Abstract
BACKGROUND
Blockade of androgen activity is a major effective therapy for advanced prostate cancer. Estrogen analogs have been used for prostate cancer therapy for years presumably by inhibiting testosterone biosyntheses, but with considerable adverse events due to their classic estrogenic activity. With the discovery of the estrogen receptor (ER) β and its presence in prostate tumor cells, evaluation of estrogen analogs with less classic estrogenic activity in prostate cancer therapy is emerging.
METHODS
The effects of 17α-estradiol (αE2), a stereo-isomer of 17β-estradiol (βE2), on dihydrotestosterone (DHT)-induced cell growth and gene expressions were examined in androgen-dependent LAPC-4 prostatic tumor cells and in LAPC-4 xenograft animals, and compared to those of βE2.
RESULTS
Both αE2 and βE2 attenuated DHT induction of PSA gene expression, cell proliferation, and cell growth in cultured LAPC-4 cells. The inhibition of cell proliferation was associated with a blockade of DHT-induced cyclin A and cyclin D1 expression by αE2 and βE2. In LAPC-4 xenograft mice, αE2 significantly inhibited tumor growth without altering the plasma testosterone level, while βE2 failed to inhibit tumor growth even though it significantly inhibited PSA gene expression.
CONCLUSION
αE2 is an effective agent for inhibition of DHT-induced PSA, cyclin A, cyclin D1 gene expression, and cell proliferation in LAPC-4 cells, and tumor growth in LAPC-4 xenograft mice.
Keywords: androgen, prostate cancer, 17α-estradiol, cyclins
INTRODUCTION
Prostate cancer is one of the most common malignancies and the second leading cause of tumor-related mortality in American males [1]. Androgens play key roles in the development and growth of prostate cancer. Androgen ablation is still the mainstay for the treatment of advanced prostate cancer [2]. It is a strategy established to inhibit the effect of androgens on the stimulation of prostate cancer and can be accomplished by surgery or medical castration using hormones including estrogens [3]. Estrogens have been used for the treatment of advanced prostate cancer since studies pioneered by Huggins et al. in the 1940’s [4]. They presumably act by inhibiting testosterone biosynthesis through the negative feedback of the hypothalamic–pituitary–gonadal axis [5]. The use of estrogens in androgen ablation therapy is however limited in clinical practice due to cardiovascular side effects [6]. The recent discovery of estrogen receptor (ER) isoform, ERβ, and the demonstration of direct inhibition of androgen receptor (AR) activity by estrogens in prostate cells have stimulated the development of ER isoform specific ligands, which appear to have less classic estrogenic side effects while retaining tumor inhibitory action. These findings have also promoted the re-evaluation of the implications of estrogen analogs in prostate cancer prevention and treatment [7–9].
17α-Estradiol (αE2), an isomer of 17β-estradiol (βE2), has been shown to act differently from βE2 in that it binds weakly to the ER, and the αE2–ER complex only transiently binds to the estrogen-responsive element [2,10,11]. Consequently, αE2 is significantly less active as a classic estrogen than βE2 [12,13] and is incapable of stimulating uterine growth [10]. It has been demonstrated that αE2 has no carcinogenic effect on mammalian model systems [12–14], and is less effective on the vascular smooth muscle system [15]. αE2, however, does share some important functions with βE2. Its microtubule disruption potential is equal to that of diethylstilbesterol or βE2 [16]. αE2 and βE2 both protect the neuroblastoma cell line, SK-N-SH cell, from serum starvation [17]. Furthermore, αE2 is as effective as βE2 in repressing prostatic cancer cell growth [18]. Taken together, it suggests that αE2 has potential as a new and novel candidate for the prevention and treatment of prostate cancer.
We have previously shown that estrogens including αE2 and βE2 which act on ERs are able to inhibit androgen-induced PSA gene expression and prostatic tumor cell growth [18]. In the present study, we further analyzed the effects of αE2 and βE2 in LAPC-4 prostatic tumor cells, and explored their in vivo effectiveness in inhibiting tumor growth in xenograft animals with LAPC-4 prostate cancer. The results of this study suggest that androgen-induced LAPC-4 cell growth is mainly mediated via regulation of cyclin activity, which is inhibited by the concomitant administration of αE2 and βE2; and that αE2 is effective in inhibiting tumor growth in xenograft animals with LAPC-4 prostate cancer, warranting further investigation.
MATERIALS AND METHODS
Chemicals, Antibodies, and Reagents
αE2, βE2, dihydrotestosterone (DHT) were purchased from Sigma Co. (St. Louis, MO), and dissolved in absolute ethanol at a stock concentration of 10−2 M. R1881 (methytrienolone) was obtained from Dupont NEN Life Science Products (Boston, MA). Roscovitine and antibodies against human cyclin A (C4710), and α-tubulin were obtained from Sigma. All real-time PCR reagents were purchased from Invitrogen (Carlsbad, CA). Hormone pellets for animal study were purchased from Hormone Pellet Press (Leawood, KS).
Cell Proliferation and Caspase 3/7 Activity Assays
LAPC-4 prostate tumor cells (a gift from Dr. C. Sawyer), an androgen-dependent cell line [19], were cultured in Isove’s modified Eagle’s medium (IMEM) which was supplemented with 15% fetal bovine serum, 2 mM l-glutamine, 1 nM R1881, 50 units/ml of penicillin, and 50 µg/ml of streptomycin. R1881 was withdrawn 48 hr before cell passage to conduct the experiments. LAPC-4 cells were plated in 96-well plates with the density indicated in the experiments in phenol-red free IMEM with 5% stripped fetal bovine serum. Twenty-four hours later, they were treated with various hormones as indicated in each experiment, and the media and hormone treatment were replenished every 2–3 days. The numbers of viable cells and the caspase 3/7 activity, a common pathway in cell apoptosis, were determined using the Cell Titer One Solution Cell Proliferation Assay kit and the Caspase-Glo 3/7 Assay kit from Promega (Madison, WI) following the manufacturer’s instruction, respectively.
Bromodeoxyuridine (BrdU) Incorporation Assay
LAPC-4 cells were seeded in 96-well plates. Twenty-four hours later, the cells were treated with DHT, αE2, or βE2 alone or in combination for 72 hr. At the end of experiments, the bromodeoxyuridine (BrdU) incorporation was assayed using a BrdU Cell Proliferation Assay kit from Calbiochem (San Diego, CA) according to the instructions of the manufacturer.
Flow Cytometry
Approximately 1 × 106 LAPC-4 cells were plated in 60-mm plates and treated with vehicle control or 10 nM of DHT for 72 hr. At the end of treatment, cells were collected, washed with phosphate buffered saline (PBS) and fixed with 70% ethanol. For DNA content, cells were stained with propidium iodide (50 µg/ml) plus RNase A (5 µg/ml) in PBS. Stained cells were analyzed using a FACSCalibus flow cytometer (Becton Dickinson, Mountain View, CA). The data from 1.0 × 104 cells per sample were collected, stored, and analyzed using Cellquest software (Becton Dickinson).
