Abstract
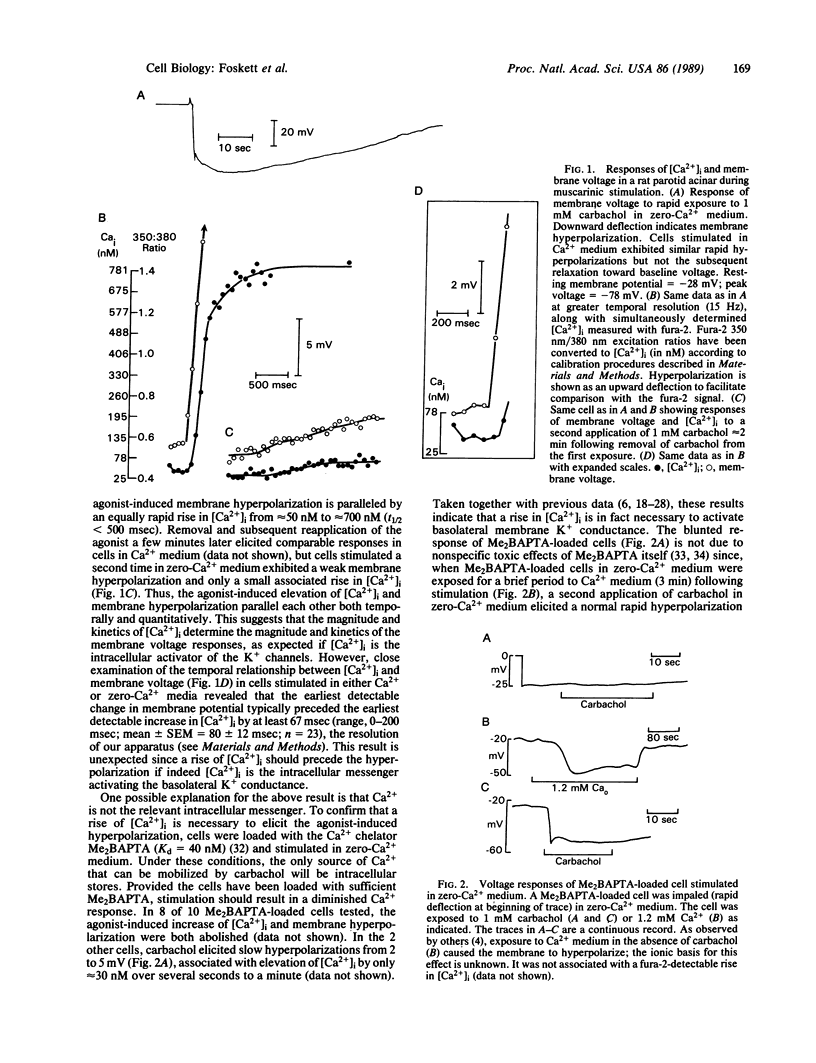
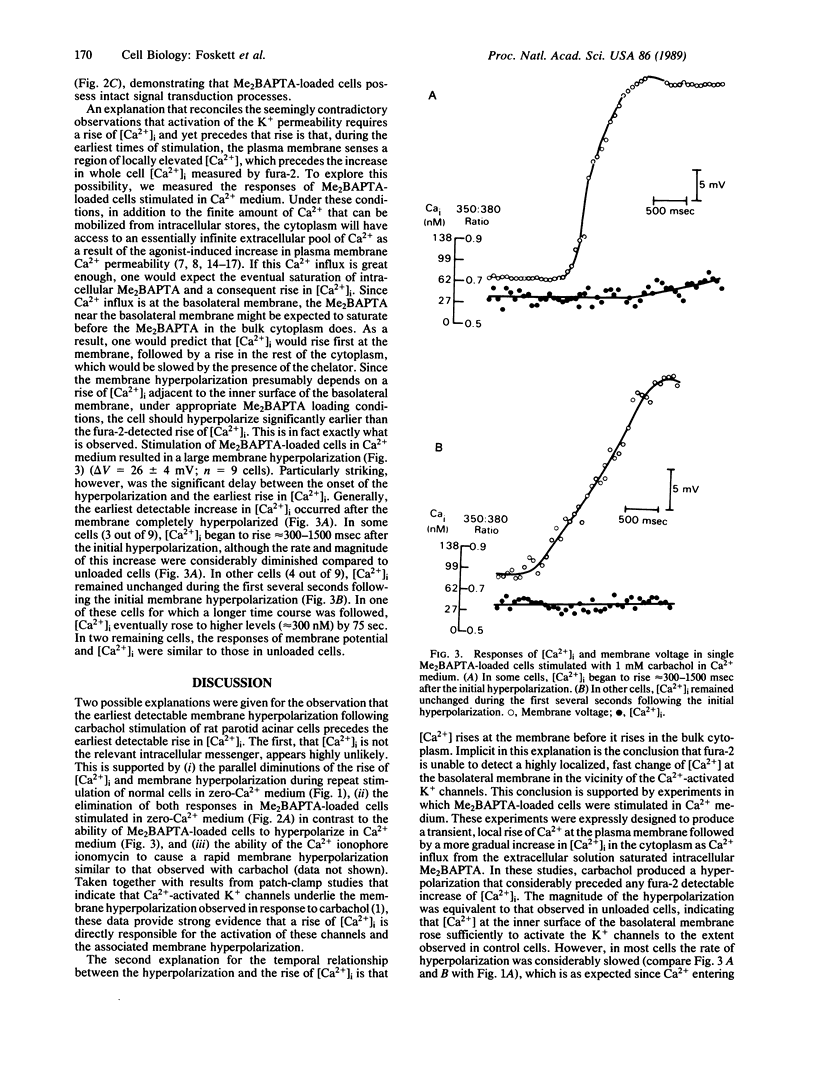
Muscarinic stimulation of fluid secretion by mammalian salivary acinar cells is associated with a rise in the level of intracellular free calcium ([Ca2+]i) and activation of a calcium-sensitive potassium (K+) conductance in the basolateral membrane. To test in the intact cell whether the rise of [Ca2+]i precedes activation of the K+ conductance (as expected if Ca2+ is the intracellular messenger mediating this response), [Ca2+]i and membrane voltage were measured simultaneously in carbachol-stimulated rat parotid acinar cells by using fura-2 and an intracellular microelectrode. Unexpectedly, the cells hyperpolarize (indicating activation of the K+ conductance) before fura-2 detectable [Ca2+]i begins to rise. This occurs even in Ca2+-depleted medium where intracellular stores are the only source of mobilized Ca2+. Nevertheless, when the increase in [Ca2+]i was eliminated by loading cells with the Ca2+ chelator bis(2-amino-5-methylphenoxy)ethane-N,N,N',N'-tetraacetate (Me2BAPTA) and stimulating in Ca2+-depleted medium, membrane hyperpolarization was also eliminated, indicating that a rise of [Ca2+] is required for the agonist-induced voltage response. Stimulation of Me2BAPTA-loaded cells in Ca2+-containing medium dramatically accentuates the temporal dissociation between the activation of the K+ conductance and the rise of [Ca2+]i. The data are consistent with the hypothesis that muscarinic stimulation results in a rapid localized increase in [Ca2+]i at the acinar basolateral membrane followed by a somewhat delayed increase in total [Ca2+]i. The localized increase cannot be detected by fura-2 but is sufficient to open the Ca2+-sensitive K+ channels located in the basolateral membrane. We concluded that a receptor-mobilized intracellular store of Ca2+ is localized at or near the basolateral membrane.
