Abstract
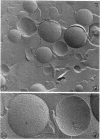
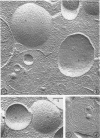
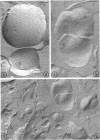
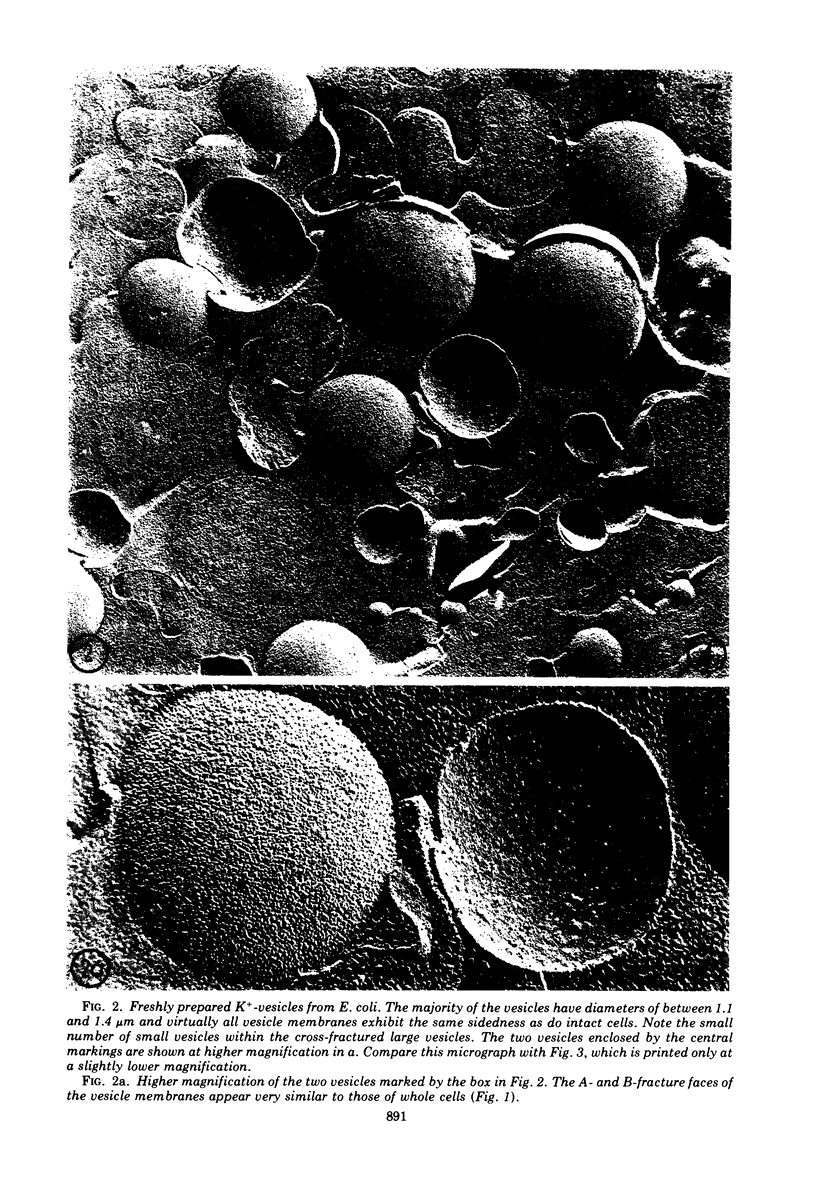
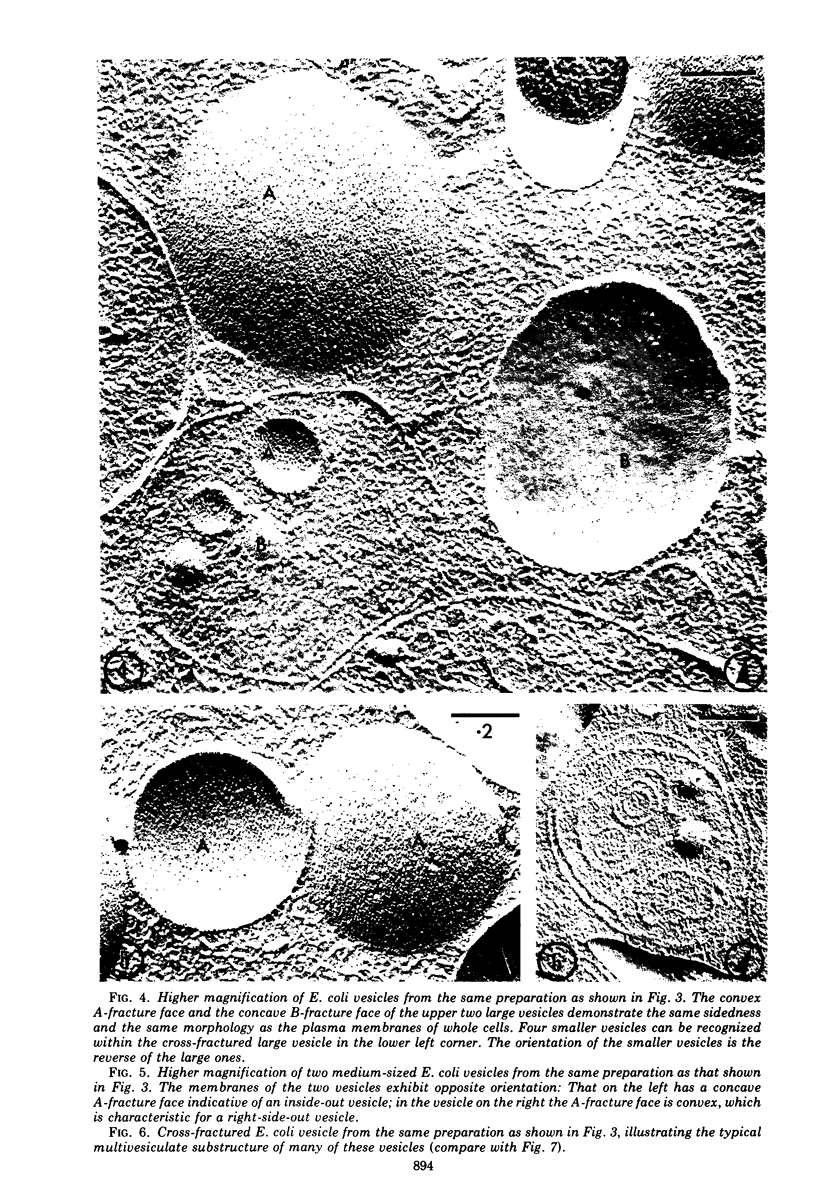
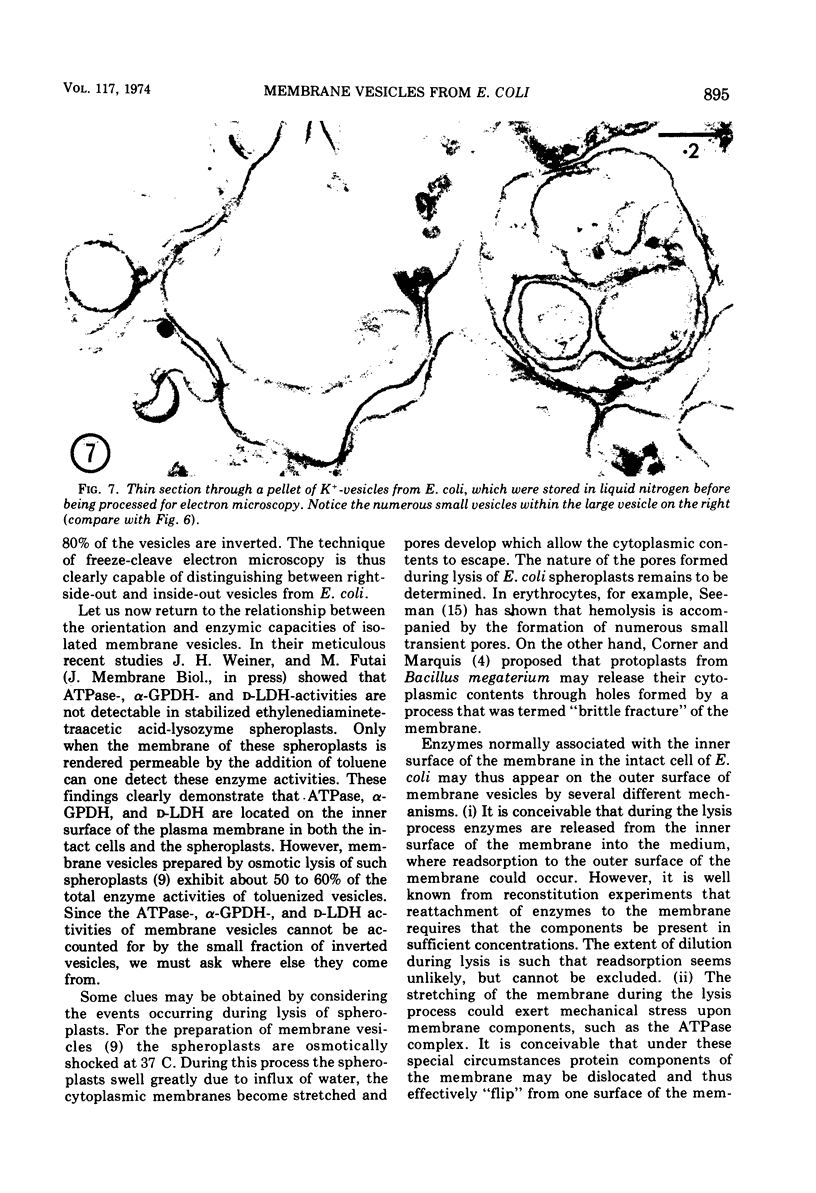
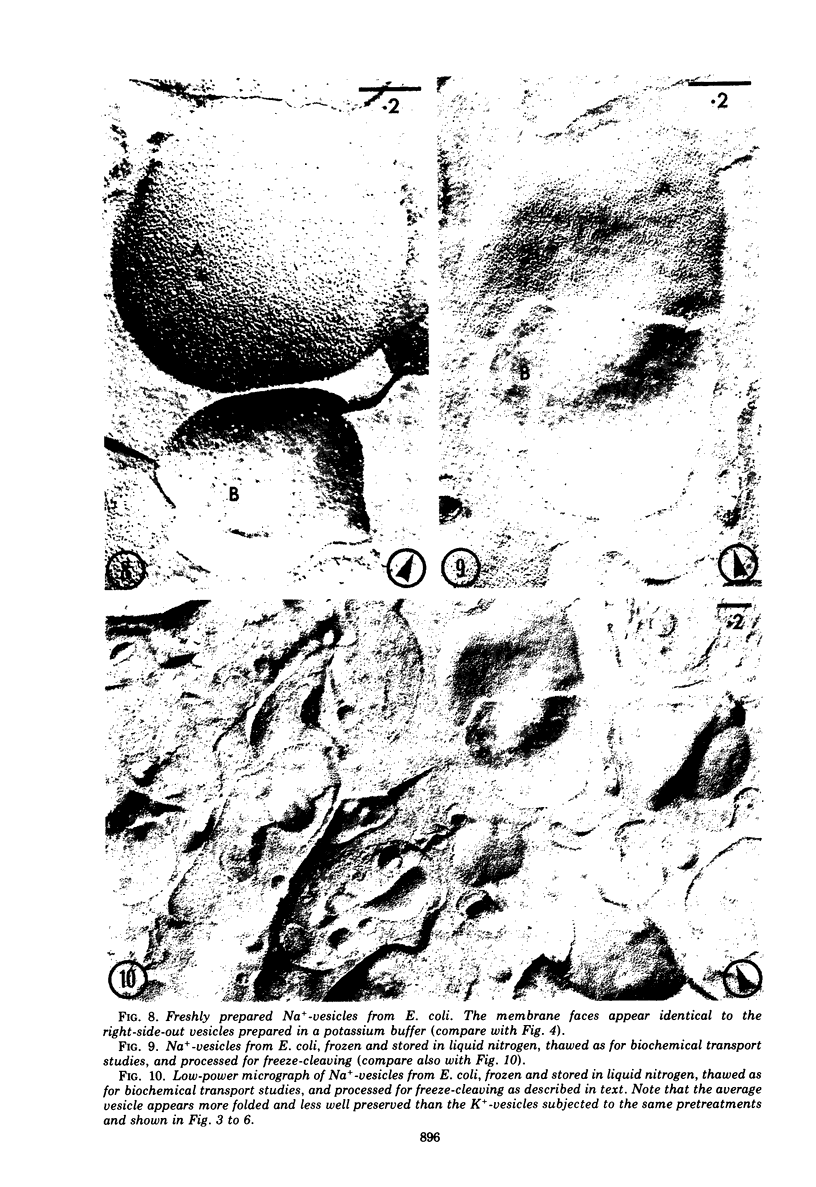
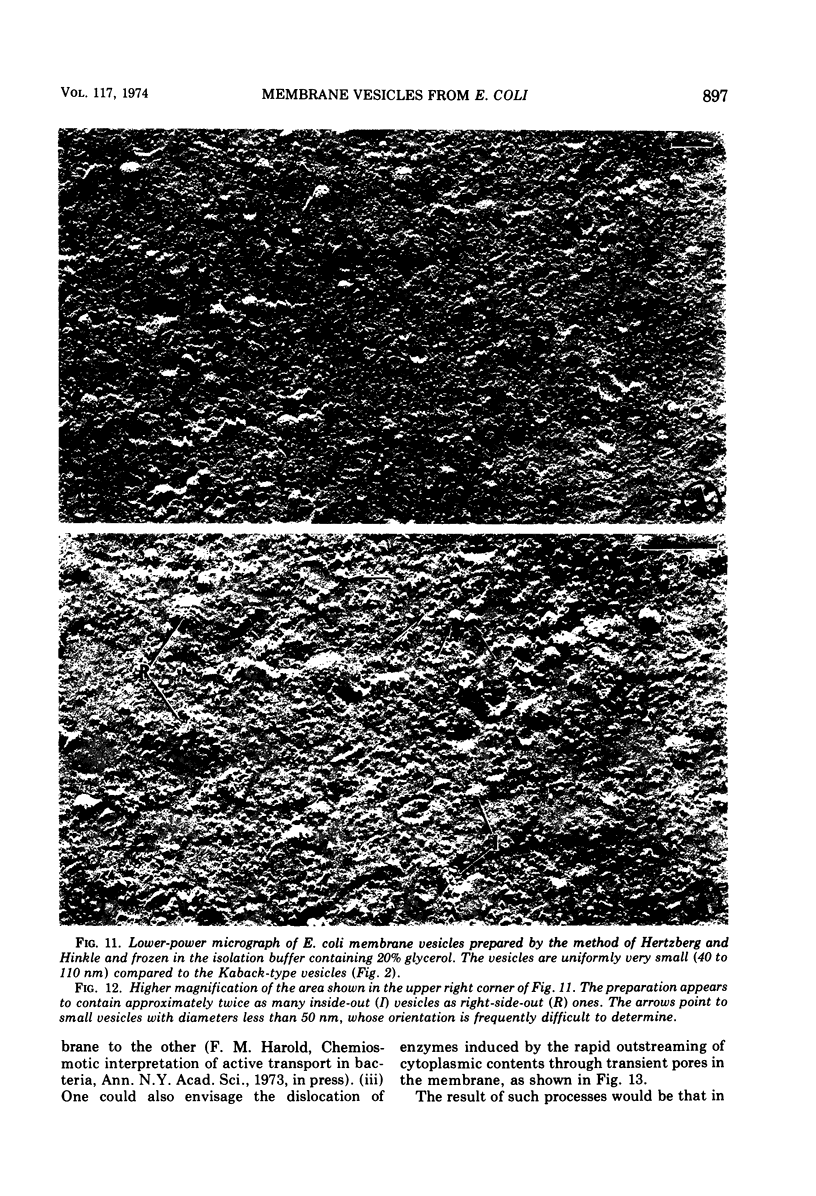
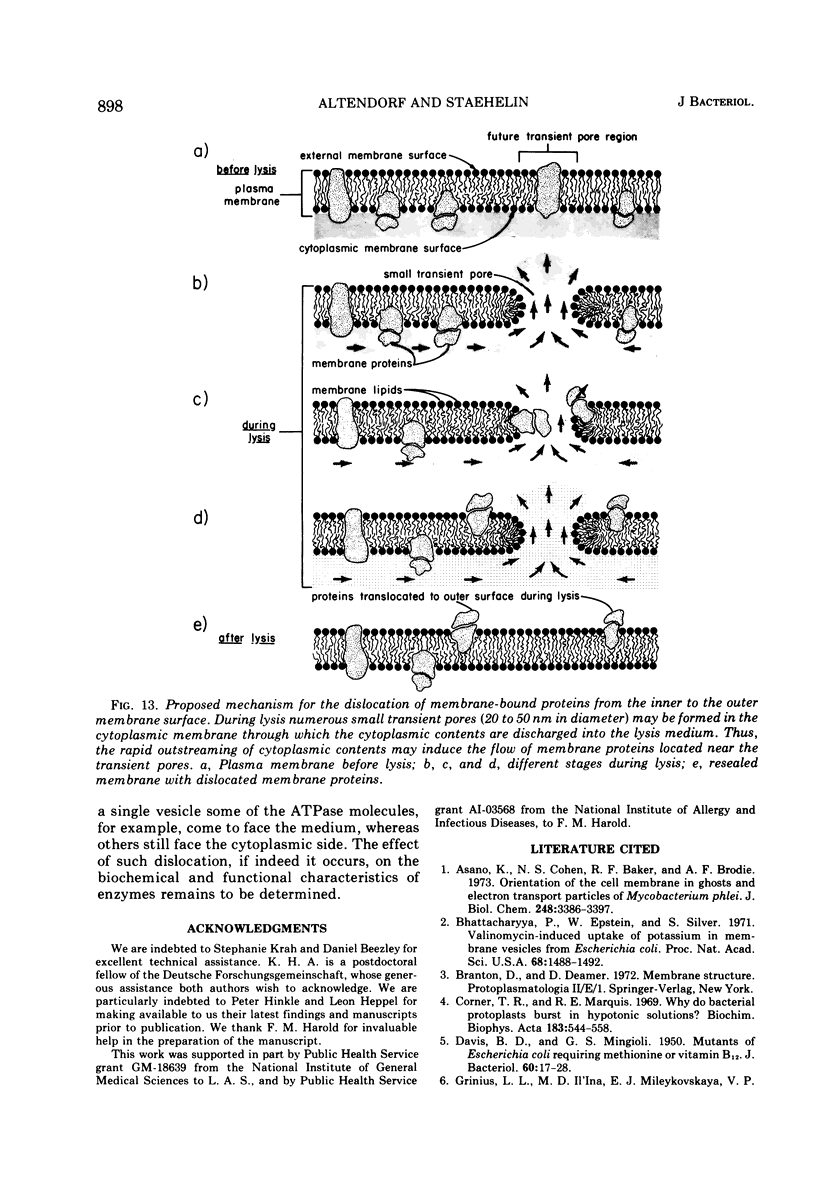