Real-Time RT-PCR
Real-time PCR was performed using the comparative CT method according to the instructions of the manufacturer on the ABI Prism 7700 Sequence Detection System (PE Applied Biosystems, Foster City, CA) with some modifications. In brief, total RNA was isolated from cells cultured in 96-well plates with TriPure Isolation Reagent (Roche Diagnostics Corporation, Indianapolis, IN). The total RNA was subjected to two-step realtime RT-PCR using SuperSript™ III Platinum® Two-Step qRT-PCR Kit (Invitrogen). PCR condition was set according to the protocol provided from Invitrogen. PCR primers are listed in Table I. Glyceraldehydes-3-phosphate dehydrogenase (GAPDH) was used as an internal control. The difference between each sample was calculated by following the instructions of the manufacturer (PE Applied Biosystems).
TABLE I.
Primers for Real-Time PCR
| Genes | Primers |
|---|---|
| GAPDH | Forward: 5′-GAAGGTGAAGGTCGGAGTC-3′ |
| Reverse: 5′-GAAGATGGTGATGGGATTTC-3′ | |
| PSA | Forward: 5′-TTGTCTTCCTCACCCTGTCC-3′ |
| Reverse: 5′-CAGGGTTGGGAATGCTTCT-3′ | |
| Cyclin A1 | Forward: 5′-GGGCTCCCAGATTTCGTCT-3′ |
| Reverse: 5′-CTGCAGTGCATTGCTTCAGA-3′ | |
| Cyclin D1 | Forward: 5′-AGGAGAACAAACAGATCATCCG-3′ |
| Reverse: 5′-GAGGGCGGATTGGAAATGAACT-3′ |
Western Blot Analysis
LAPC-4 cells were cultured and treated as described above. At the end of treatment, cells were harvested and the pellets were dissolved in a passive lysis buffer (Promega) and analyzed by Western blot using specific antibodies against cyclin A and α-tubulin as previously described [20]. The specific signals of cyclin A and α-tubulin were quantitated by the Image J software. The difference in cyclin A levels was calculated by comparison to control after normalizing protein input based on α-tubulin levels.
Xenograft Animal Study
A xenograft LAPC-4 tumor model was prepared and monitored as previously described with modifications [19]. Briefly, LAPC-4 cells were cultured and harvested from subconfluent cultures, pelleted by centrifugation, and resuspended in medium. The viable cell numbers were estimated by counting trypan blue excluding cells. The cell suspension was mixed with 50% volume of Matrigel (Collaborative Biomedical Products/Becton Dickinson, Bedford, MA) to a final concentration of 5 × 106 cells per 0.2 ml. An aliquot of 0.2 ml (5 × 106 cells) of the cell suspension were injected into the subcutaneous flank of the intact adult male SCID mice (Harlan Bioproducts for Science Inc, Indianapolis, IN). These animals were housed aseptically in the Animal Facility of Weill Medical College. Tumor growth, body weight and mobility change were checked twice a week. Tumor development was followed in individual animals by caliper measurements of length and width of the tumor. Tumor volume was calculated using the formula: volume = (width)2 × length/2 [21]. The animal study was approved by the Institutional Animal Care And Use Committee and conducted in accordance with accepted standards of humane animal care.
When the tumor was approximately 200 mm3, the animals were randomly assigned to one of the three groups, and implanted subcutaneously with a placebo (20 mg of cholesterol, n = 5), αE2 (2 mg of αE2 plus 18 mg of cholesterol, n = 5), or βE2 (2 mg of βE2 plus 18 mg of cholesterol, n = 4) pellet on the opposite flank. The treatment lasted for 4 weeks and the tumor size was monitored twice a week after pellet implantation. At the end of the experiment, the animals were euthanized by carbon dioxide, and plasma and tumor samples were collected and stored at −80°C until analysis.
Determination of PSA and Testosterone Levels
The levels of PSA in the cell culture media and animal plasma were measured using an ELISA assay, and the levels of total plasma testosterone were measured using a radioimmunoassay from Diagnostic Systems Laboratory (Webster, TX) following the manufacturer’s instructions.
Statistical Analysis
The data are presented as mean ± standard error of the mean (SEM). One-way analysis of variance (ANOVA) following post-hoc Student–Newman–Keuls test was used to determine the difference among multiple groups. A P-value less than 0.05 was considered as statistically significant.
RESULTS
Both αE2 and βE2 Inhibited DHT-Induced PSA Gene Expression and Cell Proliferation in LAPC-4 Prostatic Tumor Cells
To test the influence of αE2 and βE2 on DHT-regulated gene expression, the expression of PSA, an androgen inducible gene, was determined by ELISA for PSA protein in cell culture media and by realtime RT-PCR analysis for PSA mRNA in the cells (Fig. 1A,B). As shown in Figure 1A, treatment with DHT at a dose of 10 nM for 72 hr produced an approximately four-fold induction of PSA in culture medium of LAPC-4 cells. This DHT-induced PSA expression was significantly inhibited by concomitant treatment with either αE2 or βE2 in a dose-dependent manner. The effect of βE2 was more potent than αE2. Changes in PSA mRNA (Fig. 1B) in LAPC-4 cells were parallel to the changes in medium PSA concentration. These results are in agreement with our previous demonstration [18].
