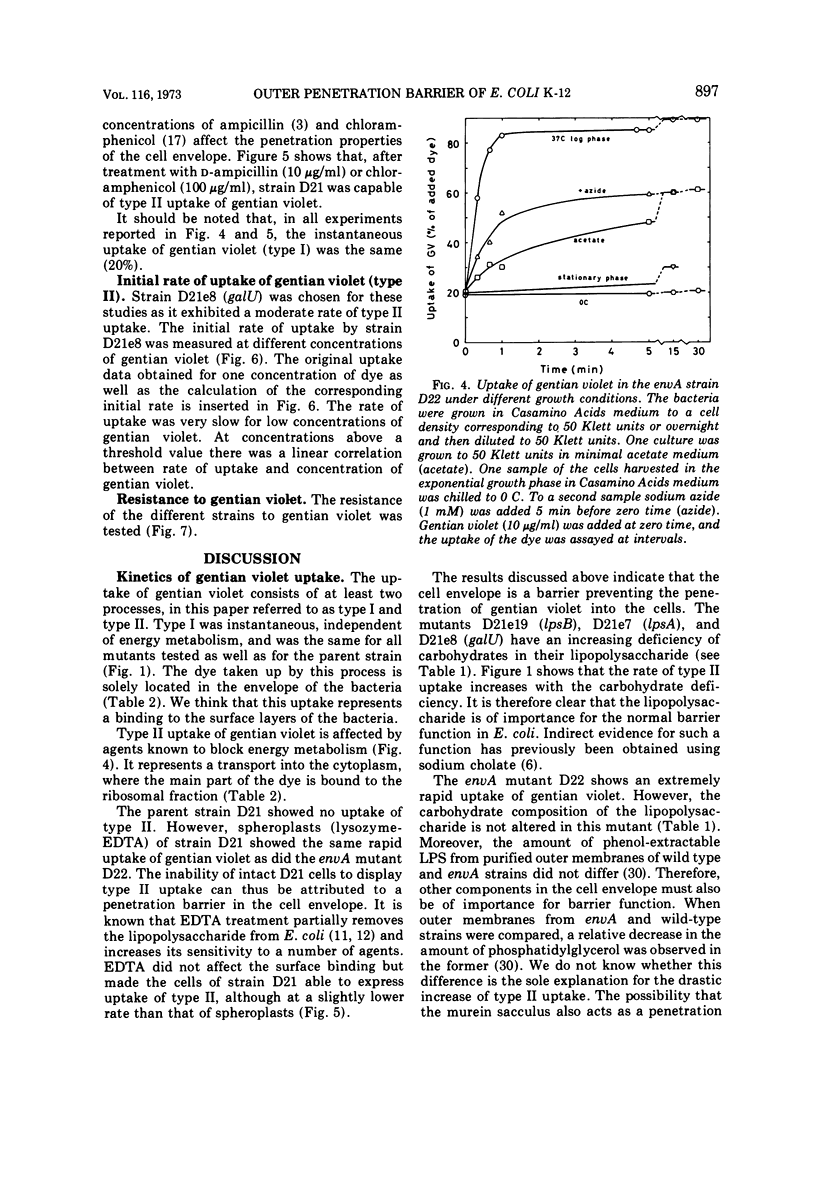
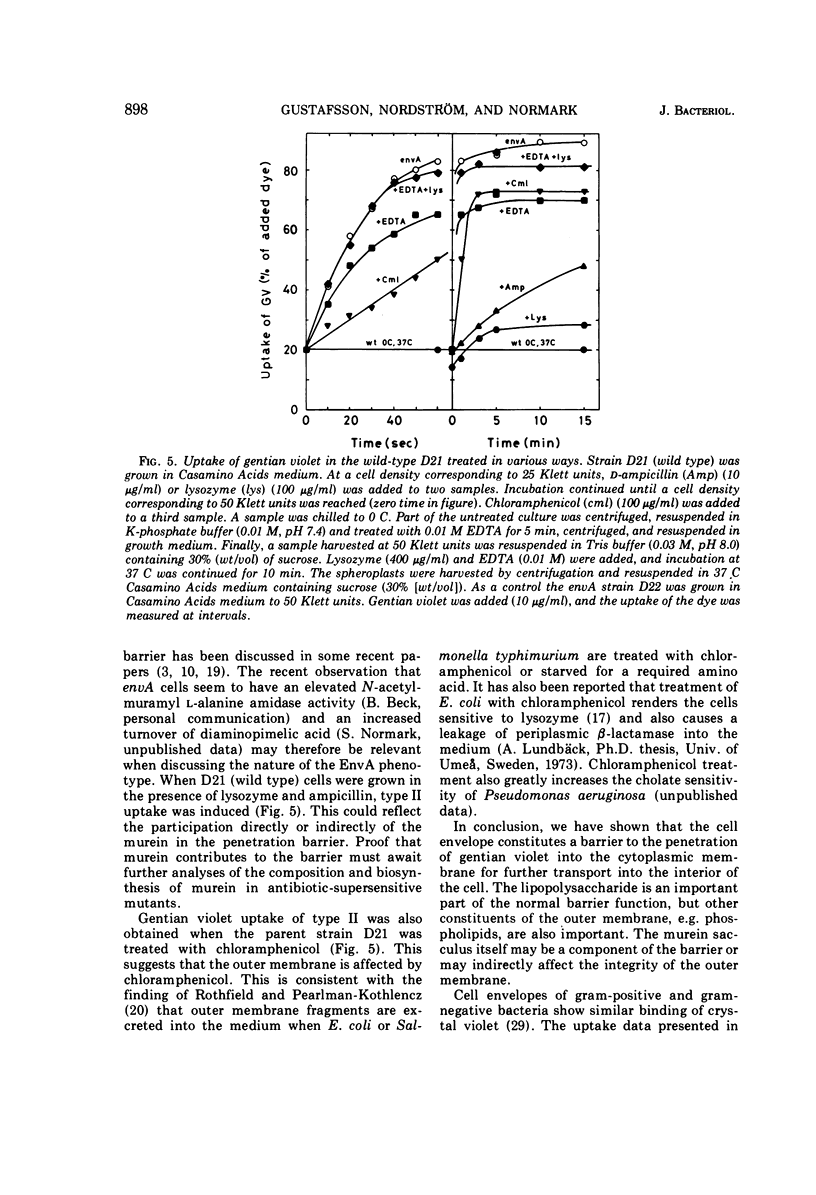
Wild-type strains of Escherichia coli K-12 adsorb gentian violet to the cell surface, but the dye is not transported into the cytoplasm. However, when some mutants that have an altered outer membrane are exposed to gentian violet, the dye is also found in the ribosomal fraction. The transport into the cytoplasm is inhibited at 0 C and requires that the concentration of gentian violet exceeds a threshold value. The initial rate of uptake as well as the amount of gentian violet found in the cytoplasm increases with the concentration of the dye in the medium. The rate of transport of the dye into the cytoplasm is much lower for stationary mutant cells than for exponentially growing cells. The rate of uptake into the cytoplasm increases with increasing deficiency of carbohydrate in the lipopolysaccharide (carbohydrate content lpsB > lpsA > galU). However, other components are also responsible for the barrier since an envA mutant which is not altered in the lipopolysaccharide carbohydrates show an extremely rapid uptake of the dye. The rate of uptake for the envA mutant was the highest found and the same as that of spheroplasts. Growth in the presence of agents affecting the murein sacculus, e.g., lysozyme and sublethal concentrations of penicillin, increased the rate of uptake of gentian violet. Brief treatments with tris(hydroxymethyl)aminomethane-ethylenediaminetetraacetic acid drastically impaired the barrier function. Inhibition of protein synthesis by chloramphenicol also opened the barrier to gentian violet. In conclusion, the outer part of the bacterial envelope is a penetration barrier for gentian violet and probably also for other substances. The lipopolysaccharide, the murein and also other components are important for the function of this barrier. Resistance to gentian violet was found to be inversely correlated to the rate of penetration of the dye into the cytoplasm.
