Abstract
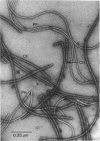
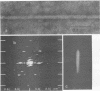
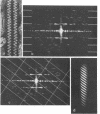
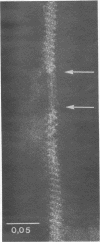
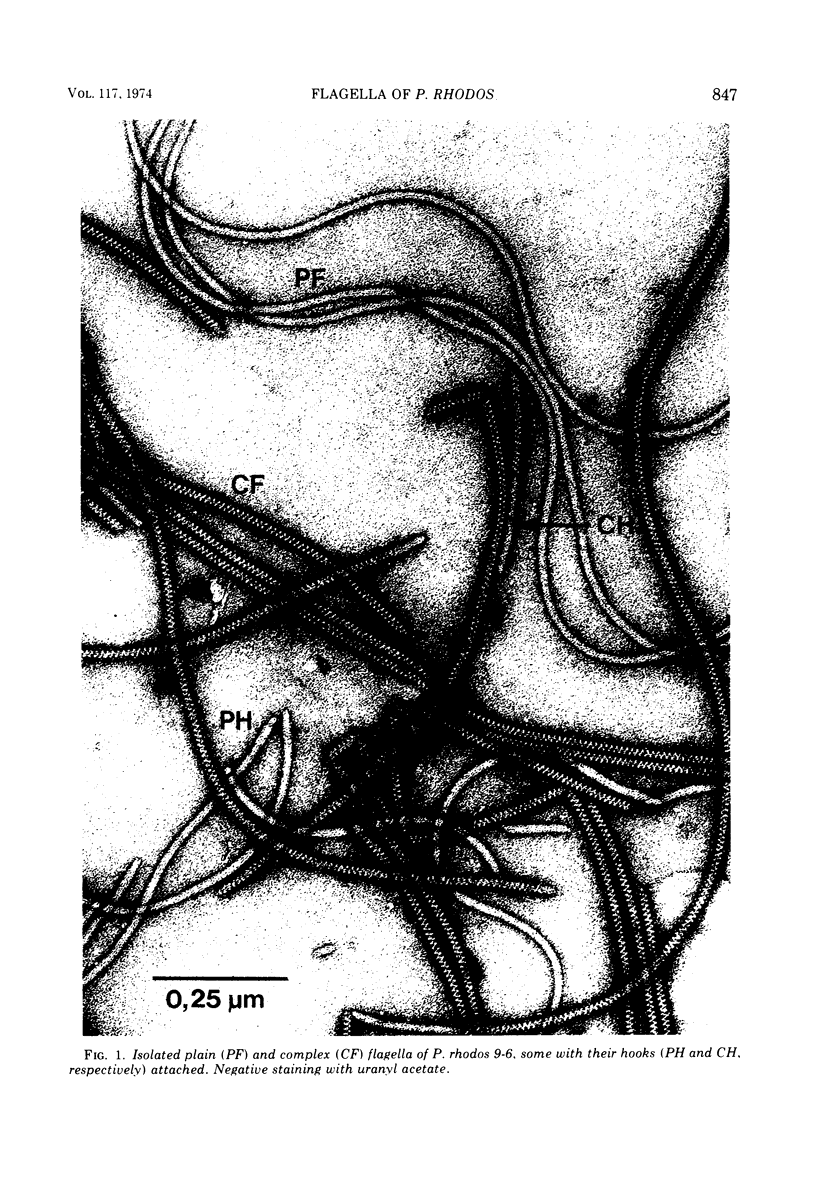
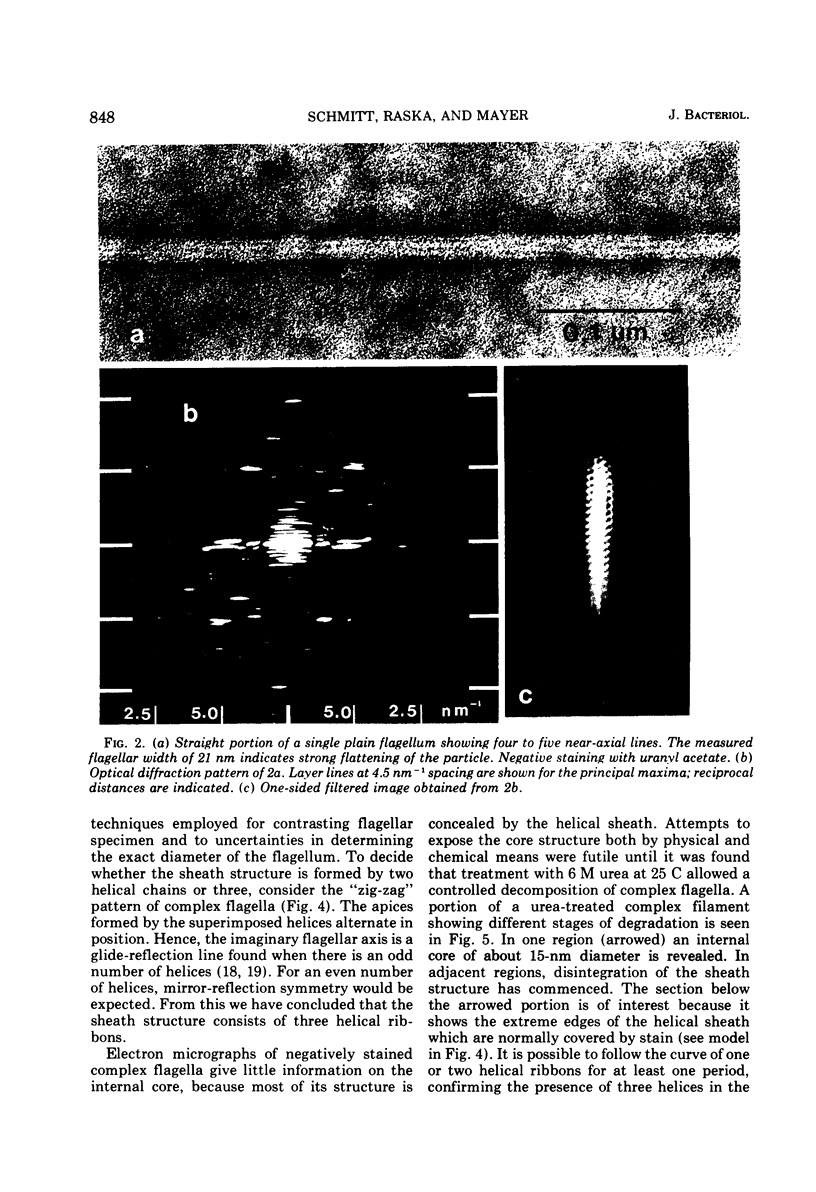
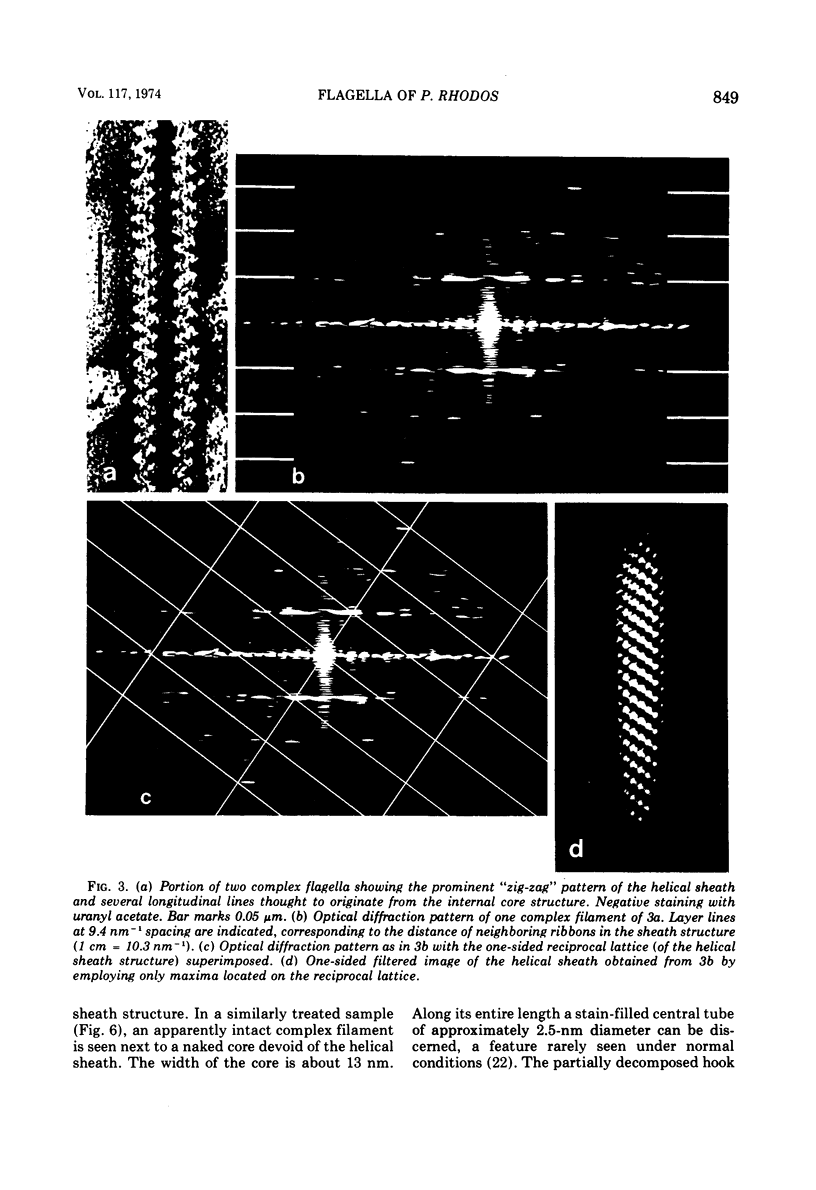
