Abstract
Epigenetics was originally defined as the interaction of genes with their environment that brings the phenotype into being. It now refers to the study of heritable changes in gene expression that occur without a change in DNA sequence. To date, the best understood epigenetic mechanisms are CpG DNA methylation and histone modifications. DNA methylation in particular has been the subject of intense interest because of its recently recognized role in disease, as well as in the development and normal function of organisms. Much of the focus of disease-related research has been on cancer because of the recognition that epigenetic alterations are common in cancer and probably cooperate with genetic alterations to drive cancer formation. Our understanding of epigenetic mechanisms in controlling gene expression has resulted from the study of cell line systems and simple model systems, such as Arabidopsis thaliana. We are now moving into an era of more complex model systems, such as transgenic and knockout mouse models, which will lead to further insight into epigenetics in development and human disease. The current models have revealed complex, tissue-specific effects of epigenetic mechanisms and have further informed our understanding of the role of DNA methylation and histone modifications on disease and development. The current state of these models is the subject of this Commentary.
Many diseases, and cancer in particular, are a consequence of alterations in gene expression patterns leading to deranged biological functions in cells. In cancer, studies over the last four decades have clearly shown that genetic mutations alter the expression and/or function of genes, and that these mutations are a primary molecular mechanism driving the cancer phenotype. More recently, it has become clear that, in addition to DNA sequence mutations, epigenetic alterations can also lead to changes in gene expression in cancers, as well as in other diseases. There is a growing understanding that the epigenome is widely perturbed in most cancers, raising questions about which of the hundreds to thousands of epigenetic alterations are functionally important in cancer. Fundamental questions now being raised are centered on determining how many of the global epigenetic alterations are pathogenic versus how many are simply an indirect consequence of other molecular events in the tumor cells. In order to understand the role of epigenetic regulation and deregulation in disease, mouse models have been developed (or are being developed) to provide systems in which to assess the effect of epigenetic gene regulation on cell behavior and disease states.
Epigenetic information refers to any heritable change in a cell that does not involve a change in the primary DNA sequence. In the context of cancer research, the somatic epigenetic alterations that have been studied most intensely are those that involve the promoter regions of genes and those that affect, or that are predicted to affect, the silencing of gene expression by changes either in the chromatin structure of the gene (e.g. modification of nucleosomes), or to increased site-specific CpG DNA methylation (Fig. 1). In this Commentary, we will focus on DNA methylation, but it should be appreciated that chromatin dynamics and DNA methylation appear to be interdependent in many, if not all, regions of the genome, and moreover, that additional chromatin factors and nucleosome modifications are likely to play a role in the epigenetics of cancer and will ultimately be shown to be as important as DNA methylation in the molecular pathology of cancer (Cedar and Bergman, 2009).
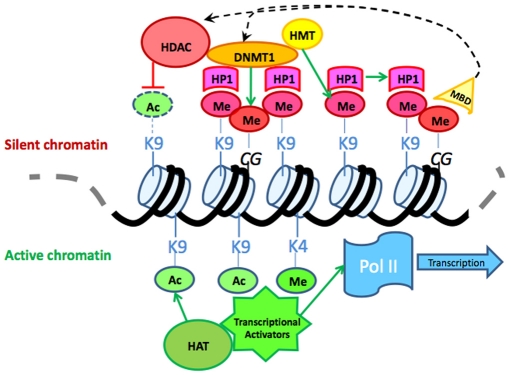
Fig. 1.
Epigenetic regulation. Schematic diagram of DNA and associated epigenetic modifications: extensive crosstalk between DNA methyltransferases, histone modification enzymes and chromatin remodeling proteins has been documented. For example, methyl-binding proteins, such as MBD2, can directly or indirectly recruit both histone deacetylases and histone methyltransferases to nucleosomes in methylated loci. Methylation of histone H3 lysine 9 can be bound by HP1, which in turn can recruit histone and DNA methyltransferases reinforcing chromatin compaction and silencing. HDAC, histone deacetylase; DNMT1, DNA methyltransferase 1; HP1, heterochromatin protein 1; HMT, histone methyltransferase; MBD, methyl binding domain protein; HAT, histone acetyltransferase; Ac, acetyl; Me, methyl; Pol II, RNA polymerase II.
Generally considered to be the most stable epigenetic mark, DNA methylation is the covalent addition of a methyl group to a cytosine base, generally in the context of a CpG dinucleotide. Two main classes of DNA methyltransferase (DNMT) enzymes catalyze this reaction at different times during the cell cycle. In mammals, the first class of enzymes consists of only Dnmt1, which maintains the pattern of DNA methylation after DNA replication. This enzyme requires a hemi-methylated DNA substrate and will faithfully reproduce the pattern of DNA methylation on the newly synthesized strand. The second, larger class of enzymes is considered to be ‘de-novo’ DNA methyltransferases, and includes the enzymes Dnmt3a and Dnmt3b. These methyltransferase enzymes appear to be targeted to sites in both cell-specific and temporal manners; however, some evidence suggests that these enzymes have overlapping roles for specific loci in some cell types (Rhee et al., 2000). In addition, DNA can also be ‘demethylated’ by a process involving the deamination of cytosine bases followed by replacement of the ‘damaged’ cytosine with an unmethylated cytosine by members of the base excision repair (BER) system. However, despite an intense search, no direct DNA demethylases have been discovered to date.
