Abstract
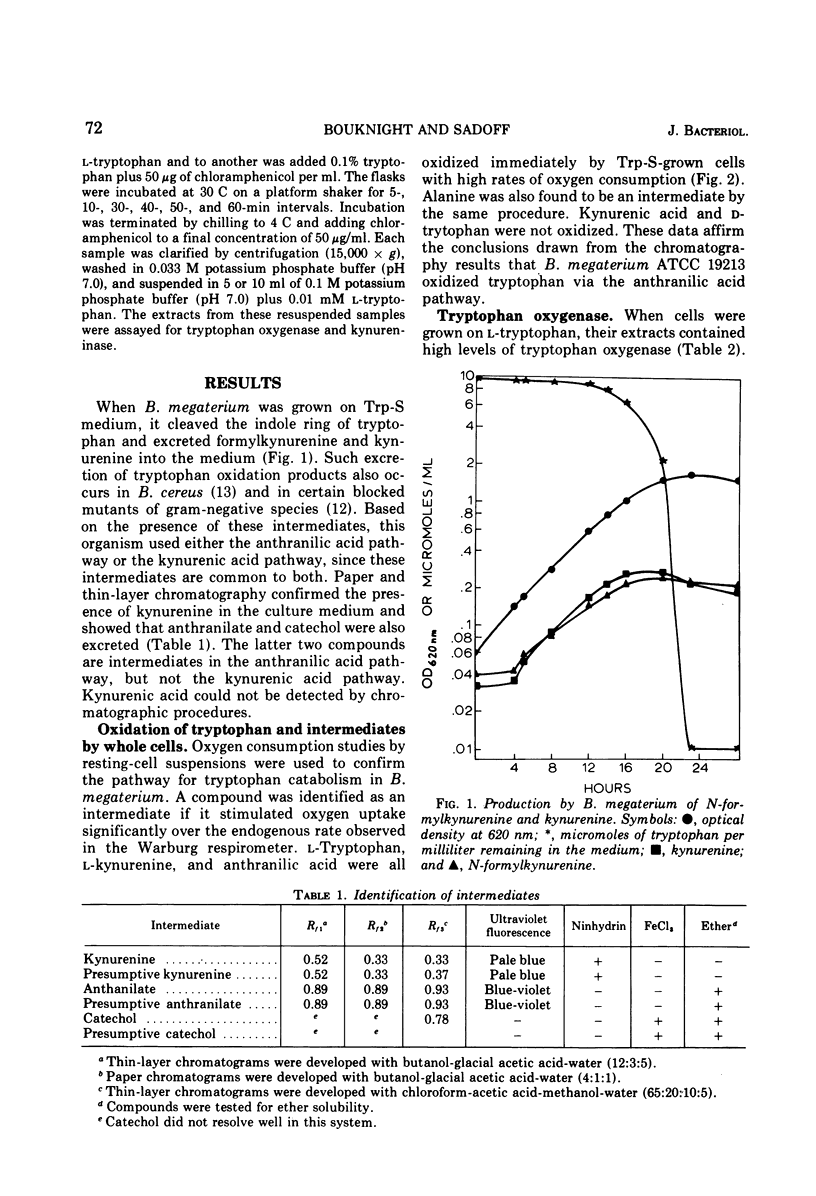
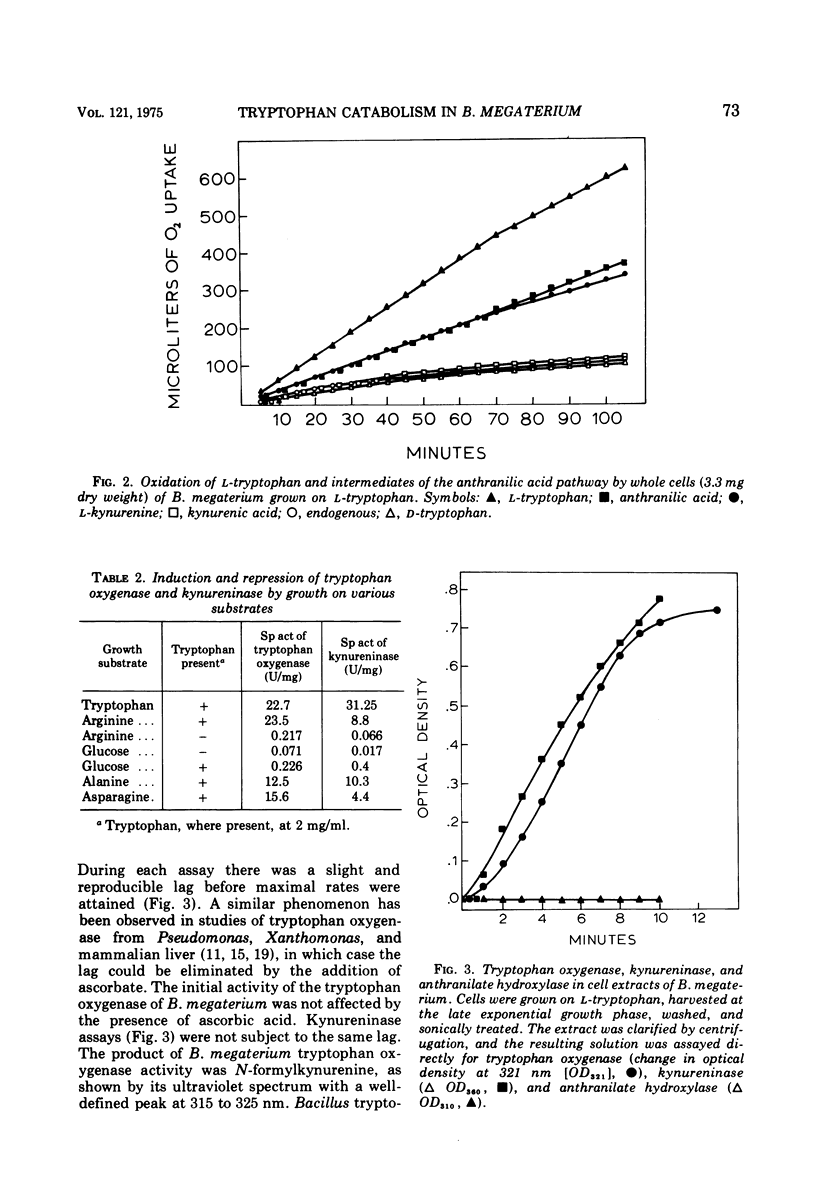
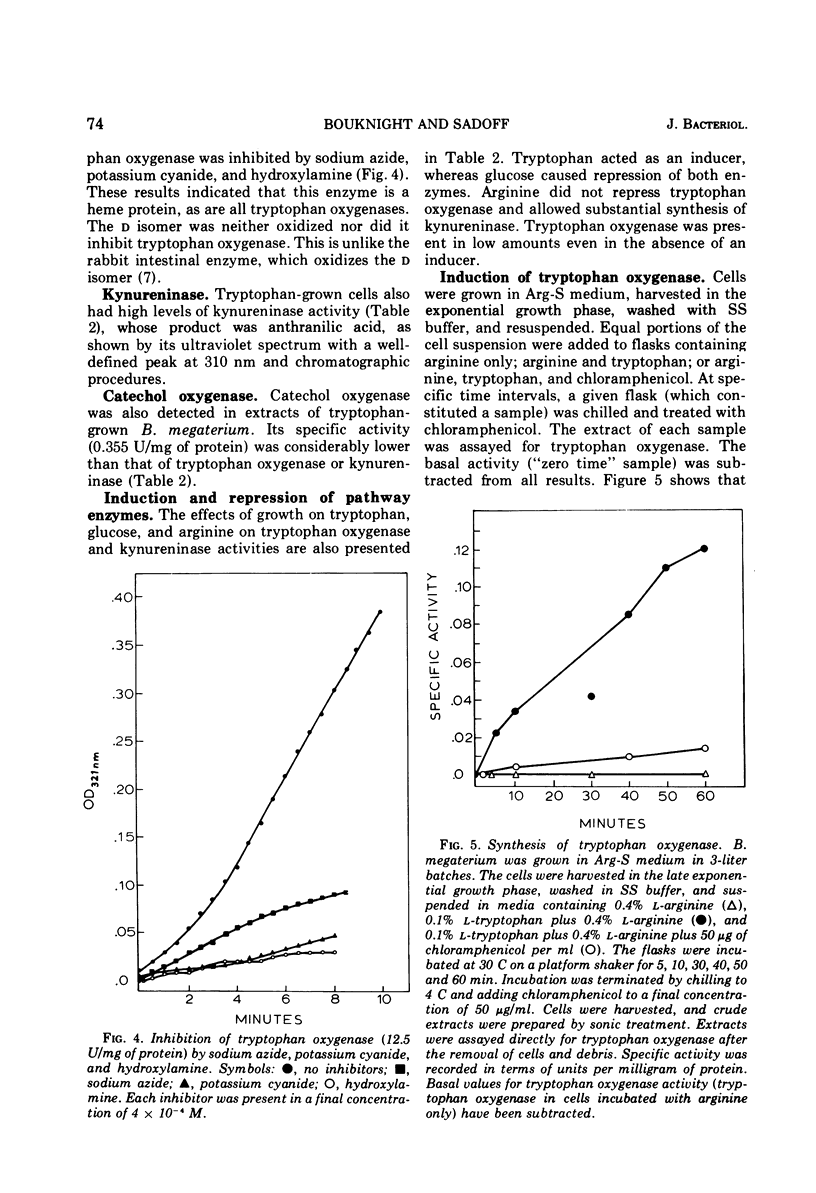
Bacillus megaterium grows in a medium containing L-tryptophan as the sole carbon, nitrogen, and energy source. Kynurenine, anthranilic acid, and catechol are metabolic intermediates, suggesting that this organism used the anthranilic acid pathway for tryptophan degradation. Cells that grow on L-tryptophan oxidize kynurenine, alanine, and anthranilic acid and the presence of tryptophan oxygenase (EC 1.13.1.12), kynureninase (EC 3.7.1.3), and catechol oxygenase (EC 1.13.1.1) in cell extracts provide additional evidence for the degradative pathway in B. megaterium. Tryptophan oxygenase is inhibited by sodium azide, potassium cyanide, and hydroxylamine, indicating that the enzyme has a functional heme group. D-Tryptophan is not a substrate for tryptophan oxygenase, and the D-isomer does not inhibit this enzyme. Formamidase (EC 3.5.1.9) and anthranilate hydroxylase are not detectable in extracts. Tryptophan catabolism is inducible in B megaterium and is subject to catabolite repression by glucose and glutamate. Arginine does not cause repression, and kynurenine induces both tryptophan oxygenase and kynureninase.