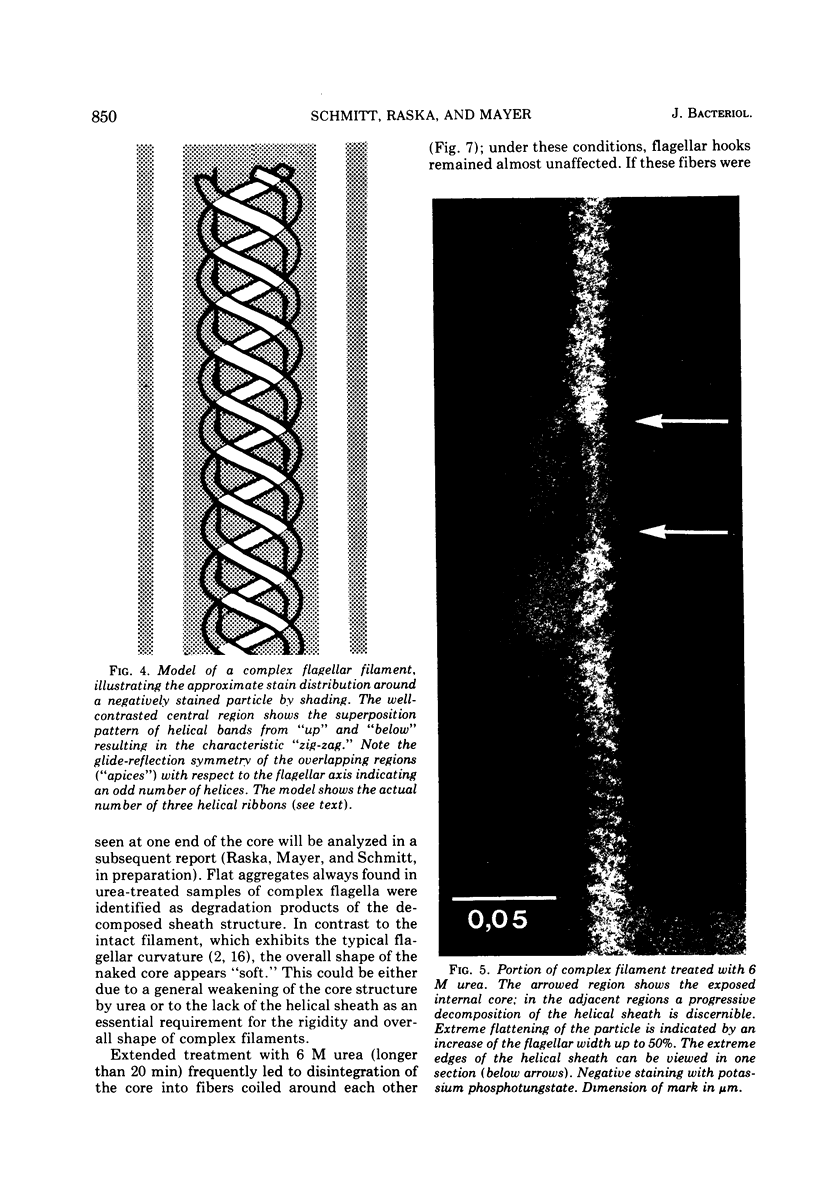
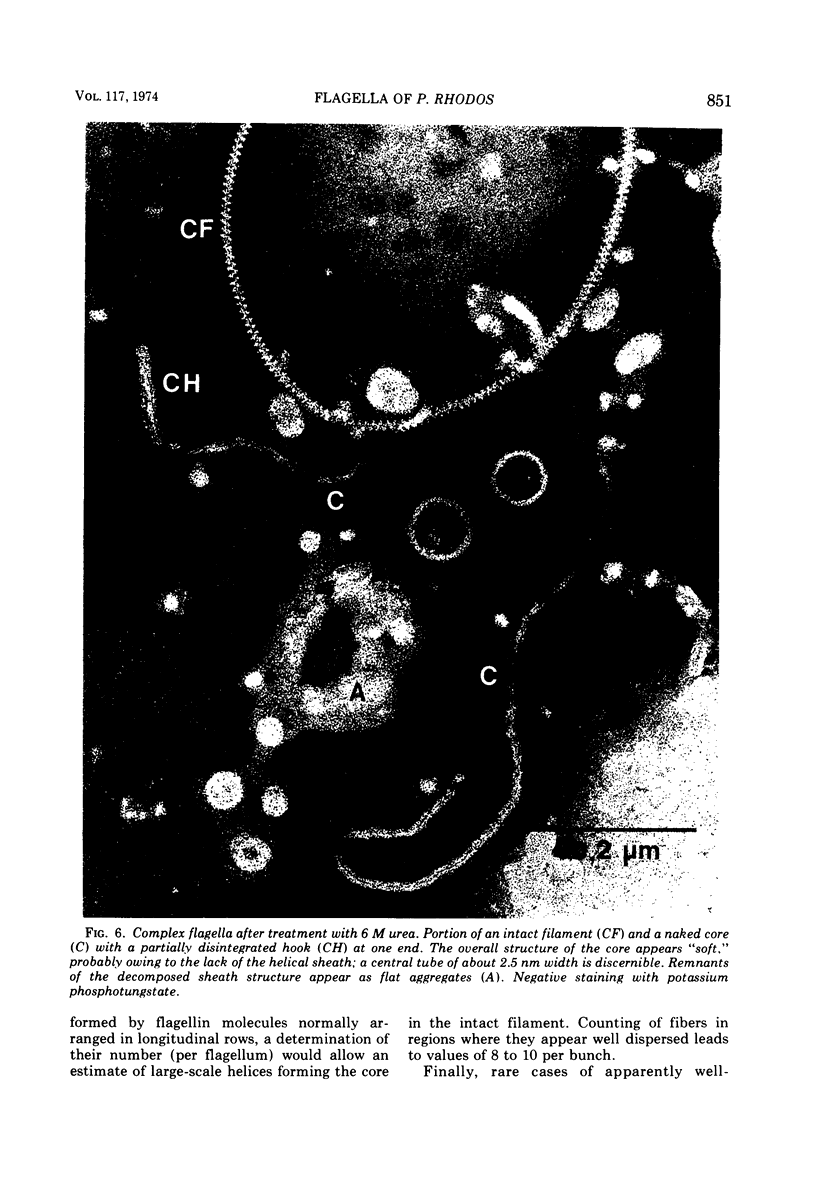
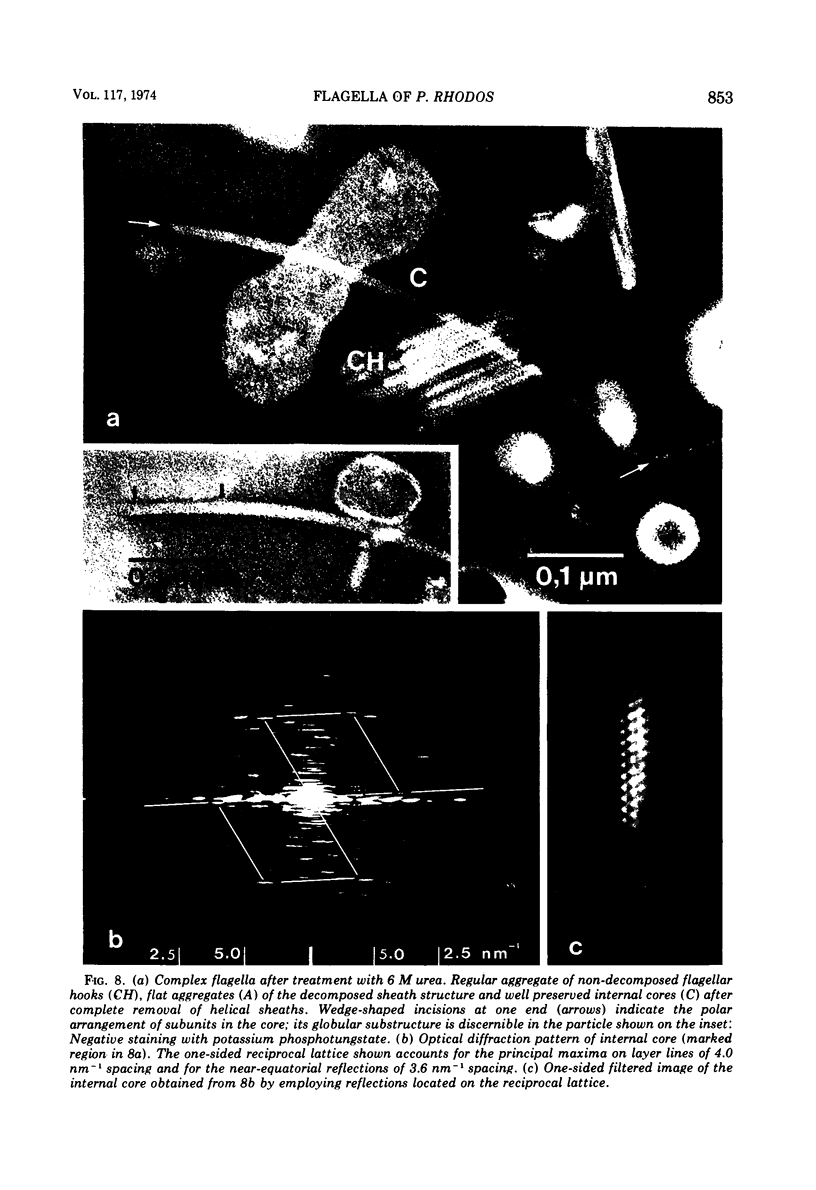
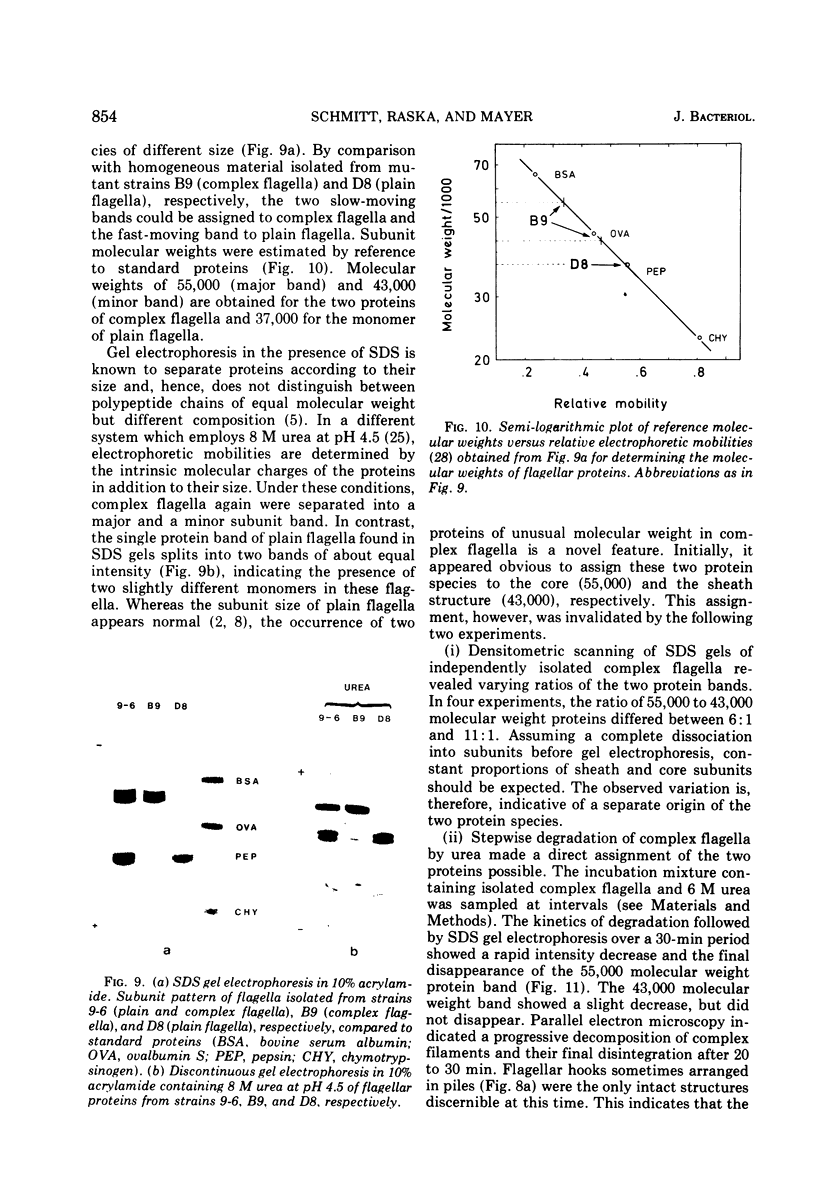
Cells of Pseudomonas rhodos 9-6 produce two morphologically distinct flagella termed plain and complex, respectively. Fine structure analyses by electron microscopy and optical diffraction showed that plain flagellar filaments are cylinders of 13-nm diameter composed of globular subunits like normal bacterial flagella. The structure comprises nine large-scale helical rows of subunits intersecting four small-scale helices of pitch angle 25°. Complex filaments have a conspicuous helical sheath, 18-nm wide, of three close-fitting helical bands, each about 4.7-nm wide, separated by axial intervals, 4.7 nm wide, running at an angle of 27°. The internal core has similar but not identical substructure to plain filaments. Unlike plain flagella, the complex species is fragile and does not aggregate in bundles. Mutants bearing only one of two types of flagellum were isolated. Cells with plain flagella showed normal translational motion, and cells with complex flagella showed rapid spinning. Isolated plain flagella consist of a 37,000-dalton subunit separable into two isoproteins. Complex filaments consist of a 55,000-dalton protein; a second 43,000-dalton protein was assigned to complex flagellar hooks. The results indicate that plain and complex flagella are entirely different in structure and composition and that the complex type represents a novel flagellar species. Its possible mode of action is discussed.