The mammalian genome is predominantly methylated with the exception of CpG-rich regions, which are generally found in gene promoters and are known as CpG islands. Intergenic DNA methylation helps to silence parasitic genetic elements, such as retrotransposons, and contributes to genomic stability. DNA methylation can also impact gene expression, particularly if the methylation is present in CpG islands, which are found in approximately 50% of promoters. DNA methylation alters gene expression levels primarily through regulating methylation state-dependent interactions with transcriptional activators or repressors, and chromatin remodeling enzymes. Several classes of methyl-DNA binding proteins, including factors such as methyl-CpG-binding protein 2 (MeCP2), methyl binding domain protein (MBD) and Kaiso, bind to methylated DNA and repress transcription, either by directly disrupting the formation of the RNA polymerase complex and associated factors at the transcriptional start site, or by recruiting other chromatin modifiers that result in impaired transcription (Tate and Bird, 1993). These additional modifiers may reposition nucleosomes or induce changes in post-translational histone modification states leading to chromatin compaction and the prevention of RNA polymerase complex formation (Nan et al., 1998; Bakker et al., 2002; Lopes et al., 2008). In addition, recent work in Arabidopsis thaliana has demonstrated an interdependent anti-correlation between DNA methylation status and occupancy of the conserved histone variant H2A.Z. In differentiated mammalian cells, H2A.Z is generally found positioned over active transcriptional start sites, raising the possibility that one mechanism for gene repression by DNA methylation is the exclusion of this histone in gene promoters (Zilberman et al., 2008).
DNA methylation – its role in normal cells and disease states
In order to understand the role of aberrant DNA methylation in cancer, it is important to appreciate the state of DNA methylation in normal cells. Normally, DNA methylation has its primary effects on gene regulation during embryonic development, when it can affect organism-wide gene expression, and in differentiation, where its role is restricted to specific tissue types. With regard to the effect of DNA methylation on organism-wide gene expression, this occurs mainly in the context of the germline transmission of heritable epigenetic states. In the germline, a major role of DNA methylation in mammals is to ensure the expression of only one allele for specific genes based on the parent of origin, which is a phenomenon known as imprinting (Kaneda, 2004). In mammals, failure to methylate and ‘imprint’ the correct parental allele leads to a spectrum of diseases, including Silver-Russell, Beckwith-Wiedemann and Prader-Willi syndromes (Eggermann, 2009). Two of the best-characterized imprinting-related diseases are Angelman’s syndrome (AS), an imprinted neurodevelopmental disorder caused by maternal 15q11–q13 or ubiquitin protein ligase E3A (UBE3A) deficiency, and Prader-Willi syndrome (PWS), which is a neurobehavioral disorder that results from paternal deficiency of the same chromosomal fragment. The 15q11–q13 region contains a number of imprinted genes that are regulated by an imprinting center (PWS/AS-IC), which contains the functional elements PWS-SRO and AS-SRO. The loss of either the maternal or paternal imprinting center leads to abnormal DNA methylation in this locus and abnormal expression of the affected genes. Consequently, a chromosome pair lacking the paternal PWS-SRO has only the maternal epigenetic modifications and gene expression state, and a chromosome lacking the maternally transmitted AS-SRO (but containing the PWS-SRO) has only the paternal state of epigenetic modifications and gene expression (White et al., 2006; Horsthemke and Wagstaff, 2008). In addition to developmental disorders, the deregulation of a number of imprinted loci has been implicated in cancer. Examples of this phenomenon include loss of imprinting (LOI) of PEG1/MEST in lung cancer, CDKN1C in pancreatic cancer and IGF2 in colorectal cancer (Iacobuzio-Donahue, 2009; Cui et al., 2003; Nakanishi et al., 2004; Sato et al., 2005).
Disorders such as AS and PWS demonstrate that the induction of abnormal DNA methylation patterns alone can cause disease. However, it is also clear that proteins involved in binding to methylated DNA are also important for the epigenetic control of gene expression and the regulation of homeostasis of the organism. For example, the importance of methyl-binding proteins in the regulation of gene expression is highlighted by Rett syndrome, an autism spectrum neurodevelopmental disorder caused by loss-of-function mutations in the gene encoding the methyl DNA binding protein MeCP2. These mutations prevent MeCP2 from binding to methylated DNA and recruiting other chromatin modifiers, resulting in the inability to silence specific genes in a subset of neurons during development (Amir et al., 1999). This disease demonstrates a role for both DNA methylation and the DNA-protein interactions that accompany DNA methylation in the normal regulation of gene expression and, additionally, that inactivation of these processes can cause human disease (Prokhortchouk and Defossez, 2008).
In addition to its role in regulating the expression of imprinted genes, DNA methylation is also important for the epigenetic regulation of gene expression in specific tissues. In contrast to imprinted genes, where only one of the two alleles is methylated throughout all the cells in the organism, genes whose expression is regulated by DNA methylation in specific tissues exhibit biallelic methylation. For example, upon differentiation to muscle cells, stem cell genes such as OCT4 (also known as POU5F1) and NANOG are stably repressed by mechanisms that involve DNA methylation (Shiota et al., 2002; Eckhardt et al., 2006; Li et al., 2007). In addition to de novo methylation events, demethylation of DNA by the BER system is another mechanism that can alter the epigenetic state of a gene, and this system may be used to prevent methylation of genes required for terminal differentiation while in the embryonic state. For example, two cytosine deaminases, Aid and Apobec1, are co-expressed with embryonic transcription factors, including Nanog and Stella, in pluripotent tissues and appear to function by opposing DNA methylation-induced silencing of these genes in self-renewing cells (Morgan et al., 2004). Because epigenetic processes are so closely intertwined with normal somatic cell function, it is no surprise that deregulation of DNA methylation can lead to a wide spectrum of diseases.