Full text
PDF


Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Boman H. G., Eriksson-Grennberg K. G., Normark S., Matsson E. Resistance of Escherichia coli to penicillins. IV. Genetic study of mutants resistant to D,L-ampicillin concentrations o 100 mu-g-ml. Genet Res. 1968 Oct;12(2):169–185. doi: 10.1017/s0016672300011782. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Burman L. G., Nordström K., Bloom G. D. Murein and the outer penetration barrier of Escherichia coli K-12, Proteus mirabilis, and Pseudomonas aeruginosa. J Bacteriol. 1972 Dec;112(3):1364–1374. doi: 10.1128/jb.112.3.1364-1374.1972. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Burman L. G., Nordström K., Boman H. G. Resistance of Escherichia coli to penicillins. V. Physiological comparison of two isogenic strains, one with chromosomally and one with episomally mediated ampicillin resistance. J Bacteriol. 1968 Aug;96(2):438–446. doi: 10.1128/jb.96.2.438-446.1968. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Burman L. G., Nordström K. Colicin tolerance induced by ampicillin or mutation to ampicillin resistance in a strain of Escherichia coli K-12. J Bacteriol. 1971 Apr;106(1):1–13. doi: 10.1128/jb.106.1.1-13.1971. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ennis H. L. Mutants of Escherichia coli sensitive to antibiotics. J Bacteriol. 1971 Aug;107(2):486–490. doi: 10.1128/jb.107.2.486-490.1971. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Eriksson-Grennberg K. R., Nordström K., Englund P. Resistance of Escherichia coli to penicillins. IX. Genetics and physiology of class II ampicillin-resistant mutants that are galactose negative or sensitive to bacteriophage C21, or both. J Bacteriol. 1971 Dec;108(3):1210–1223. doi: 10.1128/jb.108.3.1210-1223.1971. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Franklin T. J., Higginson B. Active accumulation of tetracycline by Escherichia coli. Biochem J. 1970 Jan;116(2):287–297. doi: 10.1042/bj1160287. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hamilton-Miller J. M. Damaging effects of ethylenediaminetetra-acetate and penicillins on permeability barriers in Gram-negative bacteria. Biochem J. 1966 Sep;100(3):675–682. doi: 10.1042/bj1000675. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kushner D. J., Khan S. R. Proflavine Uptake and Release in Sensitive and Resistant Escherichia coli. J Bacteriol. 1968 Oct;96(4):1103–1114. doi: 10.1128/jb.96.4.1103-1114.1968. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- LEIVE L. A NONSPECIFIC INCREASE IN PERMEABILITY IN ESCHERICHIA COLI PRODUCED BY EDTA. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1965 Apr;53:745–750. doi: 10.1073/pnas.53.4.745. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lazdunski C., Shaprio B. M. Relationship between permeability, cell division, and murein metabolism in a mutant of Escherichia coli. J Bacteriol. 1972 Aug;111(2):499–509. doi: 10.1128/jb.111.2.499-509.1972. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Leive L., Shovlin V. K., Mergenhagen S. E. Physical, chemical, and immunological properties of lipopolysaccharide released from Escherichia coli by ethylenediaminetetraacetate. J Biol Chem. 1968 Dec 25;243(24):6384–6391. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nakamura H., Suganuma A. Membrane mutation associated with sensitivity to acriflavine in Escherichia coli. J Bacteriol. 1972 Apr;110(1):329–335. doi: 10.1128/jb.110.1.329-335.1972. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nelson B. W., Roantree R. J. Analyses of lipopolysaccharides extracted from penicillin-resistant, serum-sensitive salmonella mutants. J Gen Microbiol. 1967 Aug;48(2):179–188. doi: 10.1099/00221287-48-2-179. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Normark S., Boman H. G., Matsson E. Mutant of Escherichia coli with anomalous cell division and ability to decrease episomally and chromosomally mediated resistance to ampicillin and several other antibiotics. J Bacteriol. 