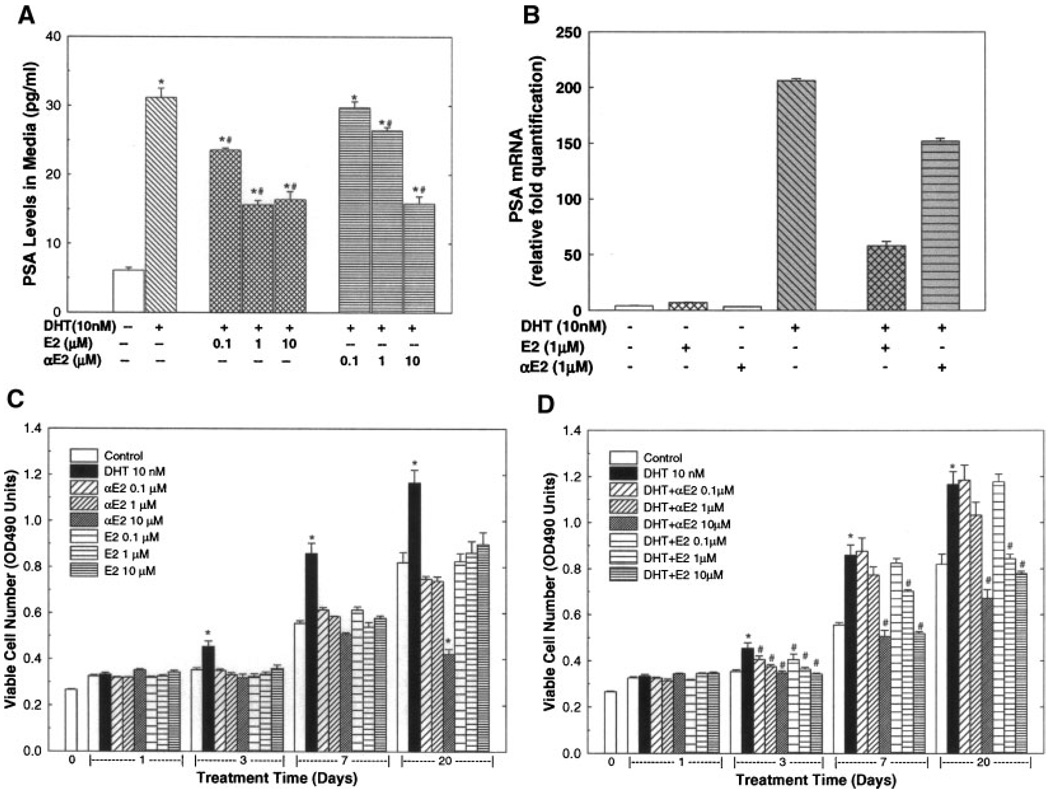
Fig. 1.
The dihydrotestosterone (DHT)-induced prostate specific antigen (PSA) gene expression (A–B) and cell growth (C–D) in LAPC-4 cells were inhibited by estrogens. LAPC-4 cells were cultured as described in the Section “MATERIALS AND METHODS.” In panels A and B, LAPC-4 cells were treated with vehicle control (0.2% ethanol) or DHT (10 nM) with or without various doses of 17β-estradiol (βE2), or 17α-estradiol (αE2) for 72 hr. PSA levels in culture media were determined by ELISA (Panel A). The values are the mean ± SEM of six samples obtained in two independent triplicate experiments. Panel B shows a representative experiment of real-time RT-PCR determination of PSA mRNA in LAPC-4 cells. The values are the mean ± SEM of a duplicate assay. In panels C and D, LAPC-4 cells were treated with vehicle control (0.2% ethanol) or DHT (10 nM) with or without various doses of βE2, or αE2 for 1–20 days. The number of viable cells was determined as described in the Section “MATERIALS AND METHODS” and expressed as OD490 absorbance units. The data are the mean ± SEM of six individual samples of two independent triplicate experiments. *P < 0.05 compared to vehicle control, and #P < 0.05 compared to DHT treatment at the same time point.
To further assess the roles of DHT, αE2, and βE2 in cell growth, LAPC-4 cells were treated with DHT, αE2, or βE2 alone (Fig. 1C), or in combination (Fig. 1D) for various durations up to 20 days, and the numbers of viable cells were determined at the end of experiments. As shown in Figure 1C, treatment with DHT (10 nM) alone produced a time-dependent increase in viable cell number. Compared to the parallel vehicle control, the viable cell numbers were significantly increased by approximately 28, 55, and 43%, respectively, at 3, 7, and 20 days of DHT treatment while a one-day treatment had no significant effect. This DHT-induced cell growth was inhibited by the addition of αE2, or βE2 in a dose dependent manner (Fig. 1D). At doses ranging from 0.1 µM to 10 µM, both αE2 and βE2 significantly attenuated, or completely blocked the DHT-induced cell growth at 3 days of treatment. Similar inhibition of cell growth by αE2 and βE2 were observed at 7 and 20 days of treatment. Treatment with αE2 or βE2 alone at doses of 0.1–10 µM did not significantly affect viable cell numbers except αE2 treatment at 10 µM for 20 days significantly decreased cell growth as shown in Figure 1C.
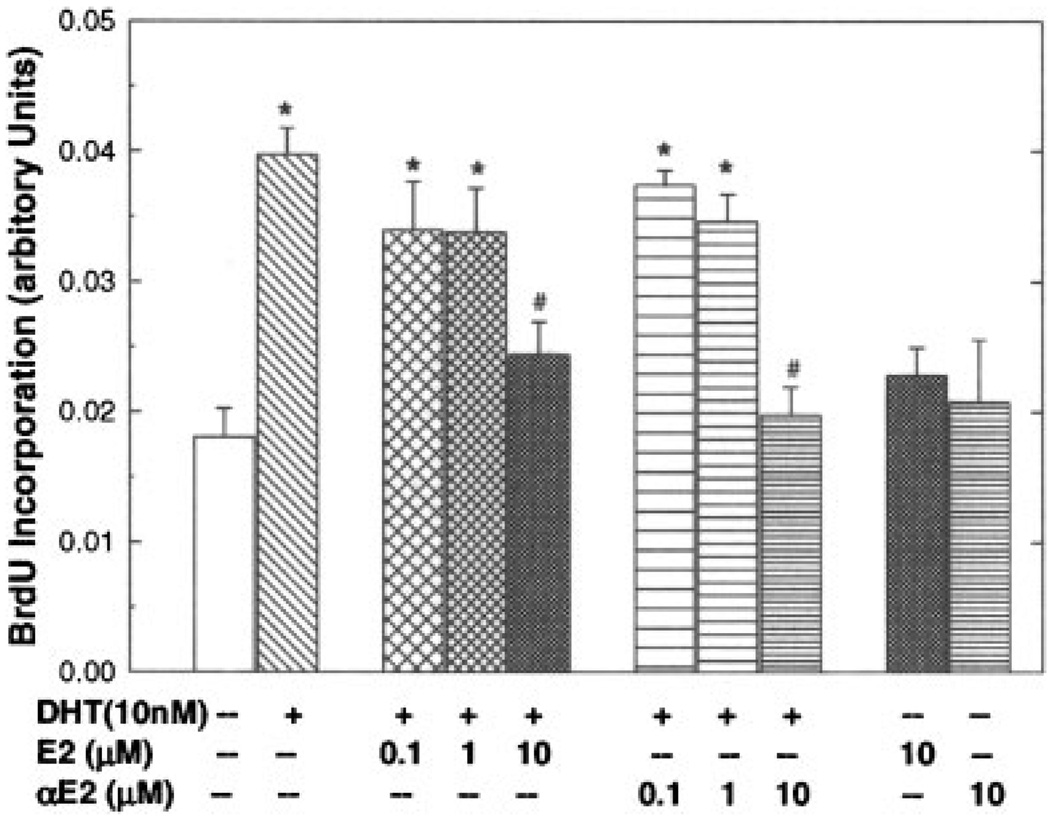
DHT-induced cell growth was associated with increases in DNA biosynthesis and quiescent cells entering into cell cycle. As shown in Figure 2, DNA biosynthesis as measured by BrdU incorporation in LAPC-4 cells was greatly elevated after DHT (10 nM) treatment for 72 hr. This DHT-induced DNA biosynthesis was significantly inhibited by the coadministration of αE2 or βE2 in a dose-dependent manner. Moreover, treatment with DHT (10 nM) for 72 hr resulted in a decrease in G1 cells from 37 to 28%, while an increase in percentage of cells in S and G2/M phases from 49 to 57% as determined by flow cytometry without notable change in sub-G1 fraction (7.2% in control vs. 7.0% in DHT group), the apoptotic cell fraction (data not shown). The effects of these steroid hormones on cell apoptosis were further evaluated by analyzing cell caspase 3/7 activity and DNA fragmentation. Treatment with DHT (10 nM), or αE2 (0.1–10 µM), or βE2 (0.1–10 µM) alone or in combination for 20 days neither altered caspase 3/7 activity, nor caused DNA fragmentation in LAPC-4 cells (data not shown).
