Abstract
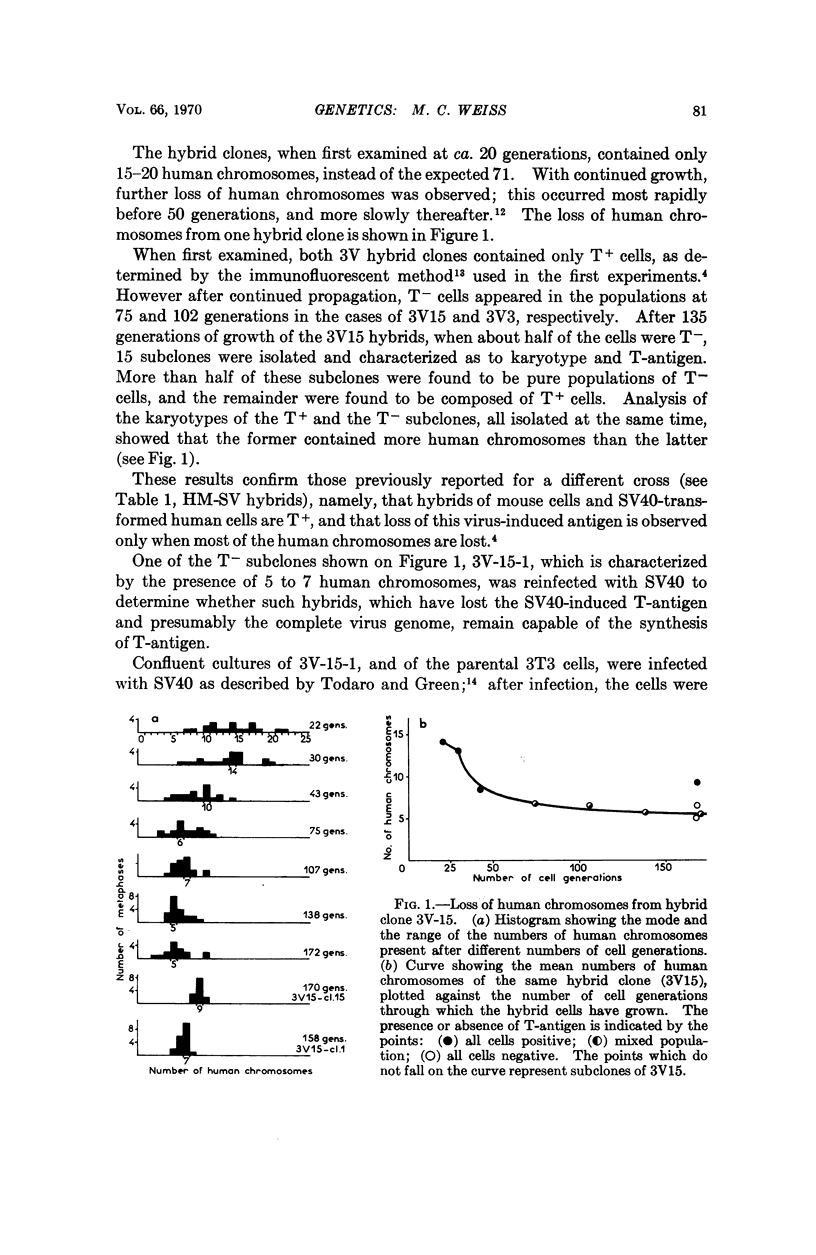
The study of hybrids from three crosses between mouse cells and SV40-transformed human cells have established a positive correlation between the loss of human chromosomes and that of the SV40-induced T-antigen from the hybrid cells. These results, as well as those of other workers, provide strong support for the hypothesis of the integration of the SV40 genome in the chromosomes of transformed cells. Further, it has been shown that hybrid cells which have lost T-antigen are capable of synthesizing this antigen upon infection with SV40, thereby demonstrating that loss of the viral antigen from the hybrid cells is not due to loss of some cellular gene required for the expression of the viral genome. Results of karyological analyses of the hybrid cells argue against the existence of a single specific integration site for the SV40 genome in human cells.