1969 Mar;97(3):1334–1342. doi: 10.1128/jb.97.3.1334-1342.1969. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Normark S. Phenethyl alcohol as a suppressor of the envA phenotype associated with the envA gene in Escherichia coli K-12. J Bacteriol. 1971 Oct;108(1):51–58. doi: 10.1128/jb.108.1.51-58.1971. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Normark S., Westling B. Nature of the penetration barrier in Escherichia coli K-12: effect of macromolecular inhibition of penetrability in strains containing the envA gene. J Bacteriol. 1971 Oct;108(1):45–50. doi: 10.1128/jb.108.1.45-50.1971. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Richmond M. H., Sykes R. B. The beta-lactamases of gram-negative bacteria and their possible physiological role. Adv Microb Physiol. 1973;9:31–88. doi: 10.1016/s0065-2911(08)60376-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rodolakis A., Thomas P., Starka J. Morphological mutants of Escherichia coli. Isolation and ultrastructure of a chain-forming envC mutant. J Gen Microbiol. 1973 Apr;75(2):409–416. doi: 10.1099/00221287-75-2-409. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rothfield L., Pearlman-Kothencz M. Synthesis and assembly of bacterial membrane components. A lipopolysaccharide-phospholipid-protein complex excreted by living bacteria. J Mol Biol. 1969 Sep 28;44(3):477–492. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(69)90374-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- SMITH J. T. Penicillinase and ampicillin resistance in a strain of Escherichia coli. J Gen Microbiol. 1963 Feb;30:299–306. doi: 10.1099/00221287-30-2-299. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schlecht S., Westphal O. Antibiotica-Empfindlichkeit bei S- und R-Formen von Salmonella minnesota. Naturwissenschaften. 1968 Oct;55(10):494–495. doi: 10.1007/BF00599721. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schlecht S., Westphal O. Untersuchungen zur Typisierung von Salmonella-R-Formen. 4. Typisierung von S. minnesota-R-Mutanten mittels Antibiotica. Zentralbl Bakteriol Orig. 1970 Apr;213(3):356–380. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sugino Y. Mutants of Escherichia coli sensitive to methylene blue and acridines. Genet Res. 1966 Feb;7(1):1–11. doi: 10.1017/s0016672300009423. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tamaki S., Sato T., Matsuhashi M. Role of lipopolysaccharides in antibiotic resistance and bacteriophage adsorption of Escherichia coli K-12. J Bacteriol. 1971 Mar;105(3):968–975. doi: 10.1128/jb.105.3.968-975.1971. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Taylor A. L., Trotter C. D. Linkage map of Escherichia coli strain K-12. Bacteriol Rev. 1972 Dec;36(4):504–524. doi: 10.1128/br.36.4.504-524.1972. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- VOGEL H. J., BONNER D. M. Acetylornithinase of Escherichia coli: partial purification and some properties. J Biol Chem. 1956 Jan;218(1):97–106. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Voll M. J., Leive L. Release of lipopolysaccharide in Escherichia coli resistant to the permeability increase induced by ethylenediaminetetraacetate. J Biol Chem. 1970 Mar 10;245(5):1108–1114. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wistreich G., Bartholomew J. W. The binding of crystal violet by isolated bacterial cell-wall material. J Gen Microbiol. 1969 Dec;59(2):223–227. doi: 10.1099/00221287-59-2-223. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wolf-Watz H., Normark S., Bloom G. D. Rapid method for isolation of large quantities of outer membrane from Escherichia coli K-12 and its application to the study of envelope mutants. J Bacteriol. 1973 Sep;115(3):1191–1197. doi: 10.1128/jb.115.3.1191-1197.1973. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


