Abstract
Purpose
Salivary gland impairment following high activity radioiodine therapy of differentiated thyroid cancer (DTC) is a severe side effect. Dosimetric calculations using planar gamma camera scintigraphy (GCS) with 131I and ultrasonography (US) provided evidence that the average organ dose per administered 131I activity (ODpA) is too low to account for observed radiation damages to the salivary glands. The objective of this work was to re-estimate the ODpA using 124I PET(/CT) as a more reliable approach than 131I GCS/US.
Methods
Ten DTC patients underwent a series of six (or seven) PET scans and one PET/CT scan after administration of ~23 MBq 124I-iodide. Volumes of interest (VOIs) drawn on the CT and serial PET images were used to determine the glandular volumes and the imaged 124I activities. To enable identical VOIs to be drawn on serial PET images, each PET was co-registered with the CT image. To correct for partial volume effect and for the artificial bias in the activity concentration due to cascading gamma coincidences occurring in 124I decay, the imaged activity was effectively corrected using isovolume recovery coefficients (RCs) based on recovery phantom measurements. A head-neck phantom, which contained 124I-filled spheres, was manufactured to validate the isovolume recovery correction method with a realistic patient-based phantom geometry and for a range of activity concentration regimes. The mean±standard deviation (range) ODpA projected for 131I was calculated using the absorbed dose fraction method.
Results
The ODpAs (in Gy/GBq) for the submandibular and parotid glands were 0.32±0.13 (0.18–0.55) and 0.31±0.10 (0.13–0.46), respectively. No significant differences (p>0.2) in the mean ODpA between 124I PET(/CT) and 131I GCS/US dosimetry was found. The validation experiment showed that the percentage deviations between RC-corrected and true activity concentrations were <10%.
Conclusion
124I PET(/CT) dosimetry also corroborates the low ODpAs to the salivary glands. A voxel-based calculation taking into account the nonuniform activity distributions in the glands is necessary to possibly explain the radiation-induced salivary gland damage.
Keywords: Radioiodine therapy, Differentiated thyroid cancer, Salivary gland, 124I, Dosimetry
Introduction
Radioiodine therapy is an effective method in the treatment of patients with differentiated thyroid cancer (DTC). Salivary dysfunction is the most common side effect associated with “high-dose” radioiodine therapy [1] and correlates with the cumulated administered 131I activity [2, 3]. For example, administration of a single activity of 6 GBq or fractionated administration leading to a cumulated administered activity of 24 GBq results in a 30% or 90% loss of parenchymal function, respectively. Higher cumulated administered activity is associated with higher absorbed dose to the salivary gland. A recent study from our group [4] calculated this average organ dose per administered 131I activity (ODpA) using 131I planar gamma camera scintigraphy (GCS) and ultrasonography (US). This 131I GCS/US dosimetry used the absorbed fraction method and provided evidence that averaged over the gland the ODpA was too low to account for the radiation-induced damages to the salivary glands. Specifically, the mean ODpA was about one order of magnitude lower than the expected ODpA of ~5 Gy/GBq that was estimated by comparing the dose-response relationship of the radioiodine therapy and of external beam radiotherapy, taking the difference in biological effectiveness of external beam and radionuclide therapies into account [4]. Solving this discrepancy between observed and expected ODpA could be an important contribution towards comprehending the mechanism of and discovering ways of possibly diminishing the radiation-induced salivary gland damage in radioiodine therapy.
The first suggestion is that the observed disagreement may be associated with the shortcomings of the 131I GCS/US imaging approach to determine the dose-relevant parameters. For example, the planar gamma camera images required several corrections in obtaining the glandular 131I activity such as background and absorption correction, and the US-based volume estimations assumed a simple glandular volume model [4]. The accuracy of 131I GCS/US dosimetry may be questioned. As a consequence, a more reliable imaging approach than 131I GCS/US is needed to corroborate the unexpectedly low ODpA.
Positron emission tomography (PET) with 124I as tracer is probably the most accurate imaging method for the assessment of the radioiodine activity in organs or living tissues [5] and is increasingly used in pre-therapeutic dosimetry in 131I thyroid cancer therapy [6-10]. Computed tomography (CT) is an imaging method, whose resolution enables reliable determination of organ volumes, even those that are irregularly shaped such as the parotid glands. However, there is a major drawback in 124I PET imaging. 124I possesses a relatively low positron branching ratio of ~23% and a complex decay scheme with high-energy γ radiations [11]. In particular, the 603-keV prompt photon is partially emitted in cascade with one positron decay branch (about half of the positrons emitted) and may cause an artificial gamma coincidence with one of the 511-keV annihilation photon. We demonstrated that a more accurate 124I PET lesion quantification in “hot spot” imaging is easily achievable by application of recovery coefficients (RCs)—the ratio of imaged to true 124I activity concentration as measured with a dose calibrator—to effectively correct primarily for the partial volume effect, but also for the artificial bias in the imaged activity concentration, mainly due to cascading gamma coincidences [12].
The aim of this study was to examine whether 124I PET (/CT) is able to deliver a reliable estimate of ODpA to the parotid and submandibular glands.
Materials and methods
Isovolume activity concentration and isovolume RC
The (absolute) RC is the ratio of imaged activity concentration (Cimg) to the true (prepared) activity concentration (Ctrue) and is used to correct the imaged activity concentration for partial volume effect. The RC values are generally derived from phantoms containing objects of different sizes. To determine the imaged activity concentration in the object, a circular region of interest (ROI) with a diameter being equal to the scanner resolution is often used [12, 13]. This resolution ROI is placed around the maximum activity concentration (“hot spot” location), which is normally the center of the object itself. This study used a different approach to determine the imaged activity concentration, which intuitively appears to be more accurate and robust than the resolution-based ROI approach, especially for the determination of the low activity concentration observed in the salivary gland.
In the salivary glands the “hot spot” varied spatially and temporally due to low glandular activity (low counting statistics). For the determination of the RC value, a volume of interest (VOI) that was equal to the object volume (Vobj) was drawn in the CT image to determine the entire imaged activity (Atot) and used to obtain a better estimate of the (average) imaged activity concentration (=Atot/Vobj). This imaged activity concentration will be referred to as the isovolume activity concentration, Ciso, and was used as the reference quantity in the definition of the RC value referred to as the isovolume RC value, that is, RCiso=Ciso/Ctrue. Note that the isovolume RC for 124I is “effective” in that it corrects not only for the limited resolution of a PET system (partial volume effect) but it also takes into account the artificial bias mainly caused by cascading gamma coincidences of the 124I decay (artificial coincidence effect).
