Abstract
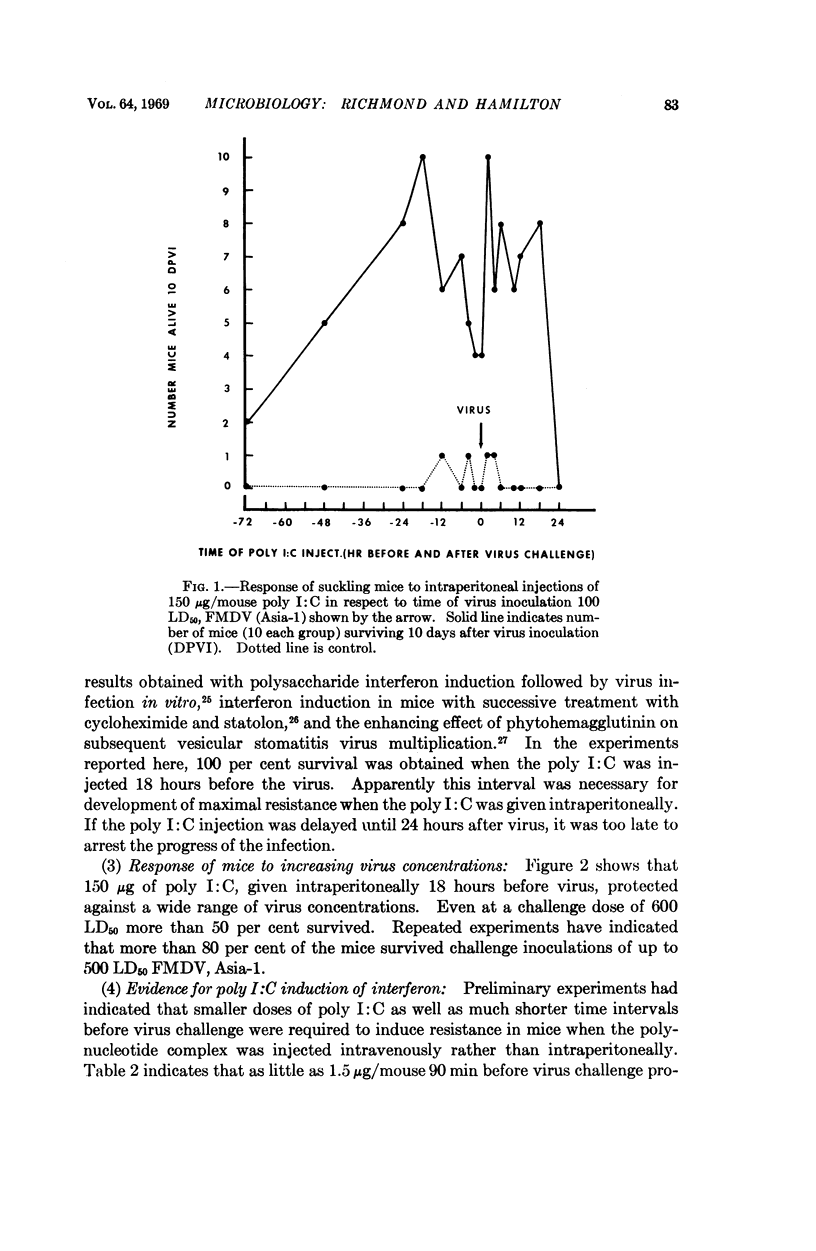
Synthetic 2-stranded RNA—a helical complex formed by duplexing homopolymers of polyriboinosinic and polyribocytidylic acids (poly I:C)—induced host resistance to foot-and-mouth disease virus when microgram quantities were injected into mice. There was a graded response as shown by titrations of polynucleotide complex or virus. Protection was effective for >48 hours after a single injection of polynucleotide complex. Survival and serum interferon titers were directly related.
