Abstract
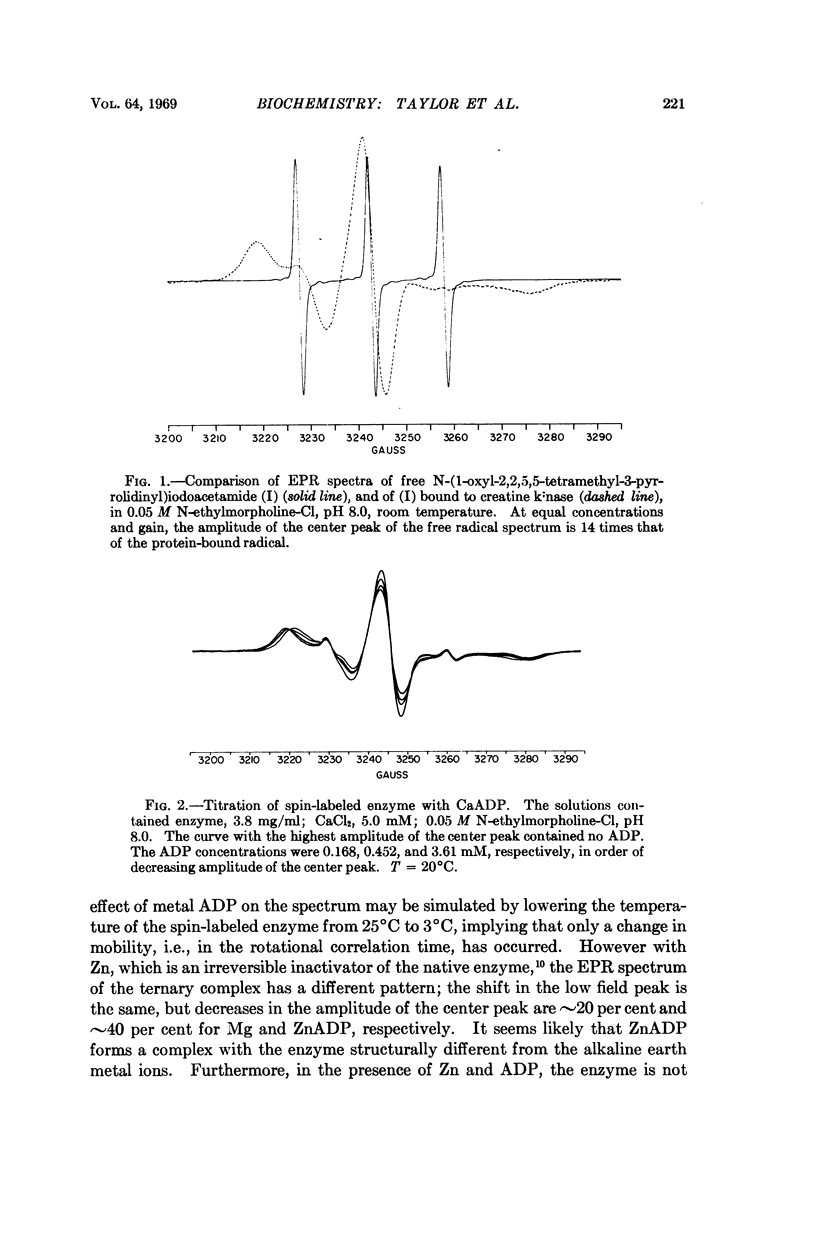
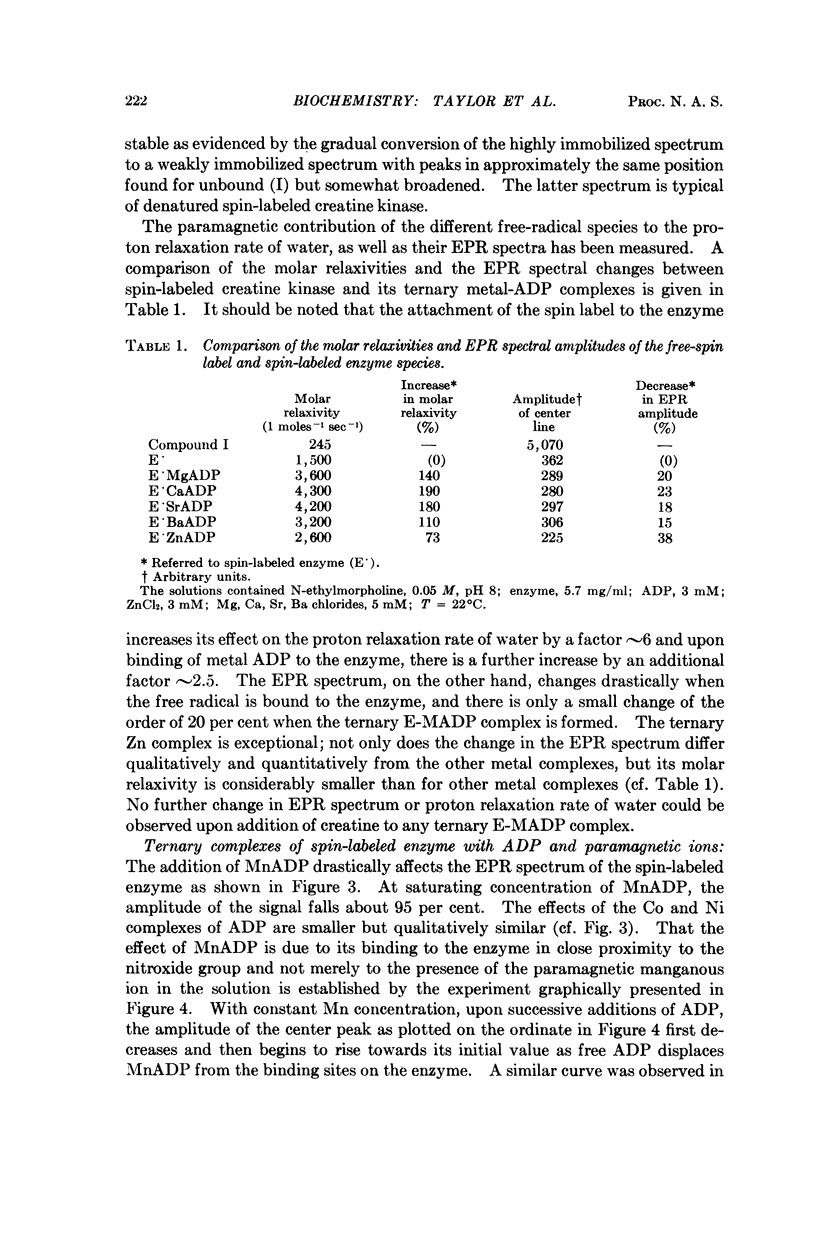
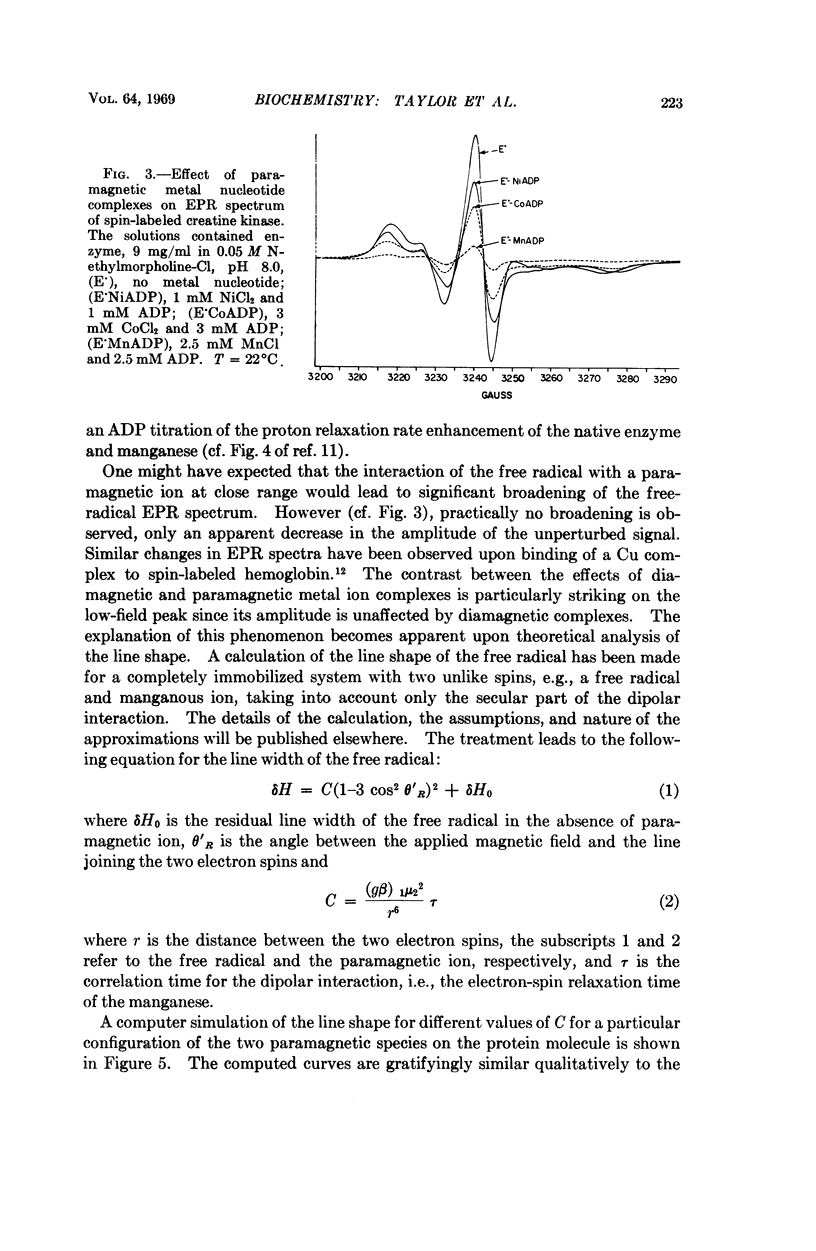
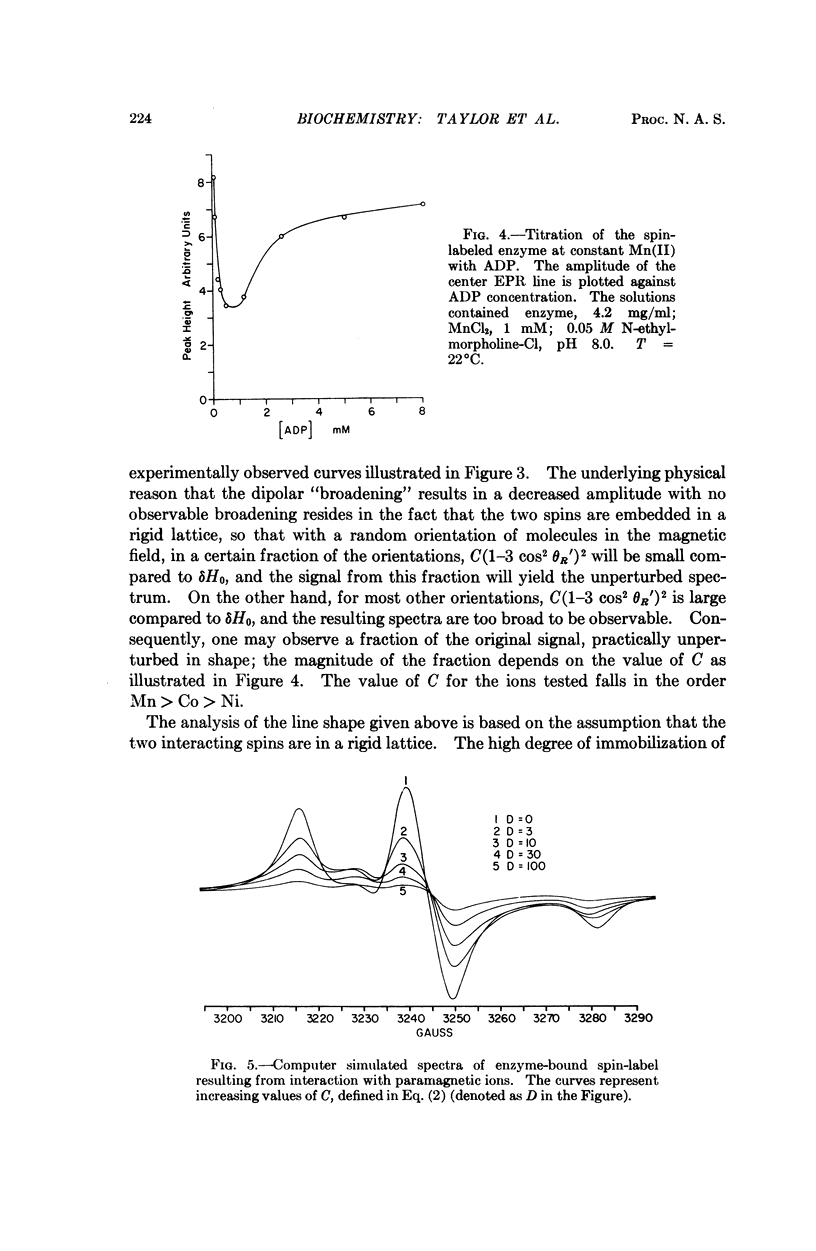
Creatine kinase from rabbit muscle has been specifically labeled with a derivative of a nitroxide free radical on the two essential sulfhydryl groups, one per active site. The conformation in the environment of the enzyme-bound free radical and the change in conformation induced upon binding of the substrate, metal adenosine diphosphate, has been monitored by two parameters of the bound spin label, its electron paramagnetic resonance spectrum and its contribution to the proton relaxation rate of water. The specificity in activation of the enzymic reaction of the series of alkaline earth ions, Mg, Ca, Sr, Ba, was not reflected by differences in conformation of the ternary enzyme metal substrate complexes observable with the spin probe. However, with the inhibitory zinc ion, the conformation of ternary complex was distinctly different. The