Abstract
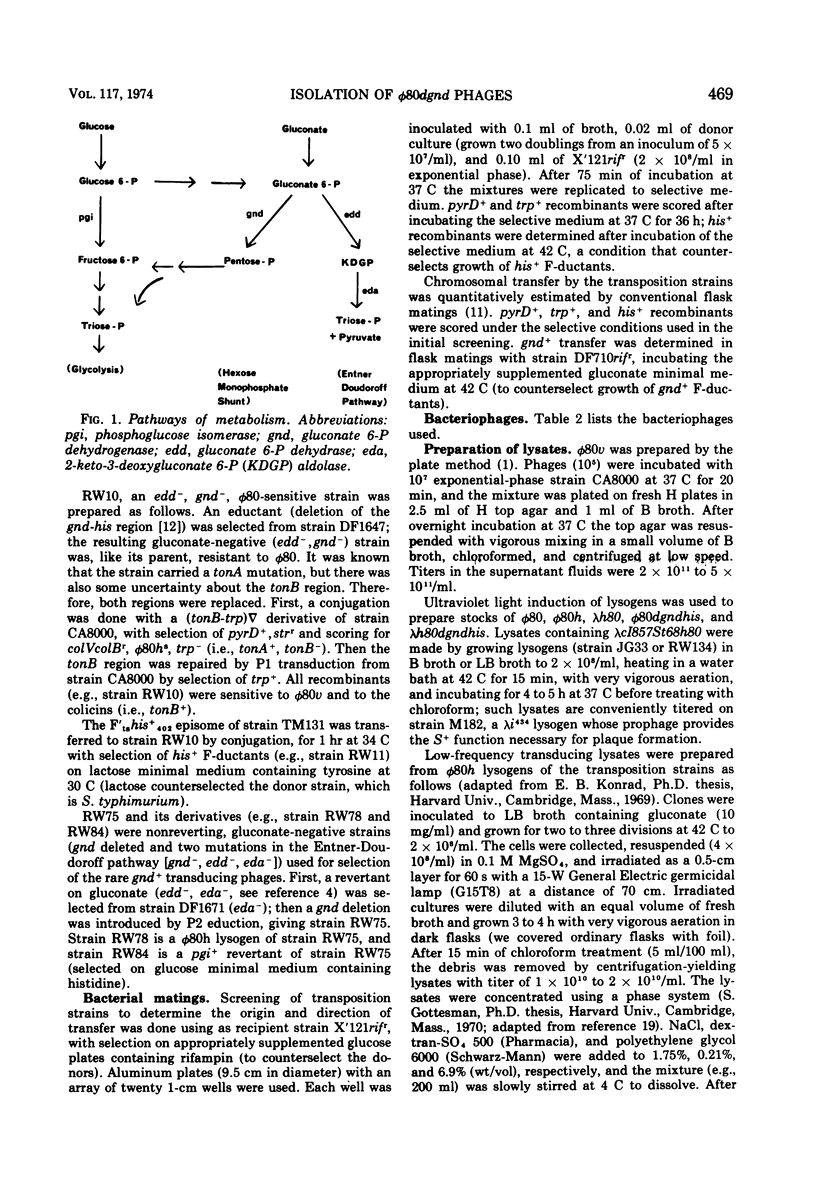
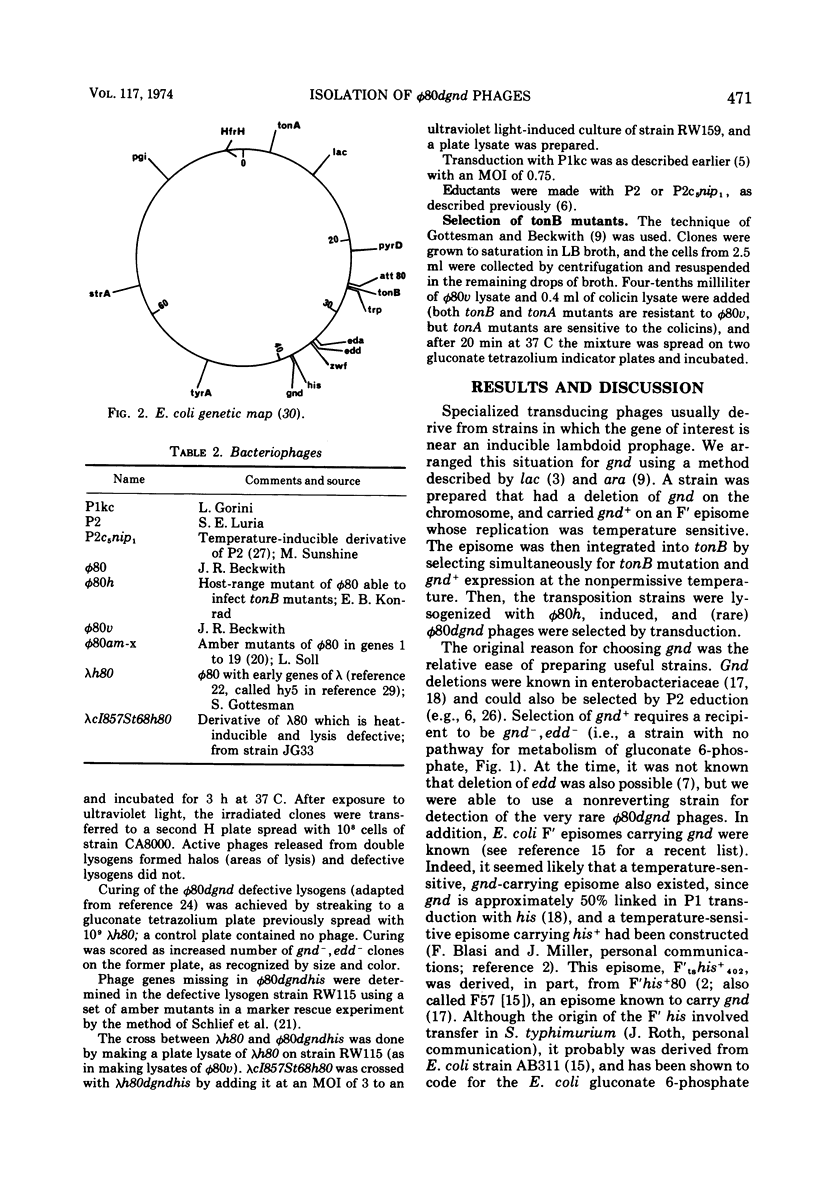
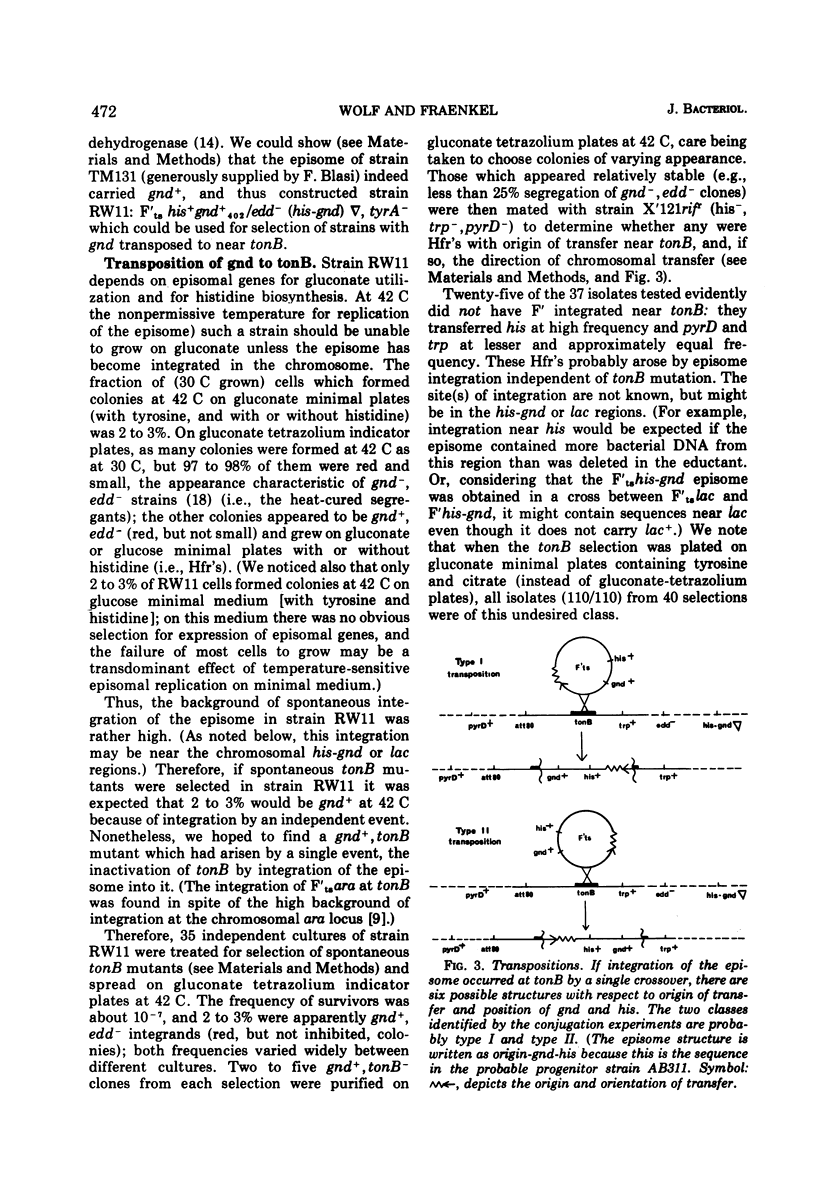
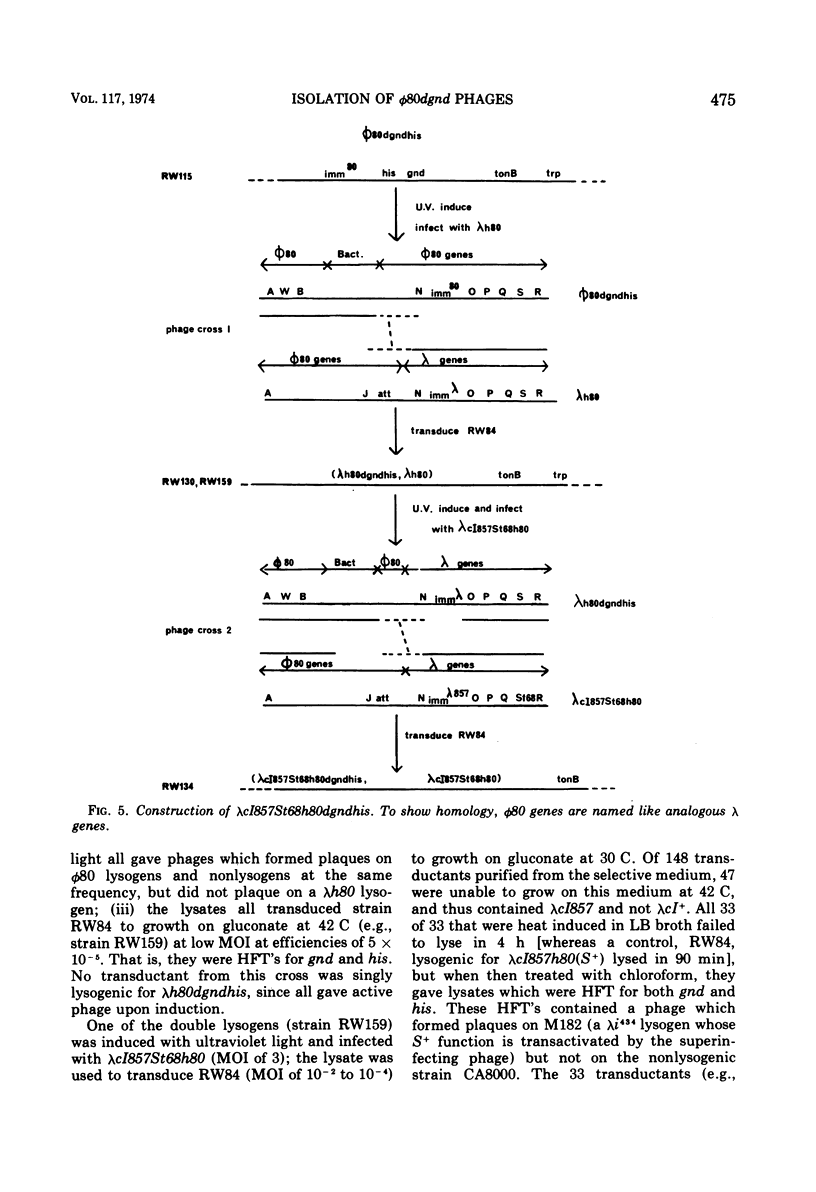
Specialized transducing phages for gluconate 6-phosphate dehydrogenase (gnd), a constitutive enzyme in Escherichia coli, have been isolated using a method previously described for other genes. The gnd-his region, carried on an F′ episome, was first transposed to tonB. Rare phages carrying gnd were selected, by transduction, from φ80 lysogens of these strains; one phage also carried his (φ80gndhis). From the transductants, high-frequency transducing lysates were obtained; low multiplicity of infection then yielded defective lysogens. tonB deletion analysis of the φ80dgndhis lysogen shows the order of genes in the prophage to be imm80...hisOGD...gnd; according to a marker rescue experiment most phage late genes have been replaced by bacterial deoxyribonucleic acid. A heat-inducible, lysis-defective λ-φ80 hybrid derivative of φ80dgndhis has been prepared.
Full text
PDF




Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Avitabile A., Carlomagno-Cerillo S., Favvre R., Blasi F. Isolation of transducing bacteriophages for the histidine and isoleucine-valine operons in Escherichia coli K-12. J Bacteriol. 1972 Oct;112(1):40–47. doi: 10.1128/jb.112.1.40-47.1972. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Beckwith J. R., Signer E. R. Transposition of the lac region of Escherichia coli. I. Inversion of the lac operon and transduction of lac by phi80. J Mol Biol. 1966 Aug;19(2):254–265. doi: 10.1016/s0022-2836(66)80003-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fradkin J. E., Fraenkel D. G. 2-keto-3-deoxygluconate 6-phosphate aldolase mutants of Escherichia coli. J Bacteriol. 