Full text
PDF



Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- DINTER Z. An inhibitor of viral activity in cell cultures infected with the virus of foot-and-mouth disease. Acta Pathol Microbiol Scand. 1960;49:270–271. doi: 10.1111/j.1699-0463.1960.tb01138.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- DINTER Z., PHILIPSON L. An interferon produced by foot and mouth disease virus (FMDV) in calf kidney cells. Proc Soc Exp Biol Med. 1962 Apr;109:893–897. doi: 10.3181/00379727-109-27370. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Edelman R., Wheelock E. F. Specific role of each human leukocyte type in viral infections. II. Phytohemagglutinin-treated lymphocytes as host cells for vesicular stomatitis virus replication in vitro. J Virol. 1968 May;2(5):440–448. doi: 10.1128/jvi.2.5.440-448.1968. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- FULLER W., WILKINS M. H., WILSON H. R., HAMILTON L. D. THE MOLECULAR CONFIGURATION OF DEOXYRIBONUCLEIC ACID. IV. X-RAY DIFFRACTION STUDY OF THE A FORM. J Mol Biol. 1965 May;12:60–76. doi: 10.1016/s0022-2836(65)80282-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Field A. K., Lampson G. P., Tytell A. A., Nemes M. M., Hilleman M. R. Inducers of interferon and host resistance, IV. Double-stranded replicative form RNA (MS2-Ff-RNA) from E. coli infected with MS2 coliphage. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1967 Nov;58(5):2102–2108. doi: 10.1073/pnas.58.5.2102. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Field A. K., Tytell A. A., Lampson G. P., Hilleman M. R. Inducers of interferon and host resistance. II. Multistranded synthetic polynucleotide complexes. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1967 Sep;58(3):1004–1010. doi: 10.1073/pnas.58.3.1004. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- HAMILTON L. D., BARCLAY R. K., WILKINS M. H., BROWN G. L., WILSON H. R., MARVIN D. A., EPHRUSSI-TAYLOR H., SIMMONS N. S. Similarity of the structure of DNA from a variety of sources. J Biophys Biochem Cytol. 1959 May 25;5(3):397–404. doi: 10.1083/jcb.5.3.397. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hamilton L. D. DNA: models and reality. Nature. 1968 May 18;218(5142):633–637. doi: 10.1038/218633a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lampson G. P., Tytell A. A., Field A. K., Nemes M. M., Hilleman M. R. Inducers of interferon and host resistance. I. Double-stranded RNA from extracts of Penicillium funiculosum. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1967 Aug;58(2):782–789. doi: 10.1073/pnas.58.2.782. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lampson G. P., Tytell A. A., Nemes M. M., Hilleman M. R. Multiple molecular species of interferons of mouse and of rabbit origin. Proc Soc Exp Biol Med. 1966 Feb;121(2):377–384. doi: 10.3181/00379727-121-30783. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- MARVIN D. A., SPENCER M., WILKINS M. H., HAMILTON L. D. The molecular configuration of deoxyribonucleic acid. III. X-ray diffraction study of the C form of the lithium salt. J Mol Biol. 1961 Oct;3:547–565. doi: 10.1016/s0022-2836(61)80021-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Park J. H., Baron S. Herpetic keratoconjunctivitis: therapy with synthetic double-stranded RNA. Science. 1968 Nov 15;162(3855):811–813. doi: 10.1126/science.162.3855.811. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Richmond J. Y. An interferon-like inhibitor of foot-and-mouth disease virus induced by phytohemagglutinin in swine leukocyte cultures. Arch Gesamte Virusforsch. 1969;27(2):282–289. doi: 10.1007/BF01249650. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- SELLERS R. F. Multiplication, interferon production and sensitivity of virulent and attenuated strains of the virus of foot-and-mouth disease. Nature. 1963 Jun 22;198:1228–1229. doi: 10.1038/1981228a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- SELLERS R. F. VIRULENCE AND INTERFERON PRODUCTION OF STRAINS OF FOOT-AND MOUTH DISEASE VIRUS. J Immunol. 1964 Jul;93:6–12. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- SKINNER H. H. Propagation of strains of foot-and-mouth disease virus in unweaned white mice. Proc R Soc Med. 1951 Dec;44(12):1041–1044. doi: 10.1177/003591575104401213. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- THELY M., CHOAY J., DHENNIN L., DHENNIN L. [Virostasis induced in vivo by non-infectious ribonucleic acids]. C R Hebd Seances Acad Sci. 1963 Jan 21;256:1048–1050. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tytell A. A., Lampson G. P., Field A. K., Hilleman M. R. Inducers of interferon and host resistance. 3. Double-stranded RNA from reovirus type 3 virions (reo 3-RNA). Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1967 Oct;58(4):1719–1722. doi: 10.1073/pnas.58.4.1719. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Youngner J. S., Stinebring W. R. Comparison of interferon production in mice by bacterial endotoxin and statolon. Virology. 1966 Jun;29(2):310–316. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(66)90038-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zygraich N., Willems R. Etude d'un interféron induit par le vius aphteux C (Loupoigne) sur cellules testiculaires de veau. Bull Off Int Epizoot. 1967 May-Jun;67(5):731–744. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]



