Abstract
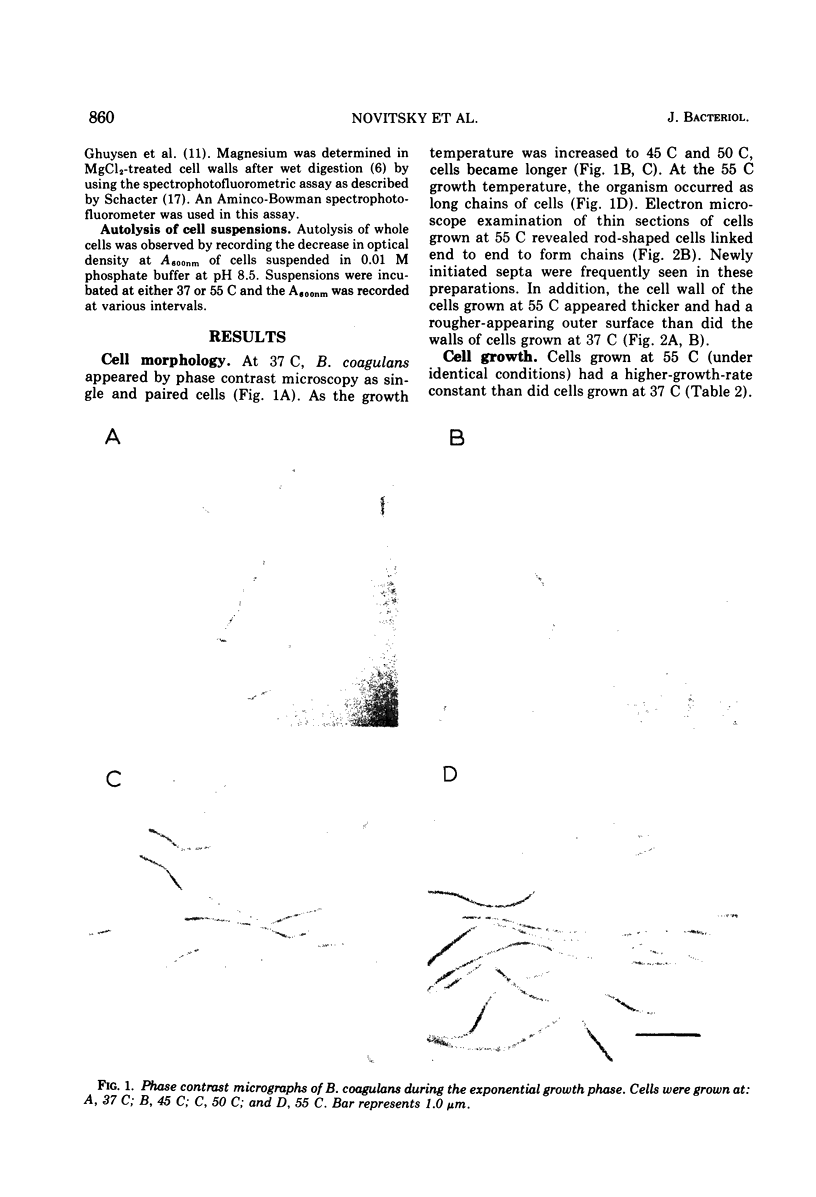
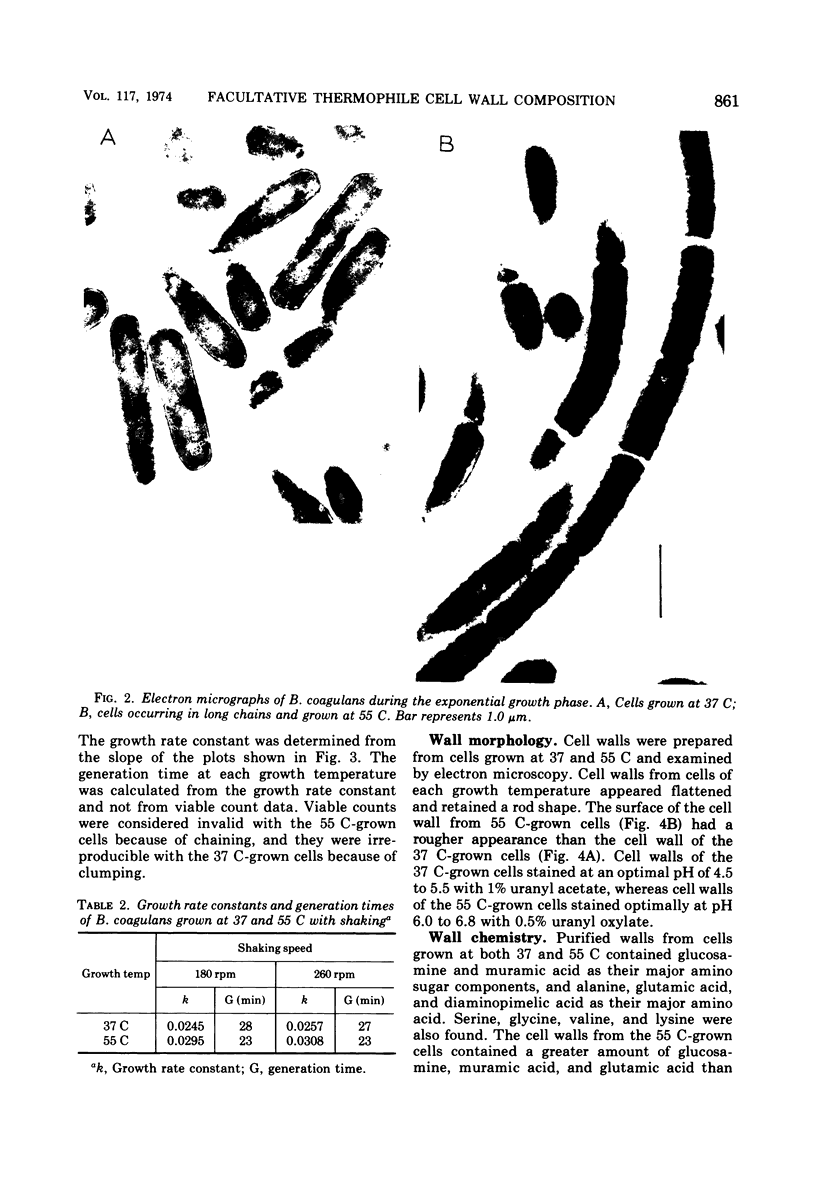
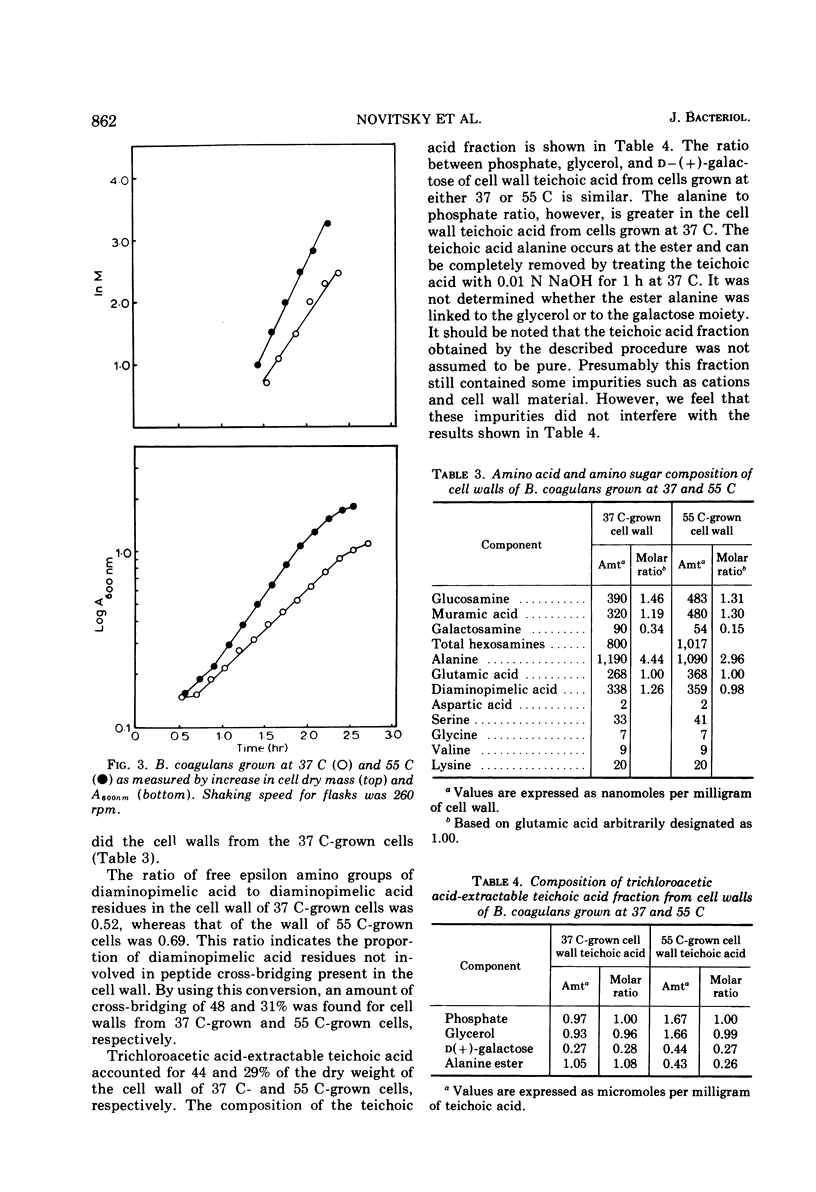
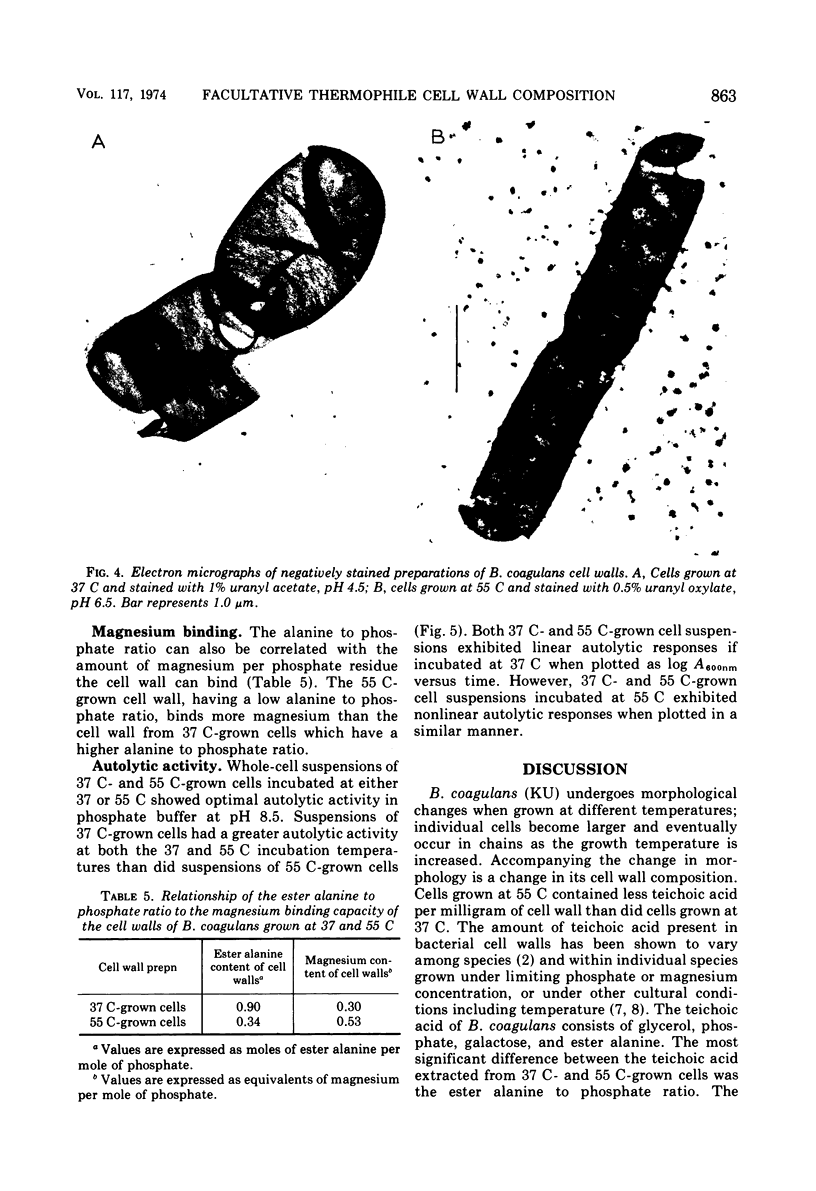
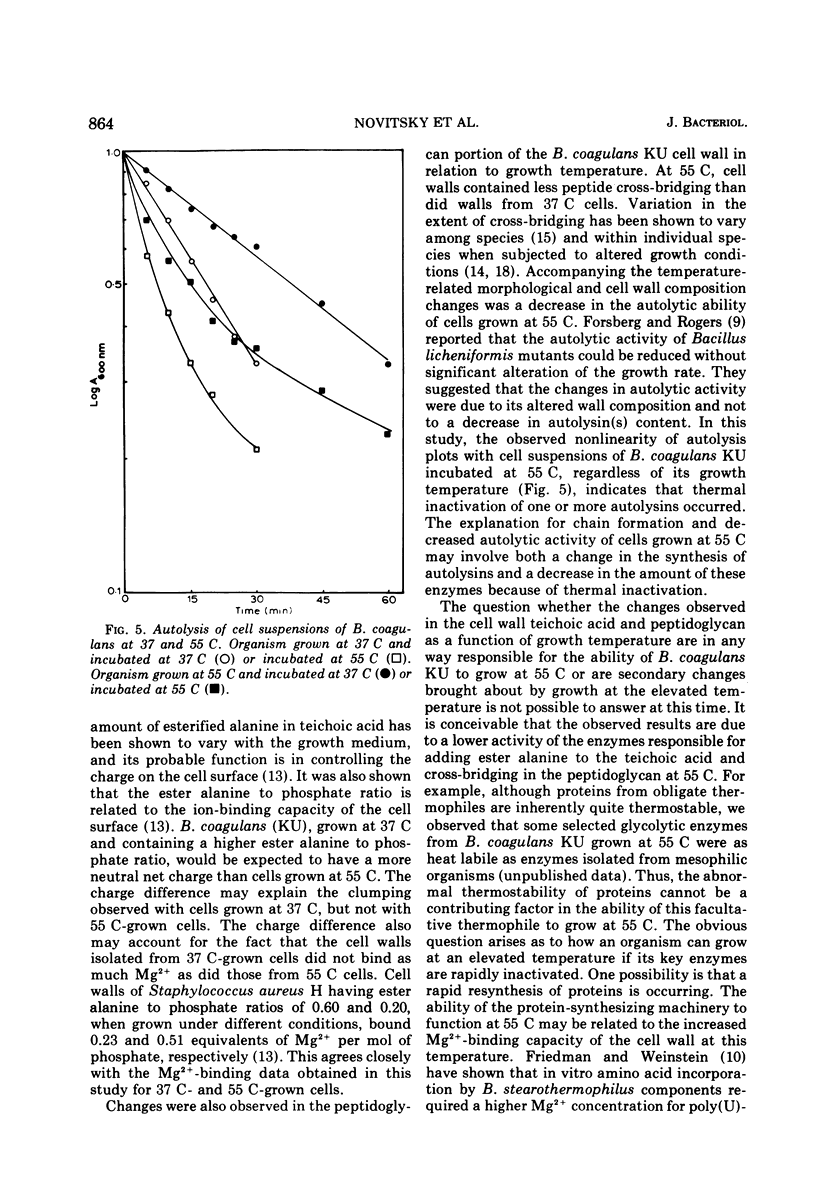
The morphology and cell wall composition of Bacillus coagulans, a facultative thermophile, were examined as a function of growth temperature. The morphology of the organism varied when it was grown at different temperatures; at 37 C the organism grew as individual cells which increased in length with increasing growth temperature. At 55 C it grew in long chains of cells. Cell wall prepared from cells grown at 37 C contained 44% teichoic acid by weight, whereas cells grown at 55 C contained 29% teichoic acid. Teichoic acid from these cells was a polymer of glycerol phosphate containing galactose and