Abstract
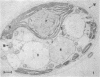
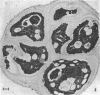
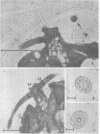
Palmelloids induced in the unicellular green alga Chlamydomonas eugametos by chloroplatinic acid treatment have been studied electron microscopically. Thin-sectioned specimens revealed the multilayer nature of the cell walls after second division within the palmelloid. Although synchrony in cell division is lost, to a certain degree, within the palmelloid, the cells themselves appeared normal, and the presence of normal flagellar structure was confirmed. The presence of the eyespot was observed at the optical level as well as in the freeze-etched specimens. The above results support the hypothesis that the palmelloid condition of Chlamydomonas eugametos induced by chloroplatinic acid is due to an abnormality in cell wall formation rather than flagellar malfunction or loss.
Full text
PDF





Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Bray D. F., Nakamura K., Costerton J. W., Wagenaar E. B. Ultrastructure of Chlamydomonas eugametos as revealed by freeze-etching: cell wall, plasmalemma and chloroplast membrane. J Ultrastruct Res. 1974 May;47(2):125–141. doi: 10.1016/s0022-5320(74)80065-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- GIBBS S. P., LEWIN R. A., PHILPOTT D. E. The fine structure of the flagellar apparatus of Chlamydomonas moewusii. Exp Cell Res. 1958 Dec;15(3):619–622. doi: 10.1016/0014-4827(58)90112-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- GOWANS C. S. Some genetic investigations on Chlamydomonas eugametos. Z Vererbungsl. 1960;91:63–73. doi: 10.1007/BF00889999. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Moor H. Freeze-etching. Int Rev Cytol. 1969;25:391–412. doi: 10.1016/s0074-7696(08)60209-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- RANDALL J., WARR J. R., HOPKINS J. M., MCVITTIE A. A SINGLE-GENE MUTATION OF CHLAMYDOMONAS REINHARDII AFFECTING MOTILITY: A GENETIC AND ELECTRON MICROSCOPE STUDY. Nature. 1964 Aug 29;203:912–914. doi: 10.1038/203912a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- REYNOLDS E. S. The use of lead citrate at high pH as an electron-opaque stain in electron microscopy. J Cell Biol. 1963 Apr;17:208–212. doi: 10.1083/jcb.17.1.208. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ringo D. L. The arrangement of subunits in flagellar fibers. J Ultrastruct Res. 1967 Feb;17(3):266–277. doi: 10.1016/s0022-5320(67)80048-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rosenberg B., Renshaw E., Vancamp L., Hartwick J., Drobnik J. Platinum-induced filamentous growth in Escherichia coli. J Bacteriol. 1967 Feb;93(2):716–721. doi: 10.1128/jb.93.2.716-721.1967. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rosenberg B., VanCamp L., Trosko J. E., Mansour V. H. Platinum compounds: a new class of potent antitumour agents. Nature. 1969 Apr 26;222(5191):385–386. doi: 10.1038/222385a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Spurr A. R. A low-viscosity epoxy resin embedding medium for electron microscopy. J Ultrastruct Res. 1969 Jan;26(1):31–43. doi: 10.1016/s0022-5320(69)90033-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Walne P. L. The effects of colchicine on cellular organization in Chlamydomonas. I. Light microscopy and cytochemistry. Am J Bot. 1966 Oct;53(9):908–916. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]