Abstract
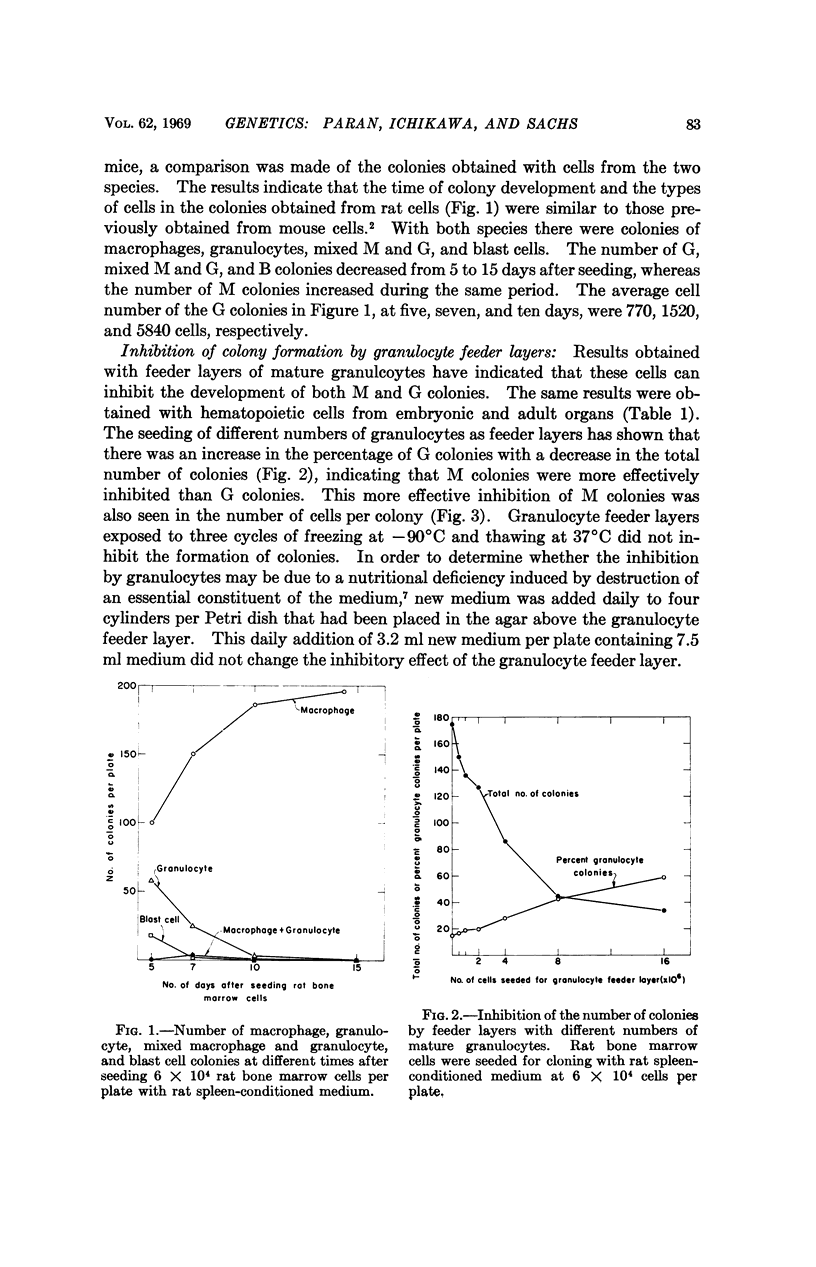
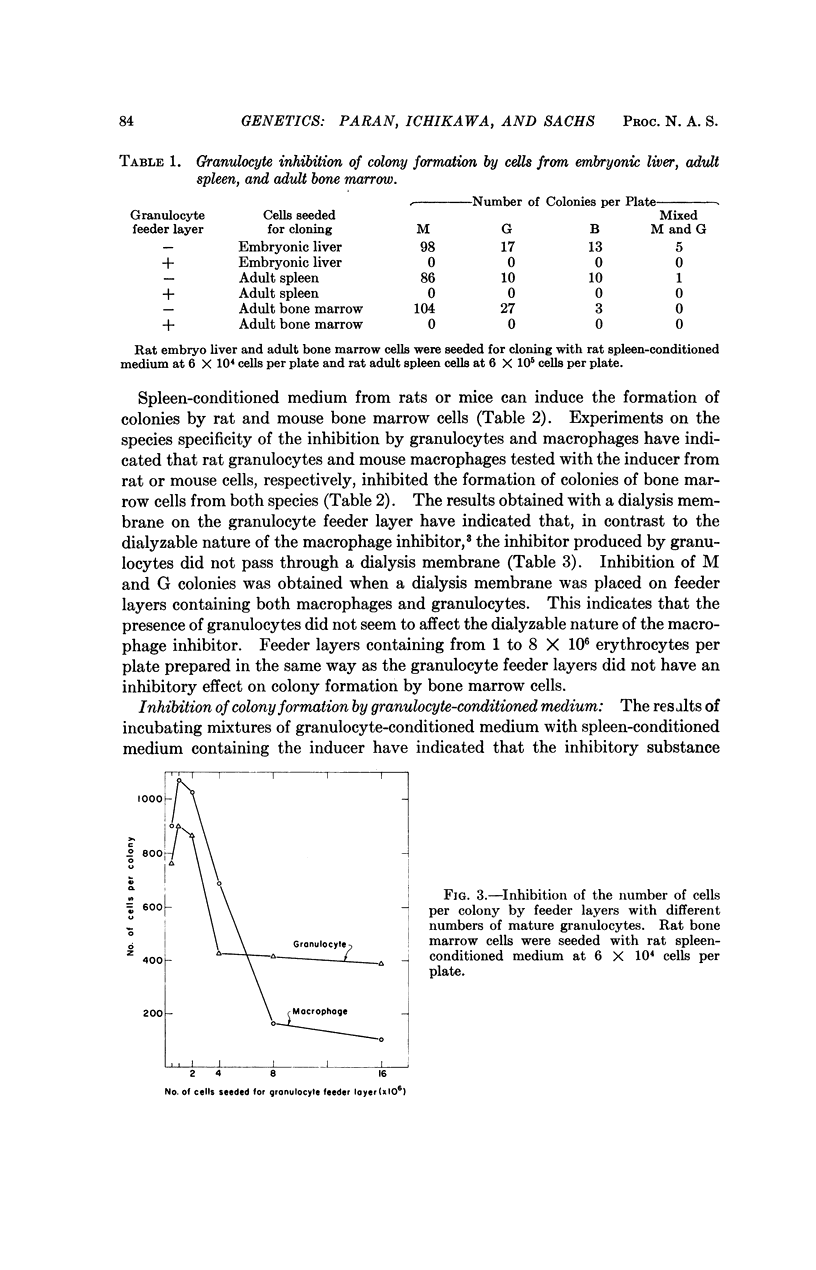
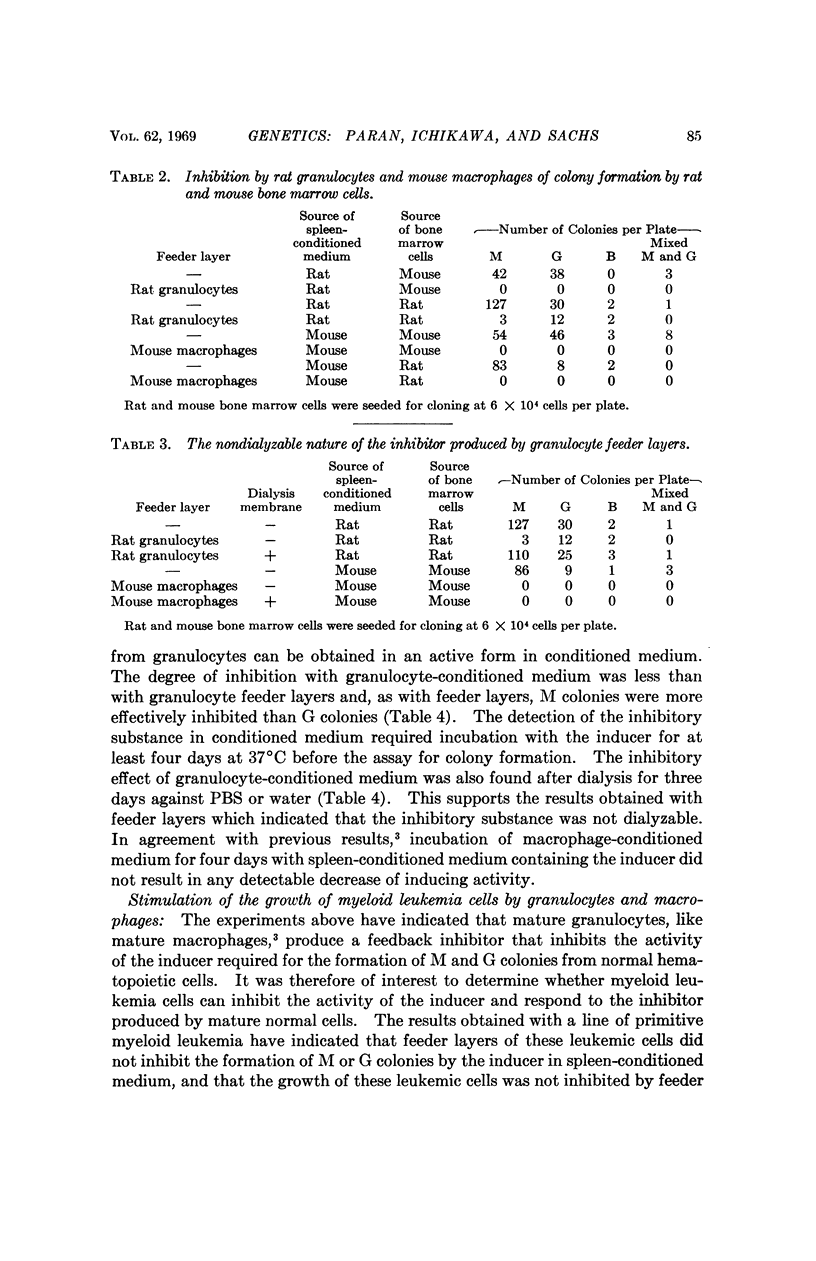
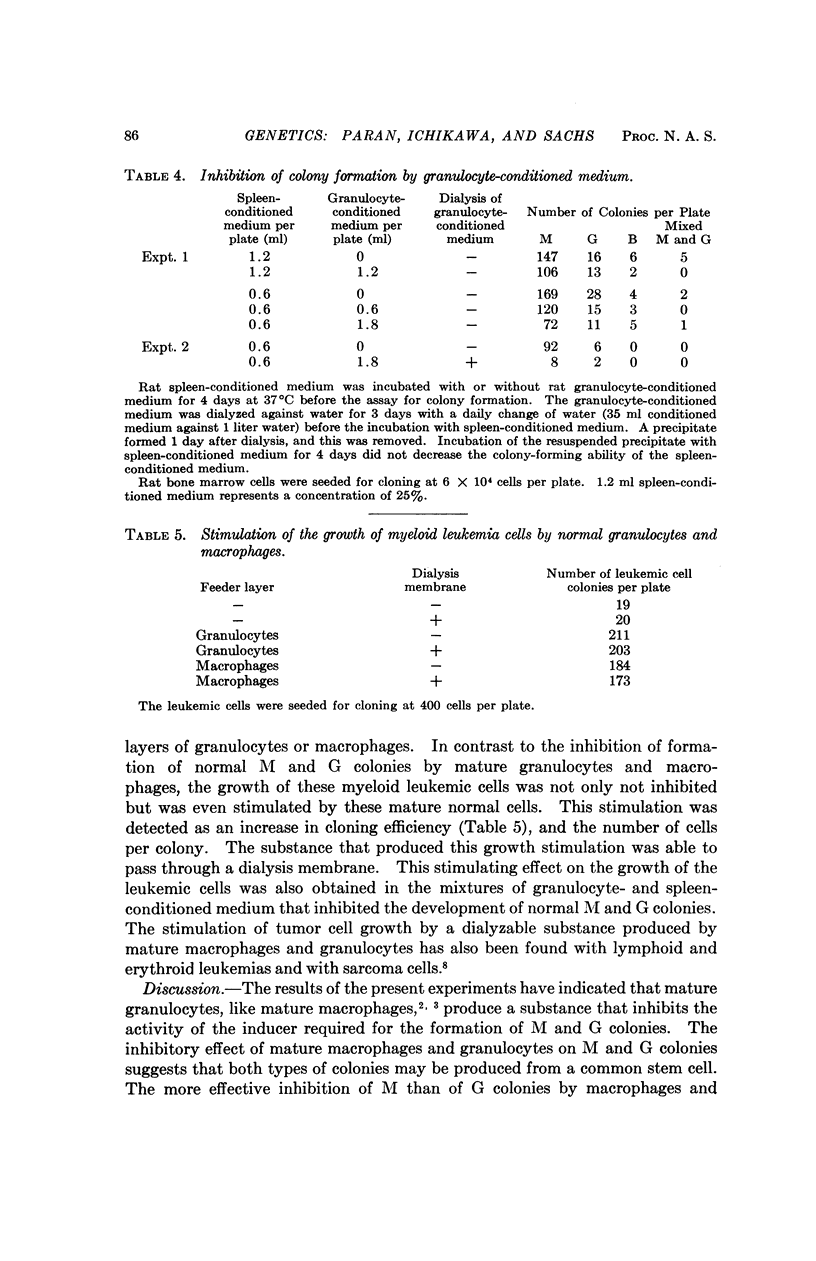
It has been shown that mature normal rat granulocytes produce a substance that inhibits the activity of the inducer required for the development of macrophages (M) and granulocyte (G) colonies from normal hematopoietic cells seeded in soft agar. The granulocyte inhibitor inhibited the activity of the inducer when tested with normal hematopoietic cells from embryonic or adult organs. The inhibitor was not dialyzable, and was obtained in an active form in granulocyte-conditioned medium. The