Abstract
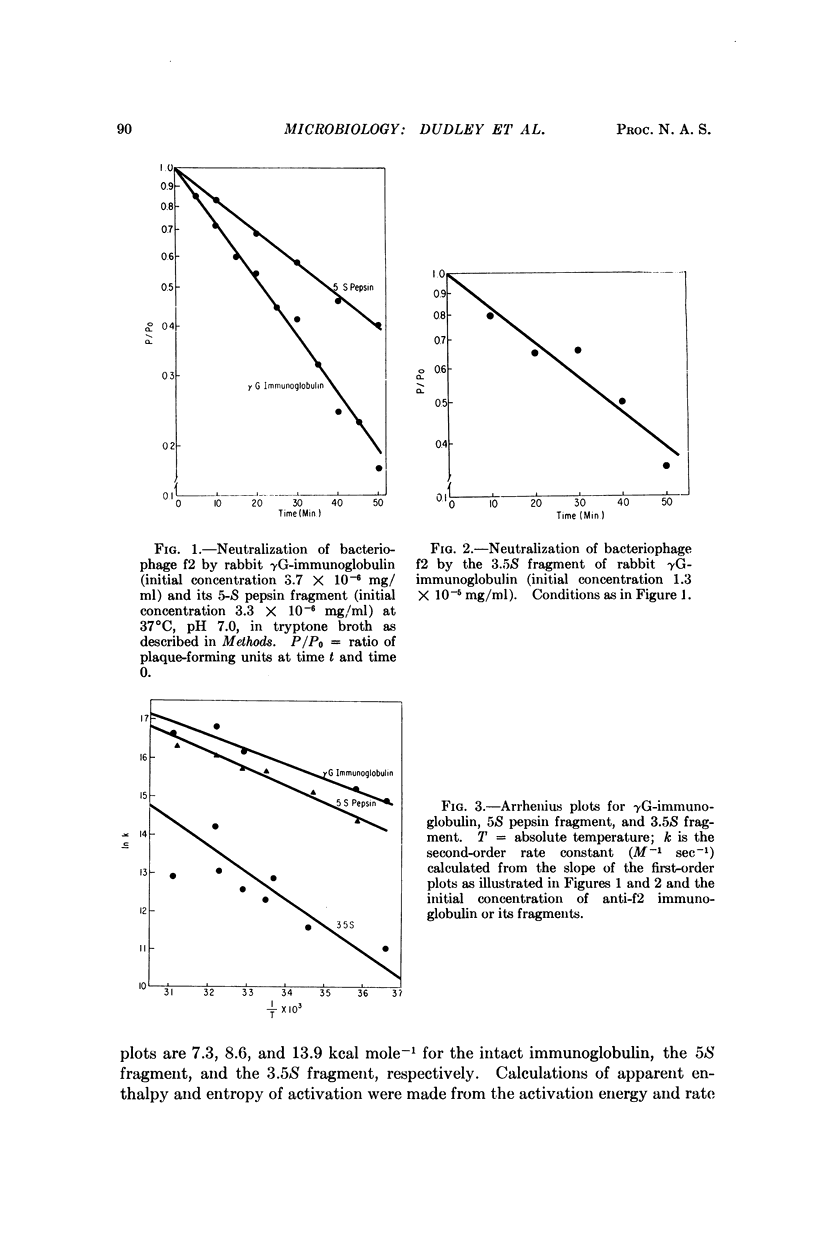
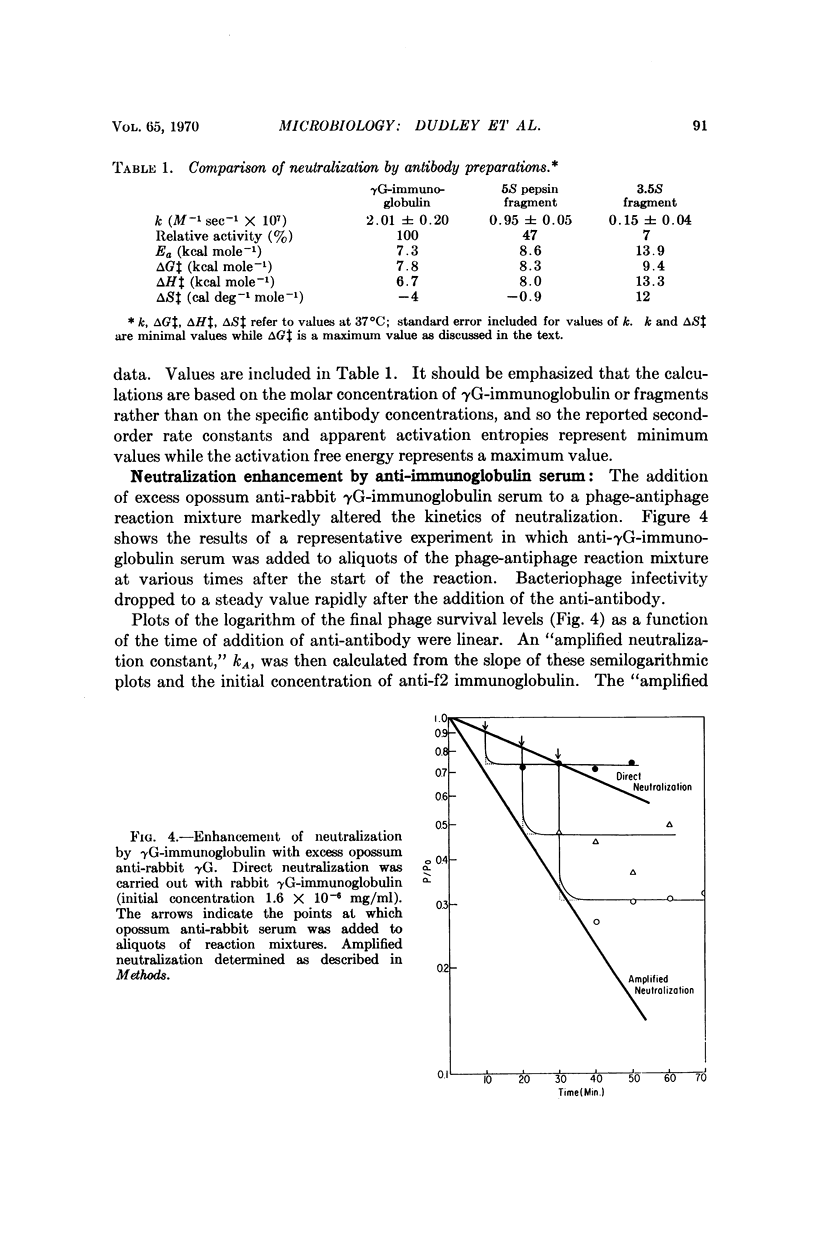
The neutralization of bacteriophage f2 by intact γG-immunoglobulin or fragments is first order with respect to both bacteriophage and antibody. Minimum values for the rate constants are of the order of 107 M-1 sec-1. The temperature dependence of the rates corresponds to the activation parameters: ΔH‡ = 6.7 kcal mole-1 and ΔS‡ = -4 cal deg-1 mole-1 (γG-immunoglobulin); ΔH‡ = 8.0 kcal mole-1 and ΔS‡ = -0.9 cal deg-1 mole-1 (5S pepsin fragment); and ΔH‡ = 13.3 kcal mole-1 and ΔS‡ = 12 cal deg-1 mole-1 (3.5S fragment). The kinetic observations are consistent with the view that the binding of a single antibody molecule can bring about phage neutralization. There are two ways in which a single antibody molecule can affect neutralization: (1) binding at or near some critical site on the phage may block its function, (2) binding may disturb the general architectural design of the protein shell of the phage. Although the rate of neutralization varied directly with antibody size, consideration of the activation parameters speaks against the dependence of neutralization on simple steric factors. Addition of antibodies directed against rabbit γG-immunoglobulin or the 5S pepsin fragment caused approximately a threefold neutralization enhancement. This enhancement may result from the detection of a class of infectious bacteriophage antibody complexes.
Full text
PDF





Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- CRICK F. H., WATSON J. D. Structure of small viruses. Nature. 1956 Mar 10;177(4506):473–475. doi: 10.1038/177473a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- DULBECCO R., VOGT M., STRICKLAND A. G. A study of the basic aspects of neutralization of two animal viruses, western equine encephalitis virus and poliomyelitis virus. Virology. 1956 Apr;2(2):162–205. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(56)90017-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- FINCH J. T., KLUG A. Structure of poliomyelitis virus. Nature. 1959 Jun 20;183(4677):1709–1714. doi: 10.1038/1831709a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- GOODMAN J. W., DONCH J. J. NEUTRALIZATION OF BACTERIOPHAGE BY INTACT AND DEGRADED RABBIT ANTIBODY. J Immunol. 