Full text
PDF






Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Abram D., Mitchen J. R., Koffler H., Vatter A. E. Differentiation within the bacterial flagellum and isolation of the proximal hook. J Bacteriol. 1970 Jan;101(1):250–261. doi: 10.1128/jb.101.1.250-261.1970. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Asakura S. Polymerization of flagellin and polymorphism of flagella. Adv Biophys. 1970;1:99–155. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bode W., Engel J., Winklmair D. A model of bacterial flagella based on small-angle x-ray scattering and hydrodynamic data which indicated an elongated shape of the flagellin protomer. Eur J Biochem. 1972 Apr 11;26(3):313–327. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1972.tb01770.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Champness J. N. X-ray and optical diffraction studies of bacterial flagella. J Mol Biol. 1971 Mar 14;56(2):295–310. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(71)90465-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dunker A. K., Rueckert R. R. Observations on molecular weight determinations on polyacrylamide gel. J Biol Chem. 1969 Sep 25;244(18):5074–5080. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fishbein W. N. Quantitative densitometry of 1-50 g protein in acrylamide gel slabs with Coomassie blue. Anal Biochem. 1972 Apr;46(2):388–401. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(72)90312-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Iino T. Genetics and chemistry of bacterial flagella. Bacteriol Rev. 1969 Dec;33(4):454–475. doi: 10.1128/br.33.4.454-475.1969. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Klug A., De Rosier D. J. Optical filtering of electron micrographs: reconstruction of one-sided images. Nature. 1966 Oct 1;212(5057):29–32. doi: 10.1038/212029a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- LABAW L. W., MOSLEY V. M. Periodic structure in the flagella and cell walls of a bacterium. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1954 Nov;15(3):325–331. doi: 10.1016/0006-3002(54)90033-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- LOWRY O. H., ROSEBROUGH N. J., FARR A. L., RANDALL R. J. Protein measurement with the Folin phenol reagent. J Biol Chem. 1951 Nov;193(1):265–275. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- LOWY J., HANSON J. ELECTRON MICROSCOPE STUDIES OF BACTERIAL FLAGELLA. J Mol Biol. 1965 Feb;11:293–313. doi: 10.1016/s0022-2836(65)80059-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lowy J., Spencer M. Structure and function of bacterial flagella. Symp Soc Exp Biol. 1968;22:215–236. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lowy J. Structure of the proximal ends of bacterial flagella. J Mol Biol. 1965 Nov;14(1):297–299. doi: 10.1016/s0022-2836(65)80251-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- MARX R., HEUMANN W. [On the flagellar fine structure and fimbriae in 2 Pseudomonas strains]. Arch Mikrobiol. 1962;43:245–254. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Moody M. F. Structure of the sheath of bacteriophage T4. I. Structure of the contracted sheath and polysheath. J Mol Biol. 1967 Apr 28;25(2):167–200. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(67)90136-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- O'Brien E. J., Bennett P. M. Structure of straight flagella from a mutant Salmonella. J Mol Biol. 1972 Sep 14;70(1):133–152. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(72)90168-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shapiro A. L., Viñuela E., Maizel J. V., Jr Molecular weight estimation of polypeptide chains by electrophoresis in SDS-polyacrylamide gels. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1967 Sep 7;28(5):815–820. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(67)90391-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Silverman M. R., Simon M. I. Flagellar assembly mutants in Escherichia coli. J Bacteriol. 1972 Nov;112(2):986–993. doi: 10.1128/jb.112.2.986-993.1972. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sleytr U. B., Glauert A. M. Evidence for an empty core in a bacterial flagellum. Nature. 1973 Feb 23;241(5391):542–543. doi: 10.1038/241542a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Smith R. W., Koffler H. Bacterial flagella. Adv Microb Physiol. 1971;6:219–339. doi: 10.1016/s0065-2911(08)60070-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tauschel H. D. Der Geisselapparat von Rhodopseudomonas palustris. IV. Isolierung der Geissel und ihrer Komponenten. Arch Mikrobiol. 1970;74(3):193–206. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Valentine R. C., Shapiro B. M., Stadtman E. R. Regulation of glutamine synthetase. XII. Electron microscopy of the enzyme from Escherichia coli. Biochemistry. 1968 Jun;7(6):2143–2152. doi: 10.1021/bi00846a017. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wardi A. H., Michos G. A. Alcian blue staining of glycoproteins in acrylamide disc electrophoresis. Anal Biochem. 1972 Oct;49(2):607–609. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(72)90472-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Weber K., Osborn M. The reliability of molecular weight determinations by dodecyl sulfate-polyacrylamide gel electrophoresis. J Biol Chem. 1969 Aug 25;244(16):4406–4412. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]