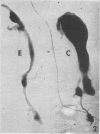
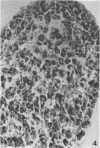
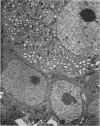
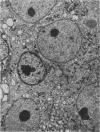
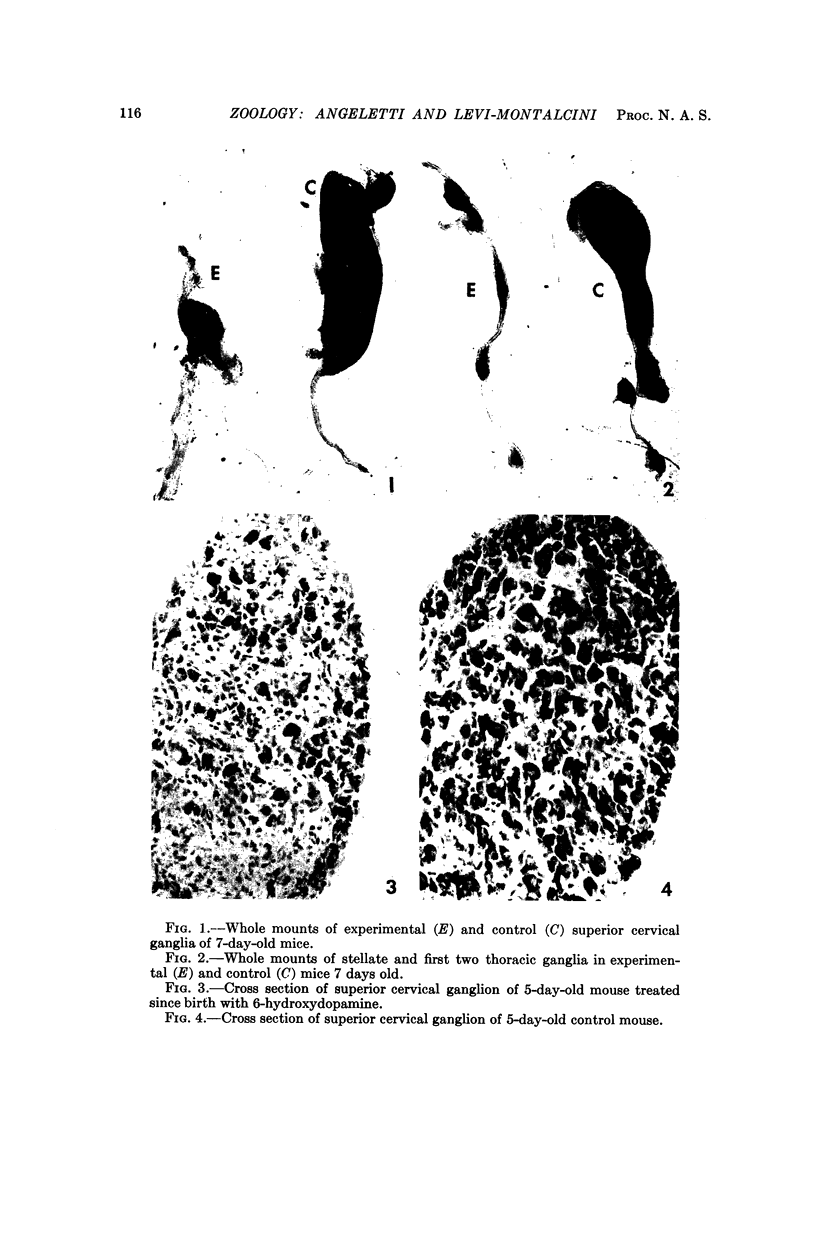
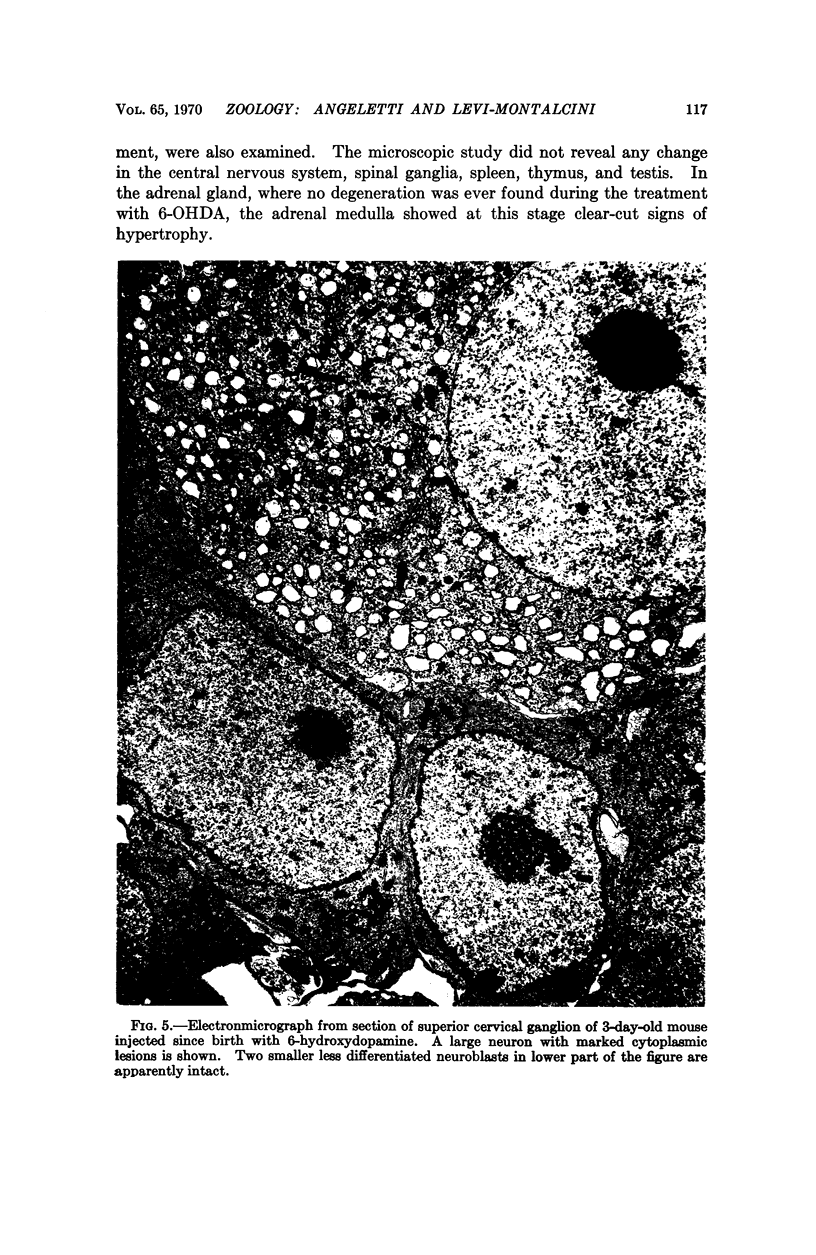
Abstract
A selective and permanent destruction of sympathetic ganglia was achieved by injecting 6-hydroxydopamine in newborn animals. A lifelong chemical sympathectomy may thus be obtained. The process of cell damage and destruction is substantially different from that produced with an antiserum to a specific nerve growth factor.
Full text
PDF





Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Angeletti P. U., Levi-Montalcini R., Calissano P. The nerve growth factor (NGF): chemical properties and metabolic effects. Adv Enzymol Relat Areas Mol Biol. 1968;31:51–75. doi: 10.1002/9780470122761.ch2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cohen S. PURIFICATION OF A NERVE-GROWTH PROMOTING PROTEIN FROM THE MOUSE SALIVARY GLAND AND ITS NEURO-CYTOTOXIC ANTISERUM. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1960 Mar;46(3):302–311. doi: 10.1073/pnas.46.3.302. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Levi-Montalcini R., Angeletti P. U. Nerve growth factor. Physiol Rev. 1968 Jul;48(3):534–569. doi: 10.1152/physrev.1968.48.3.534. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Levi-Montalcini R., Angeletti P. U. Second symposium on catecholamines. Modification of sympathetic function. Immunosympathectomy. Pharmacol Rev. 1966 Mar;18(1):619–628. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Levi-Montalcini R., Booker B. EXCESSIVE GROWTH OF THE SYMPATHETIC GANGLIA EVOKED BY A PROTEIN ISOLATED FROM MOUSE SALIVARY GLANDS. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1960 Mar;46(3):373–384. doi: 10.1073/pnas.46.3.373. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Levi-Montalcini R., Caramia F., Angeletti P. U. Alterations in the fine structure of nucleoli in sympathetic neurons following NGF-antiserum treatment. Brain Res. 1969 Jan;12(1):54–73. doi: 10.1016/0006-8993(69)90055-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Levi-Montalcini R., Cohen S. IN VITRO AND IN VIVO EFFECTS OF A NERVE GROWTH-STIMULATING AGENT ISOLATED FROM SNAKE VENOM. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1956 Sep;42(9):695–699. doi: 10.1073/pnas.42.9.695. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Levi-Montalcini R. The nerve growth factor: its mode of action on sensory and sympathetic nerve cells. Harvey Lect. 1966;60:217–259. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- PORTER C. C., TOTARO J. A., STONE C. A. Effect of 6-hydroxydopamine and some other compounds on the concentration of norepinephrine in the hearts of mice. J Pharmacol Exp Ther. 1963 Jun;140:308–316. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Porter C. C., Totaro J. A., Burcin A. The relationship between radioactivity and norepinephrine concentrations in the brains and hearts of mice following administration of labeled methyldopa or 6-hydroxydopamine. J Pharmacol Exp Ther. 1965 Oct;150(1):17–22. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Thoenen H., Tranzer J. P. Chemical sympathectomy by selective destruction of adrenergic nerve endings with 6-Hydroxydopamine. Naunyn Schmiedebergs Arch Exp Pathol Pharmakol. 1968;261(3):271–288. doi: 10.1007/BF00536990. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tranzer J. P., Thoenen H. An electron microscopic study of selective, acute degeneration of sympathetic nerve terminals after administration of 6-hydroxydopamine. Experientia. 1968 Feb 15;24(2):155–156. doi: 10.1007/BF02146956. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tranzer J. P., Thoenen H., Snipes R. L., Richards J. G. Recent developments on the ultrastructural aspect of adrenergic nerve endings in various experimental conditions. Prog Brain Res. 1969;31:33–46. doi: 10.1016/S0079-6123(08)63225-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zanini A., Angeletti P., Levi-Montalcini R. Immunochemical properties of the nerve growth factor. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1968 Nov;61(3):835–842. doi: 10.1073/pnas.61.3.835. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]