Abstract
The replication terminator protein Fob1 of Saccharomyces cerevisiae is multifunctional, and it not only promotes polar replication fork arrest at the tandem Ter sites located in the intergenic spacer region of rDNA but also loads the NAD-dependent histone deacetylase Sir2 at Ter sites via a protein complex called RENT (regulator of nucleolar silencing and telophase exit). Sir2 is a component of the RENT complex, and its loading not only silences intrachromatid recombination in rDNA but also RNA polymerase II-catalyzed transcription. Here, we present three lines of evidence showing that the two aforementioned activities of Fob1 are independent of each other as well as functionally separable. First, a Fob1 ortholog of Saccharomyces bayanus expressed in a fob1Δ strain of S. cerevisiae restored polar fork arrest at Ter but not rDNA silencing. Second, a mutant form (I407T) of S. cerevisiae Fob1 retained normal fork arresting activity but was partially defective in rDNA silencing. We further show that the silencing defect of S. bayanus Fob1 and the Ι407Τ mutant of S. cerevisiae Fob1 were caused by the failure of the proteins to interact with two members of the S. cerevisiae RENT complex, namely S. cerevisiae Sir2 and S. cerevisiae Net1. Third, deletions of the intra-S phase checkpoint proteins Tof1 and Csm3 abolished fork arrest by Fob1 at Ter without causing loss of silencing. Taken together, the data support the conclusion that unlike some other functions of Fob1, rDNA silencing at Ter is independent of fork arrest.
Keywords: DNA/Recombination, DNA/Replication, DNA-binding Protein, Protein-DNA Interaction, Yeast Transcription, Histone Deacetylase, Replication Terminator Protein, Replication Terminus, rDNA Silencing, Transcriptional Silencing
Introduction
The rDNA of Saccharomyces cerevisiae is organized in 200 tandem copies of a ∼9.1-kb repeating unit present in chromosome XII of yeast (1). Each repeating unit encodes a sequence that is transcribed from left to right by RNA polymerase I and another that is transcribed from right to left by RNA polymerase III to generate 35 S and the 5 S RNA, respectively. The coding regions of these RNAs are separated by two intergenic spacers (IGSs)4 called IGS1 and IGS2 that contain two tandem Ter sites and a single autonomously replicating sequence, respectively (see Fig. 1A) (2). The replication terminator protein Fob1 binds to the Ter1 and Ter2 sites to promote polar fork arrest that prevents the leftward moving replication forks from invading the region of 35 S RNA that is transcribed from the opposite direction (see Fig. 1A) (3, 4).
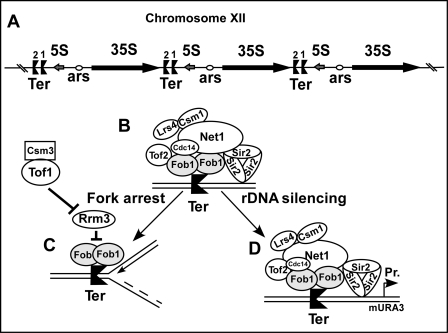
FIGURE 1.
Model showing termination and silencing functions of Fob1 in rDNA of S. cerevisiae. A, rDNA array in chromosome XII, each rDNA unit has 35 S and 5 S-encoding sequences punctuated by two nontranscribed spacers. Note the ARS in spacer 2 and twin Ter sites in spacer 1. B, shown is the protein complex containing Fob1, Tof2, Csm1, Lrs4, and the RENT complex (containing Net1, Cdc14, and Sir2). C, shown is a schematic representation of Fob1-mediated fork arrest at the Ter sites. In C, the protein components necessary for fork arrest are shown, and the silencing complex has been omitted to simplify the picture. It does not imply that the silencing complex has to be removed before fork arrest occurs; D, shown is the rDNA-silencing RENT complex consisting of the indicated component proteins. ars, origin of replication; Pr, promoter.
In addition to Fob1, stable fork arrest at Ter1 and Ter2 requires the intra-S phase checkpoint proteins Tof1 and Csm3, which form a complex that antagonizes the Rrm3 helicase/“sweepase”(5, 6). Rrm3 apparently displaces Fob1 from Ter sites during fork passage. Rrm3 also appears to sweep away other non-histone proteins bound to DNA from in front of the advancing replication forks, and, therefore, deletion of Rrm3 causes fork arrest at multiple sites in the chromosomes (7).
The presence of so many copies of tandem repeating sequences in the rDNA is potentially problematic because of its propensity to cause unscheduled intrachromatid recombination that, if not strictly controlled, would cause instability of the rDNA repeat length. Therefore, the organism has evolved multiple mechanisms to suppress unscheduled intrachromatid recombination (8). It should be noted that interchromatid recombination, which apparently is not suppressed in the rDNA, would result in exchanges between identical sequences of homologous chromatids. Therefore, these events would not be expected to cause any change in the natural nucleotide sequence and thus would remain phenotypically silent.
On the one hand, binding of Fob1 protein to the Ter sites causes fork arrest that provokes recombination (6, 9), but, on the other hand, it also suppresses recombination by recruiting a protein complex called RENT (regulator of nucleolar silencing and telophase exit) to the Ter sites (9–12). RENT includes the nucleolar protein Net1, the NAD-dependent histone deacetylase Sir2, CDC14 phosphatase (that catalyzes escape from telophase), and three other proteins (Tof2, Lrs4, and Csm1) that recruit cohesin to Ter sites (11). The RENT complex is also recruited to the promoter enhancer region of 35 S RNA through a protein-protein interaction involving two subunits of RNA polymerase I (11, 13). Loading of Sir2 (and the RENT complex) causes rDNA silencing that is manifested in the suppression of both intrachromatid recombination and transcription catalyzed by RNA polymerases II, although transcription catalyzed by RNA polymerase I and III remain unaffected (14, 15).
Sir2 suppresses intrachromatid recombination by preventing RNA polymerase II-catalyzed transcription from the bipolar promoter E-pro. This transcriptional event causes cohesin removal from the region about the Ter sites. The cohesin rings apparently hold the homologous chromatid pairs in the register, and the paired chromatids are constrained to undergo only interchromatid but not intrachromatid recombination (15). The Tof2, Lrs4, and Csm1 protein components associated with the RENT complex apparently participate in recruitment of cohesin (13).
