Abstract
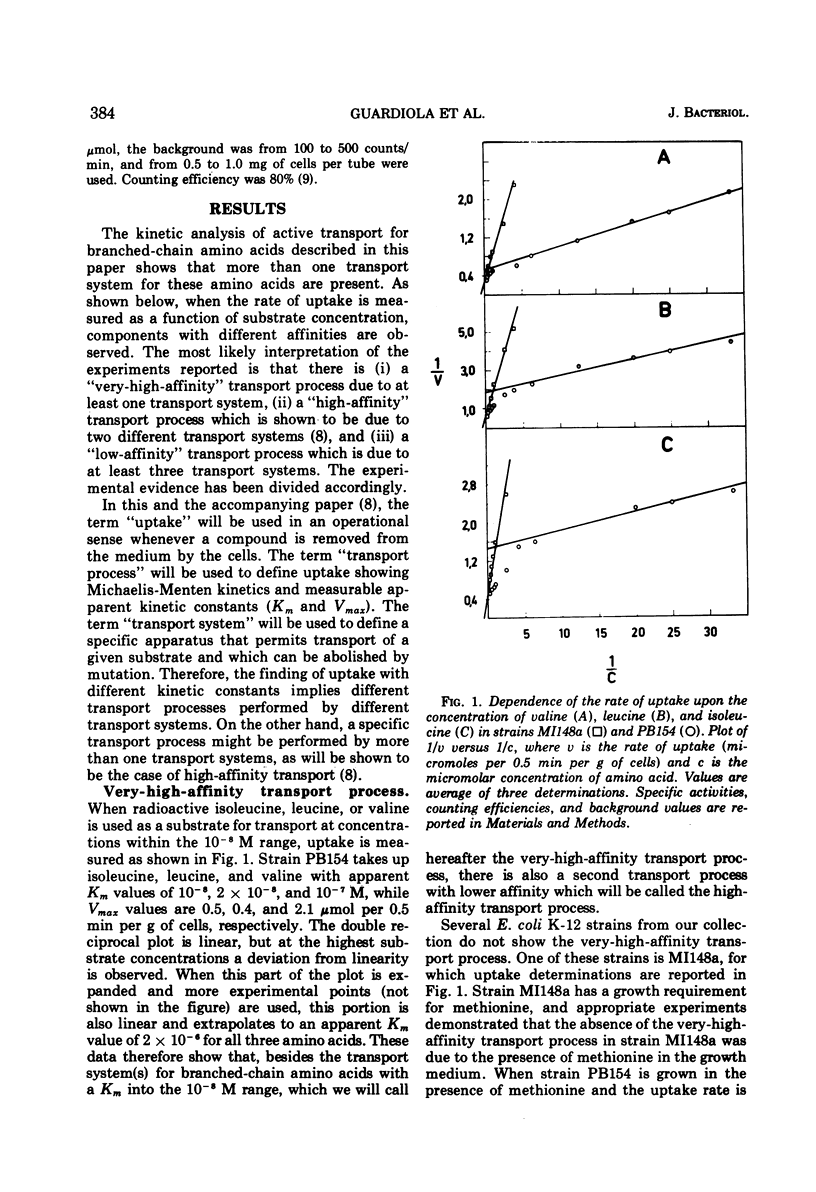
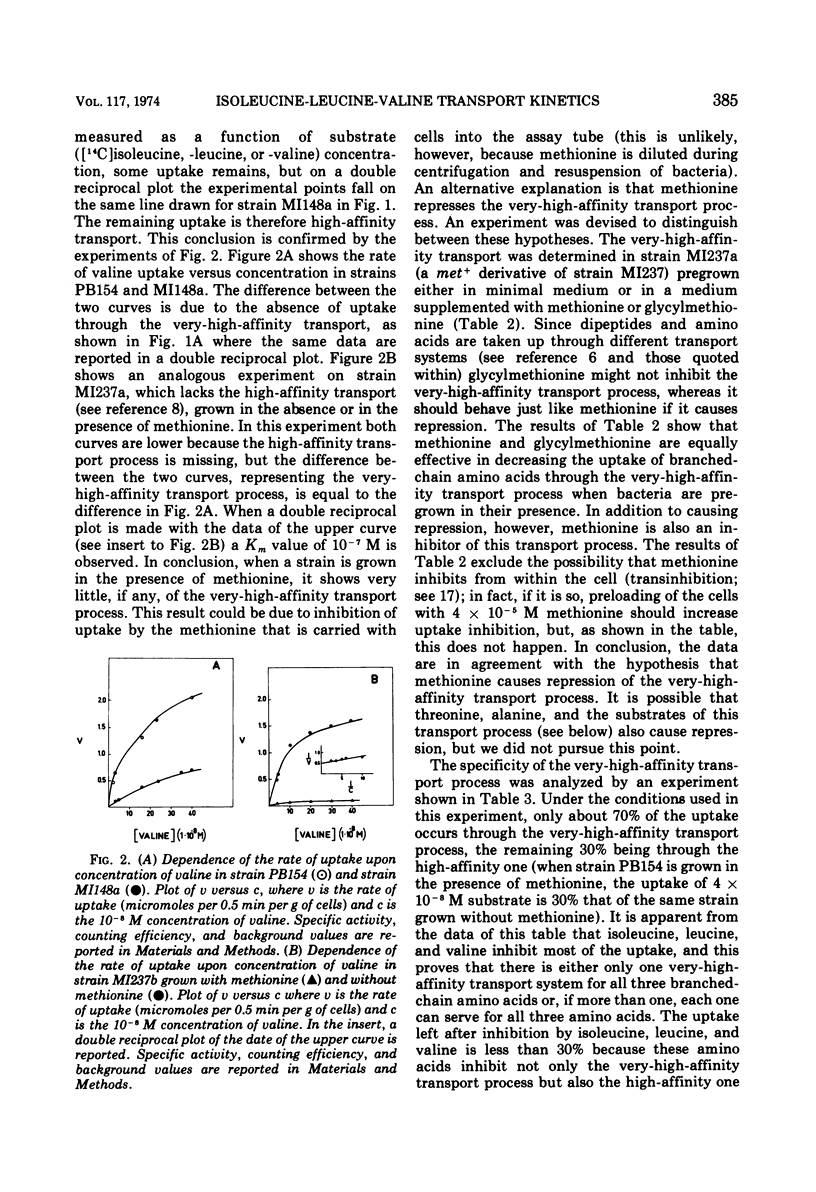
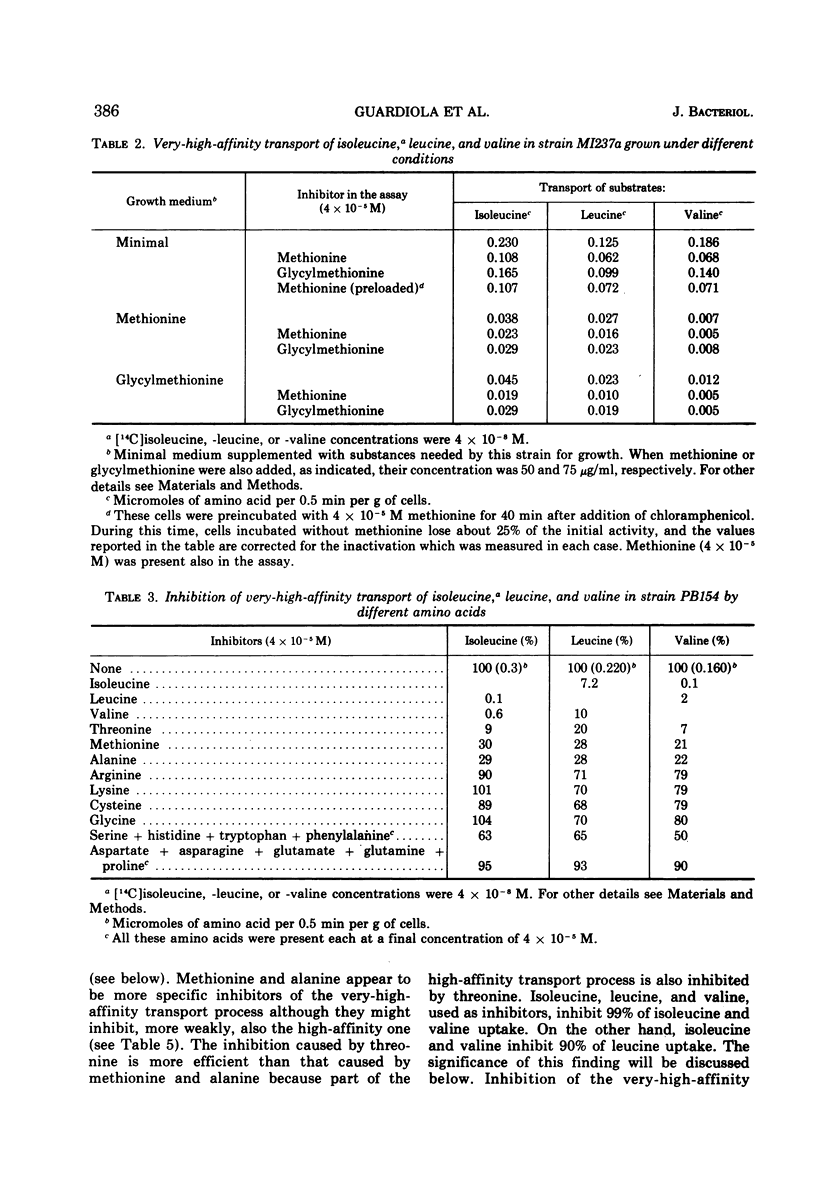
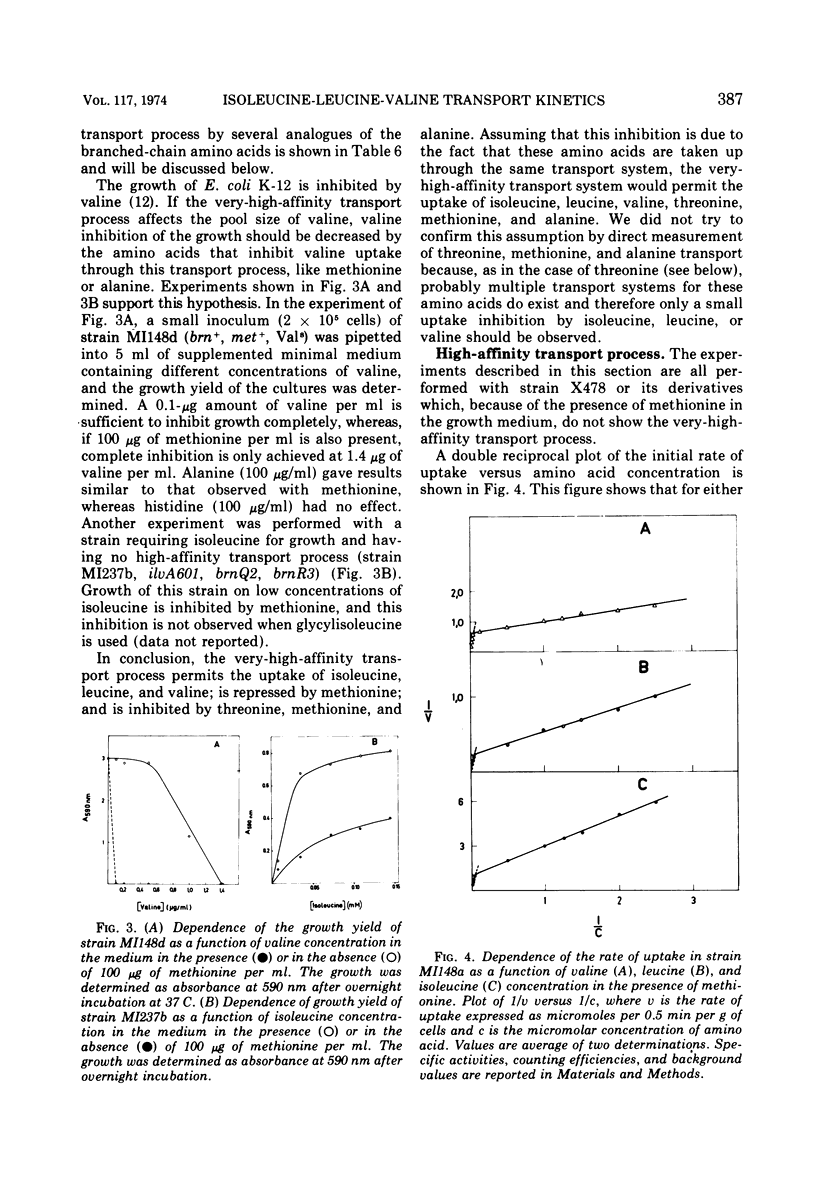
The kinetics of isoleucine, leucine, and valine transport in Escherichia coli K-12 has been analyzed as a function of substrate concentration. Such analysis permits an operational definition of several transport systems having different affinities for their substrates. The identification of these transport systems was made possible by experiments on specific mutants whose isolation and characterization is described elsewhere. The transport process with highest affinity was called the “very-high-affinity”process. Isoleucine, leucine, and valine are substrates of this transport process and their apparent Km values are either 10−8, 2 × 10−8, or 10−7 M, respectively. Methionine, threonine, and alanine inhibit this transport process, probably because they are also substrates. The very-high-affinity transport process is absent when bacteria are grown in the presence of methionine, and this is due to a specific repression. Methionine and alanine were also found to affect the pool size of isoleucine and valine. Another transport process is the “high-affinity” process. Isoleucine, leucine, and valine are substrates of this transport process, and their apparent Km value is 2 × 10−6 M for all three. Methionine and alanine cause very little or no inhibition, whereas threonine appears to be a weak inhibitor. Several structural analogues of the branched-chain amino acids inhibit the very-high-affinity or the high-affinity transport process in a specific way, and this confirms their existence as two separate entities. Three different “low-affinity” transport processes, each specific for either isoleucine or leucine or valine, show apparent Km values of 0.5 × 10−4 M. These transport processes show a very high substrate specificity since no inhibitor was found among other amino acids or among many branched-chain amino acid precursors or analogues tried. The evolutionary significance of the observed redundancy of transport systems is discussed.