Preparation of radionuclides and their activity measurement
Two radionuclides, 124I and 18F, were used in this study. The nonstandard positron emitter 124I was used primarily, whereas the standard emitter 18F was applied only in one phantom measurement for comparison purposes. Details on radionuclide production and calibrated activity measurement using a dose calibrator CRC-15R (Capintec Inc., Ramsey, NJ, USA) and a 1480 Wizard gamma counter (Perkin-Elmer, Wellesley, MA, USA) have been published elsewhere [12].
Phantom and its preparation
Recovery phantom
A cylindrical phantom (20 cm in axial length, 20 cm outside diameter) was used to determine the isovolume RC values for different objects. The cavity contained six refillable glass objects—three spheres and three rotational ellipsoids (glass thickness of 0.7±0.2 mm)—mimicking the salivary glands. The outer diameters (inner volumes) of the spheres were 23.8 mm (5.73 ml), 29.6 mm (11.49 ml), and 39.0 mm (26.52 ml); the outer lengths of the major [minor] axes (inner volume) of the rotational ellipsoids were 35.2 [22.9] mm (7.50 ml), 40.9 [25.4] mm (10.69 ml), and 51.9 [35.0] mm (25.40 ml).
Head-neck phantom
A head-neck phantom, which contained refillable and hollow objects, was manufactured to validate the isovolume recovery correction method using a realistic patient-based phantom geometry. The validation phantom is illustrated in Fig. 1. The outer geometry was a hollow plastic wig head holder (E&E Collection, Dreieich, Germany). The head and neck lengths were 18 and 8 cm, respectively; the circumferences were 55 cm for the head and 31 cm for the neck. Three hollow glass objects were mounted in the interior of the head chamber to mimic maxillary and sphenoidal sinuses. The geometry of the hollow objects was based on CT images acquired from several patients. Specifically, two identical spheres with outer diameters of 38 mm were fixed, left and right, at the level of the cheekbone to simulate the maxillary sinuses. The other one was a hollow rotational ellipsoid mounted at the nose level to mimic sphenoidal sinus; the outer length of the major [minor] axis was 60 [30] mm. In addition, five refillable glass spheres, which are referred to as S1, S2, P1, P2, and R in Fig. 1, were mounted in the head-neck phantom to simulate salivary glands. Spheres S and P were fixed in the corresponding positions of the submandibular and parotid glands (head region), and sphere R was mounted in the neck region to mimic thyroid remnant tissue. The spheres S1 and S2 as well as P1 and P2 had identical geometries, respectively. More precisely, spheres S had outer diameters (inner volumes) of 28.8 mm (10.93 ml) and spheres P of 37.1 mm (23.42 ml). The diameter (inner volume) of the sphere R in the neck region was 19.8 mm (3.74 ml).
Fig. 1.
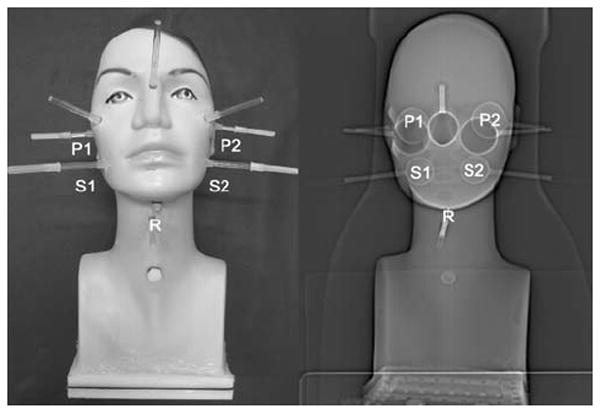
Head-neck phantom (left) containing five 124I-filled spheres, designated with the symbols S1, S2, P1, P2, and R, and three hollow objects simulating maxillary and sphenoidal sinuses. The corresponding CT topogram (right) illustrates the objects in the interior of the phantom cavity
Preparation
The selection of the 124I activity concentration was based on the mean imaged radioiodine activity concentrations in the salivary gland on the first day (0.5–24 h) after administration of ~23 MBq 124I. Similar imaged activity concentrations for 124I (and 18F) were used in the phantom study and their values are given in the phantom acquisition section.
Patients
The patients were thyroidectomized adults with histologically confirmed advanced DTC, who received pre-therapeutic 124I PET(/CT) dosimetry prior to their first planned radioiodine therapy. Only those individuals (seven women and three men) were selected that had neither a medical history of salivary gland disease nor external beam radiotherapy to the neck or head. In addition, patients were excluded with anticholinergic medication. The patients’ clinical characteristics were as follows: DTC histology was papillary in seven and follicular in three cases. The mean value±standard deviation (range) was 50±14 (31–73) years for their age and 78±14 (54–96) kg for their weight. The thyroid-stimulating hormone (TSH) stimulation was achieved by withdrawal of thyroid hormone in eight cases for about 4 weeks and by injection of recombinant human TSH (Thyrogen, Genzyme, GmbH, Frankfurt, Germany) in two cases; the mean±standard deviation (range) of TSH level before imaging was 83±38 (30–145) μIU/ml. The mean administered 124I activity±standard deviation (range) was 23.1±1.5 (20.5–24.7) MBq.
Tomography
PET imaging was performed using two (ECAT) EXACT HR+ PET scanners: one a stand-alone system (CTI/Siemens, Erlangen, Germany), which was the main scanner used in this study, and the other the PET component of a combined PET/CT scanner, the Biograph Emotion Duo (Siemens Medical Solutions, Hoffman Estates, IL, USA). The CT component of the Biograph combined PET/CT scanner was a dual-slice spiral CT scanner. Standard cross-calibration of both PET systems was performed using 18F [12]. For both scanners the emission images were acquired in three-dimensional (3-D) mode. The stand-alone PET possessed 68Ge/68Ga rod sources to perform transmission scans in two-dimensional mode. The PET systems in this study had a reconstructed spatial resolution of ~8 mm [12].
Acquisition protocols
The phantom measurements were all one-bed scans, in which the phantom was placed centrally within the scanner field of view, whereas the patient examinations were either one-bed or more-bed scans. Two acquisition protocols were applied: the acquisition protocol with high quality to obtain data with high precision and the clinical acquisition protocol.
Acquisition protocol with high quality
This protocol was only applied for the phantom study. On the stand-alone PET system the emission time was ≥4 h and the transmission time 1 h per bed position to ensure high counting statistics. The acquisition on the PET/CT system started with a CT scan with the following CT parameters: 145 mAs, 130 kVp, slice width 2 mm, rotation time of 0.8 s, and a table speed of 2 mm per rotation. The PET emission time was also ≥4 h.