We wished to study not only the role of Fob1 in replication termination but also to investigate its other multiple functions such as rDNA silencing and recombination at Ter (6). As a first step toward such an endeavor, we wished to determine whether the Fob1-dependent fork arrest at Ter (see Fig. 1C) and rDNA silencing (see Fig. 1D) were interdependent events or whether the two processes were independent and separable. Previously, attempts were made to understand rDNA silencing by Sir2 under nonphysiological conditions by artificially fusing Sir2 with the DNA-binding domain of Gal4 and forcing the complex to load at ectopically integrated upstream activating sequence of Gal4 in rDNA (16). The manipulations apparently bypassed the requirements of the proteins of the RENT complex that are essential for regulated silencing of rDNA. Maintenance of rDNA silencing by RENT suppresses excessive intrachromatid recombination while permitting limited recombination that permits repeat length expansion and contraction in response to physiological cues (11, 13, 14). It was therefore necessary to dissect the various functions of Fob1 and study these under natural conditions (see Fig. 1D), which preserved the association of Fob1 and Sir2 with the RENT complex.
Using three different experimental approaches, we endeavored to separate Fob1-mediated fork arrest at Ter sites from Fob1-promoted loading of the RENT complex at the sites. First, we examined the abilities of two orthologs of S. cerevisiae Fob1 from Saccharomyces bayanus and from Saccharomyces paradoxus to complement a fob1Δ strain of S. cerevisiae and discovered that S. paradoxus Fob1 could fully complement both the fork arresting and silencing activities of S. cerevisiae Fob1. But, in contrast, S. bayanus Fob1 could only complement the former but not the latter activity. Second, we performed random mutagenesis of the open reading frame (ORF) of S. cerevisiae Fob1 with the goal of recovering mutants that would abolish or reduce its silencing activity without impairing its fork-arresting function and were able to identify one such mutant, namely I407T, which clearly separated the two functions of Fob1. Finally, we analyzed rDNA silencing in the absence of the intra-S phase checkpoint protein complex of Tof1 and Csm3 and observed that although fork arrest was abolished in their absence, rDNA silencing was unaffected. The latter strategy was used because none of the Fob1 mutants that are unable to arrest forks but are able to retain Ter binding have been identified to date despite extensive mutagenesis of the FOB1 ORF. All three sets of observations were consistent with each other, and taken together, supported the conclusion that although Fob1 binding to Ter sites in rDNA is needed to promote polar fork arrest and rDNA silencing, the two processes occurred independently of each other.
EXPERIMENTAL PROCEDURES
Strains
The following yeast strains were used in the study: (i) S. cerevisiae YSB348 (MAT his3200 leu21 ura3-167 RDN1(50L)::mURA3-HIS3), (ii) S. cerevisiae NTS1::mURA3 (Matα his3Δ200 leu2Δ1 ura3-167 RDN1-NTS1::Ty1-mURA3), and (iii) S. cerevisiae PJ69-4A (MATa trp1-901 leu2-3,112 ura3-52 his3-200 gal4(deleted) gal80(deleted) LYS2::GAL1-HIS3 GAL2-ADE2 met2::GAL7-lacZ) (17), which were gifts from Drs. J. Smith (University of Virginia), D. Moazed (Harvard University), and P. James (University of Wisconsin), respectively. Gene deletions were carried out using the one-step gene disruption method (18–20). Single deletions of FOB1 and TOF1 were constructed by using a G418 cassette, and CSM3 was deleted in the fob1Δ (G418) strain using a phleomycin cassette.
Plasmids
S. cerevisiae Fob1 was cloned in pGAD424 and pGBT9 as a BamHI-SalI fragment (4). Random mutagenesis of the FOB1 gene and cloning of mutants in pGAD424 have been described previously (4). FOB1 point mutants, including I407T, were obtained by this method. S. bayanus Fob1 was PCR amplified from genomic DNA prepared from S. bayanus and cloned as a BamHI-SalI fragment in pGAD424. S. paradoxus Fob1 was PCR amplified from DNA prepared from S. paradoxus and cloned as an EcoRI-BamHI fragment in pGAD424. S. cerevisiae Net1 was cloned in pGAD424 and pGBT9 as a SmaI-Pst1 fragment, whereas the S. cerevisiae SIR2 gene was cloned in pGAD424 and pGBT9 as an EcoRI-SalI fragment. The pRS315 vector was obtained from P. Hieter (21).
Silencing Assay
Two yeast strains, namely YSB348 (22) and NTS1::mURA3 (11), were used to study silencing of the mURA3 reporter gene. In the strain YSB348, the mURA3 cassette has been cloned 50 bp downstream of the end of rDNA array (see Fig. 2B). A single Ter2 sequence consisting of inverted repeats and inverted repeat-associated sequence (4) is present upstream of the mURA3 cassette in this strain. Fob1 and TOF1 were deleted from this strain by the G418 cassette, whereas CSM3 was deleted in the fob1Δ derivative by a phleomycin cassette (18–20). In the strain IGS1::mURA3 the mURA3 reporter has been cloned at the Ter sites present in the middle of the rDNA array (see Fig. 6A). Overnight cultures grown in yeast extract, peptone, dextrose or synthetic complete medium were washed and suspended in water. Absorbance (A600) was adjusted to 2.4 in all cultures. Cultures were then serially diluted 10-fold with water, and 2.5 μl of each dilution was spotted on synthetic complete and SD/Ura− plates. To study silencing by Fob1, its mutant forms, or orthologs, the plasmid vector or vectors containing these different ORFs were transformed into the fob1Δ and fob1Δcsm3Δ derivatives of YSB348 and selected on SD/Leu− plates. Overnight liquid cultures in SD/Leu− medium were washed with water, adjusted to an A600 of 2.4 in water, and 10-fold serial dilutions of different cultures were spotted on SD/Leu− and SD/Leu−Ura− plates. All plates were incubated at 30 °C before scanning and recording of the data.