Importantly, with regards to human disease, deregulation of the mechanisms that control DNA methylation in somatic tissues, and subsequent alteration of DNA methylation patterns, is a common phenomenon in cancer. The aberrant methylation of DNA in cancer appears to be regional and results in both the hypermethylation of CpG islands in the promoter regions of genes, and global DNA hypomethylation (generally in pericentric heterochromatin). The aberrant methylation of gene promoters that is observed in many cancers is believed to contribute to the darwinian evolution of the tumors by favoring the clonal expansion of cells that have acquired the aberrantly methylated genes. This is because DNA methylation in specific promoters can silence tumor suppressor genes such as CDKN2A, DAPK1 and CDH1 (Table 1). Methylation of tumor suppressor genes such as these can promote the acquisition of tumorigenic behaviors, such as increased proliferation, escape from apoptosis and enhanced invasiveness (Merlo et al., 1995; Kim et al., 2001; Nakata et al., 2006). In contrast to hypermethylation of a selected subset of promoters, hypomethylation of heterochromatin can impair the cells ability to silence parasitic DNA elements, such as endogenous retroviral elements, whose expression or movement throughout the genome may lead to cancer formation (Gaudet et al., 2003). Indeed, global DNA hypomethylation has been correlated with genetic instability, and in somatic cells, this instability can contribute to both mutator phenotypes, which increase the mutation rates in tumors cells, and to large-scale chromosomal abnormalities such as translocations. These phenotypes can ultimately result in cancer by favoring the accumulation of gene mutations that lead to oncogene activation or the inactivation of tumor suppressor genes (Eden et al., 2003; Gaudet et al., 2003; Kim et al., 2004). Similar to hypomethylation of parasitic elements in heterochromatin, hypomethylation of some gene promoters may increase their expression and cause them to function as oncogenes. For example, hypomethylation and oncogenic overexpression have been observed for NAT1 in breast cancer and CD30 (also known as TNFRSF8) in anaplastic large cell lymphoma (Kim et al., 2008; Watanabe et al., 2008).
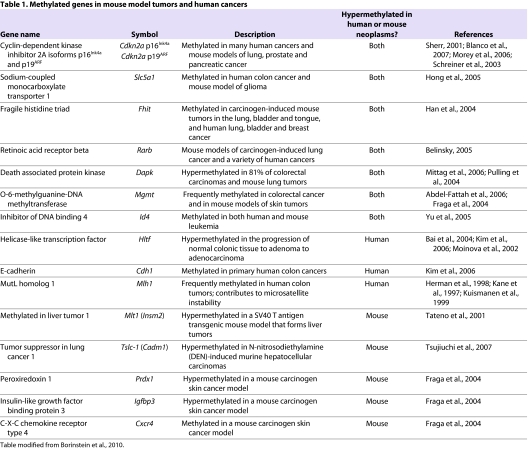
Table 1.
Methylated genes in mouse model tumors and human cancers
The current paradigm regarding the effect of DNA methylation on cancer formation regards the aberrant methylation leading to cancer as a somatic phenomenon without consideration for the specific cells in a tissue that are being affected by the epigenetic alteration. There is growing evidence to suggest that cancers may originate from alterations of adult stem cells rather than of more differentiated cells. Alternatively, a differentiated cell may be induced to de-differentiate and return to a stem cell-like state through alterations in the epigenetic state of these cells. Adult stem cells are thought to function as long-lived, multipotent and self-renewable cells that serve to replace cells in a given tissue as needed. One of the best-studied adult stem cell populations is the hematopoietic stem cells (HSCs). These cells reside in the bone marrow and are capable of becoming all types of hematopoietic cells, and some evidence suggests that they can occasionally differentiate into other cell types as well (Uchida et al., 1994; Petersen et al., 1999). In HSCs, differentiation requires the interplay of a large number of transcriptions factors, and one of these, PU.1, is itself regulated by DNA methylation and can complex with DNMT3a and DNMT3b to methylate a number of targets genes. Consequently, altering the methylation status of the PU.1 promoter can lead to both lymphoma and leukemia. Thus, epigenetic alterations appear to play a significant role in the abnormal regulation of cancer stem cells and may be a dominant mechanism governing this aspect of tumor biology. In order to more definitively address this hypothesis, mouse models will be needed to assess the interplay between stem cell regulation and epigenetic factors in cancer.
Mouse models for the study of epigenetic alterations in disease: focus on cancer and aberrant DNA methylation
Currently, there are two main approaches that have been employed with regards to the use of mouse models to study the role of epigenetic changes in cancer: (1) mouse models that have been genetically manipulated to overexpress or to lack specific genes that are direct regulators of DNA methylation and methylation-related gene expression; and (2) genetic or carcinogen-induced mouse models of cancer with assessment of somatic epigenetic alterations that arise in the tumors.
In the former approach, the creation of mouse models by manipulation of genes that are involved directly in DNA methylation has been complicated by embryonic lethality owing to the fundamental role of DNA methylation in development. Thus, most models developed for direct manipulation of these genes have employed haploinsufficient mice, such as Dnmt1wt/− mice, or mice that have tissue-specific gene alterations. An example of the former approach combines the ApcMin/wt mouse, a model system for intestinal cancer, with mice that have hypomorphic expression of Dnmt3b or Mbd2. In the ApcMin/wt mice, somatic events occur in the intestines that cooperate with the mutant Apc allele to cause adenoma formation. The double mutant mice lack either the ability to establish new methylation patterns (Dnmt3b hypomorph), or the ability to repress genes that are associated with methylated DNA (Mbd2 hypomorph). This approach has allowed researchers to test the role of DNA methylation in cancer formation and progression. In both cases, the double mutant mice had a dramatic reduction in the progression of the adenomas to adenocarcinomas, suggesting that aberrant de novo DNA methylation is an important part of the oncogenic process (Eads et al., 2002; Sansom et al., 2003; Lin et al., 2006; Linhart et al., 2007).
