Abstract
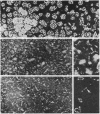
Ultracentrifugal and electron microscopic studies of human serum low-density lipoprotein (LDL) and several of its derivatives led to the formulation of a model in which the 20 protein subunits, probably globular, are arranged in a dodecahedral pattern with icosahedral symmetry. In such a model the LDL surface is occupied by both protein and lipids, predominantly phospholipids, as supported by the results of the hydrolysis of LDL by phospholipase A and C. Neutral lipids (cholesterol esters and glycerides) would be in the interior of the molecule.
Full text
PDF




Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Bruckdorfer K. R., Edwards P. A., Green C. Properties of aqueous dispersions of phospholipid and cholesterol. Eur J Biochem. 1968 May;4(4):506–511. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1968.tb00241.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Day C. E., Levy R. S. Determination of the molecular weight of apoprotein subunits from low density lipoprotein by gel filtration. J Lipid Res. 1968 Nov;9(6):789–793. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fischbach F. A., Harrison P. M., Hoy T. G. The structural relationship between ferritin protein and its mineral core. J Mol Biol. 1969 Jan 14;39(1):235–238. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(69)90344-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gotto A. M., Levy R. I., Lindgren F. T., Fredrickson D. S. Partial delipidation of human serum beta-lipoprotein by sodium decyl sulfate. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1969 Apr 29;176(3):667–669. doi: 10.1016/0005-2760(69)90241-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Granda J. L., Scanu A. Solubilization and properties of the apoproteins of the very low- and low-density lipoproteins of human serum. Biochemistry. 1966 Oct;5(10):3301–3308. doi: 10.1021/bi00874a032. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hade E. P., Tanford C. Isopiestic compositions as a measure of preferential interactions of macromolecules in two-component solvents. Application to proteins in concentrated aqueous cesium chloride and guanidine hydrochloride. J Am Chem Soc. 1967 Sep 13;89(19):5034–5040. doi: 10.1021/ja00995a036. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jeffrey P. D. An associating low-sulfur protein from wool. Biochemistry. 1968 Oct;7(10):3352–3360. doi: 10.1021/bi00850a007. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Scanu A. M. Factors affecting lipoprotein metabolism. Adv Lipid Res. 1965;3:63–138. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Scanu A., Pollard H., Hirz R., Kothary K. On the conformational instability of human serum low-density lipoprotein: effect of temperature. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1969 Jan;62(1):171–178. doi: 10.1073/pnas.62.1.171. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Scanu A., Pollard H., Reader W. Properties of human serum low density lipoproteins after modification by succinic anhydride. J Lipid Res. 1968 May;9(3):342–349. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shore B., Shore V. The protein moiety of human serum beta-lipoproteins. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1967 Sep 27;28(6):1003–1007. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(67)90080-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- VANDENHEUVEL F. A. The origin, metabolism, and structure of normal human serum lipoproteins. Can J Biochem Physiol. 1962 Sep;40:1299–1326. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- YPHANTIS D. A. EQUILIBRIUM ULTRACENTRIFUGATION OF DILUTE SOLUTIONS. Biochemistry. 1964 Mar;3:297–317. doi: 10.1021/bi00891a003. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]