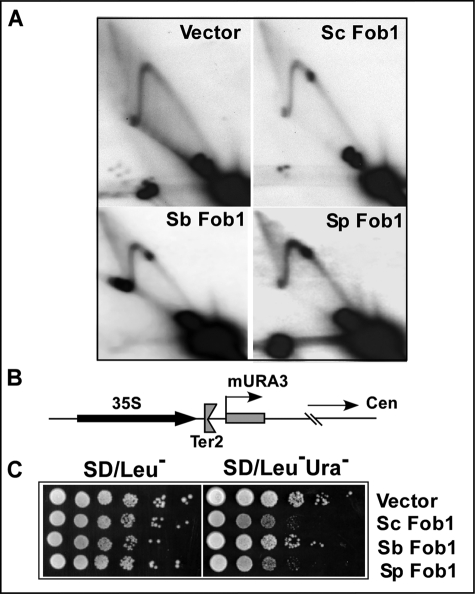
FIGURE 2.
Separation of replication fork arrest and silencing functions of Fob1 in S. cerevisiae orthologs. A, two-dimensional agarose gel analysis of replication intermediates from a fob1Δ derivative of S. cerevisiae (YSB348) strain containing vector (pGAD424) alone, S. cerevisiae Fob1 (Sc Fob1), S. bayanus Fob1 (Sb Fob1), and S. paradoxus Fob1 (Sp Fob1). B, schematic diagram showing the silencing cassette (mURA3) located 50-bp downstream of the single Ter2 site present at the end of rDNA array in chromosome XII. C, silencing assay in fob1ΔYSB348 containing Fob1 orthologs. The data show that S. cerevisiae Fob1 and S. paradoxus Fob1 are proficient in silencing, but S. bayanus Fob1 is defective in silencing of the expression of the mURA3 cassette.
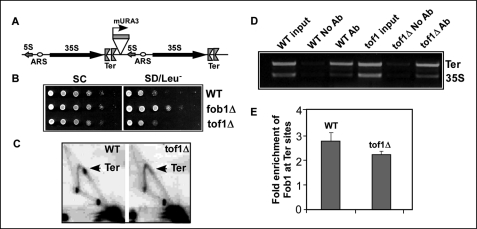
FIGURE 6.
Fob1-dependent silencing at the Ter sites in the middle of the rDNA array does not require replication fork protection proteins. A, a schematic view of the mURA3 silencing cassette cloned downstream of Ter sites in the middle of rDNA array. B, silencing of the mURA3 cassette occurs in both the WT and the tof1Δ strains. C, two-dimensional agarose gel analysis of replication intermediates showing abolition of fork arrest in the tof1Δ strain. D and E, ChiP assay showing binding of Fob1 to Ter sites in a tof1Δ strain. Ab, antibody; ARS, origin of replication.
Yeast Two-hybrid Assay
Two-hybrid assays were carried out using the yeast strain PJ69-4A as described before (4, 17). S. cerevisiae Sir2, S. cerevisiae Net1, S. cerevisiae Fob1, its deletions and mutants, and Fob1 orthologs from S. bayanus and S. paradoxus were cloned in appropriate two-hybrid vectors. The plasmids were transformed in pairs into PJ69-4A, and colonies containing the plasmid pairs were patched on SD/Leu−Trp− and SD/Leu−Trp−Ade− plates. The β-galactosidase assay was performed by inoculating cells from SD/Leu−Trp− plates in SD/Leu−Trp− liquid medium and conducting the assay as described in the Clontech manual.
Purification of Fob1 Protein and Anti-Fob1 Antibody
Fob1 ORF was cloned as a BamHI fragment in the vector pBJ842 (23) (obtained from Dr. Satya Prakash, University of Texas, Galveston, TX). Fob1 was expressed in S. cerevisiae as a GST fusion protein in this vector and purified on a glutathione-agarose column as described below. The plasmid pBJ842-FOB1 was transformed into the yeast strain BJ5464, and cells were grown in SD/Leu− plates as described for the pBJ842-derived clones (23). Colonies from SD/Leu− plates were inoculated in SD/Leu− medium containing 2% glucose, 2% glycerol, and 1.8% lactate. Overnight cultures were washed and then inoculated into fresh SD/Leu− medium containing 2% glycerol and 1.8% lactate with a 1:30 dilution. Six liters of the culture were grown for 16 h, and then galactose was added to it to a final concentration of 2%. The culture was induced for 6 h. At this time, the culture was harvested in a Sorvall RC5C centrifuge, and the cell pellet was frozen in liquid nitrogen and stored at −70 °C. The cell pellet was suspended in lysis buffer (50 mm Tris-HCl, pH 7.5, 10% sucrose, 500 mm NaCl, 1 mm EDTA, 0.5 mm benzamidine, and EDTA-free protease inhibitors mixture (Roche Applied Science). The cell suspension was frozen in liquid nitrogen and lysed by a bead beater. The lysed powder was thawed at 4 °C, and then the lysate was centrifuged at 40,000 rpm for 30 min at 4 °C in a Beckman Ti70 rotor. The supernatant was mixed with glutathione-agarose beads, which was previously equilibrated with lysis buffer, and incubated for 1 h at 4 °C. The beads were washed three times with the wash buffer (50 mm Tris-HCl, pH 7.5, 10% glycerol, 150 mm NaCl, 1 mm EDTA, 0.5 mm benzamidine, and EDTA-free protease inhibitors mixture). The GST-Fob1 protein bound to the beads was treated with precision enzyme (GE Healthcare) at 4 °C for 10 h (1 international unit of enzyme with ∼100 μg of GST-Fob1). The eluted protein was tested for its site-specific binding to 32P-labeled Ter fragments by gel shift assay. Antibody against purified Fob1 protein was raised by Antagene Inc., Mountain View, California.