Notably, in contrast to the apparent necessity for DNA methylation in the progression of intestinal cancer in the ApcMin/wt model, depletion of DNA methylation caused by a partial loss of the maintenance methyltransferase Dnmt1 leads to aggressive T-cell lymphomas (Gaudet et al., 2003). One explanation for the discrepant role of DNA methylation in cancer formation that is observed between these two model systems may be that, in T cells, the early loss of DNA methylation, particularly in pericentric heterochromatin, activates oncogenes or mobilizes retroelements that cause the tumorigenic transition. In addition, mice with reduced levels of Dnmt1 and an impaired DNA mismatch repair system acquire both B-cell and T-cell lymphomas. However, these same mice develop fewer intestinal tumors than mice with impaired mismatch repair systems alone (Trinh et al., 2002). Thus, perturbation of methylation patterns can have very different outcomes depending on the genes involved and the tissues affected. Consequently, assessing the role of epigenetic alterations in cancer by using mouse models that directly deregulate DNA methylation is likely to be complex and will require a variety of models in order to obtain a full understanding of the role of aberrant DNA methylation in cancer (Table 2).
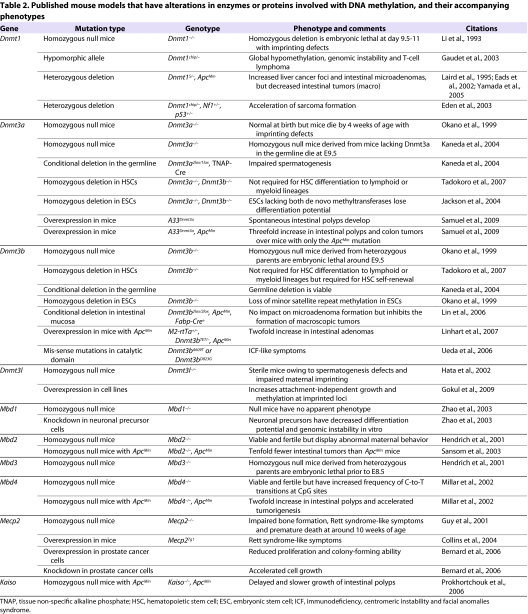
Table 2.
Published mouse models that have alterations in enzymes or proteins involved with DNA methylation, and their accompanying phenotypes
A second approach using mouse models to study the effect of epigenetic alterations in cancers is the assessment of somatic alterations in the tumors arising in mouse models of cancer. The majority of these studies have taken a candidate gene approach when assessing for methylation changes in specific promoters associated with known tumor suppressor genes. Other studies have employed a whole-genome approach in an effort to identify methylation changes in an unbiased way. An example of the latter approach is a study of DNA methylation in a mouse model of leukemia, in which transgenes were used to drive the proliferation of T cells. Some of these cells eventually acquired enough secondary mutations, either by genetic or epigenetic means, to give rise to either T-cell lymphomas or acute lymphoblastic leukemias. In order to identify both hyper- and hypomethylation events in the induced benign proliferative state that preceded the formation of the tumors, as well as events in the established tumors, investigators used restriction landmark genome scanning (RLGS) to survey the methylome (Yu et al., 2005; Opavsky et al., 2007). In addition to identifying the hypermethylation of known tumor suppressor genes and a number of novel genes, the investigators also noted a non-random distribution of hypermethylated sites in the genome. In these studies, aberrant DNA methylation was not observed in the early proliferative state, but was identified in the established tumors (Table 1).
Interestingly, in contrast to the observation in T cells that aberrant methylation occurs late in the tumorigenesis process, in an epithelial-based model system several important tumor suppressor genes have been observed to be methylated early in tumorigenesis. In an epithelial multi-step tumorigenesis model of squamous cell cancer formation, the tumors are induced and promoted by a chemical exposure protocol that results in discrete cancer stages, allowing an assessment of the events occurring at different steps in the carcinogenesis process. By comparing benign papillomas to invasive carcinomas using epigenetic unmasking techniques, the investigators identified novel tumor suppressors and classified them based on the stage of disease (Fraga et al., 2004; Fraga et al., 2005). Surprisingly, several tumor suppressor genes, including Cdkn2a, were found to be consistently methylated very early in disease progression, suggesting that methylation of these genes may be crucial to the formation of tumors in this system.
The discrepancy in the results of the two systems outlined above, begs the question: why is there a difference in the observed timing of hypermethylation events and is this difference relevant to human disease? The disparity may reflect biological differences between the tissue origin of the tumors studied (hematopoietic versus epithelial), or the differences may be the result of either the mouse model used and/or of the distinct methodologies for methylation detection. In the cases illustrated above, the detection method used in the epithelial cancer study is likely to be more comprehensive because it does not rely on methylation changes at a restriction enzyme site. RLGS, as with other assays such as methylation bead-chip arrays (Illumina), can only detect the methylation state of a defined subset of all the CpG dinucleotides. Consequently, an assessment of the entire epigenome is not possible with these methods, and it is not possible to determine whether the altered methylation states that were detected have any affect on transcription. This is important because many genes that have been identified as hypermethylated in tumors show no change in expression levels between the tumor and wild-type tissues, suggesting that these changes may have no biological role in tumorigenesis (Chen et al., 2005). Other global methods for assessing DNA methylation rely on either a protein fragment or on antibodies that specifically bind to methylated DNA to enrich for methylated regions of the genome. This method, termed methylated DNA immunoprecipitation (methyl DIP), entails the hybridization of immunoprecipitated methylated DNA to microarrays or deep sequencing of the immunoprecipitated DNA to assess the methylome. This approach is less biased than others, but has its own limitations including low resolution when using microarrays, difficulty in obtaining sufficient coverage when deep sequencing is used, and high false discovery rates (Weber et al., 2005; Irizarry et al., 2008; Hodges et al., 2009). Thus, the technique used to assess the cancer methylome in these model systems is one crucial factor to include when interpreting the results of studies of epigenetic alterations in mouse models.