Clinical acquisition protocol
On the stand-alone PET system the emission time (transmission time) was 300 s (120 s) per bed position. The CT acquisition parameters were 130 mAs, 130 kVp, slice width 5 mm, rotation time of 0.8 s, and a table speed of 8 mm per rotation. The emission scan on the PET/CT system started after moving the bed to the PET gantry and also lasted 300 s.
Phantom data acquisition
Determination of the isovolume 124I (and 18F) RC values
Both the stand-alone PET and PET/CT system were used to determine the isovolume RC values for different objects. Spheres and ellipsoids were used to determine the RC values for 124I. For comparison, the RC values for 18F were also determined using spheres only. The prepared activity concentration in the objects was ~5.0 kBq/ml and in the cavity (background) was ~0.4 kBq/ml. The stand-alone PET scan was acquired first, and subsequently the same phantom was scanned with the PET/CT system. The acquisition protocol with high quality was used.
Validation of the isovolume recovery correction method
The validation experiment was performed with the head-neck phantom using the stand-alone PET system only. The five spheres and the phantom cavity were filled with 124I-iodine. The spheres in the head region (S1, S2, P1, P2) were filled from a stock solution with a prepared activity concentration of ~5 kBq/ml. The sphere R in the neck region was filled with a considerably higher prepared activity concentration of ~50 kBq/ml, which corresponds to an uptake of 1% in thyroid remnant tissue, assuming an administered 124I activity of 20 MBq. The cavity of the head-neck phantom was filled with a prepared activity concentration of ~0.5 kBq/ml. Three consecutive scans were acquired first using the clinical acquisition protocol, and subsequently, a fourth scan was performed using the acquisition protocol with high quality. It is worth noting that the phantom’s position within the field of view was identical for each scan. This procedure was repeated every ~4 days (corresponding to the 124I half-life) with the same phantom until the prepared activity concentration for the spheres S and P decayed to ~0.5 kBq/ml.
Patient data acquisition
The patients underwent a series of six (or seven) PET scans and one PET/CT scan. On the basis of the 131I GCS/US dosimetry protocol published by our group [4], PET imaging was acquired at about 0.5, 1, 2, 4, 24, 48, and ≥96 h after oral intake of a capsule containing [124I]NaI. The imaging at ~24 h for five patients was performed using both the stand-alone PET (~23 h) and subsequently the PET/CT (~26 h) system; for logistical reasons, the other five patients were scanned using the PET/CT (~22 h) system only.
The pre-therapeutic 124I PET(/CT) dosimetry protocol as well as the previous protocol using 131I GCS/US [4] were performed under salivary-induced stimulation. This protocol is designed to, in principle, decrease toxicity to the salivary gland. More precisely, over the entire first treatment day, the patients started chewing lemon slices ~20 min after capsule intake and were instructed to continue chewing lemon slices and to drink at least 2 l of water. The patients ate lunch after 2–4 h, a snack after 6–7 h, and dinner 9–10 h after 124I administration.
Image reconstruction
PET image reconstruction
The reconstructions of the emission images for both PET systems and of the transmission image were identical for both acquisition protocols. The emission images were reconstructed using the iterative attenuation-weighted ordered subset expectation maximization algorithm with 4 iterations and 16 subsets. A post-reconstruction 5-mm 3-D Gaussian smoothing filter was applied. The emission images were corrected for attenuation by measured 68Ge/68Ga transmission including image segmentation in stand-alone PET, while PET/CT used the CT-based attenuation correction approach. Standard scatter, attenuation, and dead-time correction provided by the manufacturer were used. For the transmission image reconstruction, the filtered backprojection algorithm with a post-reconstruction 5-mm 3-D Gaussian filter was used, and subsequently the transmission image was segmented. The reconstructed transaxial emission and transmission images had 256×256 voxels (voxel size 1.7× 1.7×2.4 mm3).
CT image reconstruction
In contrast to the PET images, the CT reconstruction parameters were different for the two acquisition protocols. The CT image (512×512 voxels) of the acquisition protocol with high quality was reconstructed with a reconstruction interval of 1.0 mm and the reconstructed image had a voxel size of 1.0×1.0×1.0 mm3. The CT image (512×512 voxels) of the clinical acquisition protocol was reconstructed using a reconstruction interval of 2.4 mm and the reconstructed image had a voxel size of 1.0×1.0×2.4 mm3. The standard reconstruction kernel B40s was used for both protocols.
Image co-registration
The transmission and emission data sets (floating data set) were interpolated into the voxel size of the CT data set (reference data set) and were reformatted into a new spatial orientation using the rigid body transformation method. The image co-registration was performed manually using PMOD 2.5 software (PMOD Technologies Ltd., Zurich, Switzerland).
Phantom analysis
Determination of the isovolume RCs for 124I (and 18F)
A VOI encompassing the entire sphere or ellipsoid was manually drawn in the CT images and projected to the co-registered PET emission image. The isovolume RC value for each object was determined based on the isovolume and true activity concentration. To ascertain the deviation between the isovolume RC values of the differently sized ellipsoids and spheres, the data points of the spheres were fitted first using a sigmoid function, RCiso (Vobj) = α[1 + (γ/Vobj)β]−1, with three fitting parameters (α, β, γ) [12]. Thereafter, the deviations between the parameterized and isovolume RC values of the ellipsoid were calculated.
Validation of the isovolume recovery correction method
Since the position of the head-neck phantom in the field of view was identical for the four consecutive scans, the location of the spheres in the four emission images was also identical. The emission image acquired with high counting statistics was used to initially position spherical VOIs with a diameter identical to the known inner diameter of the spheres. Each VOI was then projected to the emission images acquired with the clinical acquisition protocol. The isovolume imaged activity concentration was determined for each sphere and corrected using the parameterized isovolume RC value. For the three scans acquired with the clinical acquisition protocol, the individual percentage deviations between RC-corrected and true activity concentrations (physical decay corrected to the first scan) were determined.
Patient analysis
PET-CT image co-registration
The VOIs encompassing each salivary gland were manually drawn in the CT image and projected to the emission image to determine the imaged isovolume activity concentration. Registration across time was performed by matching the transmission images at each time point with the CT portion of the PET/CT image. The transformation parameters were then applied to the respective, matched PET image at each time point. The transmission image was used as a bridge for indirect co-registration of the serial emission with the CT data set. It is assumed that the transmission and the subsequent emission images were already registered (no motion artifacts).
It has to be noted that the emission images were not directly used, since a precise delineation of the representation of anatomical structure in the emission images of the head and neck was often hampered for the early time points (≤24 h) and not possible for later time points (≥48 h). In contrast, in the transmission image the boundary of the head and neck as well as regions with low 511-keV attenuation coefficients such as maxillary and sphenoidal sinuses were visible.