The application of freeze-cleave electron microscopy to whole cells of Escherichia coli revealed that the particles exposed on the resulting two inner membrane faces are asymmetrically distributed. This method can therefore be used to determine the orientation of membrane vesicles from E. coli. Membrane vesicles freshly prepared in potassium phosphate buffer (K+-vesicles) by osmotic lysis of spheroplasts consisted almost entirely of right-side-out vesicles. Their size suggested that each cell gives rise to one vesicle. When the membrane vesicles were subjected to one cycle of freezing and thawing, the number of inside-out vesicles rose to about 25%. However, due to the small size of most of the inside-out vesicles, these contribute only 2 to 3% of the total membrane surface area of the preparation. The inside-out vesicles appear to arise from infoldings of the membrane of right-side-out vesicles. They also accumulate within the latter, thus producing multivesicular membrane sacs. Na+-vesicles (vesicles prepared in sodium phosphate buffer) subjected to freezing and thawing appeared to lose structural rigidity more than did K+-vesicles. In contrast to the membrane vesicles prepared by the osmotic lysis of spheroplasts, those obtained by breaking intact cells by a single passage through a French pressure cell were uniformly very small (only 40 to 110 nm in diameter); approximately 60 to 80% were inside-out. To reconcile the polarity of the membrane vesicles with the enzymic activities of such preparations, we propose that “dislocation” of membrane proteins occurs during osmotic lysis of spheroplasts.