Fig. 2.
Both 17α-estradiol (αE2) and 17β-estradiol(βE2) inhibited DHT-induced BrdU incorporation in LAPC-4 cells. LAPC-4 cells were treated as indicated for 72 hr. BrdU incorporation assay was performed as described in the Section “Materials and Methods.” The relative absorbance values were calculated by the real absorbance values from various treated samples divided by percentage of cell number that were obtained from cell proliferation assay when the vehicle control (0.2% ethanol) was considered as 100 percent. The values are the mean ± SEM of a triplicate experiment. *P < 0.05 compared to vehicle control, and P < 0.05 compared to DHT treatment. Similar result was obtained from another independent experiment.
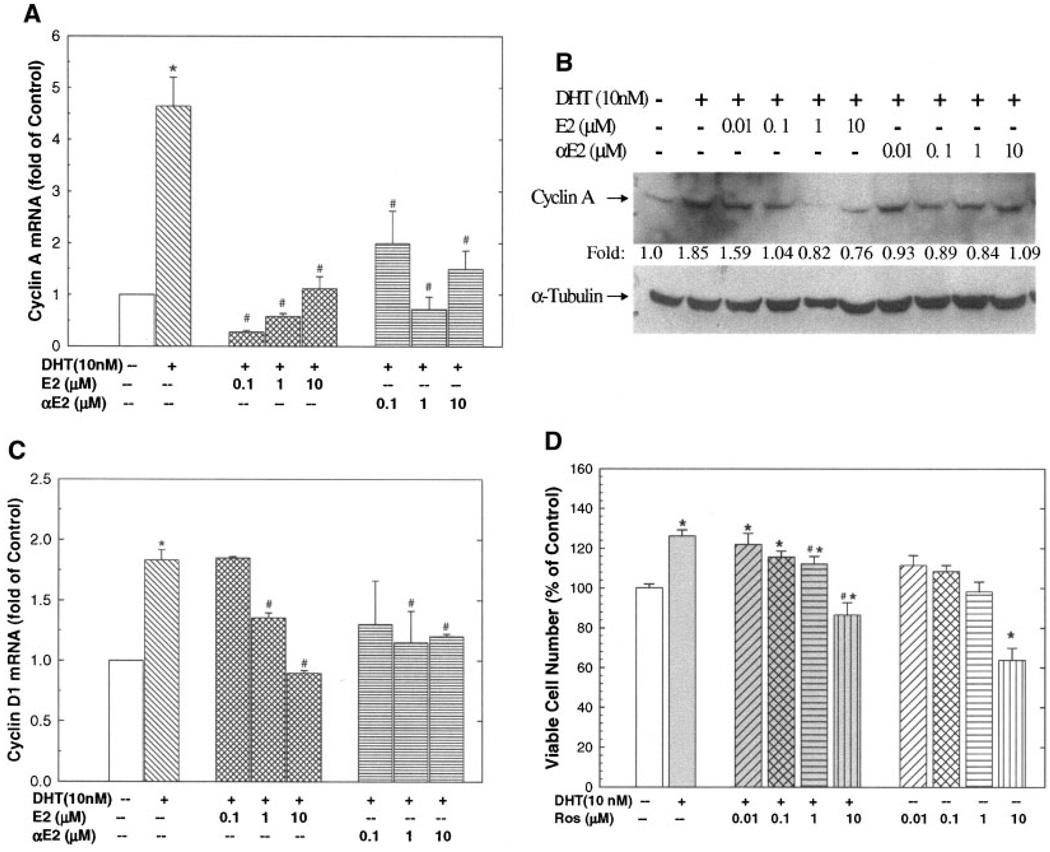
DHT-Induced Cyclin A and Cyclin D1 Expression in LAPC-4 Cells, Which Were Inhibited by αE2 or βE2
To decipher the potential molecular mechanisms of DHT and estrogen actions on LAPC-4 cell growth, the expression of cell cycle genes were investigated. Androgen and estrogen have been reported to regulate the expression of cell cycle genes such as cyclin D1, cyclin A, and cyclin B1, and therefore interfere with cell cycle progression and cell proliferation [22,23]. As shown in Figure 3, treatment with DHT (10 nM) for 72 hr elevated cyclin A gene expression as demonstrated by real-time RT-PCR analysis of cyclin A mRNA (Fig. 3A) and Western blot analysis of cyclin A protein (Fig. 3B). This DHT treatment also increased the cyclin D1 expression (Fig. 3C) without significant effect on cyclin B1 expression (data not shown). Moreover, the DHT-induced cyclin expression in LAPC-4 cells was significantly blocked by the coadministration of either αE2 or βE2 at doses ranging from 0.1 to 10 µM (Figs. 3A and C). Similar inhibition of DHT-induced cyclin A protein by αE2 and βE2 was observed using Western blot analysis (see Fig. 3B).
Fig. 3.
Dihydrotestosterone (DHT) induced expression of cyclin A and cyclin D1 were inhibited by estrogens (A–C) and DHT-induced cell growth was dependent on cyclin activity (D). LAPC-4 cells were treated as indicated in each panel for 72 hr. In panels A and C, Real-time qPCR was done for transcriptional expression of cyclin A1 and cyclin D1. The data are mean ± SEM of 3–5 individual samples. *P < 0.05 compared to vehicle control, and #P < 0.05 compared to DHT treatment alone. Panel B shows a representative Western blot analysis of cyclin A1 for samples treated with or without hormones, and α-tubulin was used as an internal control. The quantitative data expressed as fold of control are presented. In panel D, LAPC-4 cells were treated with or without DHT (10 nM) in the presence or absence of various doses of roscovitine (Ros), a specific cyclin-dependent kinase inhibitor for 72 hr. The number of viable cells was determined by Cell Titer one solution cell proliferation assay and was expressed as a percentage of vehicle control. The data are the mean ± SEM of 6–12 individual samples of 2 – 4 independent experiments. *P < 0.05 compared to vehicle control; #P < 0.05 compared to DHT treatment alone.