Chromatin Immunoprecipitation (ChiP) and Polymerase Chain Reaction
ChiP assays were carried out as described previously (5) with minor modifications. Anti-Fob1 antibody was added to the cleared lysate at a 1:200 dilution for precipitation of the protein-DNA complexes. Polymerase chain reaction to amplify the DNA samples was carried out with Vent DNA polymerase (New England Biolabs). 1/200th of input DNA and 1/50th of immunoprecipitated samples were used in a 100-μl reaction buffer for PCR reactions. The primers used were: RFBNK, 5′-GCAAAGATGGGTTGAAAGAGAAAG-3′; P4EXP2NK, 5′-CACCCTCGTTTAGTTGCTTCTTAT-3′; CHIPC5NK, 5′-TTCACCTACGGAAACCTTGTTACG-3′; and CHIPC3NK, 5′-TGGCCGAGAGGTCTTGGTAATCTT-3′.
Relative enrichment of Fob1 protein at Ter sites over the control 35 S region was calculated as in Ref. 5. The intensity of both Ter and 35 S bands of no antibody control was subtracted from the respective bands of input DNA and anti-Fob1-precipitated DNA. The relative enrichment of Fob1 at the Ter site over the 35 S region was calculated as: Ab(Ter/35 S) × input(35 S/Ter).
Two-dimensional Agarose Gel Electrophoresis
Neutral-neutral two-dimensional agarose gel electrophoretic analysis for fork arrest at rDNA twin Ter sites was carried out as described previously (4–6, 24). The IGS1::mURA3 strain and its derivatives and YSB348 and its derivatives were grown in YPD when the strains did not contain plasmids. The pGAD424-based plasmids containing FOB1, its derivatives, or orthologs were transformed into the fob1Δ derivative of YSB348 and plated on SD/Leu− plates. Overnight cultures were inoculated in fresh SD/Leu− liquid medium, and cultures were processed for two-dimensional gel analysis. DNA samples were digested either with BglII or BglII/EcoRV enzymes for two-dimensional analysis, and blots were probed with a 1.5-kb rDNA fragment that spans the Ter region.
RESULTS
Biochemical Activities of S. cerevisiae Fob1 Orthologs
The two functions of Fob1, namely polar fork arrest at Ter and rDNA silencing, are schematically shown in Fig. 1, C and D, respectively. Comparative biochemical analysis of orthologs of a gene are known to be an effective tool for the determination of structure-function relationships by enabling assignments of functions to different domains of a multidomain, multifunctional protein (25). The orthologs can be regarded as fully folded, biologically active, naturally existing mutant forms of a multifunctional protein. A comparison of amino acid sequences of S. cerevisiae Fob1 with S. bayanus Fob1 and S. paradoxus Fob1 (sequences deposited in the S. cerevisiae database from the University of Washington and the Massachusetts Institute of Technology) shows 83 and 91% homology and 88 and 94% similarity, respectively. To gain insight into the similarities and differences among the three Fob1 proteins, we cloned the corresponding ORFs as in-frame fusions with the Gal4 activation domain in the pGAD424 plasmid so that the fusion proteins were expressed under the transcriptional control of the same ADH1 promoter. We introduced the plasmids, one at a time, into the fob1Δ S. cerevisiae strain YSB348 and made comparative analyses of replication termination, gene silencing, and protein-protein interactions with S. cerevisiae Net1 and S. cerevisiae Sir2.
We transformed the plasmid pGAD424 or the recombinant plasmids carrying S. cerevisiae Fob1, S. bayanus Fob1, or S. paradoxus Fob1 into the fob1Δ-silencing strain YSB348 and conducted two-dimensional agarose gel electrophoresis of the rDNA replication intermediates as described in the “Experimental Procedures.” Analyses of fork arrest in the replication intermediates showed that both S. paradoxus Fob1 and S. bayanus Fob1 complemented the S. cerevisiae fob1Δ cells to a level indistinguishable from that of S. cerevisiae Fob1 (Fig. 2A) as measured by the average intensity of the termination spot divided by the integrated intensities of the rest of the Y arcs.
We then performed rDNA-silencing assays using the integrated mURA3 reporter that was located at the end of rDNA array as shown in Fig. 2B. The mURA3 cassette was present 50 bp downstream of the Ter2 site of the last rDNA repeating unit in chromosome XII (22). We deleted Fob1 from this reporter strain and observed that silencing was completely abolished (data not shown). We then transformed the blank pGAD424 or the recombinant pGAD424 plasmids carrying S. cerevisiae Fob1, S. bayanus Fob1, or S. paradoxus Fob1 into this strain, repeated the silencing assays, and observed that both S. cerevisiae Fob1 and S. paradoxus Fob1 were able to silence the mURA3 reporter, whereas S. bayanus Fob1 failed to do so, as revealed by the extent of growth of colonies on Ura dropout plates (Fig. 2C).
The experiments described above, although well controlled, were carried out using a fusion protein consisting of an N-terminal pGAD424 sequence driven by the ADH1 promoter. To determine the experimental outcome when S. cerevisiae Fob1, S. bayanus Fob1, etc. were transcribed from the natural S. cerevisiae FOB1 promoter, constructs of S. cerevisiae Fob1 and S. bayanus Fob1 were expressed from the FOB1 promoter in the Cen plasmid pRS315 (21), and the silencing experiments were repeated. The data shown in the supplemental data (supplemental Fig. S1) clearly demonstrate that the proteins expressed from the natural S. cerevisiae FOB1 promoter yielded results identical to those obtained from the pGAD fusion proteins shown in Fig. 2.