Full text
PDF




Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Asano A., Cohen N. S., Baker R. F., Brodie A. F. Orientation of the cell membrane in ghosts and electron transport particles of Mycobacterium phlei. J Biol Chem. 1973 May 25;248(10):3386–3397. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bhattacharyya P., Epstein W., Silver S. Valinomycin-induced uptake of potassium in membrane vesicles from Escherichia coli. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1971 Jul;68(7):1488–1492. doi: 10.1073/pnas.68.7.1488. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Corner T. R., Marquis R. E. Why do bacterial protoplasts burst in hypotonic solutions? Biochim Biophys Acta. 1969;183(3):544–558. doi: 10.1016/0005-2736(69)90168-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- DAVIS B. D., MINGIOLI E. S. Mutants of Escherichia coli requiring methionine or vitamin B12. J Bacteriol. 1950 Jul;60(1):17–28. doi: 10.1128/jb.60.1.17-28.1950. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Grinius L. L., Il'ina M. D., Mileykovskaya E. I., Skulachev V. P., Tikhonova G. V. Conversion of biomembrane-produced energy into electric form. V. Membrane particles of Micrococcus lysodeikticus and pea chloroplasts. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1972 Dec 14;283(3):442–455. doi: 10.1016/0005-2728(72)90261-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Harold F. M. Conservation and transformation of energy by bacterial membranes. Bacteriol Rev. 1972 Jun;36(2):172–230. doi: 10.1128/br.36.2.172-230.1972. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hirata H., Altendorf K., Harold F. M. Role of an electrical potential in the coupling of metabolic energy to active transport by membrane vesicles of Escherichia coli. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1973 Jun;70(6):1804–1808. doi: 10.1073/pnas.70.6.1804. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kaback H. R. Transport across isolated bacterial cytoplasmic membranes. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1972 Aug 4;265(3):367–416. doi: 10.1016/0304-4157(72)90014-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pinto da Silva P. Translational mobility of the membrane intercalated particles of human erythrocyte ghosts. pH-dependent, reversible aggregation. J Cell Biol. 1972 Jun;53(3):777–787. doi: 10.1083/jcb.53.3.777. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Reeves J. P. Transient pH changes during D-lactate oxidation by membrane vesicles. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1971 Nov;45(4):931–936. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(71)90427-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Seeman P. Transient holes in the erythrocyte membrane during hypotonic hemolysis and stable holes in the membrane after lysis by saponin and lysolecithin. J Cell Biol. 1967 Jan;32(1):55–70. doi: 10.1083/jcb.32.1.55. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Singer S. J., Nicolson G. L. The fluid mosaic model of the structure of cell membranes. Science. 1972 Feb 18;175(4023):720–731. doi: 10.1126/science.175.4023.720. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Staehelin L. A., Chlapowski F. J., Bonneville M. A. Lumenal plasma membrane of the urinary bladder. I. Three-dimensional reconstruction from freeze-etch images. J Cell Biol. 1972 Apr;53(1):73–91. doi: 10.1083/jcb.53.1.73. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Steck T. L., Weinstein R. S., Straus J. H., Wallach D. F. Inside-out red cell membrane vesicles: preparation and purification. Science. 1970 Apr 10;168(3928):255–257. doi: 10.1126/science.168.3928.255. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- West I., Mitchell P. Proton-coupled beta-galactoside translocation in non-metabolizing Escherichia coli. J Bioenerg. 1972 Aug;3(5):445–462. doi: 10.1007/BF01516082. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]