In summary, the use of mouse models to assess DNA methylation in disease is an area of investigation that is still in its early stages, but is showing considerable promise for providing insights into human disease. A number of issues will need to be addressed in order to advance this field, including the identification of appropriate mouse models of disease and the identification of the most robust technique for assessing DNA methylation, particularly in relation to technical reproducibility and coverage of the methylome. Studies that address these issues are underway in a variety of laboratories and will lead to mouse models that can be used widely to study the role of DNA methylation in cancer.
Acknowledgments
Work in the corresponding author’s laboratory was supported by a Burroughs Welcome Fund Clinical Scientist in Translational Research Award and NIH grant P30 CA015704 (to W.M.G.). Deposited in PMC for release after 12 months.
Footnotes
COMPETING INTERESTS
The authors declare no competing financial interests.
REFERENCES
- Abdel-Fattah R, Glick A, Rehman I, Maiberger P, Hennings H. (2006). Methylation of the O6-methylguanine-DNA methyltransferase promoter suppresses expression in mouse skin tumors and varies with the tumor induction protocol. Int J Cancer 118, 527–531 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Amir RE, Van den Veyver IB, Wan M, Tran CQ, Francke U, Zoghbi HY. (1999). Rett syndrome is caused by mutations in X-linked MECP2, encoding methyl-CpG-binding protein 2. Nat Genet. 23, 185–188 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bai AHC, Tongg JHM, To K-F, Chan MWY, Man EPS, Lo K-W, Lee JFY, Sung JJY, Leung WK. (2004). Promoter hypermethylation of tumor-related genes in the progression of colorectal neoplasia. Int J Cancer 112, 846–853 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bakker J, Lin X, Nelson WG. (2002). Methyl-CpG binding domain protein 2 represses transcription from hypermethylated pi-class glutathione S-transferase gene promoters in hepatocellular carcinoma cells. J Biol Chem. 277, 22573–22580 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Belinsky SA. (2005). Silencing of genes by promoter hypermethylation: key event in rodent and human lung cancer. Carcinogenesis 26, 1481–1487 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bernard D, Gil J, Dumont P, Rizzo S, Monte D, Quatannens B, Hudson D, Visakorpi T, Fuks F, de Launoit Y. (2006). The methyl-CpG-binding protein MECP2 is required for prostate cancer cell growth. Oncogene 25, 1358–1366 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Blanco D, Vicent S, Fraga MF, Fernandez-Garcia I, Freire J, Lujambio A, Esteller M, Ortiz-de-Solorzano C, Pio R, Lecanda F, et al. (2007). Molecular analysis of a multistep lung cancer model induced by chronic inflammation reveals epigenetic regulation of p16 and activation of the DNA damage response pathway. Neoplasia 9, 840–852 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Borinstein SC, Conerly M, Dzieciatkowski S, Biswas S, Washington MK, Trobridge P, Henikoff S, Grady WM. (2010). Aberrant DNA methylation occurs in colon neoplasms arising in the azoxymethane colon cancer model. Mol Carcinog. 49, 94–103 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cedar H, Bergman Y. (2009). Linking DNA methylation and histone modification: patterns and paradigms. Nat Rev Genet. 10, 295–304 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chen WD, Han ZJ, Skoletsky J, Olson J, Sah J, Myeroff L, Platzer P, Lu S, Dawson D, Willis J, et al. (2005). Detection in fecal DNA of colon cancer-specific methylation of the nonexpressed vimentin gene. J Natl Cancer Inst. 97, 1124–1132 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Collins AL, Levenson JM, Vilaythong AP, Richman R, Armstrong DL, Noebels JL, David Sweatt J, Zoghbi HY. (2004). Mild overexpression of MeCP2 causes a progressive neurological disorder in mice. Hum Mol Genet. 13, 2679–2689 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cui H, Cruz-Correa M, Giardiello FM, Hutcheon DF, Kafonek DR, Brandenburg S, Wu Y, He X, Powe NR, Feinberg AP. (2003). Loss of IGF2 imprinting: a potential marker of colorectal cancer risk. Science 299, 1753–1755 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Eads CA, Nickel AE, Laird PW. (2002). Complete genetic suppression of polyp formation and reduction of CpG-island hypermethylation in Apc(Min/+) Dnmt1-hypomorphic mice. Cancer Res. 62, 1296–1299 [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Eckhardt F, Lewin J, Cortese R, Rakyan VK, Attwood J, Burger M, Burton J, Cox TV, Davies R, Down TA, et al. (2006). DNA methylation profiling of human chromosomes 6, 20 and 22. Nat Genet. 38, 1378–1385 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Eden A, Gaudet F, Waghmare A, Jaenisch R. (2003). Chromosomal instability and tumors promoted by DNA hypomethylation. Science 300, 455. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Eggermann T. (2009). Silver-Russell and Beckwith-Wiedemann syndromes: opposite (epi)mutations in 11p15 result in opposite clinical pictures. Horm Res. 71, 30–35 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fraga MF, Herranz M, Espada J, Ballestar E, Paz MF, Ropero S, Erkek E, Bozdogan O, Peinado H, Niveleau A, et al. (2004). A mouse skin multistage carcinogenesis model reflects the aberrant DNA methylation patterns of human tumors. Cancer Res. 64, 5527–5534 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fraga MF, Ballestar E, Villar-Garea A, Boix-Chornet M, Espada J, Schotta G, Bonaldi T, Haydon C, Ropero S, Petrie K, et al. (2005). Loss of acetylation at Lys16 and trimethylation at Lys20 of histone H4 is a common hallmark of human cancer. Nat Genet. 