Full text
PDF






Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- BLACK P. H., ROWE W. P., TURNER H. C., HUEBNER R. J. A SPECIFIC COMPLEMENT-FIXING ANTIGEN PRESENT IN SV40 TUMOR AND TRANSFORMED CELLS. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1963 Dec;50:1148–1156. doi: 10.1073/pnas.50.6.1148. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Coon H. G., Weiss M. C. A quantitative comparison of formation of spontaneous and virus-produced viable hybrids. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1969 Mar;62(3):852–859. doi: 10.1073/pnas.62.3.852. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Di Mayorca G., Callender J., Marin G., Giordano R. Temperature-sensitive mutants of polyoma virus. Virology. 1969 May;38(1):126–133. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(69)90134-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Eckhart W. Complementation and transformation by temperature-sensitive mutants of polyoma virus. Virology. 1969 May;38(1):120–125. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(69)90133-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- HARRIS H., WATKINS J. F. HYBRID CELLS DERIVED FROM MOUSE AND MAN: ARTIFICIAL HETEROKARYONS OF MAMMALIAN CELLS FROM DIFFERENT SPECIES. Nature. 1965 Feb 13;205:640–646. doi: 10.1038/205640a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Koprowski H., Jensen F. C., Steplewski Z. Activation of production of infectious tumor virus SV40 in heterokaryon cultures. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1967 Jul;58(1):127–133. doi: 10.1073/pnas.58.1.127. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- LITTLEFIELD J. W. SELECTION OF HYBRIDS FROM MATINGS OF FIBROBLASTS IN VITRO AND THEIR PRESUMED RECOMBINANTS. Science. 1964 Aug 14;145(3633):709–710. doi: 10.1126/science.145.3633.709. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Marin G., Littlefield J. W. Selection of morphologically normal cell lines from polyoma-transformed BHK21/13 hamster fibroblasts. J Virol. 1968 Jan;2(1):69–77. doi: 10.1128/jvi.2.1.69-77.1968. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Matsuya Y., Green H., Basilico C. Properties and uses of human-mouse hybrid cell lines. Nature. 1968 Dec 21;220(5173):1199–1202. doi: 10.1038/2201199a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Matsuya Y., Green H. Somatic cell hybrid between the established human line D98 (presumptive HeLa) and 3T3. Science. 1969 Feb 14;163(3868):697–698. doi: 10.1126/science.163.3868.697. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Migeon B. R., Miller C. S. Human-mouse somatic cell hybrids with single human chromosome (group E): link with thymidine kinase activity. Science. 1968 Nov 29;162(3857):1005–1006. doi: 10.1126/science.162.3857.1005. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- POPE J. H., ROWE W. P. DETECTION OF SPECIFIC ANTIGEN IN SV40-TRANSFORMED CELLS BY IMMUNOFLUORESCENCE. J Exp Med. 1964 Aug 1;120:121–128. doi: 10.1084/jem.120.2.121. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pollack R. E., Green H., Todaro G. J. Growth control in cultured cells: selection of sublines with increased sensitivity to contact inhibition and decreased tumor-producing ability. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1968 May;60(1):126–133. doi: 10.1073/pnas.60.1.126. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- RAPP F., BUTEL J. S., MELNICK J. L. VIRUS-INDUCED INTRANUCLEAR ANTIGEN IN CELLS TRANSFORMED BY PAPOVAVIRUS SV40. Proc Soc Exp Biol Med. 1964 Aug-Sep;116:1131–1135. doi: 10.3181/00379727-116-29472. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sambrook J., Westphal H., Srinivasan P. R., Dulbecco R. The integrated state of viral DNA in SV40-transformed cells. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1968 Aug;60(4):1288–1295. doi: 10.1073/pnas.60.4.1288. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- TODARO G. J., GREEN H. Quantitative studies of the growth of mouse embryo cells in culture and their development into established lines. J Cell Biol. 1963 May;17:299–313. doi: 10.1083/jcb.17.2.299. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Todaro G. J., Green H. High frequency of SV40 transformation of mouse cell line 3T3. Virology. 1966 Apr;28(4):756–759. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(66)90261-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tordaro G. J., Green H. An assay for cellular transformation by SV40. Virology. 1964 May;23(1):117–119. doi: 10.1016/s0042-6822(64)80018-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Watkins J. F., Dulbecco R. Production of SV40 virus in heterokaryons of transformed and susceptible cells. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1967 Oct;58(4):1396–1403. doi: 10.1073/pnas.58.4.1396. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Weiss M. C., Ephrussi B., Scaletta L. J. Loss of T-antigen from somatic hybrids between mouse cells and SV40-transformed human cells. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1968 Apr;59(4):1132–1135. doi: 10.1073/pnas.59.4.1132. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Weiss M. C., Green H. Human-mouse hybrid cell lines containing partial complements of human chromosomes and functioning human genes. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1967 Sep;58(3):1104–1111. doi: 10.1073/pnas.58.3.1104. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Weiss M. C., Todaro G. J., Green H. Properties of a hybrid between lines sensitive and insensitive to contact inhibition of cell division. J Cell Physiol. 1968 Feb;71(1):105–107. doi: 10.1002/jcp.1040710112. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Westphal H., Dulbecco R. Viral DNA in polyoma- and SV40-transformed cell lines. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1968 Apr;59(4):1158–1165. doi: 10.1073/pnas.59.4.1158. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]