After applying the rigid body transformation parameters to the emission data set, a final manual fine tuning of the registration was performed to ensure optimal spatial alignment. This fine tuning registration was carried out only for early emission scans acquired at time points ≤4 h since in this early phase a sufficient uptake in the salivary glands was observed. The transformation parameters of the fine tuning registration and the percentage deviation of the isovolume activity concentration in the salivary glands before and after fine tuning were determined.
Gland volume
The volume of the salivary gland, Vgl, was determined from the CT data set by manual contouring (VOI technique) using the soft tissue window setting (center: 50 HU, width: 350 HU). For a better identification and delineation of the contour, the CT and emission data set (2 or 4 h) were fused after image co-registration. This image fusion was in particular necessary in transversal CT slices, in which the delineation was hampered due to artifacts from dental implants. The manual contour drawing of the CT-based volumes generally depend on the observer, and its interindividual variation was estimated by two physicians (AS, AB) and one physicist (WJ).
Residence time
The residence time is the time integral of the time-activity curve divided by the administered activity. Two corrections were necessary to estimate the 131I activity at different time points t. First, the difference in the physical half-lives of 124I and 131I must be taken into account according to the radioactive decay law. Second, the imaged isovolume 124I activity concentration, , was corrected using the parameterized isovolume RC value, RCiso, to obtain the true isovolume 124I activity concentration. The “projected” 131I activity A131(t) was given by:
| (1) |
On the basis of the previously published work [4], the area under the time-activity curve A131(t) representing the projected cumulated activity (Ã131) was determined by applying the trapezoid rule with a truncation at ~96 h. No single or multiple exponential decay function was used because of the strong fluctuation in the time-activity curves [4]. The 131I residence time τ was calculated by dividing the cumulated activity Ã131 with the administered tracer 124I activity. The truncation effect at 96 h was analyzed by fitting the last three data points (24–96 h) to a mono-exponential function. This fitted decay constant was then used together with the 96-h activity to estimate the contribution of the residual (≥96 h) to the main residence time (0–96 h) assuming a monoexponential decay after 96 h.
ODpA
The total absorbed dose (D) of 131I consists of two contributions arising from the β (Dβ) and γ radiation (Dγ). Both contributions were estimated using the absorbed fraction method. In the case of 131I dosimetry of salivary glands, the total absorbed dose essentially arose from self-irradiation. The radiation contributions from extraglandular sources such as adjacent salivary glands or thyroid remnants were neglected in this study. In the framework of the absorbed fraction method the (average) self-absorbed radiation dose per administered 131I activity A0—assuming a uniform distribution of 131I activity in a homogeneous absorbing tissue—is given by [14]:
| (2) |
The symbol Δβ [= 0.110 Gy g/(MBq h)] is the mean energy of the β particles emitted per unit cumulated 131I activity [15] and ρ (=1.05 g/ml) is the gland density [16]. The parameter ε is the contribution of the γ to β absorbed dose, which depends on the volume (or mass) and shape of the salivary gland. Assuming that salivary gland is taken as a sphere with an effective radius R, this ratio can be estimated with the average geometric factor (ḡ) approach for internal γ ray dosimetry using ḡ = 3 π R [17]:
| (3) |
The symbol Г [= 0.579 10−3 Gy cm2/(MBq h)] is the specific gamma ray constant of 131I in tissue [15]. After substituting the sphere radius for the volume Vgl according to in Eq. 3, Eq. 2 can be re-written in the form of a practicable unit equation:
| (4) |
Statistics
The data were checked for normality (Kolmogorov-Smirnov test). If the data passed the normality test, the data are given as the mean±standard deviation; otherwise, the median and the range (minimum and maximum) are given. Differences among the groups were evaluated by Mann-Whitney U test (nonparametric test). Statistically significant differences were assumed at a significance level p<0.05.
Results
Phantom
Isovolume RC value of spheres and ellipsoids
The isovolume 124I (and 18F) RC values of the stand-alone PET system are illustrated in Fig. 2; similar results were obtained with the PET/CT system (mean absolute deviation percentage was 3%). The parameters to the fit to the isovolume RC phantom data of the spheres were α=0.76, β=0.57, γ=1.80 ml for 124I. The mean and standard deviation of the absolute deviation percentage between the 124I RC value of the ellipsoid and the parameterized isovolume RC values of the sphere was 1.5±0.3%. It can be stated that “moderate” alterations in spherical geometry resulted in insignificant changes in the isovolume 124I RC values. As can be seen in Fig. 2, the isovolume 18F RC values are slightly higher than the isovolume RC values of 124I. Specifically, the 124I recovery curves (solid line) matched well with the 18F recovery curve (dashed line in Fig. 2) using a scaling factor of 1.13 or, equivalently, a fitting parameter of α=0.86 for 18F.
Fig. 2.
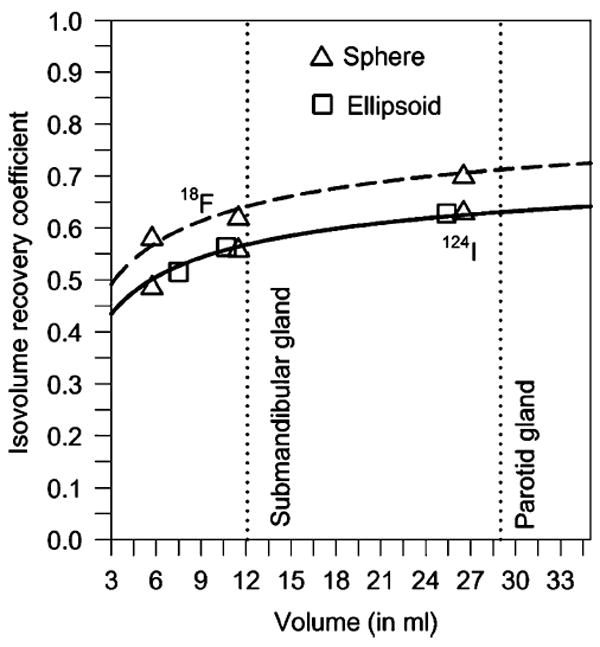
Isovolume recovery curves of 124I (solid line) and of 18F (dashed line) for EXACT HR+ PET scanners measured with a cylindrical phantom containing radionuclide-filled spheres and rotational ellipsoids. The ratio of the prepared objects’ to the background activity concentration was 12. The data points were fitted using a three-parameter sigmoid function (solid line). The dashed line was obtained by multiplying the 124I fitting curve with a scaling factor of 1.13. The dotted lines represent the mean submandibular and parotid gland volumes observed in this study
Validation of the isovolume recovery correction method
The individual deviations are depicted in Fig. 3. The validation experiment showed that the relative uncertainty of the RC-corrected activity concentration ranged from −9 to 6% for typical single salivary gland volumes. The mean absolute deviation percentage±standard deviation between the RC-corrected and true activity concentrations over the entire activity concentration regime (0.6–5 kBq/ml) were 2.8±2.3% for the spheres S and P.