37, 391–400 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gaudet F, Hodgson JG, Eden A, Jackson-Grusby L, Dausman J, Gray JW, Leonhardt H, Jaenisch R. (2003). Induction of tumors in mice by genomic hypomethylation. Science 300, 489–492 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gokul G, Ramakrishna G, Khosla S. (2009). Reprogramming of HeLa cells upon DNMT3L overexpression mimics carcinogenesis. Epigenetics 4, 322–329 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Guy J, Hendrich B, Holmes M, Martin JE, Bird A. (2001). A mouse Mecp2-null mutation causes neurological symptoms that mimic Rett syndrome. Nat Genet. 27, 322–326 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Han SY, Iliopoulos D, Druck T, Guler G, Grubbs CJ, Pereira M, Zhang Z, You M, Lubet RA, Fong LY, et al. (2004). CpG methylation in the Fhit regulatory region: relation to Fhit expression in murine tumors. Oncogene 23, 3990–3998 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hata K, Okano M, Lei H, Li E. (2002). Dnmt3L cooperates with the Dnmt3 family of de novo DNA methyltransferases to establish maternal imprints in mice. Development 129, 1983–1993 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hendrich B, Guy J, Ramsahoye B, Wilson VA, Bird A. (2001). Closely related proteins MBD2 and MBD3 play distinctive but interacting roles in mouse development. Genes Dev. 15, 710–723 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Herman JG, Umar A, Polyak K, Graff J, Ahuja N, Issa J-P, Markowitz S, Willson JKV, Hamilton S, Kinzler K, et al. (1998). Incidence and functional consequences of hMLH1 promoter hypermethylation in colorectal carcinoma. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 95, 6870–6875 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hodges E, Smith AD, Kendall J, Xuan Z, Ravi K, Rooks M, Zhang MQ, Ye K, Bhattacharjee A, Brizuela L, et al. (2009). High definition profiling of mammalian DNA methylation by array capture and single molecule bisulfite sequencing. Genome Res. 19, 1593–1605 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hong C, Maunakea A, Jun P, Bollen AW, Hodgson JG, Goldenberg DD, Weiss WA, Costello JF. (2005). Shared epigenetic mechanisms in human and mouse gliomas inactivate expression of the growth suppressor SLC5A8. Cancer Res. 65, 3617–3623 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Horsthemke B, Wagstaff J. (2008). Mechanisms of imprinting of the Prader-Willi/Angelman region. Am. J. Med. Genet. A 146A, 2041–2052 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Iacobuzio-Donahue CA. (2009). Epigenetic changes in cancer. Annu Rev Pathol. 4, 229–249 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Irizarry RA, Ladd-Acosta C, Carvalho B, Wu H, Brandenburg SA, Jeddeloh JA, Wen B, Feinberg AP. (2008). Comprehensive high-throughput arrays for relative methylation (CHARM). Genome Res. 18, 780–790 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jackson M, Krassowska A, Gilbert N, Chevassut T, Forrester L, Ansell J, Ramsahoye B. (2004). Severe global DNA hypomethylation blocks differentiation and induces histone hyperacetylation in embryonic stem cells. Mol Cell Biol. 24, 8862–8871 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kane M, Loda M, Gaida G, Lipman J, Mishra R, Goldman H, Jessup JM, Kolodner R. (1997). Methylation of the hMLH1 promoter correlates with lack of expression of hMLH1 in sporadic colon tumors and mismatch repair-defective human tumor cell lines. Cancer Res. 57, 808–811 [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kaneda M, Okano M, Hata K, Sado T, Tsujimoto N, Li E, Sasaki H. (2004). Essential role for de novo DNA methyltransferase Dnmt3a in paternal and maternal imprinting. Nature 429, 900–903 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kim DH, Nelson HH, Wiencke JK, Christiani DC, Wain JC, Mark EJ, Kelsey KT. (2001). Promoter methylation of DAP-kinase: association with advanced stage in non-small cell lung cancer. Oncogene 20, 1765–1770 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kim M, Trinh BN, Long TI, Oghamian S, Laird PW. (2004). Dnmt1 deficiency leads to enhanced microsatellite instability in mouse embryonic stem cells. Nucl Acids Res. 32, 5742–5749 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kim SJ, Kang HS, Chang HL, Jung YC, Sim HB, Lee KS, Ro J, Lee ES. (2008). Promoter hypomethylation of the N-acetyltransferase 1 gene in breast cancer. Oncol Rep. 19, 663–668 [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kim YH, Petko Z, Dzieciatkowski S, Lin L, Ghiassi M, Stain S, Chapman WC, Washington MK, Willis J, Markowitz SD, et al. (2006). CpG island methylation of genes accumulates during the adenoma progression step of the multistep pathogenesis of colorectal cancer. Genes Chromosomes Cancer 45, 781–789 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kuismanen SA, Holmberg MT, Salovaara R, Schweizer P, Aaltonen LA, de la Chapelle A, Nystrom-Lahti M, Peltomaki P. (1999). Epigenetic phenotypes distinguish microsatellite-stable and -unstable colorectal cancers. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 96, 12661–12666 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Laird PW, Jackson-Grusby L, Fazeli A, Dickinson SL, Jung WE, Li E, Weinberg RA, Jaenisch R. (1995). Suppression of intestinal neoplasia by DNA hypomethylation. Cell 81, 197–205 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Li E, Beard C, Jaenisch R. (1993). Role for DNA methylation in genomic imprinting. Nature 366, 362–365 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Li J-Y, Pu M-T, Hirasawa R, Li B-Z, Huang Y-N, Zeng R, Jing N-H, Chen T, Li E, Sasaki H, et al. (2007). Synergistic function of DNA methyltransferases Dnmt3a and Dnmt3b in the methylation of Oct4 and Nanog. Mol Cell Biol. 27, 8748–8759 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lin H, Yamada Y, Nguyen S, Linhart H, Jackson-Grusby L, Meissner A, Meletis K, Lo G, Jaenisch R. (2006). Suppression of intestinal neoplasia by deletion of Dnmt3b. Mol Cell Biol. 26, 2976–2983 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Linhart HG, Lin H, Yamada Y, Moran E, Steine EJ, Gokhale S, Lo G, Cantu E, Ehrich M, He T, et al. (2007). Dnmt3b promotes tumorigenesis in vivo by gene-specific de novo methylation and transcriptional silencing. Genes Dev. 21, 3110–3122 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lopes EC, Valls E, Figueroa ME, Mazur A, Meng F-G, Chiosis G, Laird PW, Schreiber-Agus N, Greally JM, Prokhortchouk E, et al. (2008). Kaiso contributes to DNA methylation-dependent silencing of tumor suppressor genes in colon cancer cell lines. Cancer Res. 68, 7258–7263 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Merlo A, Herman JG, Mao L, Lee DJ, Gabrielson E, Burger PC, Baylin SB, Sidransky D. (1995). 5′ CpG island methylation is associated with transcriptional silencing of the tumour suppressor p16/CDKN2/MTS1 in human cancers. Nat Med. 1, 686–692 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Millar CB, Guy J, Sansom OJ, Selfridge J, MacDougall E, Hendrich B, Keightley PD, Bishop SM, Clarke AR, Bird A. (2002). Enhanced CpG mutability and tumorigenesis in MBD4-deficient mice. Science 297, 403–405 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mittag F, Kuester D, Vieth M, Peters B, Stolte B, Roessner A, Schneider-Stock R. (2006). DAPK promotor methylation is an early event in colorectal carcinogenesis. Cancer Lett. 240, 69–75 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Moinova HR, Chen WD, Shen L, Smiraglia D, Olechnowicz J, Ravi L, Kasturi L, Myeroff L, Plass C, Parsons R, et al. (2002). HLTF gene silencing in human colon cancer. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 99, 4562–4567 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Morey SR, Smiraglia DJ, James SR, Yu J, Moser MT, Foster BA, Karpf AR. (2006). DNA methylation pathway alterations in an autochthonous murine model of prostate cancer. Cancer Res. 66, 11659–11667 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Morgan HD, Dean W, Coker HA, Reik W, Petersen-Mahrt SK. (2004). Activation-induced cytidine deaminase deaminates 5-methylcytosine in DNA and is expressed in pluripotent tissues: implications for epigenetic reprogramming. J Biol Chem. 279, 52353–52360 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nakanishi H, Suda T, Katoh M, Watanabe A, Igishi T, Kodani M, Matsumoto S, Nakamoto M, Shigeoka Y, Okabe T, et al. (2004). Loss of imprinting of PEG1/MEST in lung cancer cell lines. Oncol Rep. 12, 1273–1278 [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nakata S, Sugio K, Uramoto H, Oyama T, Hanagiri T, Morita M, Yasumoto K. (2006). The methylation status and protein expression of CDH1, p16(INK4A), and fragile histidine triad in nonsmall cell lung carcinoma: epigenetic silencing, clinical features, and prognostic significance. Cancer 106, 2190–2199 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nan X, Ng HH, Johnson CA, Laherty CD, Turner BM, Eisenman RN, Bird A. (1998). Transcriptional repression by the methyl-CpG-binding protein MeCP2 involves a histone deacetylase complex. Nature 393, 386–389 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Okano M, Bell DW, Haber DA, Li E. (1999). DNA methyltransferases Dnmt3a and Dnmt3b are essential for de novo methylation and mammalian development. Cell 99, 247–257 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Opavsky R, Wang SH, Trikha P, Raval A, Huang Y, Wu YZ, Rodriguez B, Keller B, Liyanarachchi S, Wei G, et al. (2007). CpG island methylation in a mouse model of lymphoma is driven by the genetic configuration of tumor cells. PLoS Genet. 3, 1757–1769 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Petersen BE, Bowen WC, Patrene KD, Mars WM, Sullivan AK, Murase N, Boggs SS, Greenberger JS, Goff JP. (1999). Bone marrow as a potential source of hepatic oval cells. Science 284, 1168–1170 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Prokhortchouk E, Defossez PA. (2008). The cell biology of DNA methylation in mammals. Biochim Biophys Acta 1783, 2167–2173 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Prokhortchouk A, Sansom O, Selfridge J, Caballero IM, Salozhin S, Aithozhina D, Cerchietti L, Meng FG, Augenlicht LH, Mariadason JM, et al. (2006). Kaiso-deficient mice show resistance to intestinal cancer. Mol Cell Biol. 26, 199–208 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pulling LC, Vuillemenot BR, Hutt JA, Devereux TR, Belinsky SA. (2004). Aberrant promoter hypermethylation of the death-associated protein kinase gene is early and frequent in murine lung tumors induced by cigarette smoke and tobacco carcinogens. Cancer Res. 64, 3844–3848 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rhee I, Jair KW, Yen RW, Lengauer C, Herman JG, Kinzler KW, Vogelstein B, Baylin SB, Schuebel KE. (2000). CpG methylation is maintained in human cancer cells lacking DNMT1. Nature 404, 1003–1007 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Samuel MS, Suzuki H, Buchert M, Putoczki TL, Tebbutt NC, Lundgren-May T, Christou A, Inglese M, Toyota M, Heath JK, et al. (2009). Elevated Dnmt3a activity promotes polyposis in Apc(Min) mice by relaxing extracellular restraints on Wnt signaling. Gastroenterology 137, 902–913 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sansom OJ, Berger J, Bishop SM, Hendrich B, Bird A, Clarke AR. (2003). Deficiency of Mbd2 suppresses intestinal tumorigenesis. Nat Genet. 