1971 Dec;108(3):1277–1283. doi: 10.1128/jb.108.3.1277-1283.1971. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fraenkel D. G., Banerjee S. A mutation increasing the amount of a constitutive enzyme in Escherichia coli, glucose 6-phosphate dehydrogenase. J Mol Biol. 1971 Feb 28;56(1):183–194. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(71)90093-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fraenkel D. G., Banerjee S. Deletion mapping of zwf, the gene for a constitutive enzyme, glucose 6-phosphate dehydrogenase in Escherichia coli. Genetics. 1972 Aug;71(4):481–489. doi: 10.1093/genetics/71.4.481. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fraenkel D. G. Genetic mapping of mutations affecting phosphoglucose isomerase and fructose diphosphatase in Escherichia coli. J Bacteriol. 1967 May;93(5):1582–1587. doi: 10.1128/jb.93.5.1582-1587.1967. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fraenkel D. G., Levisohn S. R. Glucose and gluconate metabolism in an Escherichia coli mutant lacking phosphoglucose isomerase. J Bacteriol. 1967 May;93(5):1571–1578. doi: 10.1128/jb.93.5.1571-1578.1967. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gottesman S., Beckwith J. R. Directed transposition of the arabinose operon: a technique for the isolation of specialized transducing bacteriophages for any Escherichia coli gene. J Mol Biol. 1969 Aug 28;44(1):117–127. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(69)90408-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Josephson B. L., Fraenkel D. G. Transketolase mutants of Escherichia coli. J Bacteriol. 