To address the functional significance of DHT-induced cyclin expression, the effect of roscovitine (Ros), a cyclin-dependent kinase (Cdk) inhibitor, on DHT-induced cell growth was examined. As shown in Figure 3D, Ros blocked DHT-induced cell growth in a dose-dependent manner, indicating that DHT-induced cell growth is mediated, at least in part, through regulation of cyclin-Cdk activity in LAPC-4 cells.
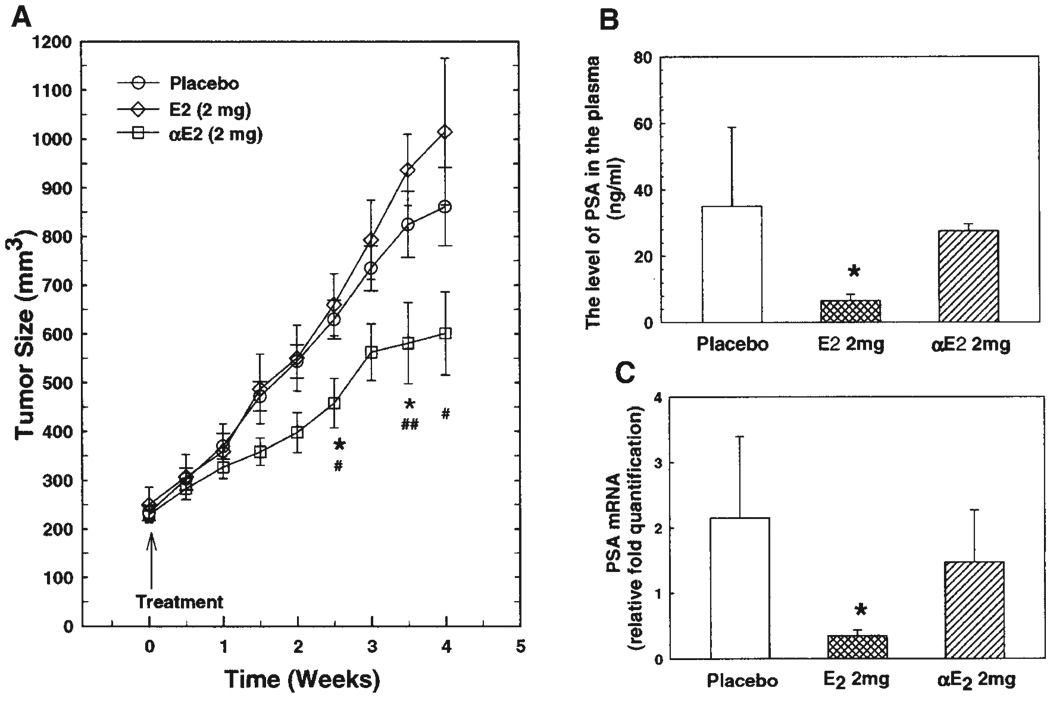
αE2 Inhibited Tumor Growth in a Xenograft Animal Model With LAPC-4 Prostate Cancer Without Altering Circulating Testosterone Level
In order to evaluate the in vivo effectiveness of αE2 in prostate cancer treatment, xenograft animals with LAPC-4 prostate cancer were treated with placebo, αE2, and βE2 as described in the Section “Materials and Methods.” As shown in Figure 4A, treatment with a 2 mg αE2 pellet (2 mg of αE2 plus 18 mg of cholesterol) significantly inhibited the tumor growth as estimated by tumor size compared to placebo and βE2-treated group. The initial tumor sizes among the three groups were almost the same with an average size of approximately 235 mm3. αE2 produced a notable effect beginning at weeks of pellet implantation. It significantly decreased the tumor size at approximately weeks, and approached a maximal effect by 3 weeks of treatment. Surprisingly, treatment with the same dose of βE2 failed to inhibit tumor growth in the present experiment. The tumor size in the βE2 group was not significantly different from that in the placebo group at all time points. Notably, the tumor size between Weeks 3 and 4 was slightly larger in the βE2 group than in the placebo group though not statistically significant due to small sample size and large variation.
Fig. 4.
The effects of αE2 and βE2 on tumor growth (A) and PSA gene expression (B and C) in xenograft animals with LAPC-4 prostatic tumor. SCID mice were inoculated with LAPC-4 tumor cells on the left flank. When tumor size reaches approximately 200 mm3, the animals were treated with placebo (n = 5), βE2 (2 mg, n = 4), or αE2 (2 mg, n = 5) for 4 weeks. Tumor size was recorded twice a week. The levels of circulating PSA (B) and primary tumor PSA mRNA (C) were determined at the end of experiment by ELISA and real-time RT-PCR respectively as described in the Section “Materials and Methods.” The data are presented as mean ± SEM. *P < 0.05 compared to placebo group, #P < 0.05 compared to E2 group.
The effects of estrogens on PSA gene expression was accessed through determination of PSA levels in circulation by ELISA, and PSA mRNA levels in primary tumor tissues by RT-PCR as described in the Section “Materials and Methods.” In agreement with in cell culture study, βE2 at the dose tested significantly decreased circulating PSA level, and PSA mRNA in the tumor tissues. However, αE2 had a lesser effect on PSA gene expression as shown in Figures 4B,C, which is in parallel with in vitro cell culture analysis (Figs. 1A,B).
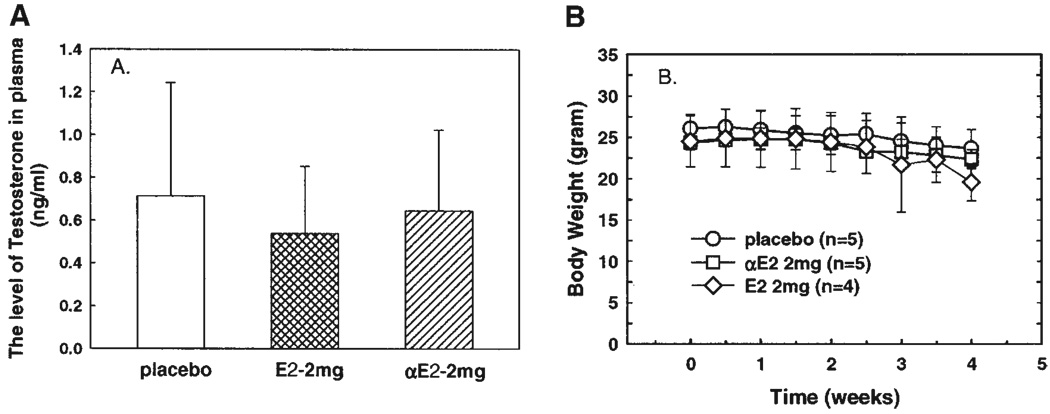
To determine whether αE2 treatment inhibits androgen production, the levels of plasma testosterone were assayed in these animals at the end of experiment. As shown in Figure 5A, plasma testosterone levels among these three groups were not significantly different though it was slightly decreased in the βE2-treated group.