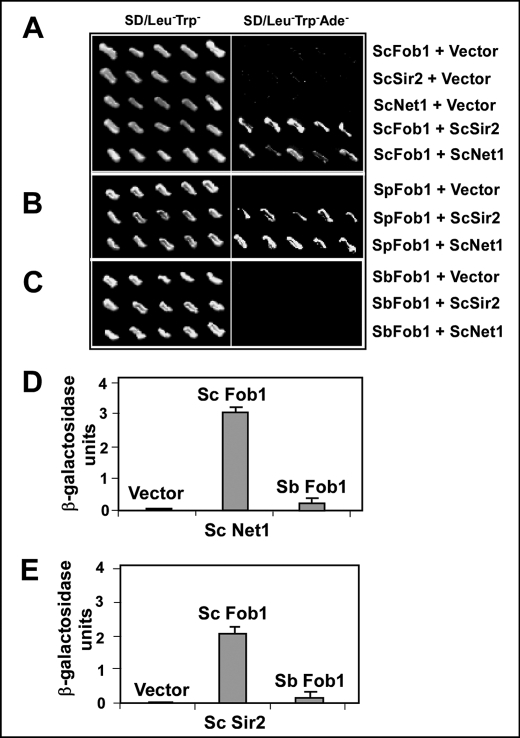
S. cerevisiae Fob1 and S. paradoxus Fob1, but Not S. bayanus Fob1, Interacted with S. cerevisiae Net1 and S. cerevisiae Sir2
The histone deacetylase Sir2 is loaded as a part of the RENT complex at Ter sites of the rDNA through interaction with the Ter-bound Fob1 protein (10, 11). Pulldown assays had shown that both Net1 and Sir2 of RENT associate with Fob1 (11). We reexamined the issue by performing yeast two-hybrid interaction of both Net1 and Sir2 with Fob1 from all of the three species by transforming the appropriate plasmids in pairs into the two-hybrid indicator strain that contained three reporters, namely HIS3, ADE2, and lacZ of Escherichia coli (17). We replica plated the transformants selected on Leu-Trp dropout plates onto SD/Leu−Trp− and SD/Leu−Trp−Ade− plates. The results showed that S. cerevisiae Fob1, as expected, interacted with both of the full-length clones of S. cerevisiae Net1 and S. cerevisiae Sir2 (Fig. 3A). Similarly, S. paradoxus Fob1 showed interaction with S. cerevisiae Net1 and S. cerevisiae Sir2 (Fig. 3B). However, S. bayanus Fob1 consistently failed to interact with S. cerevisiae Net1 and S. cerevisiae Sir2 (Fig. 3C). We also conducted β-galactosidase assays to quantitatively determine these interactions. As shown in Fig. 3, D and E, S. cerevisiae Fob1 showed relatively strong interaction with both S. cerevisiae Net1 and S. cerevisiae Sir2, whereas S. bayanus Fob1 did not show any detectable interactions with either S. cerevisiae Net1 or S. cerevisiae Sir2.
FIGURE 3.
Two-hybrid interactions of Fob1 orthologs with S. cerevisiae Net1 and S. cerevisiae Sir2 showing defect in the protein-protein interaction of S. bayanus Fob1. A, interaction of pGAD424 S. cerevisiae Fob1 (ScFob1) with pGBT9 S. cerevisiae Net1 (ScNet1) and pGBT9 S. cerevisiae Sir2 (ScSir2). B, interaction of pGAD424 S. paradoxus Fob1 (SpFob1) with pGBT9 S. cerevisiae Net1 (ScNet1) and pGBT9 S. cerevisiae Sir2. C, interaction of pGAD424 S. bayanus Fob1 (SbFob1) with pGBT9 S. cerevisiae Net1 and pGBT9 S. cerevisiae Sir2. D and E, β-galactosidase assay of yeast two-hybrid interactions of S. cerevisiae Fob1 and S. bayanus Fob1 with S. cerevisiae Net1 and S. cerevisiae Sir2, respectively.
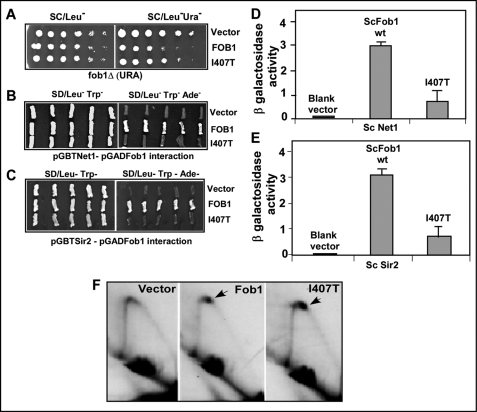
A S. cerevisiae Fob1 Mutant with Reduced Silencing Activity Was Proficient in Fork Arrest
To determine whether S. cerevisiae Fob1 has separate domains for fork arrest and rDNA silencing, we analyzed several mutants of Fob1 that were isolated in a previous study (4). We introduced either a pGAD424 plasmid containing in-frame fusions with the WT Fob1 or the I407T mutant form (and other mutant forms) and monitored silencing activity by plating on both SD/Leu− and SD/Leu−Ura− plates. 10-fold serial dilutions of an overnight culture were spotted on the plates, and the extent of growth on each of the plates was scored. The data showed that the blank vector, as expected, failed to silence the mURA3 reporter, allowing growth on SD/Leu-Ura− plates. The mutant form I407T was partially defective in silencing, in comparison with the WT Fob1 that was able to silence the reporter (Fig. 4A).
FIGURE 4.
Separation of fork arresting and silencing activities in the S. cerevisiae Fob1 I407T mutant. A, silencing of mURA3 in the fob1Δ strain containing vector (pGAD424), S. cerevisiae Fob1 (ScFob1), and its I407T derivative. B and C, two-hybrid interactions of S. cerevisiae Fob1 or its I407T derivative with S. cerevisiae Net1 and S. cerevisiae Sir2, respectively. D and E, β-galactosidase assay of yeast two-hybrid interactions of S. cerevisiae Fob1 and S. cerevisiae Fob1 mutant I407T with S. cerevisiae Net1 and S. cerevisiae Sir2, respectively. F, two-dimensional agarose gel analysis of replication intermediates from fob1Δ of YSB348 containing vector (pGAD424), pGAD424 S. cerevisiae FOB1, or pGAD424-FOB1I407T.
