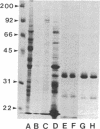
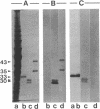
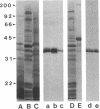
Abstract
Tropomyosin is a key component of the contractile systems found in muscle and nonmuscle cells of higher eukaryotes. Based on properties common to all tropomyosins, we have purified a protein from Saccharomyces cerevisiae that resembles tropomyosins from higher cells. The yeast protein remains soluble after heat treatment at 90 degrees C, has an apparent polypeptide molecular weight of 33,000, an isoelectric point of 4.5, a Stokes radius of 3.5 nm, and a sedimentation coefficient of 2.6 S. It binds F-actin in a Mg2+-dependent, KCl-modulated manner, up to a stoichiometry of about 1 polypeptide per 3.0 actin monomers. In all these properties it is very similar to tropomyosins from higher cells. Antigen-affinity-purified antibodies specifically recognize the Mr 33,000 polypeptide among total yeast proteins and crossreact with bovine brain tropomyosin. In addition, the antibodies specifically crossreact with heat-stable Mr 33,000 polypeptides in extracts of Schizosaccharomyces pombe and Physarum polycephalum. Our detection of tropomyosin in lower eukaryotes suggests that they might have contractile systems very similar to those found in higher organisms.
Full text
PDF


Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Bidlingmeyer B. A., Cohen S. A., Tarvin T. L. Rapid analysis of amino acids using pre-column derivatization. J Chromatogr. 1984 Dec 7;336(1):93–104. doi: 10.1016/s0378-4347(00)85133-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bretscher A. Smooth muscle caldesmon. Rapid purification and F-actin cross-linking properties. J Biol Chem. 1984 Oct 25;259(20):12873–12880. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bretscher A. Thin filament regulatory proteins of smooth- and non-muscle cells. Nature. 1986 Jun 19;321(6072):726–727. doi: 10.1038/321726b0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bretscher A., Weber K. Localization of actin and microfilament-associated proteins in the microvilli and terminal web of the intestinal brush border by immunofluorescence microscopy. J Cell Biol. 1978 Dec;79(3):839–845. doi: 10.1083/jcb.79.3.839. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bretscher A., Weber K. Tropomyosin from bovine brain contains two polypeptide chains of slightly different molecular weights. FEBS Lett. 1978 Jan 1;85(1):145–148. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(78)81267-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Côté G. P., Smillie L. B. Preparation and some properties of equine platelet tropomyosin. J Biol Chem. 1981 Nov 10;256(21):11004–11010. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Côté G. P., Smillie L. B. The interaction of equine platelet tropomyosin with skeletal muscle actin. J Biol Chem. 1981 Jul 25;256(14):7257–7261. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Côté G. P. Structural and functional properties of the non-muscle tropomyosins. Mol Cell Biochem. 1983;57(2):127–146. doi: 10.1007/BF00849190. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gallwitz D., Sures I. Structure of a split yeast gene: complete nucleotide sequence of the actin gene in Saccharomyces cerevisiae. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1980 May;77(5):2546–2550. doi: 10.1073/pnas.77.5.2546. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Greer C., Schekman R. Actin from Saccharomyces cerevisiae. Mol Cell Biol. 1982 Oct;2(10):1270–1278. doi: 10.1128/mcb.2.10.1270. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Korn E. D. Acanthamoeba castellanii: methods and perspectives for study of cytoskeleton proteins. Methods Cell Biol. 1982;25(Pt B):313–332. doi: 10.1016/s0091-679x(08)61431-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Korn E. D. Actin polymerization and its regulation by proteins from nonmuscle cells. Physiol Rev. 1982 Apr;62(2):672–737. doi: 10.1152/physrev.1982.62.2.672. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Marston S. B., Smith C. W. The thin filaments of smooth muscles. J Muscle Res Cell Motil. 1985 Dec;6(6):669–708. doi: 10.1007/BF00712237. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ng R., Abelson J. Isolation and sequence of the gene for actin in Saccharomyces cerevisiae. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1980 Jul;77(7):3912–3916. doi: 10.1073/pnas.77.7.3912. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Payne M. R., Rudnick S. E. Tropomyosin. Structural and functional diversity. Cell Muscle Motil. 1985;6:141–184. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shortle D., Haber J. E., Botstein D. Lethal disruption of the yeast actin gene by integrative DNA transformation. Science. 1982 Jul 23;217(4557):371–373. doi: 10.1126/science.7046050. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sobieszek A., Small J. V. Effect of muscle and non-muscle tropomyosins in reconstituted skeletal muscle actomyosin. Eur J Biochem. 1981 Sep 1;118(3):533–539. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1981.tb05552.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Spudich J. A. Dictyostelium discoideum: methods and perspectives for study of cell motility. Methods Cell Biol. 1982;25(Pt B):359–364. doi: 10.1016/s0091-679x(08)61433-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Spudich J. A., Watt S. The regulation of rabbit skeletal muscle contraction. I. Biochemical studies of the interaction of the tropomyosin-troponin complex with actin and the proteolytic fragments of myosin. J Biol Chem. 1971 Aug 10;246(15):4866–4871. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Towbin H., Staehelin T., Gordon J. Electrophoretic transfer of proteins from polyacrylamide gels to nitrocellulose sheets: procedure and some applications. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1979 Sep;76(9):4350–4354. doi: 10.1073/pnas.76.9.4350. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Watts F. Z., Miller D. M., Orr E. Identification of myosin heavy chain in Saccharomyces cerevisiae. Nature. 1985 Jul 4;316(6023):83–85. doi: 10.1038/316083a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Watts F. Z., Shiels G., Orr E. The yeast MYO1 gene encoding a myosin-like protein required for cell division. EMBO J. 1987 Nov;6(11):3499–3505. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1987.tb02675.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]