Fig. 5.
Neither plasma testosterone concentration (A) nor animal body weight (B) was altered by estrogen treatment in LAPC-4 xenograft mice. The levels of plasma testosterone were determined using RIA at the end of experiment. Animal body weight was recorded twice a week. The data are presented as mean ± SEM of 4–5 individual samples.
The body weight among these three groups was similar (Fig. 5B), and there was no significant change after estrogen treatment, although it was marginally but not statistically significantly decreased at 4 weeks of βE2 treatment. In addition, there were no notable differences in animal mobility among these three groups.
DISCUSSION
Regulation of the cell cycle plays an essential role in cell proliferation, differentiation, and cell death [24,25]. The cell cycle is controlled by the sequential activation of Cdks upon association with their partner cyclins. Both cyclin D1 and cyclin A are key regulators in cell cycle progression especially for cells to enter into S phase. Cyclin D1 works in the G1 phase and cyclin A in the S and G2 phase of the cell cycle [24,26]. The action of cyclin-Cdks in cell cycle regulation is mediated via pRb that binds and inhibits E2F in G0 and early G1. When pRb is phosphorylated by cyclin C/Cdk3, cyclin D-Cdk4/Cdk6, and cyclin E-Cdk2, E2F is relased, which induces genes that mediate G0 exit and S phase entry. It has been shown that cyclin D1 and A are over-expressed in prostate cancer cells [27], and in human prostate cancer tissues [28]. In prostate LNCaP tumor cells, over-expression of cyclin D1 results in an increase in cell growth, tumorigenicity, and resistance to androgen ablation therapy [29]. Recent studies demonstrated that AR directly regulated the expression of cell cycle genes and thus controlled prostate cancer cell proliferation and tumor growth [30,31]. Thus, the cyclin-Cdks may function to link androgens and their proliferative effects on the prostatic cells [30,32]. In agreement with previous reports [30,32], we have demonstrated in the present study that DHT induced both cyclin D1 and A expression in the androgen-dependent LAPC-4 prostatic tumor cells, leading to increases in BrdU incorporation or DNA biosynthesis, cells entering into cell cycle, and cell growth. Furthermore, treatment with roscovitine, a Cdk-inhibitor, resulted in a dose-dependent inhibition of DHT-induced cell growth (see Fig. 3D). These results support the concept that DHT-induced cell growth is mediated, at least in part, through the regulation of cyclin-Cdks activity in LAPC-4 prostatic tumor cells.
Consistent with our previous demonstration [18], coadministration of αE2 or βE2 with DHT produced a dose-dependent inhibition of DHT-induced PSA gene expression and cell growth in LAPC-4 prostatic tumor cells. Moreover, we observed in the present study that αE2 and βE2 blocked DHT-induced cyclin A and D1 gene expression as well as DHT-induced DNA biosynthesis, suggesting that inhibition of DHT-induced cyclin A and cyclin D1 expression by αE2 and βE2 may be a plausible molecular mechanism underlining estrogen inhibition of DHT-induced cell proliferation. Recently, Pravettoni et al. [33] have also reported that estrogens could modulate cyclin-Cdks activity via up-regulation of p21, a Cdk inhibitor, resulting in a reduction of cell proliferation. This direct modulation of DHT actions by αE2 and βE2 in the prostatic tumor cells is most likely mediated via interaction with ERs [18,34]. In LAPC-4 prostatic tumor cells, ERβ is the predominant ER isoform while ERα is quite low [18], suggesting that the effects of αE2 and βE2 are mainly mediated through interaction with ERβ. This concept is further supported by findings that demonstrated prostate epithelial cells proliferated much more rapidly in ERβ knockout mice compared to wild-type animals [35,36]. Moreover, Jarred et al. [37] have reported that estrogen could directly modulate androgen actions in prostate cells; and Pravettoni’s group [33] have recently demonstrated that the anti-proliferative action of estradiol was mediated through ERβ. Taken together, these results suggest that ligand-ERβ in the prostate cells can inhibit cell proliferation, which may be mediated via interfering androgen actions.
To evaluate the in vivo effects of estrogens on prostatic tumor growth, animals with xenograft LAPC-4 prostatic tumors were treated with placebo, αE2, or βE2. Consistent with in cell culture studies, treatment with αE2 (20 mg pellet containing 2 mg αE2) significantly inhibited prostate tumor growth while, surprisingly, administration of the same dose of βE2 failed to inhibit tumor growth (Fig. 4A). The dose of 17β-estradiol used in the current study was selected according to the reported dosage used by Li’s group [38], in which the level of circulating βE2 is reported to reach the physiological concentration of 17β-estradiol in females. This βE2 dose was clearly effective in the animal as the PSA level in the circulation and PSA mRNA level in the tumor tissues were significantly decreased in βE2-treated animals compared to placebo controls (Figs. 4B–C). The reasons for the discrepancy between the in vitro and in vivo effect of βE2 and the differential effects between αE2 and βE2 are currently unclear and remain to be elucidated.
Although αE2, a stereo-isomer of βE2 and a phytochemical in pomegranate [39], is much less active as a transactivating hormone, and has much weaker classic estrogenic activity than βE2 [40,41], it has similar potency as βE2 in inhibiting DHT-induced PSA gene expression and cell growth in prostatic tumor cells [18], and it is as potent as βE2 in protecting neuronal cells from ischemic damage [42]. In cotransfection assays and in prostatic tumor cell cultures, we [18] have shown that both βE2 and αE2 via ERs can inhibit androgen-induced AR transactivation activity, which was further confirmed in the current study (see Fig. 1). However, it was also shown that they possess distinctive features which may involve different molecular mechanisms. αE2 blocks DHT-induced PSA transcription via either ERα or ERβ, while βE2 is effective via ERα but has a much weaker effect via ERβ in the same cotransfection system [18]. Although both αE2 and βE2 inhibit DHT action via ERα, distinctive functional domains of ERα are involved in their actions [18]. Collectively, these data suggest that estrogen modulation of DHT effects on PSA expression and prostatic tumor cell growth may involve other mechanisms in addition to those associated with classic estrogenic activity.