Fig. 3.
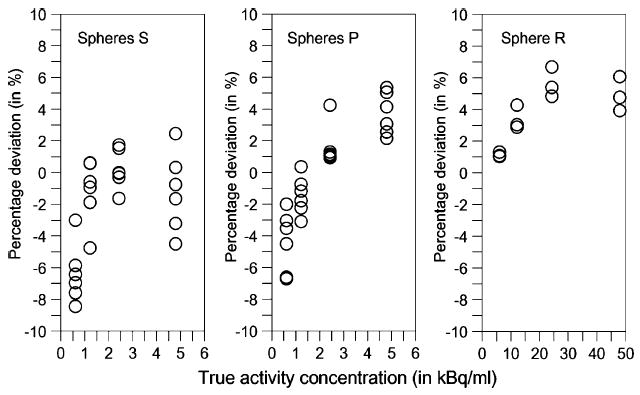
Deviation between RC-corrected and true activity concentration in percentage of the true activity concentration for the spheres S1 and S2 (left), spheres P1 and P2 (middle), and sphere R (right) at different activity concentration regimes. The individual deviations of the three scans acquired with the clinical acquisition protocol are shown
Patients
PET-CT image co-registration error and its influence on the isovolume activity determination
The fine tuning parameters for rotation along each axis were all ≤±0.5° and negligible. This was not the case for the translation: The mean absolute shift ± standard deviation in each spatial direction was 2.0±2.0 mm, resulting in a root mean square error (of the distance) of ±4.8 mm. The mean±standard deviation of the relative difference between the imaged isovolume activity before and after fine tuning was −9±9% and −6±7% for the submandibular and parotid glands, respectively. Therefore, the PET-CT co-registration algorithm yielded an absolute root mean square error of ~5 mm and, in the worst case without fine tuning, can lead to a mean relative underestimation of the imaged isovolume activity of ~10%.
Gland volume and the corresponding isovolume RC value
Figure 4 (top images) illustrates, as an example, the ROIs drawn in the transversal CT images. These ROIs were summed across the planes to create the VOIs. Tables 1 and 2 list the individually determined CT-based volumes of the submandibular and parotid glands and the statistics, respectively. The contour drawing and therefore the glandular volume is generally observer dependent; the mean relative absolute difference±standard deviation of the volume (in percentage of the mean volume obtained from three observers) was 9.0±7% for the submandibular and 7.6±4% for the parotid gland. After defining the individual volumes, the isovolume RC values were estimated for each salivary gland using the parameterized isovolume recovery curve depicted in Fig. 2. The median (range) isovolume RC values were 0.57 (0.47–0.60) and 0.63 (0.61–0.66) for the submandibular and parotid glands, respectively.
Fig. 4.
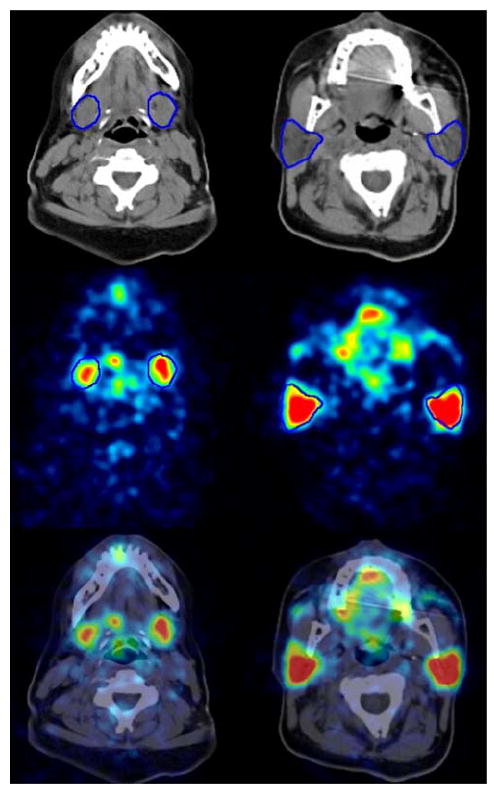
CT image (top), PET emission image (middle) 4 h after 124I administration, and fused image (bottom) of the submandibular (left) and parotid gland (right) with ROIs (in blue) delineating the boundaries of the salivary glands. The gray (CT) and color scale range (PET) were −125 to 225 HU and 0 to 2 kBq/ml, respectively
Table 1.
Individual CT-based volume (Vgl), 131I residence time (τ), and 131I ODpA averaged for the right and left glands derived from 124I PET(/CT) dosimetry (n= 10)
| Pat. ID |
Vgl (ml) |
τ (min) |
ODpA (Gy/GBq) |
|||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Subm. | Parotid | Subm.a | Parotid | Subm. | Parotid | |
| BS | 12.0 | 29.3 | 1.50 | 4.69 | 0.24 | 0.30 |
| JG b | 18.9 | 47.3 | 2.93 | 8.43 | 0.29 | 0.34 |
| MA | 15.9 | 27.4 | 4.61 | 5.53 | 0.55 | 0.39 |
| RM | 13.5 | 27.0 | 1.61 | 3.28 | 0.22 | 0.23 |
| SR | 16.1 | 37.4 | 4.61 | 10.34 | 0.53 | 0.46 |
| FL | 4.7 | 21.8 | 0.99 | 3.68 | 0.39 | 0.32 |
| RK | 9.9 | 27.8 | 1.31 | 3.66 | 0.28 | 0.25 |
| PR | 9.8 | 29.4 | 1.67 | 6.70 | 0.32 | 0.43 |
| BA | 7.2 | 15.6 | 0.84 | 2.70 | 0.22 | 0.25 |
| TCb | 11.5 | 30.7 | 1.11 | 2.09 | 0.18 | 0.13 |
Pat. ID patient identification, Subm. submandibular
Normality test failed
Patient was stimulated exogenously and not, as the other ones, endogenously
Table 2.
