Abstract
Acral lentiginous melanoma (ALM) is the most common type of cutaneous melanoma in Asians. The very early stage of ALM demonstrates only a proliferation of a few atypical melanocytes within the epidermis, and has been termed ALM in situ. A 74-year-old male patient presented with a pigmented lesion on the left great toe for 12 years, which had initially showed only a few scattered hyperplastic atypical melanocytes without dermal invasion upon biopsy 5 years ago. This time however, rebiopsy of the lesion confirmed a diagnosis of ALM, stage IIIB. It could be inferred that the lesion had slowly progressed from ALM in situ to invasive ALM over a period of 12 years. Herein we report a case of ALM in situ which progressed to invasive ALM over a long period of time. We expect this report may assist physicians in early recognition and proper management of future cases of ALM in situ.
Keywords: Acral lentiginous melanoma in situ
INTRODUCTION
Acral lentiginous melanoma (ALM) is the most common type of cutaneous melanoma in Asians1. The very early stage of ALM demonstrates only a proliferation of a few atypical melanocytes within the epidermis, and there have been debates on the establishment of the term ALM in situ. It has been called many different names, including atypical melanotic hyperplasia2, atypical melanosis of the foot3, and phase 1 of ALM in situ4. Recently, Kwon et al5 suggested that ALM in situ may have a slow evolution over many years and a prolonged radial-growth phase and added that whether there were fundamental differences between ALM in situ and other names was uncertain.
Herein, we report on an additional case which showed slow progression from ALM in situ to invasive ALM over a duration of 12 years. It is suggested that ALM in situ may be preferred to other obscure terminology which can be misleading.
CASE REPORT
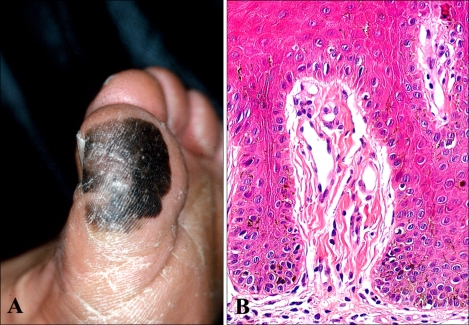
A 74-year-old Korean male patient presented with a pigmented lesion on his left great toe, which had been slowly growing for 12 years. He had visited our clinic 5 years ago, and at that time, the lesion manifested as an asymmetrical patch, 2.6×2.2 cm in size, with an irregular border and irregular brown pigmentation (Fig. 1A). He underwent multiple punch biopsies, which showed only a few scattered hyperplastic atypical melanocytes without dermal invasion (Fig. 1B). The atypical melanocytes had stained positively for both HMB-45 and S-100 protein. We had diagnosed the lesion as atypical melanocytic hyperplasia, or ALM in situ, and had recommended total excision, but the patient had refused treatment.
Fig. 1.
Acral lentiginous melanoma in situ 5 years ago. (A) Clinical photograph, (B) Histopathologic findings show minimal atypical melanocytic hyperplasia without dermal invasion (hematoxylin and eosin, ×400).
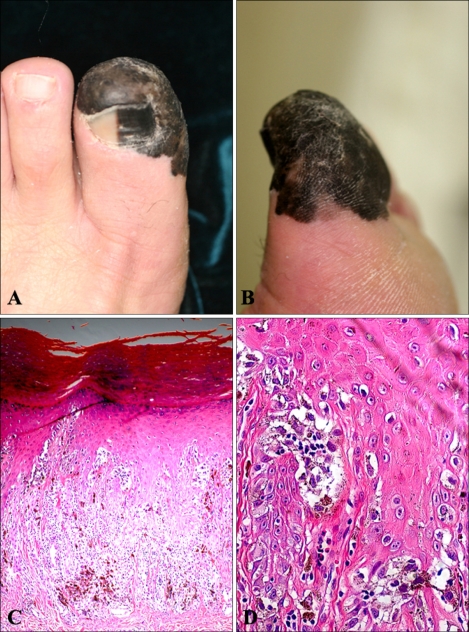
Five years later, the patient revisited our hospital with a spreading lesion that measured up to 4.6×4.2 cm in size (Fig. 2A, B). This time the biopsy exhibited features of an invasive ALM with a Breslow's thickness of 2.5 mm (Fig. 2C, D). HMB-45 and S-100 protein stains were positive, and a solitary ipsilateral inguinal lymph node metastasis was detected on the PET-CT. The patient was treated with amputation of the left great toe accompanied by complete lymph node dissection, which showed one of twelve lymph nodes to be positive. The final diagnosis was ALM, stage IIIB (T3aN1bM0). He has been receiving high dose interferon-α2b therapy at a dose of 17 million units per day, 3 times a week, for 12 months and there has been no recurrence for 6 months after end of treatment.
