Abstract
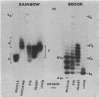
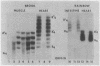
Lactate dehydrogenase is a tetrameric enzyme, generally composed of one or two kinds of subunits each encoded in a separate gene. Most vertebrates synthesize five major isozymic forms of lactate dehydrogenase, but the salmonid fish, particularly trout, synthesize many more. The numerous lactate dehydrogenase isozymes of trout can be selectively removed from tissue homogenates by suitably prepared antisera to specific lactate dehydrogenase subunits of fish. Electrophoretic resolution of such antisera-treated homogenates then permits an identification of each isozyme and a determination of its subunit composition and probable genetic basis. Such data indicate that trout are tetraploid organisms and have duplicate and slightly different loci for two and perhaps three of the lactate dehydrogenase loci found in other fish. The evolutionary relationships among the lactate dehydrogenase loci can also be assessed by these immunochemical data.
Full text
PDF





Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- APPELLA E., MARKERT C. L. Dissociation of lactate dehydrogenase into subunits with guanidine hydrochloride. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1961 Nov 20;6:171–176. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(61)90123-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bailey G. S., Wilson A. C. Homologies between isoenzymes of fishes and those of higher vertebrates. Evidence for multiple H-4 lactate dehydrogenases in trout. J Biol Chem. 1968 Nov 25;243(22):5843–5853. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cahn R. D., Zwilling E., Kaplan N. O., Levine L. Nature and Development of Lactic Dehydrogenases: The two major types of this enzyme form molecular hybrids which change in makeup during development. Science. 1962 Jun 15;136(3520):962–969. doi: 10.1126/science.136.3520.962. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- GOLDBERG E. LACTATE DEHYDROGENASES IN TROUT: EVIDENCE FOR A THIRD SUBUNIT. Science. 1965 Apr 16;148(3668):391–392. doi: 10.1126/science.148.3668.391. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- KAPLAN N. O., CIOTTI M. M. Evolution and differentiation of dehvdrogenases. Ann N Y Acad Sci. 1961 Nov 2;94:701–722. doi: 10.1111/j.1749-6632.1961.tb35567.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- KAPLAN N. O., CIOTTI M. M., HAMOLSKY M., BIEBER R. E. Molecular heterogeneity and evolution of enzymes. Science. 1960 Feb 12;131(3398):392–397. doi: 10.1126/science.131.3398.392. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Markert C. L., Faulhaber I. Lactate dehydrogenase isozyme patterns of fish. J Exp Zool. 1965 Aug;159(3):319–332. doi: 10.1002/jez.1401590304. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Markert C. L. Lactate Dehydrogenase Isozymes: Dissociation and Recombination of Subunits. Science. 1963 Jun 21;140(3573):1329–1330. doi: 10.1126/science.140.3573.1329. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Massaro E. J., Markert C. L. Isozyme patterns of salmoid fishes: evidence for multiple cistrons for lactate dehydrogenase polypeptides. J Exp Zool. 1968 Jun;168(2):223–238. doi: 10.1002/jez.1401680210. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ohno S., Wolf U., Atkin N. B. Evolution from fish to mammals by gene duplication. Hereditas. 1968;59(1):169–187. doi: 10.1111/j.1601-5223.1968.tb02169.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- WILSON A. C., KAPLAN N. O., LEVINE L., PESCE A., REICHLIN M., ALLISON W. S. EVOLUTION OF LACTIC DEHYDROGENASES. Fed Proc. 1964 Nov-Dec;23:1258–1266. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]