1969 Dec;100(3):1289–1295. doi: 10.1128/jb.100.3.1289-1295.1969. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kelly B. L., Sunshine M. G. Association of temperate phage P2 with the production of histidine negative segregants by Escherichia coli. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1967 Jul 21;28(2):237–243. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(67)90435-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- LENNOX E. S. Transduction of linked genetic characters of the host by bacteriophage P1. Virology. 1955 Jul;1(2):190–206. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(55)90016-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lew K. K., Roth J. R. Genetic approaches to determination of enzyme quaternary structure. Biochemistry. 1971 Jan 19;10(2):204–207. doi: 10.1021/bi00778a002. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Low K. B. Escherichia coli K-12 F-prime factors, old and new. Bacteriol Rev. 1972 Dec;36(4):587–607. doi: 10.1128/br.36.4.587-607.1972. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Miller J. H., Ippen K., Scaife J. G., Beckwith J. R. The promoter-operator region of the lac operon of Escherichia coli. J Mol Biol. 1968 Dec;38(3):413–420. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(68)90395-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Murray M. L., Klopotowski T. Genetic map position of the gluconate-6-phosphate dehydrogenase gene in Salmonella typhimurium. J Bacteriol. 1968 Apr;95(4):1279–1282. doi: 10.1128/jb.95.4.1279-1282.1968. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- PHILIPSON L., ALBERTSSON P. A., FRICK G. The purification and concentration of viruses by aqueous polymerphase systems. Virology. 