Mean±standard deviation (range) of the 131I ODpA, the 131I residence time (τ), and of the volume (Vgl) derived from the 124I PET(/CT) (n=10) and 131I GCS/US dosimetry (n=9) approaches as well as their relative mean deviations (Δ) between the two approaches and the corresponding significance levels (p)a
| Submandibular gland |
Parotid gland |
|||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| PET(/CT) | GCS/USb | PET(/CT) | GCS/USb | |
| ODpA (Gy/GBq) | 0.32±0.13 (0.18–0.55) | 0.40±0.13 (0.19–0.60) | 0.31±0.10 (0.13–0.46) | 0.26±0.09 (0.14–0.40) |
| Δ=+25%, p=0.206 | Δ=−16%, p=0.270 | |||
| τ (min) | 2.12±1.43 (0.84–4.61) | 2.30±0.62 (1.48–3.06) | 5.11±2.66 (2.09–10.34) | 2.38±0.78 (1.43–3.60) |
| Δ=+8%, p=0.153 | Δ=−53%, p=0.005 | |||
| Vgl (ml) | 12.0±4.3 (4.7–18.9) | 12.1±6.0 (4.5–25.3) | 29.4±8.5 (15.6–47.3) | 18.6±4.7 (8.7–24.0) |
| Δ=+1%, p=0.713 | Δ=−37%, p=0.004 | |||
Ranges are explicitly given although the data are all normally distributed except for the PET(/CT)-derived residence times of the submandibular gland. Mean relative deviation (Δ) is given in percentage of the PET(/CT)-based values
Residence time
A representative example of the time-uptake curves of the salivary glands is depicted in Fig. 5. At the beginning, large fluctuations (“spikes”) were frequently observed and appeared to be linked to the salivary-induced stimulations such as sucking lemon slices or food intake. Table 1 lists the individually determined residence times, and Table 2 gives the statistics. The mean residence time was significantly different (p<0.001) between the submandibular (2.12 min) and parotid glands (5.11 min); this finding was attributed to the difference in gland volume for the two gland types. The average contribution of the residual 131I residence time (≥96 h) to the main 131I residence time (0–96 h) was 5±4% for the submandibular and 2±2% for the parotid gland.
Fig. 5.
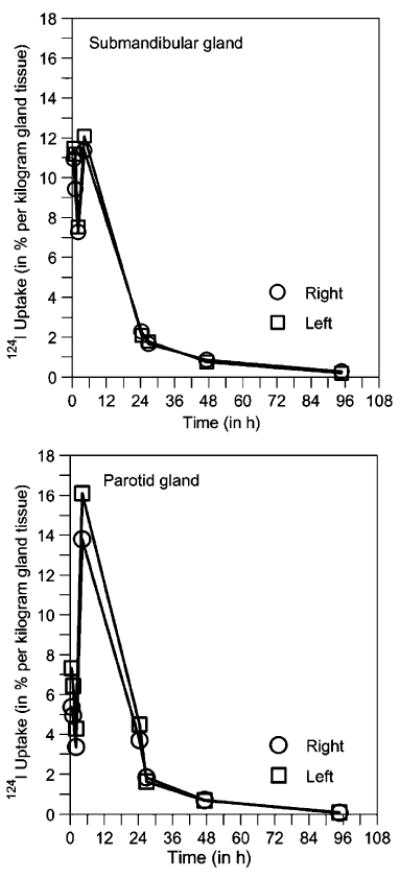
Representative examples of 124I uptake curve for the submandibular (top) and parotid gland (bottom) in percentage of administered activity per kilogram of gland tissue. The (mass-normalized) 124I time-uptake curve was selected as an equivalent illustration instead of the commonly used time-activity curve
ODpA
The individual ODpAs for each patient derived from 124I PET(/CT) dosimetry are given in Table 1; the statistics of the ODpA values are separately listed in Table 2. The ODpA value for each gland type showed a large interindividual variation: The ODpA range was 0.18–0.55 Gy/GBq for the submandibular and 0.13–0.46 Gy/GBq for the parotid gland; a relative absolute standard deviation (or interindividual variation) of ~40% was observed. No statistically significant difference was found in the mean ODpA value between the two gland types.
124I PET(/CT) versus 131I GCS/US dosimetry
The 131I GCS/US-based dosimetric investigation [4] categorized 55 patients into 3 activity groups depending on the previously administered cumulated 131I activity, i.e., low- (1 GBq), middle- (3–7 GBq), and high-activity group (9–21 GBq). The low-activity group with nine patients received only a small amount of 131I before the GCS/US dosimetry started. The authors assume that the activity of 1 GBq causes no or little functional impairment, whereas higher cumulated administered activities may already affect the salivary gland function. Hence, the patients investigated in this work (no previous radioiodine therapy) were considered equivalent to the patients belonging to the low-activity group. With this supposition it is possible to compare the ODpAs determined with 131I GCS/US and 124I PET(/CT) dosimetry approach.
Table 2 juxtaposes the ODpA values, gland volumes, and residence times determined using the 131I GCS/US and 124I PET(/CT) dosimetry approaches. The relative absolute ODpA deviation between the two dosimetry approaches was only <30% and no statistically significant difference was found (p>0.2). In contrast to the 124I PET(/CT) dosimetry, the mean GCS/US-based residence time exhibited no significant difference between the two gland types. Moreover, the mean PET(/CT)-based residence time for the parotid gland was considerably higher than the mean parotid residence time obtained from 131I GCS/US dosimetry (p=0.005). Finally, the mean US- and CT-based submandibular volumes were similar, but the mean US-based volume for the parotid gland was significantly smaller than the CT-based volume (p=0.004).
Discussion
Table 2 juxtaposes the ODpA results of both dosimetry approaches: 124I PET(/CT) dosimetric data determined in this work and 131I GCS/US dosimetric data taken from our study [4]. The 124I PET(/CT)-based ODpA was ~0.3 Gy/GBq for both gland types; the 131I GCS/US-based ODpA was ~0.4 Gy/GBq for the submandibular and ~0.3 Gy/GBq for the parotid gland. Most importantly, the discrepancy between observed and expected ODpA remains large and substantial. In other words, 124I PET(/CT) dosimetry provided submandibular and parotid gland doses of ~0.3 Gy/GBq that are also about ten times lower than the expected ODpA of ~5 Gy/GBq. From autoradiography studies in animals [18] it is known that iodide is mainly taken up by the ductal cells. This uptake pathway over the ductal system, which accounts only for about 5% of the glandular mass [19], can also be expected for the human salivary glands. This suggestion is supported by Jhiang and co-workers [20], who detected only sodium iodide symporters—a membrane protein that mediates active iodide uptake—in the ductal cells, but not in the acinar cells. Hence, the authors surmise that a nonuniform activity 131I distribution in human salivary glands is likely and is capable of solving the observed discrepancy [4]. However, further investigations are necessary to confirm this suggestion, such as autoradiography studies in human salivary glands to prove directly the nonuniform radioiodine distribution or voxel-based dosimetry approaches [21] that explicitly take into account the nonuniform activity distribution in the salivary gland.