electron paramagnetic resonance spectra of complexes with two paramagnetic probes, namely, spin-labeled enzyme with paramagnetic metal adenosine diphosphate complexes (Mn(II), Ni(II), and Co(II)) revealed a spin-spin interaction between the protein-bound free radical and the paramagnetic metal ions. From the magnitude of the interaction, the distance between the manganous ion and the electron spin of the nitroxide moiety in the MnADP-spin-labeled creatine kinase was estimated to be in the range of 7-10 Å.
Full text
PDF



Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- COHN M. MAGNETIC RESONANCE STUDIES OF METAL ACTIVATION OF ENZYMIC REACTIONS OF NUCLEOTIDES AND OTHER PHOSPHATE SUBSTRATES. Biochemistry. 1963 Jul-Aug;2:623–629. doi: 10.1021/bi00904a001. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- KUBY S. A., NODA L., LARDY H. A. Adenosinetriphosphate-creatine transphosphorylase. I. Isolation of the crystalline enzyme from rabbit muscle. J Biol Chem. 1954 Jul;209(1):191–201. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kruger G. J., Boeyens J. C. The crystal and molecular structure of the potassium salt of 2,2,5,5-tetramethyl-3-carboxypyrroline-1-oxyl. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1968 Oct;61(2):422–428. doi: 10.1073/pnas.61.2.422. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Likhtenshtein G. I., Bobodzhanov P. Kh. Issledovanie struktury i lokal'nykh konformatsionnykh perekhodov belkov i fermentov metodom dvoinykh paramagnitnykh metok. Biofizika. 1968 Sep-Oct;13(5):757–764. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- MAHOWALD T. A., NOLTMANN E. A., KUBY S. A. Studies on adenosine triphosphate transphosphorylases. III. Inhibition reactions. J Biol Chem. 1962 May;237:1535–1548. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- O'SULLIVAN W. J., MORRISON J. F. THE EFFECT OF TRACE METAL CONTAMINANTS AND EDTA ON THE VELOCITY OF ENZYME-CATALYSED REACTIONS. STUDIES ON ATP:CREATINE PHOSPHOTRANSFERASE. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1963 Sep 3;77:142–144. doi: 10.1016/0006-3002(63)90478-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- O'Sullivan W. J., Cohn M. Magnetic resonance investigations of the metal complexes formed in the manganese-activated creatine kinase reaction. J Biol Chem. 1966 Jul 10;241(13):3104–3115. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- O'Sullivan W. J., Cohn M. Magnetic resonance studies on inactivated forms of creatine kinase. J Biol Chem. 1968 May 25;243(10):2737–2744. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- O'Sullivan W. J., Cohn M. Nucleotide specificity and conformation of the active site of creatine kinase. Magnetic resonance and sulfhydryl reactivity studies. J Biol Chem. 1966 Jul 10;241(13):3116–3125. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- WATTS D. C., RABIN B. R. A study of the 'reactive' sulphydryl groups of adenosine 5'-triphosphate-creatine phosphotransferase. Biochem J. 1962 Dec;85:507–516. doi: 10.1042/bj0850507. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