1960 Jul;11:553–571. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(60)90100-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Peyru G., Fraenkel D. G. Genetic mapping of loci for glucose-6-phosphate dehydrogenase, gluconate-6-phosphate dehydrogenase, and gluconate-6-phosphate dehydrase in Escherichia coli. J Bacteriol. 1968 Apr;95(4):1272–1278. doi: 10.1128/jb.95.4.1272-1278.1968. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- SIGNER E. R. RECOMBINATION BETWEEN COLIPHAGES LAMBDA AND PHI-80. Virology. 1964 Apr;22:650–651. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(64)90090-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- SISTROM W. R. On the physical state of the intracellularly accumulates substrates of beta-galactoside-permease in Escherichia coli. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1958 Sep;29(3):579–587. doi: 10.1016/0006-3002(58)90015-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- SUSSMAN R., JACOB F. [On a thermosensitive repression system in the Escherichia coli lambda bacteriophage]. C R Hebd Seances Acad Sci. 1962 Feb 19;254:1517–1519. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sato K., Nishimune Y., Sato M., Numich R., Matsushiro A. Suppressor-sensitive mutants of coliphage phi-80. Virology. 1968 Apr;34(4):637–649. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schleif R., Greenblatt J., Davis R. W. Dual control of arabinose genes on transducing phage lambda-dara. J Mol Biol. 1971 Jul 14;59(1):127–150. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(71)90417-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Signer E. R. Interaction of prophages at the att80 site with the chromosome of Escherichia coli. J Mol Biol. 1966 Jan;15(1):243–255. doi: 10.1016/s0022-2836(66)80224-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sunshine M. G. Dependence of education on P2 int product. Virology. 1972 Jan;47(1):61–67. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(72)90239-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sunshine M. G., Kelly B. Extent of host deletions associated with bacteriophage P2-mediated eduction. J Bacteriol. 1971 Nov;108(2):695–704. doi: 10.1128/jb.108.2.695-704.1971. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Szpirer J., Thomas R., Radding C. M. Hybrids of bacteriophages lambda and phi 80: a study of nonvegetative functions. Virology. 1969 Apr;37(4):585–596. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(69)90276-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Taylor A. L., Trotter C. D. Linkage map of Escherichia coli strain K-12. Bacteriol Rev. 1972 Dec;36(4):504–524. doi: 10.1128/br.36.4.504-524.1972. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Voll M. J. Derivation of an F-merogenote and a phi-80 high-frequency transducing phage carrying the histidine operon os Salmonella. J Bacteriol. 1972 Feb;109(2):741–750. doi: 10.1128/jb.109.2.741-750.1972. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yamamoto K. R., Alberts B. M., Benzinger R., Lawhorne L., Treiber G. Rapid bacteriophage sedimentation in the presence of polyethylene glycol and its application to large-scale virus purification. Virology. 1970 Mar;40(3):734–744. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(70)90218-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]