ester alanine. The ratio of ester alanine to phosphate was significantly higher in cell walls and teichoic acid from 37 C-grown cells compared with those from 55 C-grown cells. Other differences observed were that cells grown at 55 C contained a lower level of autolytic ability, produced cell walls which bound more Mg2+, and contained less peptide cross-bridging in its peptidoglycan layer than cells grown at 37 C.
Full text
PDF


Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Baddiley J. Teichoic acids in cell walls and membranes of bacteria. Essays Biochem. 1972;8:35–77. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dul M. J., McDonald W. C. Morphological changes and antibiotic-induced thermal resistance in vegetative cells of Bacillus subtilis. J Bacteriol. 1971 May;106(2):672–678. doi: 10.1128/jb.106.2.672-678.1971. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Eagon R. G. Cell wall-associated inorganic substances from Pseudomonas aeruginosa. Can J Microbiol. 1969 Feb;15(2):235–236. doi: 10.1139/m69-039. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Forrester I. T., Wicken A. J. The chemical composition of the cell walls of some thermophilic bacilli. J Gen Microbiol. 1966 Jan;42(1):147–154. doi: 10.1099/00221287-42-1-147. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Forsberg C., Rogers H. J. Autolytic enzymes in growth of bacteria. Nature. 1971 Jan 22;229(5282):272–273. doi: 10.1038/229272a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Friedman S. M., Weinstein I. B. Protein synthesis in a subcellular system from Bacillus stearothermophilus. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1966 Mar 21;114(3):593–605. doi: 10.1016/0005-2787(66)90107-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gordon R. E., Smith N. R. AEROBIC SPOREFORMING BACTERIA CAPABLE OF GROWTH AT HIGH TEMPERATURES. J Bacteriol. 1949 Sep;58(3):327–341. doi: 10.1128/jb.58.3.327-341.1949. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Heptinstall S., Archibald A. R., Baddiley J. Teichoic acids and membrane function in bacteria. Nature. 1970 Feb 7;225(5232):519–521. doi: 10.1038/225519a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Johnson K. G., Campbell J. N. Effect of growth conditions on peptidoglycan structure and susceptibility to lytic enzymes in cell walls of Micrococcus sodonensis. Biochemistry. 1972 Jan 18;11(2):277–286. doi: 10.1021/bi00752a020. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- ROSEN H. A modified ninhydrin colorimetric analysis for amino acids. Arch Biochem Biophys. 1957 Mar;67(1):10–15. doi: 10.1016/0003-9861(57)90241-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- SCHACHTER D. Fluorometric estimation of magnesium with 8-hydroxy-5-quinolinesulfonate. J Lab Clin Med. 1961 Sep;58:495–498. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sutow A. B., Welker N. E. Chemical composition of the cell walls of Bacillus stearothermophilus. J Bacteriol. 1967 Apr;93(4):1452–1457. doi: 10.1128/jb.93.4.1452-1457.1967. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- WICKEN A. J., BADDILEY J. Structure of intracellular teichoic acids from group D streptococci. Biochem J. 1963 Apr;87:54–62. doi: 10.1042/bj0870054. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]