Full text
PDF

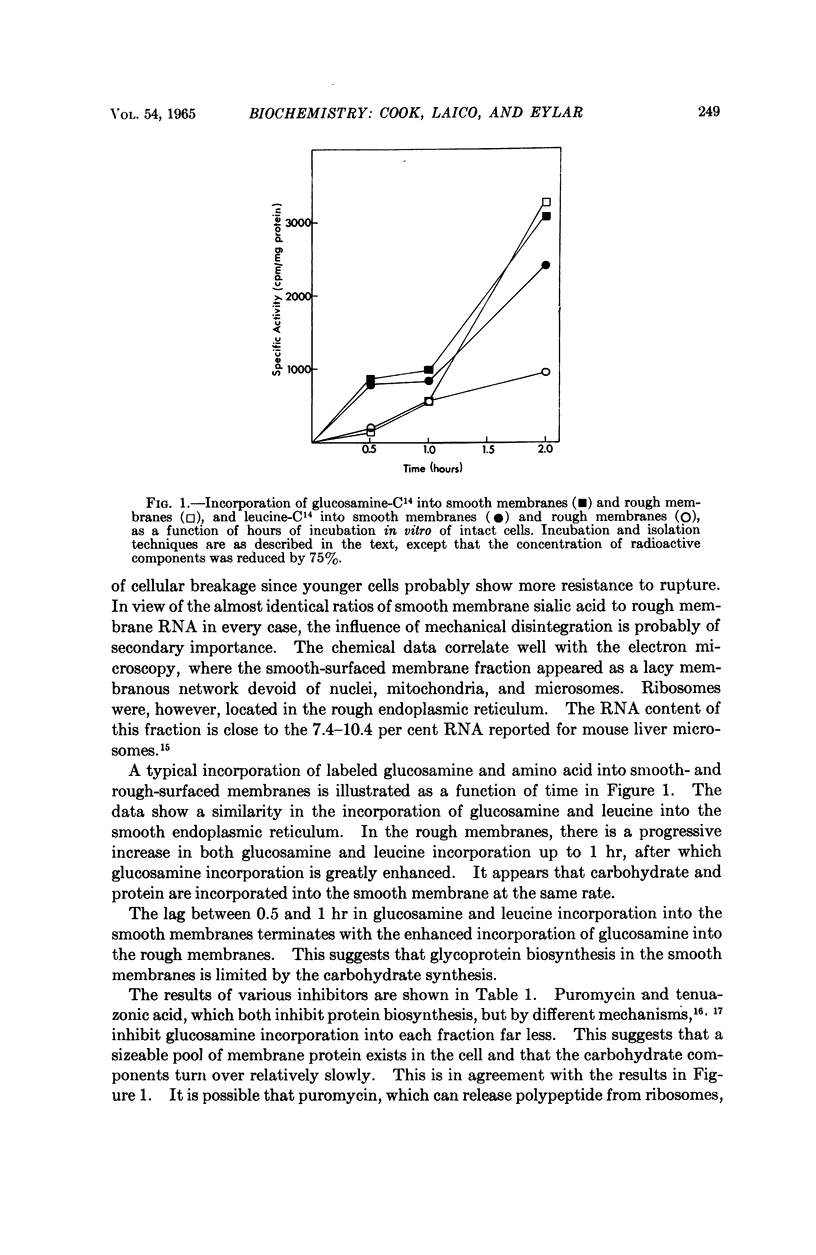

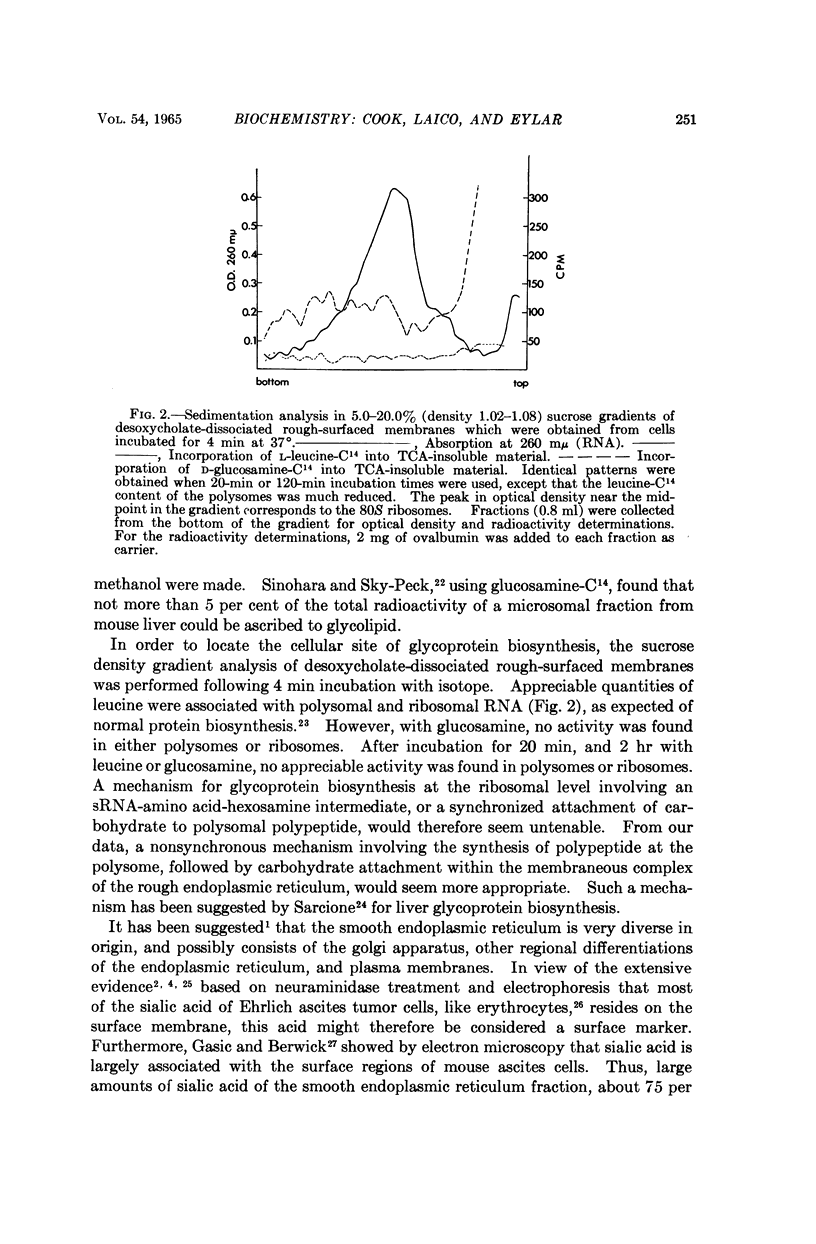

Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- CERIOTTI G. Determination of nucleic acids in animal tissues. J Biol Chem. 1955 May;214(1):59–70. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- COOK G. M., EYLAR E. H. SEPARATION OF THE M AND N BLOOD-GROUP ANTIGENS OF THE HUMAN ERYTHROCYTE. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1965 Mar 1;101:57–66. doi: 10.1016/0926-6534(65)90030-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- COOK G. M., HEARD D. H., SEAMAN G. V. The electrokinetic characterization of the Ehrlich ascites carcinoma cell. Exp Cell Res. 1962 Oct;28:27–39. doi: 10.1016/0014-4827(62)90309-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- EYLAR E. H., MADOFF M. A., BRODY O. V., ONCLEY J. L. The contribution of sialic acid to the surface charge of the erythrocyte. J Biol Chem. 1962 Jun;237:1992–2000. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- GASIC G., BERWICK L. HALE STAIN FOR SIALIC ACID-CONTAINING MUCINS. ADAPTATION TO ELECTRON MICROSCOPY. J Cell Biol. 1963 Oct;19:223–228. doi: 10.1083/jcb.19.1.223. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- GIERER A. Function of aggregated reticulocyte ribosomes in protein synthesis. J Mol Biol. 1963 Feb;6:148–157. doi: 10.1016/s0022-2836(63)80131-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- GOA J. A micro biuret method for protein determination; determination of total protein in cerebrospinal fluid. Scand J Clin Lab Invest. 1953;5(3):218–222. doi: 10.3109/00365515309094189. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- KREBS H. A. Body size and tissue respiration. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1950 Jan;4(1-3):249–269. doi: 10.1016/0006-3002(50)90032-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- LANGLEY O. K., AMBROSE E. J. ISOLATION OF A MUCOPEPTIDE FROM THE SURFACE OF EHRLICH ASCITES TUMOUR CELLS. Nature. 