Fig. 2.
(A, B) Invasive acral lentiginous melanoma. (C, D) Clinical photographs. The histopathologic findings show nest formation by melanoma cells (hematoxylin and eosin, C: ×100, D: ×400).
DISCUSSION
ALM can occur on the palms, soles, digits or beneath the nail plate. The lesion is characterized clinically by a tan, brown to black flat lesion with variations in color, and irregular borders. Papules or nodules are often present5. ALM is traditionally believed to have a less favorable prognosis than other forms of melanoma. However, this may be due to the delayed diagnosis of more advanced cases; and ALM and other types of melanoma with same tumor thickness have been shown to have an equal prognosis. The early stages of ALM usually show a biphasic growth pattern, demonstrating only a proliferation of atypical melanocytes within the epidermis, termed ALM in situ6.
Several articles have addressed the clinicopathological characteristics of early lesions of melanoma that affect the acral areas. Saida4 proposed different phases of tumor growth corresponding to the histopathological features of pigmented macules of melanoma in situ on acral skin. His phase 1 features both cytologically normal and abnormal melanocytes in increased numbers, disposed singly, largely in the basal layer of epidermis, with larger numbers of cells, abnormal cells and cells above the junction in phase 2, and almost exclusively abnormal cells, with many above the junction in phase 3. Frankel7 suggested a similar classification for intraepithelial melanocytic proliferation in the spectrum of melanoma in situ, in part to circumvent that term. Frankel's concept involves the progression of intraepithelial melanocytic proliferation (IMN-I through-III). Our case largely corresponds to Saida's phase 1 or Frankel's IMN-I lesions.
Cho et al2 reported two cases showing black discoloration of the thumb nail which were histologically found to be ALM in situ. Their cases were particularly interesting because atypical melanocytic hyperplasia was confined to the epidermis despite the lesion being present for a long time: 12 years and 30 years, respectively. Nogita et al3 reported a series of cases with only a few scattered foci of single cell melanocytic proliferation with minimal atypia, and they designated their cases as atypical melanosis of the foot.
Recently, Kwon et al5 identified 9 patients who had ALM clinically, but their lesions showed melanocytes with minimal cytologic atypia confined to the epidermis, and this was regarded as ALM in situ. The duration of time starting from when these patients first noticed the pigmented lesions up to when they first visited the clinic ranged from 5 to 30 years (average duration: 13.3 years).
Our case had also shown a few hyperplastic, atypical melanocytes, which were scattered in a single fashion. These melanocytes had remained confined within the epidermis over a 7-year period; the lesion developed into an invasive ALM during an overall 12-year period. We overlooked the malignant potential of the initial lesion, and it had unfortunately progressed. Our case supports the suggestion that ALM in situ may exist before the evolution of invasive ALM, and it can present with a minimal number of atypical melanocytes.
In conclusion, the separation between ALM in situ and atypical melanosis of the foot may be quite difficult; therefore, we suggest that ALM in situ be preferred to other rather obscure diagnoses such as atypical melanotic hyperplasia and atypical melanosis of the foot. Any atypical melanocytic lesion on the foot should be considered as ALM in situ, and must be totally excised, along with a thorough pathological examination of the specimen and close follow-up of the patient.
References
- 1.Seiji M, Takematsu H, Hosokawa M, Obata M, Tomita Y, Kato T, et al. Acral melanoma in Japan. J Invest Dermatol. 1983;80(Suppl):56s–60s. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 2.Cho KH, Kim BS, Chang SH, Lee YS, Kim KJ. Pigmented nail with atypical melanocytic hyperplasia. Clin Exp Dermatol. 1991;16:451–454. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2230.1991.tb01234.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 3.Nogita T, Wong TY, Ohara K, Mizushima J, Mihm MC, Jr, Kawashima M. Atypical melanosis of the foot. A report of three cases in Japanese populations. Arch Dermatol. 1994;130:1042–1045. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 4.Saida T. Malignant melanoma in situ on the sole of the foot. Its clinical and histopathologic characteristics. Am J Dermatopathol. 1989;11:124–130. doi: 10.1097/00000372-198911020-00003. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 5.Kwon IH, Lee JH, Cho KH. Acral lentiginous melanoma in situ: a study of nine cases. Am J Dermatopathol. 2004;26:285–289. doi: 10.1097/00000372-200408000-00004. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 6.Rhodes AR, Mihm MC, Jr, Weinstock MA. Dysplastic melanocytic nevi: a reproducible histologic definition emphasizing cellular morphology. Mod Pathol. 1989;2:306–319. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 7.Frankel KA. Intraepithelial melanocytic neoplasia: a classification by pattern analysis of proliferations of atypical melanocytes. Am J Dermatopathol. 1987;9:80–81. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]