34, 145–147 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sato N, Matsubayashi H, Abe T, Fukushima N, Goggins M. (2005). Epigenetic down-regulation of CDKN1C/p57KIP2 in pancreatic ductal neoplasms Identified by gene expression profiling. Clin Cancer Res. 11, 4681–4688 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schreiner B, Baur DM, Fingerle AA, Zechner U, Greten FR, Adler G, Sipos B, Kloppel G, Hameister H, Schmid RM. (2003). Pattern of secondary genomic changes in pancreatic tumors of Tgf alpha/Trp53+/− transgenic mice. Genes Chromosomes Cancer 38, 240–248 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sherr CJ. (2001). The INK4a/ARF network in tumour suppression. Nat Rev Mol Cell Biol. 2, 731–737 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shiota K, Kogo Y, Ohgane J, Imamura T, Urano A, Nishino K, Tanaka S, Hattori N. (2002). Epigenetic marks by DNA methylation specific to stem, germ and somatic cells in mice. Genes Cells 7, 961–969 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tadokoro Y, Ema H, Okano M, Li E, Nakauchi H. (2007). De novo DNA methyltransferase is essential for self-renewal, but not for differentiation, in hematopoietic stem cells. J Exp Med. 204, 715–722 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tate PH, Bird AP. (1993). Effects of DNA methylation on DNA-binding proteins and gene expression. Curr Opin Genet Dev. 3, 226–231 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tateno M, Fukunishi Y, Komatsu S, Okazaki Y, Kawai J, Shibata K, Itoh M, Muramatsu M, Held WA, Hayashizaki Y. (2001). Identification of a novel member of the snail/Gfi-1 repressor family, mlt 1, which is methylated and silenced in liver tumors of SV40 T antigen transgenic mice. Cancer Res. 61, 1144–1153 [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Trinh BN, Long TI, Nickel AE, Shibata D, Laird PW. (2002). DNA methyltransferase deficiency modifies cancer susceptibility in mice lacking DNA mismatch repair. Mol Cell Biol. 22, 2906–2917 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tsujiuchi T, Sugata E, Masaoka T, Onishi M, Fujii H, Shimizu K, Honoki K. (2007). Expression and DNA methylation patterns of Tslc1 and Dal-1 genes in hepatocellular carcinomas induced by N-nitrosodiethylamine in rats. Cancer Sci. 98, 943–948 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Uchida N, Aguila HL, Fleming WH, Jerabek L, Weissman IL. (1994). Rapid and sustained hematopoietic recovery in lethally irradiated mice transplanted with purified Thy-1.1lo Lin-Sca-1+ hematopoietic stem cells. Blood 83, 3758–3779 [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ueda Y, Okano M, Williams C, Chen T, Georgopoulos K, Li E. (2006). Roles for Dnmt3b in mammalian development: a mouse model for the ICF syndrome. Development 133, 1183–1192 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Watanabe M, Ogawa Y, Itoh K, Koiwa T, Kadin ME, Watanabe T, Okayasu I, Higashihara M, Horie R. (2008). Hypomethylation of CD30 CpG islands with aberrant JunB expression drives CD30 induction in Hodgkin lymphoma and anaplastic large cell lymphoma. Lab Invest. 88, 48–57 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Weber M, Davies JJ, Wittig D, Oakeley EJ, Haase M, Lam WL, Schubeler D. (2005). Chromosome-wide and promoter-specific analyses identify sites of differential DNA methylation in normal and transformed human cells. Nat Genet. 37, 853–862 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- White HE, Durston VJ, Harvey JF, Cross NCP. (2006). Quantitative analysis of SRNPN gene methylation by pyrosequencing as a diagnostic test for Prader-Willi syndrome and Angelman syndrome. Clin Chem. 52, 1005–1013 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yamada Y, Jackson-Grusby L, Linhart H, Meissner A, Eden A, Lin H, Jaenisch R. (2005). Opposing effects of DNA hypomethylation on intestinal and liver carcinogenesis. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 102, 13580–13585 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yu L, Liu C, Vandeusen J, Becknell B, Dai Z, Wu YZ, Raval A, Liu TH, Ding W, Mao C, et al. (2005). Global assessment of promoter methylation in a mouse model of cancer identifies ID4 as a putative tumor-suppressor gene in human leukemia. Nat Genet. 37, 265–274 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zhao X, Ueba T, Christie BR, Barkho B, McConnell MJ, Nakashima K, Lein ES, Eadie BD, Willhoite AR, Muotri AR, et al. (2003). Mice lacking methyl-CpG binding protein 1 have deficits in adult neurogenesis and hippocampal function. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 100, 6777–6782 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zilberman D, Coleman-Derr D, Ballinger T, Henikoff S. (2008). Histone H2A.Z and DNA methylation are mutually antagonistic chromatin marks. Nature 456, 125–129 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]