Full text
PDF


Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Aub D. L., Putney J. W., Jr Mobilization of intracellular calcium by methacholine and inositol 1,4,5-trisphosphate in rat parotid acinar cells. J Dent Res. 1987 Feb;66(2):547–551. doi: 10.1177/00220345870660022701. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Berridge M. J., Dawson R. M., Downes C. P., Heslop J. P., Irvine R. F. Changes in the levels of inositol phosphates after agonist-dependent hydrolysis of membrane phosphoinositides. Biochem J. 1983 May 15;212(2):473–482. doi: 10.1042/bj2120473. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Berridge M. J., Irvine R. F. Inositol trisphosphate, a novel second messenger in cellular signal transduction. Nature. 1984 Nov 22;312(5992):315–321. doi: 10.1038/312315a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Berridge M. J. Regulation of ion channels by inositol trisphosphate and diacylglycerol. J Exp Biol. 1986 Sep;124:323–335. doi: 10.1242/jeb.124.1.323. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Biden T. J., Wollheim C. B., Schlegel W. Inositol 1,4,5-trisphosphate and intracellular Ca2+ homeostasis in clonal pituitary cells (GH3). Translocation of Ca2+ into mitochondria from a functionally discrete portion of the nonmitochondrial store. J Biol Chem. 1986 Jun 5;261(16):7223–7229. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bonis D., Giraud F., Rossignol B. Inositol trisphosphate-induced Ca2+ release from rat parotid subcellular fractions. Biol Cell. 1986;57(3):271–274. doi: 10.1111/j.1768-322x.1986.tb00482.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Downes C. P., Wusteman M. M. Breakdown of polyphosphoinositides and not phosphatidylinositol accounts for muscarinic agonist-stimulated inositol phospholipid metabolism in rat parotid glands. Biochem J. 1983 Dec 15;216(3):633–640. doi: 10.1042/bj2160633. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Evans M. G., Marty A. Potentiation of muscarinic and alpha-adrenergic responses by an analogue of guanosine 5'-triphosphate. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1986 Jun;83(11):4099–4103. doi: 10.1073/pnas.83.11.4099. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Findlay I. A patch-clamp study of potassium channels and whole-cell currents in acinar cells of the mouse lacrimal gland. J Physiol. 1984 May;350:179–195. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1984.sp015195. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Findlay I., Dunne M. J., Petersen O. H. High-conductance K+ channel in pancreatic islet cells can be activated and inactivated by internal calcium. J Membr Biol. 1985;83(1-2):169–175. doi: 10.1007/BF01868748. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Findlay I., Petersen O. H. Acetylcholine stimulates a Ca2+-dependent C1- conductance in mouse lacrimal acinar cells. Pflugers Arch. 1985 Mar;403(3):328–330. doi: 10.1007/BF00583609. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Foskett J. K. Simultaneous Nomarski and fluorescence imaging during video microscopy of cells. Am J Physiol. 1988 Oct;255(4 Pt 1):C566–C571. doi: 10.1152/ajpcell.1988.255.4.C566. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gallacher D. V., Morris A. P. A patch-clamp study of potassium currents in resting and acetylcholine-stimulated mouse submandibular acinar cells. J Physiol. 1986 Apr;373:379–395. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1986.sp016054. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gallacher D. V., Petersen O. H. Electrophysiology of mouse parotid acini: effects of electrical field stimulation and ionophoresis of neurotransmitters. J Physiol. 1980 Aug;305:43–57. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1980.sp013348. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- García-Sancho J. Pyruvate prevents the ATP depletion caused by formaldehyde or calcium-chelator esters in the human red cell. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1985 Feb 28;813(1):148–150. doi: 10.1016/0005-2736(85)90357-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Grynkiewicz G., Poenie M., Tsien R. Y. A new generation of Ca2+ indicators with greatly improved fluorescence properties. J Biol Chem. 1985 Mar 25;260(6):3440–3450. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Henne V., Piiper A., Söling H. D. Inositol 1,4,5-trisphosphate and 5'-GTP induce calcium release from different intracellular pools. FEBS Lett. 1987 Jun 22;218(1):153–158. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(87)81037-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Irvine R. F., Anggård E. E., Letcher A. J., Downes C. P. Metabolism of inositol 1,4,5-trisphosphate and inositol 1,3,4-trisphosphate in rat parotid glands. Biochem J. 1985 Jul 15;229(2):505–511. doi: 10.1042/bj2290505. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Irvine R. F., Letcher A. J., Lander D. J., Downes C. P. Inositol trisphosphates in carbachol-stimulated rat parotid glands. Biochem J. 1984 Oct 1;223(1):237–243. doi: 10.1042/bj2230237. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Iwatsuki N., Maruyama Y., Matsumoto O., Nishiyama A. Activation of Ca2+-dependent Cl- and K+ conductances in rat and mouse parotid acinar cells. Jpn J Physiol. 1985;35(6):933–944. doi: 10.2170/jjphysiol.35.933. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jean T., Klee C. B. Calcium modulation of inositol 1,4,5-trisphosphate-induced calcium release from neuroblastoma x glioma hybrid (NG108-15) microsomes. J Biol Chem. 1986 Dec 15;261(35):16414–16420. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Koelz H. R., Kondo S., Blum A. L., Schulz I. Calcium ion uptake induced by cholinergic and alpha-adrenergic stimulation in isolated cells of rat salivary glands. Pflugers Arch. 1977 Jul 29;370(1):37–44. doi: 10.1007/BF00707943. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Marty A., Tan Y. P., Trautmann A. Three types of calcium-dependent channel in rat lacrimal glands. J Physiol. 1984 Dec;357:293–325. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1984.sp015501. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Maruyama Y., Gallacher D. V., Petersen O. H. Voltage and Ca2+-activated K+ channel in baso-lateral acinar cell membranes of mammalian salivary glands. Nature. 1983 Apr 28;302(5911):827–829. doi: 10.1038/302827a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Maruyama Y., Petersen O. H., Flanagan P., Pearson G. T. Quantification of Ca2+-activated K+ channels under hormonal control in pig pancreas acinar cells. Nature. 1983 Sep 15;305(5931):228–232. doi: 10.1038/305228a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Melvin J. E., Kawaguchi M., Baum B. J., Turner R. J. A muscarinic agonist-stimulated chloride efflux pathway is associated with fluid secretion in rat parotid acinar cells. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1987 Jun 15;145(2):754–759. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(87)91029-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Merritt J. E., Rink T. J. Rapid increases in cytosolic free calcium in response to muscarinic stimulation of rat parotid acinar cells. J Biol Chem. 1987 Apr 15;262(11):4958–4960. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Merritt J. E., Rink T. J. The effects of substance P and carbachol on inositol tris- and tetrakisphosphate formation and cytosolic free calcium in rat parotid acinar cells. A correlation between inositol phosphate levels and calcium entry. J Biol Chem. 1987 Nov 5;262(31):14912–14916. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Miller B. E., Nelson D. L. Calcium fluxes in isolated acinar cells from rat parotid. Effect of adrenergic and cholinergic stimulation. J Biol Chem. 1977 Jun 10;252(11):3629–3636. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Muallem S., Schoeffield M., Pandol S., Sachs G. Inositol trisphosphate modification of ion transport in rough endoplasmic reticulum. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1985 Jul;82(13):4433–4437. doi: 10.1073/pnas.82.13.4433. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nauntofte B., Dissing S. Stimulation-induced changes in cytosolic calcium in rat parotid acini. Am J Physiol. 1987 Sep;253(3 Pt 1):G290–G297. doi: 10.1152/ajpgi.1987.253.3.G290. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- O'Doherty J., Stark R. J., Crane S. J., Brugge K. L. Changes in cytosolic calcium during cholinergic and adrenergic stimulation of the parotid salivary gland. Pflugers Arch. 1983 Aug;398(3):241–246. doi: 10.1007/BF00657159. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Parod R. J., Putney J. W., Jr The role of calcium in the receptor mediated control of potassium permeability in the rat lacrimal gland. J Physiol. 1978 Aug;281:371–381. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1978.sp012428. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Payne R., Fein A. Inositol 1,4,5 trisphosphate releases calcium from specialized sites within Limulus photoreceptors. J Cell Biol. 1987 Apr;104(4):933–937. doi: 10.1083/jcb.104.4.933. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Petersen O. H., Pedersen G. L. Membrane effects mediated by alpha-and beta-adrenoceptors in mouse parotid acinar cells. J Membr Biol. 1974;16(4):353–362. doi: 10.1007/BF01872423. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Poggioli J., Leslie B. A., McKinney J. S., Weiss S. J., Putney J. W., Jr Actions of ionomycin in rat parotid gland. J Pharmacol Exp Ther. 1982 Apr;221(1):247–253. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Poggioli J., Putney J. W., Jr Net calcium fluxes in rat parotid acinar cells: evidence for a hormone-sensitive calcium pool in or near the plasma membrane. Pflugers Arch. 1982 Jan;392(3):239–243. doi: 10.1007/BF00584303. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Poggioli J., Weiss S. J., McKinney J. S., Putney J. W., Jr Effects of antimycin A on receptor-activated calcium mobilization and phosphoinositide metabolism in rat parotid gland. Mol Pharmacol. 1983 Jan;23(1):71–77. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Poulsen J. H., Oakley B., 2nd Intracellular potassium ion activity in resting and stimulated mouse pancreas and submandibular gland. Proc R Soc Lond B Biol Sci. 1979 Mar 26;204(1154):99–104. doi: 10.1098/rspb.1979.0015. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Putney J. W., Jr A model for receptor-regulated calcium entry. Cell Calcium. 1986 Feb;7(1):1–12. doi: 10.1016/0143-4160(86)90026-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Putney J. W., Jr, Aub D. L., Taylor C. W., Merritt J. E. Formation and biological action of inositol 1,4,5-trisphosphate. Fed Proc. 1986 Oct;45(11):2634–2638. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Putney J. W., Jr Muscarinic, alpha-adrenergic and peptide receptors regulate the same calcium influx sites in the parotid gland. J Physiol. 1977 Jun;268(1):139–149. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1977.sp011851. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Roberts M. L., Petersen O. H. Membrane potential and resistance changes induced in salivary gland acinar cells by microiontophoretic application of acetylcholine and adrenergic agonists. J Membr Biol. 1978 Mar 20;39(4):297–312. doi: 10.1007/BF01869896. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Takemura H. Changes in cytosolic free calcium concentration in isolated rat parotid cells by cholinergic and beta-adrenergic agonists. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1985 Sep 30;131(3):1048–1055. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(85)90196-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Taylor C. W., Putney J. W., Jr Size of the inositol 1,4,5-trisphosphate-sensitive calcium pool in guinea-pig hepatocytes. Biochem J. 1985 Dec 1;232(2):435–438. doi: 10.1042/bj2320435. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tiffert T., Garcia-Sancho J., Lew V. L. Irreversible ATP depletion caused by low concentrations of formaldehyde and of calcium-chelator esters in intact human red cells. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1984 Jun 13;773(1):143–156. doi: 10.1016/0005-2736(84)90559-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tsien R. Y. New calcium indicators and buffers with high selectivity against magnesium and protons: design, synthesis, and properties of prototype structures. Biochemistry. 1980 May 27;19(11):2396–2404. doi: 10.1021/bi00552a018. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Volpe P., Krause K. H., Hashimoto S., Zorzato F., Pozzan T., Meldolesi J., Lew D. P. "Calciosome," a cytoplasmic organelle: the inositol 1,4,5-trisphosphate-sensitive Ca2+ store of nonmuscle cells? Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1988 Feb;85(4):1091–1095. doi: 10.1073/pnas.85.4.1091. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