Full text
PDF



Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Brown A. T., Wagner C. Regulation of enzymes involved in the conversion of tryptophan to nicotinamide adenine dinucleotide in a colorless strain of Xanthomonas pruni. J Bacteriol. 1970 Feb;101(2):456–463. doi: 10.1128/jb.101.2.456-463.1970. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Doering J. L., Bott K. F. Differential amino acid requirements for sporulation in Bacillus subtilis. J Bacteriol. 1972 Oct;112(1):345–355. doi: 10.1128/jb.112.1.345-355.1972. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Feigelson P., Ishimura Y., Hayaishi O. On the activation and catalytic mechanism of microbial tryptophan pyrrolase. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1964;14:96–101. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(63)90218-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gaertner F. H., Cole K. W., Welch G. R. Evidence for distinct kynureninase and hydroxykynureninase activities in Neurospora crassa. J Bacteriol. 1971 Nov;108(2):902–909. doi: 10.1128/jb.108.2.902-909.1971. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Haworth C., Walmsley T. A. A study of the chromatographic behaviour of tryptophan metabolites and related compounds by chromatography on thin layers of silica gel. I. Qualitative separation. J Chromatogr. 1972 Apr 5;66(2):311–319. doi: 10.1016/s0021-9673(01)82294-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hirata F., Hayaishi O. New degradative routes of 5-hydroxytryptophan and serotonin by intestinal tryptophan 2,3-dioxygenase. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1972 Jun 9;47(5):1112–1119. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(72)90949-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hoch S. O., DeMoss R. D. Catalytic studies on tryptophanase from Bacillus alvei. J Bacteriol. 1973 Apr;114(1):341–350. doi: 10.1128/jb.114.1.341-350.1973. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- LOWRY O. H., ROSEBROUGH N. J., FARR A. L., RANDALL R. J. Protein measurement with the Folin phenol reagent. J Biol Chem. 1951 Nov;193(1):265–275. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ornston L. N. Regulation of catabolic pathways in Pseudomonas. Bacteriol Rev. 1971 Jun;35(2):87–116. doi: 10.1128/br.35.2.87-116.1971. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- PALLERONI N. J., STANIER R. Y. REGULATORY MECHANISMS GOVERNING SYNTHESIS OF THE ENZYMES FOR TRYPTOPHAN OXIDATION BY PSEUDOMONAS FLUORESCENS. J Gen Microbiol. 1964 May;35:319–334. doi: 10.1099/00221287-35-2-319. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Prasad C., Srinivasan V. R. Tryptophan catabolism during sporulation in Bacillus cereus. Biochem J. 1970 Sep;119(2):343–349. doi: 10.1042/bj1190343. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rosenfeld H., Feigelson P. Synergistic and product induction of the enzymes of tryptophan metabolism in Pseudomonas acidovorans. J Bacteriol. 1969 Feb;97(2):697–704. doi: 10.1128/jb.97.2.697-704.1969. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- SLEPECKY R., FOSTER J. W. Alterations in metal content of spores of Bacillus megaterium and the effect on some spore properties. J Bacteriol. 1959 Jul;78(1):117–123. doi: 10.1128/jb.78.1.117-123.1959. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- TANAKA T., KNOX W. E. The nature and mechanism of the tryptophan pyrrolase (peroxidase-oxidase) reaction of Pseudomonas and of rat liver. J Biol Chem. 1959 May;234(5):1162–1170. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wagner C., Brown A. T. Regulation of tryptophan pyrrolase activity in Xanthomonas pruni. J Bacteriol. 1970 Oct;104(1):90–97. doi: 10.1128/jb.104.1.90-97.1970. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