Full text
PDF





Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- AMES G. F. UPTAKE OF AMINO ACIDS BY SALMONELLA TYPHIMURIUM. Arch Biochem Biophys. 1964 Jan;104:1–18. doi: 10.1016/s0003-9861(64)80028-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Anraku Y. Transport of sugars and amino acids in bacteria. I. Purification and specificity of the galactose- and leucine-binding proteins. J Biol Chem. 1968 Jun 10;243(11):3116–3122. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- BRITTEN R. J., McCLURE F. T. The amino acid pool in Escherichia coli. Bacteriol Rev. 1962 Sep;26:292–335. doi: 10.1128/br.26.3.292-335.1962. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brown K. D. Formation of aromatic amino acid pools in Escherichia coli K-12. J Bacteriol. 1970 Oct;104(1):177–188. doi: 10.1128/jb.104.1.177-188.1970. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- COHEN G. N., RICKENBERG H. V. Concentration spécifique réversible des amino acides chez Escherichia coli. Ann Inst Pasteur (Paris) 1956 Nov;91(5):693–720. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- De Felice M., Guardiola J., Lamberti A., Iaccarino M. Escherichia coli K-12 mutants altered in the transport systems for oligo- and dipeptides. J Bacteriol. 1973 Nov;116(2):751–756. doi: 10.1128/jb.116.2.751-756.1973. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Furlong C. E., Weiner J. H. Purification of a leucine-specific binding protein from Escherichia coli. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1970 Mar 27;38(6):1076–1083. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(70)90349-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Guardiola J., De Felice M., Klopotowski T., Iaccarino M. Mutations affecting the different transport systems for isoleucine, leucine, and valine in Escherichia coli K-12. J Bacteriol. 1974 Feb;117(2):393–405. doi: 10.1128/jb.117.2.393-405.1974. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Guardiola J., Iaccarino M. Escherichia coli K-12 mutants altered in the transport of branched-chain amino acids. J Bacteriol. 1971 Dec;108(3):1034–1044. doi: 10.1128/jb.108.3.1034-1044.1971. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kaback H. R. Transport across isolated bacterial cytoplasmic membranes. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1972 Aug 4;265(3):367–416. doi: 10.1016/0304-4157(72)90014-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kay W. W. Two aspartate transport systems in Escherichia coli. J Biol Chem. 1971 Dec 10;246(23):7373–7382. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- LEAVITT R. I., UMBARGER H. E. Isoleucine and valine metabolism in Escherichia coli. XI. Valine inhibition of the growth of Escherichia coli strain K-12. J Bacteriol. 1962 Mar;83:624–630. doi: 10.1128/jb.83.3.624-630.1962. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Oxender D. L. Membrane transport. Annu Rev Biochem. 1972;41(10):777–814. doi: 10.1146/annurev.bi.41.070172.004021. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Penrose W. R., Nichoalds G. E., Piperno J. R., Oxender D. L. Purification and properties of a leucine-binding protein from Escherichia coli. J Biol Chem. 1968 Nov 25;243(22):5921–5928. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Piperno J. R., Oxender D. L. Amino acid transport systems in Escherichia coli K-12. J Biol Chem. 1968 Nov 25;243(22):5914–5920. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rahmanian M., Oxender D. L. Derepressed leucine transport activity in Escherichia coli. J Supramol Struct. 1972;1(1):55–59. doi: 10.1002/jss.400010108. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ring K., Gross W., Heinz E. Negative feedback regulation of amino acid transport in Streptomyces hydrogenans. Arch Biochem Biophys. 1970 Mar;137(1):243–252. doi: 10.1016/0003-9861(70)90431-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tager H. S., Christensen H. N. Transport of the four isomers of 2-aminonorbornane-2-carboxylic acid in selected mammalian systems and in Escherichia coli. J Biol Chem. 1971 Dec 25;246(24):7572–7580. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Taylor A. L., Trotter C. D. Linkage map of Escherichia coli strain K-12. Bacteriol Rev. 1972 Dec;36(4):504–524. doi: 10.1128/br.36.4.504-524.1972. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Thorne G. M., Corwin L. M. Genetic locus of a gene affecting leucine transport in Salmonella typhimurium. J Bacteriol. 1972 May;110(2):784–785. doi: 10.1128/jb.110.2.784-785.1972. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- VOGEL H. J., BONNER D. M. Acetylornithinase of Escherichia coli: partial purification and some properties. J Biol Chem. 1956 Jan;218(1):97–106. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