Why is the I407T mutant form defective in silencing? To address this question, we performed yeast two-hybrid interactions analyses of S. cerevisiae Fob1 or I407T mutant with S. cerevisiae Net1. The data showed that the blank pGAD424 vector, when co-transformed with pGBT9-NET1, elicited no growth on SD/Leu−Trp−Ade− plates. The pGAD424-FOB1 showed robust interaction with pGBT9-NET1, whereas pGAD424-FOB1 I407T showed severely reduced interaction with pGBT9-NET1 (Fig. 4B). We performed a similar analysis between Fob1 and Sir2 and found that I407T also showed severely reduced interaction with pGBT9-SIR2 (Fig. 4C). We have analyzed other mutants of S. cerevisiae Fob1, such as L417E, that showed partial reduction in silencing and was also partially defective in the protein-protein interaction with S. cerevisiae Net1 and S. cerevisiae Sir2 (data not shown). A third mutant Q448H was found to be normal in silencing, and its interactions with S. cerevisiae Net1 and S. cerevisiae Sir2 were indistinguishable from that of wild type Fob1 (data not shown). Finally, we obtained several mutants that showed pleiotropic effects (loss of multiple functions of Fob1) and were suspected to be globally misfolded, thus these were not analyzed further. We also performed liquid β-galactosidase assays of the two-hybrid clones to confirm protein-protein interaction results. As shown in Fig. 4, D and E, S. cerevisiae Fob1 showed significant β-galactosidase activity with both S. cerevisiae Net1 and S. cerevisiae Sir2, whereas there was reduced β-galactosidase activity observable in the cells that contained the I407T mutant form of S. cerevisiae Fob1 along with S. cerevisiae Net1 or S. cerevisiae Sir2.
We then examined the ability of the mutant form I407T to promote fork arrest in vivo at Ter1 and Ter2 sites by performing two-dimensional agarose gel electrophoresis of replication intermediates in the fob1Δ background. Introduction of the blank pGAD424 plasmid into the fob1Δ cells failed to arrest forks at Ter, whereas a pGAD424-FOB1 plasmid and one containing the I407T mutant form caused fork arrest, as indicated by the generation of the characteristic termination spots (Fig. 4F, arrows). On the basis of the data shown in Fig. 4, we concluded that the mutation I407T in Fob1 caused partial reduction in the silencing activity without detectably reducing its replication termination function.
Checkpoint Mutants also Show That Silencing Is Independent of Fork Arrest by Fob1
Extensive mutagenesis of Fob1 over the last seven years has yielded mutants at most of the amino acid residues of the protein, and several of the mutations abolish fork arrest. However, all such mutations also abolish Fob1 binding to Ter sites (3, 4).5 Therefore, a direct mutagenesis of Fob1 to separate fork arrest from rDNA silencing could not be done because both processes require Fob1 binding to Ter. We therefore used the following alternative strategy to address the same problem.
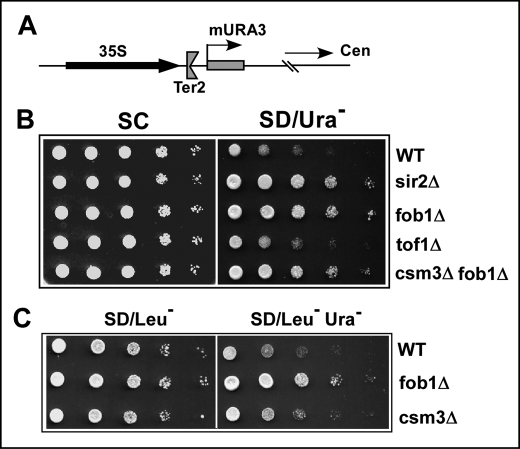
Although silencing required Fob1 binding at Ter sites, it was not known whether it also required the fork-arresting activity of the protein. We have previously reported that fork arrest at Ter sites of S. cerevisiae not only requires Fob1 binding to Ter but also the activities of two members of the intra-S phase checkpoint proteins Tof1 and Csm3 (5, 28–30). We made use of this observation to test whether silencing would still occur at Ter sites in the absence of Tof1 and Csm3. We separately deleted the SIR2, FOB1, TOF1, and CSM3 ORFs from the silencing strain YSB348 and conducted the silencing assay by monitoring cell growth on Ura dropout plates. As shown in Fig. 5B, the wild type strain showed silencing of the mURA3 cassette, whereas its sir2Δ or fob1Δ derivatives did not show any silencing activity (Fig. 5B, WT, sir2Δ, and fob1Δ, respectively). In contrast, deletion of Tof1 did not abolish or detectably reduce silencing of the URA3 reporter (Fig. 5B).
FIGURE 5.
Fob1-dependent silencing at the end of rDNA array does not require replication fork protection proteins. A, schematic representation of the end of the rDNA array showing the mURA3 cassette. B, silencing of the mURA3 cassette in wild type, sir2Δ, fob1Δ, tof1Δ, and fob1Δcsm3Δ strains. C, silencing of the mURA3 cassette in wild type, fob1Δ, and csm3Δ strains. The csm3Δ strain was derived by complementing a fob1Δcsm3Δ doubly deleted strain with a CSM3-expressing plasmid.
We also constructed a fob1Δcsm3Δ double deletion of the silencing indicator strain, and as expected, there was no detectable silencing in this strain (Fig. 5B, fob1Δcsm3Δ). We then constructed a csm3Δ by complementation by transforming the plasmid pGAD424-FOB1 into the fob1Δcsm3Δ double deletion strain. Negative control was provided by a blank plasmid vector. The wild type, fob1Δ, and csm3Δ derivatives of the reporter strain were grown in SD/Leu− medium, and 10-fold serial dilutions of these cultures were spotted onto SD/Leu− and SD/Leu−Ura− plates. As shown in Fig. 5C, the wild type strain as well the csm3Δ derivative silenced the mURA3 reporter, whereas the fob1Δ derivative, as expected, did not show any silencing. To ascertain that fork arrest did not occur in the tof1Δ strain, we carried out two-dimensional gel analysis of the replication intermediates prepared from the strain YSB348 and all of its derivatives used in Fig. 5. As expected, the wild type strain and its sir2Δ derivative showed fork arrest activity but not the fob1Δ or the tof1Δ derivatives (data not shown).