results indicate that the control mechanism that regulates the growth and development of normal macrophages and granulocytes includes a feedback inhibition of the activity of the inducer by inhibitors produced by mature granulocytes and macrophages, presumably at the end of their differentiation process. The inhibition of both M and G colonies by the feedback inhibitors produced by macrophages and granulocytes suggests that both types of colonies may be derived from a common stem cell. A line of primitive myeloid leukemia did not inhibit the activity of the inducer, and the cells of this line were not inhibited by the feedback inhibitors produced by normal granulocytes and macrophages.
Full text
PDF


Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- GALLILY R., WARWICK A., BANG F. B. EFFECT OF CORTISONE OF GENETIC RESISTANCE TO MOUSE HEPATITIS VIRUS IN VIVO AND IN VITRO. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1964 Jun;51:1158–1164. doi: 10.1073/pnas.51.6.1158. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Holley R. W. Evidence that a rat liver "inhibitor" of the synthesis of DNA in cultured mammalian cells is arginase. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1967 Sep 26;145(2):525–527. doi: 10.1016/0005-2787(67)90076-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Howard J. G., Benacerraf B. Properties of macrophage receptors for cytophilic antibodies. Br J Exp Pathol. 1966 Apr;47(2):193–200. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ichikawa Y., Pluznik D. H., Sachs L. In vitro control of the development of macrophage and granulocyte colonies. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1966 Aug;56(2):488–495. doi: 10.1073/pnas.56.2.488. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pluznik D. H., Sachs L. The induction of clones of normal mast cells by a substance from conditioned medium. Exp Cell Res. 1966 Oct;43(3):553–563. doi: 10.1016/0014-4827(66)90026-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