1964 Jul;93:96–100. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Goodman J. W., Donch J. J. Phage-neutralizing activity in light polypeptide chains of rabbit antibody. Immunochemistry. 1965 Dec;2(4):351–357. doi: 10.1016/0019-2791(65)90035-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- KLUG A., CASPAR D. L. The structure of small viruses. Adv Virus Res. 1960;7:225–325. doi: 10.1016/s0065-3527(08)60012-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Krummel W. M., Uhr J. W. A mathematical and experimental study of the kinetics of neutralization of bacteriophage phi chi 174 by antibodies. J Immunol. 1969 Mar;102(3):772–785. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- LEVY H. B., SOBER H. A. A simple chromatographic method for preparation of gamma globulin. Proc Soc Exp Biol Med. 1960 Jan;103:250–252. doi: 10.3181/00379727-103-25476. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- LOEB T., ZINDER N. D. A bacteriophage containing RNA. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1961 Mar 15;47:282–289. doi: 10.1073/pnas.47.3.282. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- NISONOFF A., WISSLER F. C., LIPMAN L. N., WOERNLEY D. L. Separation of univalent fragments from the bivalent rabbit antibody molecule by reduction of disulfide bonds. Arch Biochem Biophys. 1960 Aug;89:230–244. doi: 10.1016/0003-9861(60)90049-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rowlands D. T., Jr Precipitation and neutralization of bacteriophage f2 by rabbit antibodies. J Immunol. 1967 May;98(5):958–964. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- SCHEIDEGGER J. J. Une micro-méthode de l'immuno-electrophorèse. Int Arch Allergy Appl Immunol. 1955;7(2):103–110. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stemke G. W., Lennox E. S. Bacteriophage neutralizing activity of fragments derived from rabbit immunoglobulin by papain digestion. J Immunol. 1967 Jan;98(1):94–101. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Weber K., Notani G., Wikler M., Konigsberg W. Amino acid sequence of the f2 coat protein. J Mol Biol. 1966 Sep;20(2):423–425. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(66)90073-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]