We wished to determine whether Fob1-dependent silencing occurred independently of fork arrest, not only at Ter sites at the end of rDNA array but also at the Ter sites located within the array. These experiments were done because the last repeating unit at the right end of the rDNA array contains only the weaker Ter2 site but not the stronger Ter1.We addressed the question posed above by using the strain IGS1::mURA3, in which the mURA3 cassette was integrated downstream of the twin Ter1 and Ter2 sites located in a repeating unit in the middle of the rDNA array (Fig. 6A) (11, 13). We constructed fob1Δ and tof1Δ derivatives of this strain by one-step gene disruption and conducted silencing assays. As shown in Fig. 6B, silencing of the mURA3 reporter occurred equally well in both the WT and the tof1Δ strains (Fig. 6B). As expected, there was no silencing in the fob1Δ strain. We wanted to make sure that fork arrest did not occur in the tof1Δ strain in the given genetic background by performing two-dimensional agarose gel electrophoresis of replication intermediates from the strain IGS1::mURA3 and its tof1Δ derivative. As shown in Fig. 6C, fork arrest occurred at the Ter sites in the wild type strain, but not in the tof1Δ derivative. The fob1Δ derivative that was used as a negative control, as expected, did not show any fork arrest (data not shown). The data supported the conclusion that silencing at Ter sites, both inside the rDNA array and at the end of the array, required Fob1 binding to Ter but not its fork-arresting activity, which was abolished by the deletion of Tof1.
Because silencing at Ter sites requires Fob1 but not Tof1 or Csm3 (as shown in Fig. 5 and Fig. 6), we hypothesized that Fob1 should be physically present at Ter sites in the absence of Tof1 and Csm3, even though fork arrest did not occur in the absence of these proteins because of displacement of Fob1 from Ter by the Rrm3 sweepase (5). To determine whether Fob1 was still present at the Ter sites in the absence of the protecting activity of Tof1 and Csm3 in the cell milieu that contained Rrm3, we carried out ChiP analysis using polyclonal anti-Fob1 antibodies. Control experiments omitted the antibodies. As shown in Fig. 6D, Fob1 was enriched at Ter sites in both the wild type and tof1Δ derivative in comparison with the 35 S rDNA control (Fig. 6, D and E). Therefore, the protein sweeping action of Rrm3 must be transient and limited to the instance of fork passage through Ter; the displaced Fob1 probably rebound to the Ter sites after the fork passed through this region.
The fact that a double deletion of the sweepase Rrm3 and Tof1 restores fork arrest at Ter, but the arrest is abolished in a tof1Δ strain has been described before in at least two different strains (5, 6). However, we wished to make sure that this observation was also valid in the silencing strain used in this work. We constructed tof1Δ and tof1Δrrm3Δ derivatives of the silencing strain and performed two-dimensional gel analyses of replication fork arrest in the WT, tof1Δ, and rrm3Δ tof1Δ derivatives of the strain and observed that, as expected, the WT cells showed the termination spot that was greatly reduced in the tof1Δ derivative and partially restored in the tof1Δrrm3Δ strain (supplemental Fig. S2). Although at the present time, despite extensive mutagenesis, no confirmed mutants of FOB1 exist that separate fork arrest from Fob1 binding to Ter, the three lines of evidence presented in this work collectively and unequivocally supported the conclusion that replication termination and rDNA silencing are two independent and separable activities of Fob1.
DISCUSSION
The data presented in this work support the conclusion that the replication termination function of Fob1 is independent and separable from its action as a loader of the rDNA silencing complex at or near the Ter sites, although both are dependent on the binding of Fob1 to the Ter sequences. The latter conclusion is derived from our previous observations that the L104S mutant form of Fob1, that fails to bind to Ter DNA, also fails to arrest forks and is incapable of promoting rDNA silencing (4). This mutant form is not globally misfolded on the basis of the following criteria: the mutant form is still transported to the nucleolus, (ii) retains its ability to interact with itself, and (iii) interacts with a myeleoblastosis-like putative transcription factor encoded in the YDR026C ORF of budding yeast (4).
Several other functions have been attributed to Fob1 such as promotion of recombination at Ter sites (6), control of the release of CDC14 phosphatase from the RENT complex, which triggers escape from mitosis (32), promotion of rDNA circle formation and rDNA array disassembly in senescent cells (33–35), prevention of collision of replication from the vigorously transcribed 35 S RNA (36, 37), and induction of HOT1 recombination (38). Of these various functions, promotion of recombination at Ter sites in rDNA array, prevention of collision between replication forks and RNA polymerase I-catalyzed transcription and promotion of disassembly of rDNA into circular DNA in senescent cells are functions of Fob1 that appear to require fork arrest (30–34). On the other hand, HOT1 recombination, although Fob1-dependent, requires only Fob1 binding to Ter but not its fork-arresting activity (31) and is therefore similar in this regard to the rDNA silencing activity of the protein.
Stable replication termination by Fob1 requires the products of Tof1 and Csm3 that are orthologs of the “Timeless” (Tim) and “Timeless-interacting protein” (TIPIN) of mammalian cells that also modulate the Circadian cycle (5, 28–30). We have previously reported that Tof1 and Csm3 promote fork arrest by preventing the Rrm3 helicase from displacing Fob1 from Ter sites (5, 6). The observation reported in this paper that rDNA silencing was unaffected in tof1Δ and csm3Δ cells would require that Fob1 should remain bound to the Ter sites even in the absence of Tof1 and Csm3. The chromatin immunoprecipitation data confirmed that Fob1 remains bound to Ter even in tof1Δ cells. The observation that Tof1 and Csm3 are required to promote stable replication termination but not necessarily rDNA silencing is reconciled by invoking a mechanism that proposes that the displacement of Fob1 from Ter by the Rrm3 sweepase is transitory and limited to the instant of fork passage through the Ter sites in tof1Δ or csm3Δ cells. Consistent with this model, it has been reported that Rrm3 travels with the replication fork as a passenger (7).
Further understanding of the role of Fob1 in rDNA silencing would require answers to the following questions. Does Fob1 interact with Sir2 only indirectly, by physically interacting with Net1, which physically interacts with Sir2 (11, 26)? Alternatively, does Fob1 also interact directly with Sir2? Are there alternative pathways to Fob1-mediated Sir2 loading that come into play under different physiological conditions?