There is one issue that needs to be discussed in more detail. The relative absolute deviation between the dosimetry approaches was less than 30%—a value that was not expected, if one considers the different corrections applied and assumptions made in 131I GCS/US dosimetry approach to obtain quantitative results. Note, however, that there were significant deviations in the dose-relevant parameters for the parotid glands (Table 2): The mean volume estimations and the mean residence times derived from the 131I GCS/US dosimetry approach were significantly lower than those values obtained by the 124I PET(/CT) dosimetry approach. This was expected because the parotid glands possessed an irregular geometry and the 131I activity determination in the GCS images was impaired by surrounding 131I-accumulating regions. As a consequence, the simplified US-based cylindrical volume model and the difficulty in the delineation of the 131I-accumulating boundaries in the GCS images resulted in a systematic underestimation. Noteworthy, the ODpA deviation between the dosimetry approaches was, however, unexpectedly small, which, in the authors’ opinion, is coincidental, that is, the similar mean systematic underestimation of the volume (1.37) and residence time (1.53) was not propagated to the ODpA determination since they cancelled out according to Eq. 4.
The ODpA found in this study might be compared with a recent study by Kolbert and co-workers [6] who retrospectively analyzed 20–23 DTC patients who underwent serial scanning with 124I PET and CT. The mean ±standard deviation ODpA was 0.2±0.2 Gy/GBq that was calculated using Monte Carlo-based 3-D internal dosimetry software. Their mean ODpA value seems to be in agreement with the results in the present study; however, this was not expected for the following reasons: The three 124I PET scans were generally performed at about 4–6, 20, and 44 h after tracer administration. The number of scans and in particular the first time point (4–6 h) selected appear to be questionable to reliably estimate the cumulated activity since the maximum radioiodine uptake of the salivary glands generally occurs at a time point far below 4–6 h after administration [4]. Moreover, in the applied dosimetry protocol the use of salivation-inducing stimulations such as sucking a lemon slice or lemon candy was not given, probably inducing a significant change in the time-uptake curve [22]. Finally, DTC patients had undergone thyroid remnant ablation with 131I. Kolbert and co-workers [6] have not given the 131I ablation activities; therefore, the salivary gland function may be already impaired by the first or more radioiodine therapies.
Another interesting issue is the estimate of the total physical ODpA uncertainty and its comparison with the large interindividual ODpA variation. The determination of the ODpA requires the 124I activity concentrations at different time points and the glandular volumes. Both quantities are subjected to several types of physical uncertainties. The errors arose mainly from co-registration, volume delineation, and application of the isovolume recovery correction method and these sources of error were estimated in this work: The co-registration error resulted in a mean underestimation of the 124I activity of ~10%; the mean error in the CT-based volume determination was estimated to be ~10%. The error in the application of the isovolume recovery correction method can be separated into three parts: uncertainty arising from nonspherical shape, from difference between recovery phantom and patient geometry, and from low counting statistics.
We have shown that for accurate 124I quantification the application of an effective recovery correction method is mandatory, which is a simple way of effectively correcting both the partial volume effect and the bias due to artificial coincidences [12]. These RC values were derived from phantoms containing spherical objects of different sizes. A recent work by Jentzen [14] showed that the glandular geometry can best be approximated by cylinders (ratio of height to diameter ~1.6) or rotational ellipsoids (ratio of major to minor axes ~1.5); as such the spherical geometry used in this study is, at first glance, a potential source of uncertainty. The effect of the difference in the choice of geometrical approximation on the isovolume RC value was evaluated using rotational ellipsoids (ratio of major to minor axes ~1.6) with volumes similar to the salivary glands. The phantom measurements showed that the isovolume RC values were not significantly changed from spherical to ellipsoidal geometry, i.e., the mean relative absolute difference was only ~2.5%. This finding indicates that spherical-based isovolume recovery correction is capable of sufficiently correcting the imaged activity in the salivary glands.
At this point, one note has to be made about the magnitude of the correction for partial volume and for artificial coincidence effects. Figure 2 illustrates the measured isovolume recovery curves of 124I and 18F. Soret and co-workers [23] analytically simulated isovolume recovery curves for different PET spatial resolution values, which ranged from 2 to 20 mm. A comparison of the experimentally and analytically determined isovolume RC values exhibited that the isovolume 18F recovery curve in Fig. 2 was in good agreement with the theoretically expected isovolume recovery curve for a spatial resolution of 8 mm, a value being identical to the spatial resolution of the PET systems used in this study. Thus, it can be inferred from the recovery curves of 124I and 18F that the partial volume effect—and not the artificial coincidence effect—dominated the correction of the imaged 124I activity in the salivary glands.
Another source of error emerged due to the difference between recovery phantom and patient geometry as well as low glandular activity concentration. To estimate these uncertainties, measurements with a head-neck phantom containing 124I-filled spheres were performed at different activity concentration regimes. This validation experiment mimicked both the alteration from the recovery phantom to patient geometry (different contribution of scatter and attenuation) and from high to low counting statistics (activity concentrations at different time points in the time-activity curve). As shown in Fig. 3, the individual absolute percentage deviations between RC-corrected and true activity concentrations were <10%. This error range can also be expected for the RC-corrected activity concentration of the salivary glands in this work.
It can be stated that after applying the Gaussian error propagation law the physical mean uncertainty in the ODpA determination was overall ~20%. This uncertainty was smaller than the interindividual ODpA variation of 30–40% that can be attributed to biological fluctuation reflected by, for example, the “spikes” in the time-activity curves (Fig. 5). It seems obvious that both salivary-induced stimulations and the interindividual variation in the salivation flow rate are probably the reason for the large interindividual ODpA variation. Interestingly, a recent study [22] demonstrated that not sucking lemon on the first day might induce a decrease in the salivary gland damage, which would, in turn, decrease the ODpA to the salivary glands. Therefore, knowing the exact reasons for the large interindividual ODpA variation could be helpful in finding natural ways of diminishing the salivary gland damages in radioiodine therapy.
Conclusion
The 124I PET(/CT)-based ODpA of the salivary gland significantly deviated from the expected ODpA and corroborated the ODpA values of the 131I GCS/US dosimetry. Further investigations are required to resolve the disagreement between observed and expected ODpA, such as autoradiography studies or a voxel-based dosimetry approach that explicitly takes into account the nonuniform activity distribution in the salivary glands. The results of this voxel-based dosimetry calculation will be presented in a subsequent study.
Contributor Information
Walter Jentzen, Klinik für Nuklearmedizin, Universität Duisburg-Essen, Hufelandstrasse 55, 45122 Essen, Germany, walter.jentzen@uni-duisburg-essen.de.
Robert F. Hobbs, Department of Radiology, School of Medicine, Johns Hopkins University, Baltimore, MD, USA
Alexander Stahl, Klinik für Nuklearmedizin, Universität Duisburg-Essen, Hufelandstrasse 55, 45122 Essen, Germany.