It is well known that one of the mechanisms of systemic estrogen therapy in prostate cancer is suppression of the hypothalamic–pituitary–gonadal axis and consequently, a decrease in testosterone biosynthesis [5]. The levels of plasma testosterone in these animals were determined, and the changes in plasma testosterone levels were not correlated with the effects of estrogens on tumor growth. αE2 significantly inhibited tumor growth without notably altering circulating testosterone level (Fig. 4A). These results indicate that estrogens may possess direct effects in prostatic tumor cells, such as inhibition of DHT actions. Although the precise cellular and molecular events of αE2 and βE2 actions on prostate cancer remain to be elucidated, our current results and previous studies [18] suggest that αE2 is superior to βE2 for prostate cancer prevention and therapy as αE has less classic estrogenic activity, produces fewer side effects, and is more effective in the inhibition of tumor growth in xenograft animals with LAPC-4 prostate tumor.
CONCULSIONS
The present study demonstrated that both αE2 and βE2 were able to inhibit DHT-stimulated PSA gene expression and cell proliferation in cultured LAPC-4 prostate tumor cells, which may be mediated through the inhibition of DHT-induced cyclin activity by these estrogen analogs. However, in the xenograft animal model with LAPC-4 prostate tumor, αE2 significantly inhibited tumor growth probably mediated through direct actions on prostatic tumor cells while βE2 had no significant effect. Although the mechanisms of αE2 actions remain to be further elucidated, the results obtained indicate that αE2 may be a potential agent for prostate cancer prevention and therapy, and warrants further investigation.
ACKNOWLEDGMENTS
We thank Dr. C Sawyer in Memorial Sloan-Kettering Cancer Center for providing LAPC-4 cell line. This study was partially supported by an NIH grant (DK-061004) and a USAMRAA grant (DAMD 17-02-1-01600) to Y. S. Z. Y Qiao and Z.-K. Zhang were supported by an NIH training grant (T32 DK-07313) directed by J. Imperato-McGinley.
REFERENCES
- 1.Jemal A, Siegel R, Ward E, Murray T, Xu J, Thun MJ. Cancer statistics, 2007. CA Cancer J Clin. 2007;57:43–66. doi: 10.3322/canjclin.57.1.43. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 2.Ko YJ, Balk SP. Targeting steroid hormone receptor pathways in the treatment of hormone dependent cancers. Curr Pharm Biotechnol. 2004;5:459–470. doi: 10.2174/1389201043376616. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 3.Risbridger GP, Bianco JJ, Ellem SJ, McPherson SJ. Oestrogens and prostate cancer. Endocr Relat Cancer. 2003;10:187–191. doi: 10.1677/erc.0.0100187. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 4.Huggins C, Hodges CV. Studies on prostatic cancer I. the effect of castration, of estrogen and of androgen injection on serum phosphatases in metastatic carcinoma of the prostate. Cancer Res. 1941;1:293–297. doi: 10.3322/canjclin.22.4.232. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 5.Dowling AJ, Tannock IF. Systemic treatment for prostate cancer. Cancer Treat Rev. 1998;24:283–301. doi: 10.1016/s0305-7372(98)90062-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 6.Bush TL, Barrett-Connor E. Noncontraceptive estrogen use and cardiovascular disease. Epidemiol Rev. 1985;7:89–104. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 7.Hedlund TE, Johannes WU, Miller GJ. Soy isoflavonoid equol modulates the growth of benign and malignant prostatic epithelial cells in vitro. Prostate. 2003;54:68–78. doi: 10.1002/pros.10137. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 8.Reddel RR, Sutherland RL. Effects of pharmacological concentrations of estrogens on proliferation and cell cycle kinetics of human breast cancer cell lines in vitro. Cancer Res. 1987;47:5323–5329. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 9.Shen JC, Klein RD, Wei Q, Guan Y, Contois JH, Wang TT, Chang S, Hursting SD. Low-dose genistein induces cyclin-dependent kinase inhibitors and G(1) cell-cycle arrest in human prostate cancer cells. Mol Carcinog. 2000;29:92–102. doi: 10.1002/1098-2744(200010)29:2<92::aid-mc6>3.0.co;2-q. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 10.Clark JH, Williams M, Upchurch S, Eriksson H, Helton E, Markaverich BM. Effects of estradiol-17 alpha on nuclear occupancy of the estrogen receptor, stimulation of nuclear type II sites and uterine growth. J Steroid Biochem. 1982;16:323–328. doi: 10.1016/0022-4731(82)90184-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 11.Lubahn DB, McCarty KS, Jr, McCarty KSSr. Electrophoretic characterization of purified bovine, porcine, murine, rat, and human uterine estrogen receptors. J Biol Chem. 1985;260:2515–2526. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 12.Li JJ, Li SA. Estrogen-induced tumorigenesis in hamsters: Roles for hormonal and carcinogenic activities. Arch Toxicol. 1984;55:110–118. doi: 10.1007/BF00346048. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 13.Li JJ, Li SA. Estrogen carcinogenesis in Syrian hamster tissues: Role of metabolism. Fed Proc. 1987;46:1858–1863. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 14.Li JJ, Li SA, Oberley TD, Parsons JA. Carcinogenic activities of various steroidal and nonsteroidal estrogens in the hamster kidney: Relation to hormonal activity and cell proliferation. Cancer Res. 1995;55:4347–4351. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 15.Freay AD, Curtis SW, Korach KS, Rubanyi GM. Mechanism of vascular smooth muscle relaxation by estrogen in depolarized rat and mouse aorta. Role of nuclear estrogen receptor and Ca2+ uptake. Circ Res. 1997;81:242–248. doi: 10.1161/01.res.81.2.242. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 16.Aizu-Yokota E, Ichinoseki K, Sato Y. Microtubule disruption induced by estradiol in estrogen receptor-positive and -negative human breast cancer cell lines. Carcinogenesis. 1994;15:1875–1879. doi: 10.1093/carcin/15.9.1875. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 17.Green PS, Bishop J, Simpkins JW. 17 Alpha-estradiol exerts neuroprotective effects on SK-N-SH cells. J Neurosci. 1997;17:511–515. doi: 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.17-02-00511.1997. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 18.Zhu YS, Cai LQ, Huang Y, Fish J, Wang L, Zhang ZK, Imperato-McGinley J. Receptor isoform and ligand-specific modulation of dihydrotestosterone-induced prostate specific antigen gene expression and prostate tumor cell growth by estrogens. J Androl. 2005;26:500–508. doi: 10.2164/jandrol.05002. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 19.Klein KA, Reiter RE, Redula J, Moradi H, Zhu XL, Brothman AR, Lamb DJ, Marcelli M, Belldegrun A, Witte ON, Sawyers CL. Progression of metastatic human prostate cancer to androgen independence in immunodeficient SCID mice. Nat Med. 1997;3:402–408. doi: 10.1038/nm0497-402. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 20.Zhang ZK, Davies KP, Allen J, Zhu L, Pestell RG, Zagzag D, Kalpana GV. Cell cycle arrest and repression of cyclin D1 transcription by INI1/hS NF5. Mol Cell Biol. 2002;22:5975–5988. doi: 10.1128/MCB.22.16.5975-5988.2002. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 21.Burfeind P, Chernicky CL, Rininsland F, Ilan J, Ilan J. Antisense RNA to the type I insulin-like growth factor receptor suppresses tumor growth and prevents invasion by rat prostate cancer cells in vivo. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA. 1996;93:7263–7268. doi: 10.1073/pnas.93.14.7263. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 22.Foster JS, Henley DC, Bukovsky A, Seth P, Wimalasena J. Multifaceted regulation of cell cycle progression by estrogen: Regulation of Cdk inhibitors and Cdc25A independent of cyclin D1-Cdk4 function. Mol Cell Biol. 2001;21:794–810. doi: 10.1128/MCB.21.3.794-810.2001. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 23.Onozawa M, Fukuda K, Ohtani M, Akaza H, Sugimura T, Wakabayashi K. Effects of soybean isoflavones on cell growth and apoptosis of the human prostatic cancer cell line LNCaP. Jpn J Clin Oncol. 1998;28:360–363. doi: 10.1093/jjco/28.6.360. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 24.Hunter T, Pines J. Cyclins and cancer. II: Cyclin D and CDK inhibitors come of age. Cell. 1994;79:573–582. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(94)90543-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 25.Pestell RG, Albanese C, Reutens AT, Segall JE, Lee RJ, Arnold A. The cyclins and cyclin-dependent kinase inhibitors in hormonal regulation of proliferation and differentiation. Endocr Rev. 1999;20:501–534. doi: 10.1210/edrv.20.4.0373. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 26.Handratta VD, Vasaitis TS, Njar VC, Gediya LK, Kataria R, Chopra P, Newman D, Jr, Farquhar R, Guo Z, Qiu Y, Brodie AM. Novel C-17-heteroaryl steroidal CYP17 inhibitors/antiandrogens: Synthesis, in vitro biological activity, pharmacokinetics, and antitumor activity in the LAPC4 human prostate cancer xenograft model. J Med Chem. 2005;48:2972–2984. doi: 10.1021/jm040202w. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 27.Yasmeen A, Berdel WE, Serve H, Muller-Tidow C. E-and A-type cyclins as markers for cancer diagnosis and prognosis. Expert Rev Mol Diagn. 2003;3:617–633. doi: 10.1586/14737159.3.5.617. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 28.Amanatullah DF, Reutens AT, Zafonte BT, Fu M, Mani S, Pestell RG. Cell-cycle dysregulation and the molecular mechanisms of prostate cancer. Front Biosci. 2000;5:D372–D390. doi: 10.2741/amanatullah. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 29.Chen Y, Martinez LA, LaCava M, Coghlan L, Conti CJ. Increased cell growth and tumorigenicity in human prostate LNCaP cells by overexpression to cyclin D1. Oncogene. 1998;16:1913–1920. doi: 10.1038/sj.onc.1201719. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 30.Gregory CW, Johnson RT, Jr, Presnell SC, Mohler JL, French FS. Androgen receptor regulation of G1 cyclin and cyclin-dependent kinase function in the CWR22 human prostate cancer xenograft. J Androl. 2001;22:537–548. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 31.Zou JX, Zhong Z, Shi XB, Tepper CG, deVere White RW, Kung HJ, Chen H. ACTR/AIB1/SRC-3 and androgen receptor control prostate cancer cell proliferation and tumor growth through direct control of cell cycle genes. Prostate. 2006;66:1474–1486. doi: 10.1002/pros.20477. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 32.Chen Y, Robles AI, Martinez LA, Liu F, Gimenez-Conti IB, Conti CJ. Expression of G1 cyclins, cyclin-dependent kinases, and cyclin-dependent kinase inhibitors in androgen-induced prostate proliferation in castrated rats. Cell Growth Differ. 1996;7:1571–1578. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 33.Pravettoni A, Mornati O, Martini PG, Marino M, Colciago A, Celotti F, Motta M, Negri-Cesi P. Estrogen receptor beta (ERbeta) and inhibition of prostate cancer cell proliferation: Studies on the possible mechanism of action in DU145 cells. Mol Cell Endocrinol. 2007;263:46–54. doi: 10.1016/j.mce.2006.08.008. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 34.Kumar MV, Leo ME, Tindall DJ. Modulation of androgen receptor transcriptional activity by the estrogen receptor. J Androl. 1994;15:534–542. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 35.Krege JH, Hodgin JB, Couse JF, Enmark E, Warner M, Mahler JF, Sar M, Korach KS, Gustafsson JA, Smithies O. Generation and reproductive phenotypes of mice lacking estrogen receptor beta. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA. 1998;95:15677–15682. doi: 10.1073/pnas.95.26.15677. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 36.Weihua Z, Makela S, Andersson LC, Salmi S, Saji S, Webster JI, Jensen EV, Nilsson S, Warner M, Gustafsson JA. A role for estrogen receptor beta in the regulation of growth of the ventral prostate. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA. 2001;98:6330–6335. doi: 10.1073/pnas.111150898. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 37.Jarred RA, Cancilla B, Prins GS, Thayer KA, Cunha GR, Risbridger GP. Evidence that estrogens directly alter androgen-regulated prostate development. Endocrinology. 2000;141:3471–3477. doi: 10.1210/endo.141.9.7648. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 38.Li SA, Weroha SJ, Tawfik O, Li JJ. Prevention of solely estrogen-induced mammary tumors in female aci rats by tamoxifen: Evidence for estrogen receptor mediation. J Endocrinol. 2002;175:297–305. doi: 10.1677/joe.0.1750297. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 39.Kim ND, Mehta R, Yu W, Neeman I, Livney T, Amichay A, Poirier D, Nicholls P, Kirby A, Jiang W, Mansel R, Ramachan-dran C, Rabi T, Kaplan B, Lansky E. Chemopreventive and adjuvant therapeutic potential of pomegranate (Punica granatum) for human breast cancer. Breast Cancer Res Treat. 2002;71:203–217. doi: 10.1023/a:1014405730585. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 40.Kuiper GG, Carlsson B, Grandien K, Enmark E, Haggblad J, Nilsson S, Gustafsson JA. Comparison of the ligand binding specificity and transcript tissue distribution of estrogen receptors alpha and beta. Endocrinol. 1997;138:863–870. doi: 10.1210/endo.138.3.4979. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 41.Edwards DP, McGuire WL. 17 alpha-Estradiol is a biologically active estrogen in human breast cancer cells in tissue culture. Endocrinol. 1980;107:884–891. doi: 10.1210/endo-107-4-884. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 42.Dykens JA, Moos WH, Howell N. Development of 17alpha-estradiol as a neuroprotective therapeutic agent: Rationale and results from a phase I clinical study. Ann NY Acad Sci. 2005;1052:116–135. doi: 10.1196/annals.1347.008. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]