1964 Oct 3;204:53–54. doi: 10.1038/204053a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- MOLNAR J., ROBINSON G. B., WINZLER R. J. THE BIOSYNTHESIS OF GLYCOPROTEINS. 3. GLUCOSAMINE INTERMEDIATES IN PLASMA GLYCOPROTEIN SYNTHESIS IN LIVERS OF PUROMYCIN-TREATED RATS. J Biol Chem. 1964 Oct;239:3157–3162. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- NATHANS D. INHIBITION OF PROTEIN SYNTHESIS BY PUROMYCIN. Fed Proc. 1964 Sep-Oct;23:984–989. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- PASTERNAK C. A., HANDSCHUMACHER R. E. The biochemical activity of 6-azauridine: interference with pyrimidine metabolism in transplantable mouse tumors. J Biol Chem. 1959 Nov;234:2992–2997. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- ROSEMAN S. Metabolism of sialic acids and d-mannosamine. Fed Proc. 1962 Nov-Dec;21:1075–1083. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- SARCIONE E. J. THE INITIAL SUBCELLULAR SITE OF INCORPORATION OF HEXOSES INTO LIVER PROTEIN. J Biol Chem. 1964 Jun;239:1686–1689. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- SHIGEURA H. T., GORDON C. N. THE BIOLOGICAL ACTIVITY OF TENUAZONIC ACID. Biochemistry. 1963 Sep-Oct;2:1132–1137. doi: 10.1021/bi00905a039. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- SINOHARA H., SKY-PECK H. H. SOLUBLE RIBONUCLEIC ACID AND GLYCOPROTEIN BIOSYNTHESIS IN THE MOUSE LIVER. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1965 Mar 1;101:90–96. doi: 10.1016/0926-6534(65)90033-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- WALLACH D. F., EYLAR E. H. Sialic acid in the cellular membranes of Ehrlich ascites-carcinoma cells. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1961 Sep 30;52:594–596. doi: 10.1016/0006-3002(61)90424-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- WARREN L. The thiobarbituric acid assay of sialic acids. J Biol Chem. 1959 Aug;234(8):1971–1975. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]