Jochen Knust, Klinik für Nuklearmedizin, Universität Duisburg-Essen, Hufelandstrasse 55, 45122 Essen, Germany.
George Sgouros, Department of Radiology, School of Medicine, Johns Hopkins University, Baltimore, MD, USA.
Andreas Bockisch, Klinik für Nuklearmedizin, Universität Duisburg-Essen, Hufelandstrasse 55, 45122 Essen, Germany.
References
- 1.Hyer S, Kong A, Pratt B, Harmer C. Salivary gland toxicity after radioiodine therapy for thyroid cancer. Clin Oncol. 2007;19:83–6. doi: 10.1016/j.clon.2006.11.005. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 2.Bohuslavizki KH, Brenner W, Lassmann S, Tinnemeyer S, Tönshoff G, Sippel C, et al. Quantitative salivary gland scintigraphy in the diagnosis of parenchymal damage after treatment with radioiodine. Nucl Med Commun. 1996;17:681–86. doi: 10.1097/00006231-199608000-00006. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 3.Bohuslavizki KH, Brenner W, Lassmann S, Tinnemeyer S, Kalina S, Clausen M, et al. Quantitative salivary gland scintigraphy—a recommended examination prior to and after radioiodine therapy (in German) Nuklearmedizin. 1997;36:103–9. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 4.Jentzen W, Schneider E, Freudenberg L, Eising EG, Görges R, Müller SP, et al. Relationship between cumulative radiation dose and salivary gland uptake associated with radioiodine therapy of thyroid cancer. Nucl Med Commun. 2006;27:669–76. doi: 10.1097/00006231-200608000-00009. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 5.Flux G, Bardies M, Monsieurs M, Savolainen S, Strands SE, Lassmann M, et al. The impact of PET and SPECT on dosimetry for targeted radionuclide therapy. Z Med Phys. 2006;16:47–9. doi: 10.1078/0939-3889-00291. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 6.Kolbert KS, Pentlow KS, Pearson JR, Sheikh A, Finn RD, Humm JL, et al. Prediction of absorbed dose to normal organs in thyroid cancer patients treated with 131I by use of 124I PET and 3-dimensional internal dosimetry software. J Nucl Med. 2007;48:143–49. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 7.Freudenberg L, Jentzen W, Görges R, Petrich T, Marlowe RJ, Knust J, et al. 124I-PET dosimetry in advanced differentiated thyroid cancer: therapeutic impact. Nuklearmedizin. 2007;46:121–28. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 8.Jentzen W, Freudenberg L, Eising EG, Sonnenschein W, Knust J, Bockisch A. Optimized 124I PET dosimetry protocol for radioiodine therapy of differentiated thyroid cancer. J Nucl Med. 2008;49:1017–23. doi: 10.2967/jnumed.107.047159. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 9.Lubberink M, Abdul Fatah S, Brans B, Hoekstra OS, Teule GJJ. The role of 124I-PET in diagnosis and treatment of thyroid carcinoma. Q J Nucl Med Mol Imaging. 2008;52:30–6. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 10.Hobbs RF, Wahl RL, Lodge MA, Javadi MS, Cho SY, Chien DT, et al. 124I PET-based 3D-RD dosimetry for a pediatric thyroid cancer patient: real-time treatment planning and methodologic comparison. J Nucl Med. 2009;50:1844–7. doi: 10.2967/jnumed.109.066738. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 11.Chu SYF, Ekström LP, Firestone RB. The Lund/LBNL nuclear data search. Database version 2.0. 1999 http://nucleardata.nuclear.lu.se/nucleardata/toi/
- 12.Jentzen W, Weise R, Kupferschläger J, Freudenberg LS, Brandau W, Bares R, et al. Iodine-124 PET dosimetry in differentiated thyroid cancer: recovery coefficient in 2D and 3D modes for PET (/CT) systems. Eur J Nucl Med Mol Imaging. 2008;35:611–23. doi: 10.1007/s00259-007-0554-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 13.Geworski L, Knoop BO, de Cabrejas ML, Knapp WH, Munz DL. Recovery correction for quantitation in emission tomography: a feasibility study. Eur J Nucl Med. 2000;27:161–9. doi: 10.1007/s002590050022. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 14.Jentzen W. Dissertation 2010. University of Duisburg-Essen; Germany: Pre-therapeutic 124I PET(/CT) salivary gland dosimetry in the radioiodine therapy of differentiated thyroid carcinoma and investigation of important factors affecting the 124I quantification. [Google Scholar]
- 15.Junker D, Fitschen J. Dosimetrie inkorporierter Strahlen. In: Diethelm L, Heuck F, Olsson O, Strnad F, Vieten H, Zuppinger A, editors. Handbuch der medizinischen Radiologie/Encyclopedia of medical radiology Band/Volume 15, Teil/Part 1A. Berlin: Springer; 1980. pp. 425–82. [Google Scholar]
- 16.Ferrari P, Gualdrini G. An improved MCNP version of the NORMAN voxel phantom for dosimetry studies. Phys Med Biol. 2005;50:4299–316. doi: 10.1088/0031-9155/50/18/005. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 17.Focht EF, Quimby EH, Gershowitz M. Revised average geometric factors for cylinders in isotope dosage. Radiology. 1965;85:151–2. doi: 10.1148/85.1.151. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 18.Brown-Grant K. Extrathyroidal iodide concentrating mechanisms. Physiol Rev. 1961;41:189–213. [Google Scholar]
- 19.Junqueira LC, Carneiro J. Histologie. 3. Berlin: Springer; 1991. [Google Scholar]
- 20.Jhiang SM, Cho JY, Ryu KY, DeYoung BR, Smanik PA, McGaughy VR, et al. An immunohistochemical study of Na+/I−symporter in human thyroid tissues and salivary gland tissues. Endocrinology. 1998;139:4416–19. doi: 10.1210/endo.139.10.6329. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 21.Sgouros G, Kolbert KS, Sheikh A, Pentlow KS, Mun EF, Barth A, et al. Patient-specific dosimetry for 131I thyroid cancer therapy using 124I PET and 3-dimensional-internal dosimetry (3D-ID) software. J Nucl Med. 2004;45:1366–72. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 22.Nakada K, Ishibashi T, Takei T, Hirata K, Shinohara K, Katoh S, et al. Does lemon candy decrease salivary gland damage after radioiodine therapy for thyroid cancer? J Nucl Med. 2005;46:261–66. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 23.Soret M, Bacharach SL, Buvat I. Partial-volume effect in PET tumor imaging. J Nucl Med. 2007;48:932–45. doi: 10.2967/jnumed.106.035774. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


