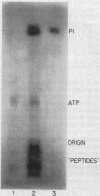
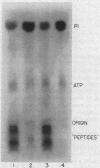
Full text
PDF





Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- ALBERS R. W., FAHN S., KOVAL G. J. THE ROLE OF SODIUM IONS IN THE ACTIVATION OF ELECTROPHORUS ELECTRIC ORGAN ADENOSINE TRIPHOSPHATASE. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1963 Sep;50:474–481. doi: 10.1073/pnas.50.3.474. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- ALDRIDGE W. N. Adenosine triphosphatase in the microsomal fraction from rat brain. Biochem J. 1962 Jun;83:527–533. doi: 10.1042/bj0830527. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- BONTING S. L., CARAVAGGIO L. L. Sodium-potassium-activated adenosine triphosphatase in the squid giant axon. Nature. 1962 Jun 23;194:1180–1181. doi: 10.1038/1941180a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Berenblum I., Chain E. An improved method for the colorimetric determination of phosphate. Biochem J. 1938 Feb;32(2):295–298. doi: 10.1042/bj0320295. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- CHARNOCK J. S., POST R. L. EVIDENCE OF THE MECHANISM OF OUABAIN INHIBITION OF CATIONACTIVATED ADENOSINE TRIPHOSPHATE. Nature. 1963 Aug 31;199:910–911. doi: 10.1038/199910a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- CHARNOCK J. S., ROSENTHAL A. S., POST R. L. STUDIES OF THE MECHANISM OF CATION TRANSPORT. II. A PHOSPHORLATED INTERMEDIATE IN THE CATION STIMULATED ENZYMIC HYDROLYSIS OF ADENOSINE TRIPHOSPHATE. Aust J Exp Biol Med Sci. 1963 Dec;41:675–686. doi: 10.1038/icb.1963.56. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- DEUL D. H., McILWAIN H. Activation and inhibition of adenosine triphosphatases of subcellular particles from the brain. J Neurochem. 1961 Dec;8:246–256. doi: 10.1111/j.1471-4159.1961.tb13550.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- DUNHAM E. T., GLYNN I. M. Adenosinetriphosphatase activity and the active movements of alkali metal ions. J Physiol. 1961 Apr;156:274–293. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1961.sp006675. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- EMMELOT P., BOS C. J. Adenosine triphosphatase in the cell-membrane fraction from rat liver. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1962 Apr 9;58:374–375. doi: 10.1016/0006-3002(62)91031-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- GLYNN I. M., SLAYMAN C. W., EICHBERG J., DAWSON R. M. THE ADENOSINE-TRIPHOSPHATASE SYSTEM RESPONSIBLE FOR CATION TRANSPORT IN ELECTRIC ORGAN: EXCLUSION OF PHOSPHOLIPIDS AS INTERMEDIATES. Biochem J. 1965 Mar;94:692–699. doi: 10.1042/bj0940692. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Glynn I. M., Chappell J. B. A simple method for the preparation of 32-P-labelled adenosine triphosphate of high specific activity. Biochem J. 1964 Jan;90(1):147–149. doi: 10.1042/bj0900147. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- HOKIN L. E., HOKIN M. R. THE INCORPORATION OF 32P FROM TRIPHOSPHATE INTO POLYPHOSPHOINOSITIDES (GAMMA-32P)ADENOSINE AND PHOSPHATIDIC ACID IN ERYTHROCYTE MEMBRANES. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1964 Oct 2;84:563–575. doi: 10.1016/0926-6542(64)90126-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- HOKIN L. E., HOKIN M. R. The incorporation of 32P into the nucleotides of ribonucleic acid in pancreas slices during enzyme synthesis and secretion. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1954 Mar;13(3):401–412. doi: 10.1016/0006-3002(54)90347-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- HOKIN L. E., YODA A. INHIBITION BY DIISOPROPYLFLUOROPHOSPHATE OF A KIDNEY TRANSPORT ADENOSINE TRIPHOSPHATASE BY PHOSPHORYLATION OF A SERINE RESIDUE. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1964 Aug;52:454–461. doi: 10.1073/pnas.52.2.454. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- HOKIN M. R., HOKIN L. E. THE SYNTHESIS OF PHOSPHATIDIC ACID AND PROTEIN-BOUND PHOSPHORYLSERINE IN SALT GLAND HOMOGENATES. J Biol Chem. 1964 Jul;239:2116–2122. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- HOKIN M. R. STUDIES ON A NA+ + K+-DEPENDENT, OUABAIN-SENSITIVE ADENOSINE TRIPHOSPHATASE IN THE AVIAN SALT GLAND. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1963 Sep 3;77:108–120. doi: 10.1016/0006-3002(63)90473-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- JARNEFELT J. Properties and possible mechanism of the Na ion and K ion stimulated microsomal adenosinetriphosphatase. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1962 Jun 4;59:643–654. doi: 10.1016/0006-3002(62)90644-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- POST R. L., MERRITT C. R., KINSOLVING C. R., ALBRIGHT C. D. Membrane adenosine triphosphatase as a participant in the active transport of sodium and potassium in the human erythrocyte. J Biol Chem. 1960 Jun;235:1796–1802. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- POST R. L., SEN A. K., ROSENTHAL A. S. A PHOSPHORYLATED INTERMEDIATE IN ADENOSINE TRIPHOSPHATE-DEPENDENT SODIUM AND POTASSIUM TRANSPORT ACROSS KIDNEY MEMBRANES. J Biol Chem. 1965 Mar;240:1437–1445. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- SKOU J. C. Preparation from mammallian brain and kidney of the enzyme system involved in active transport of Na ions and K ions. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1962 Apr 9;58:314–325. doi: 10.1016/0006-3002(62)91015-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- SKOU J. C. The influence of some cations on an adenosine triphosphatase from peripheral nerves. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1957 Feb;23(2):394–401. doi: 10.1016/0006-3002(57)90343-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- WHITTAM R., WHEELER K. P. The sensitivity of a kidney ATPase to ouabain and to sodium and potassium. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1961 Aug 19;51:622–624. doi: 10.1016/0006-3002(61)90633-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]