It is known that physiological cues appear to trigger rDNA repeat expansion and contraction (14, 27), and there is a commensurate need to expand rDNA repeat array in response to rapid cell growth and enhanced protein synthesis and contract it in quiescent cells. Therefore, it is not unreasonable to postulate a mechanism that would regulate the magnitude of rDNA silencing commensurate with rDNA repeat expansion and contraction. Experiments are in progress in our laboratory to address some of the questions mentioned above.
Supplementary Material
Acknowledgments
We thank Drs. Danesh Moazed, Jeffrey Smith, and Jure Piškur for yeast strains and Dr. Satya Prakash for the plasmid pBJ842.
This work was supported by Grant GM049264 from the NIGMS, National Institutes of Health (to D. B.).

The on-line version of this article (available at http://www.jbc.org) contains supplemental Figs. S1 and S2.
N. K. Bairwa, S. Zzaman, B. K. Mohanty, and D. Bastia, unpublished data.
- IGS
- intergenic spacer
- ORF
- open reading frame
- GST
- glutathione S-transferase; ChiP; chromatin immunoprecipitation
- WT
- wild type
- SD
- synthetic dropout.
REFERENCES
- 1.Petes T. D. (1979) Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. U.S.A. 76, 410–414 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 2.Kobayashi T., Nomura M., Horiuchi T. (2001) Mol. Cell. Biol. 21, 136–147 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 3.Kobayashi T. (2003) Mol. Cell. Biol. 23, 9178–9188 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 4.Mohanty B. K., Bastia D. (2004) J. Biol. Chem. 279, 1932–1941 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 5.Mohanty B. K., Bairwa N. K., Bastia D. (2006) Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. U.S.A. 103, 897–902 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 6.Mohanty B. K., Bairwa N. K., Bastia D. (2009) Eukaryot. Cell 8, 487–495 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 7.Ivessa A. S., Lenzmeier B. A., Bessler J. B., Goudsouzian L. K., Schnakenberg S. L., Zakian V. A. (2003) Mol. Cell 12, 1525–1536 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 8.Tsang E., Carr A. (2008) DNA Repair 10, 1613–1623 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 9.Shou W., Seol J. H., Shevchenko A., Baskerville C., Moazed D., Chen Z. W., Jang J., Charbonneau H., Deshaies R. J. (1999) Cell 97, 233–244 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 10.Straight A. F., Shou W., Dowd G. J., Turck C. W., Deshaies R. J., Johnson A. D., Moazed D. (1999) Cell 97, 245–256 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 11.Huang J., Moazed D. (2003) Genes Dev. 17, 2162–2176 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 12.Smith J. S., Boeke J. D. (1997) Genes Dev. 11, 241–254 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 13.Huang J., Brito I. L., Villén J., Gygi S. P., Amon A., Moazed D. (2006) Genes Dev. 20, 2887–2901 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 14.Kobayashi T., Horiuchi T., Tongaonkar P., Vu L., Nomura M. (2004) Cell 117, 441–453 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 15.Kobayashi T., Ganley A. R. (2005) Science 309, 1581–1584 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 16.Garcia S. N., Pillus L. (2002) Genetics 162, 721–736 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 17.James P., Halladay J., Craig E. A. (1996) Genetics 144, 1425–1436 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 18.Longtine M. S., McKenzie A., 3rd, Demarini D. J., Shah N. G., Wach A., Brachat A., Philippsen P., Pringle J. R. (1998) Yeast 14, 953–961 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 19.Güldener U., Heck S., Fielder T., Beinhauer J., Hegemann J. H. (1996) Nucleic Acids Res. 24, 2519–2524 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 20.Gueldener U., Heinisch J., Koehler G. J., Voss D., Hegemann J. H. (2002) Nucleic Acids Res. 30, e23. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 21.Sikorski R. S., Hieter P. (1989) Genetics 122, 19–27 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 22.Buck S. W., Sandmeier J. J., Smith J. S. (2002) Cell 111, 1003–1014 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 23.Johnson R. E., Prakash L., Prakash S. (2006) Methods Enzymol. 408, 390–407 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 24.Brewer B. J., Fangman W. L. (1987) Cell 51, 463–471 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 25.Chen X. W., Liu M., Ward R. (2008) PLoS ONE 3, e1562. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 26.Cuperus G., Shafaatian R., Shore D. (2000) EMBO J. 19, 2641–2651 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 27.Kobayashi T., Heck D. J., Nomura M., Horiuchi T. (1998) Genes Dev. 12, 3821–3830 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 28.Szyjka S. J., Viggiani C. J., Aparicio O. M. (2005) Mol. Cell 19, 691–697 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 29.Calzada A., Hodgson B., Kanemaki M., Bueno A., Labib K. (2005) Genes Dev. 19, 1905–1919 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 30.Tourrière H., Versini G., Cordón-Preciado V., Alabert C., Pasero P. (2005) Mol. Cell 19, 699–706 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 31.Ward T. R., Hoang M. L., Prusty R., Lau C. K., Keil R. L., Fangman W. L., Brewer B. J. (2000) Mol. Cell. Biol. 20, 4948–4957 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 32.Stegmeier F., Huang J., Rahal R., Zmolik J., Moazed D., Amon A. (2004) Curr. Biol. 14, 467–480 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 33.Sinclair D. A., Guarente L. (1997) Cell 91, 1033–1042 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 34.Sinclair D. A., Mills K., Guarente L. (1998) Trends Biochem. Sci. 23, 131–134 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 35.Sinclair D., Mills K., Guarente L. (1998) Annu. Rev. Microbiol. 52, 533–560 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 36.Serizawa N., Horiuchi T., Kobayashi T. (2004) Genes Cells 9, 305–315 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 37.Brewer B. J. (1988) Cell 53, 679–686 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 38.Defossez P. A., Prusty R., Kaeberlein M., Lin S. J., Ferrigno P., Silver P. A., Keil R. L., Guarente L. (1999) Mol. Cell 3, 447–455 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
Associated Data
This section collects any data citations, data availability statements, or supplementary materials included in this article.