Abstract
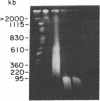
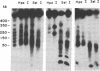
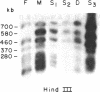
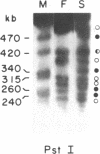
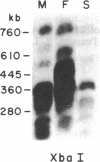
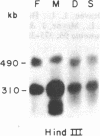
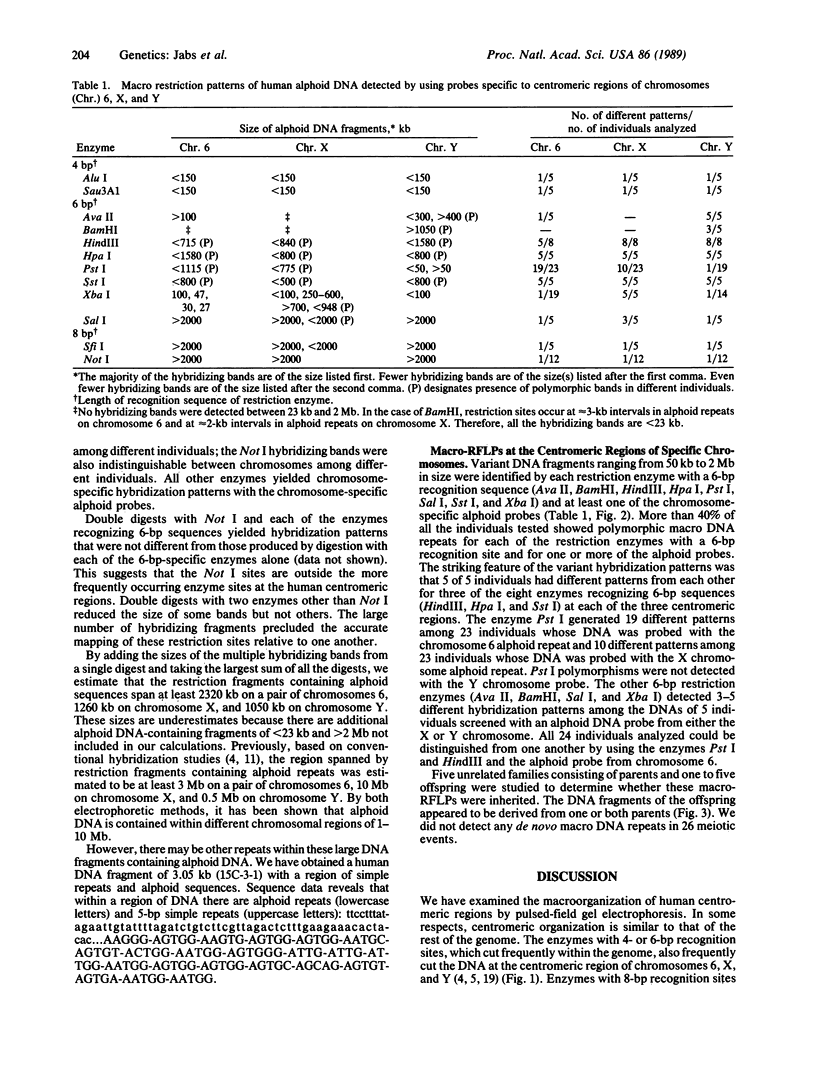
To analyze the macromolecular organization of human centromeric regions, we used alpha-satellite, or alphoid, repetitive DNA sequences specific to the centromeres of human chromosomes 6 (D6Z1), X (XC), and Y (YC-2) and the technique of pulsed-field gel electrophoresis. Genomic DNA from 24 normal, unrelated individuals was digested and separated into fragments ranging from 23 kilobases (kb) to 2 megabases (Mb) in length. Digestion with 12 different restriction enzymes with 4- to 8-base-pair recognition sequences and hybridization with alphoid sequences revealed chromosome-specific hybridization patterns. Similarities in the organization of the centromeric regions of the three chromosomes included NotI, SfiI, and SalI fragments of greater than 2 Mb and Sau3A1 and Alu I fragments of less than 150 kb. Each restriction enzyme with a 6-base-pair recognition sequence (Ava II, BamHI, HindIII, Hpa I, Pst I, Sal I, Sst I, and Xba I) detected polymorphic DNA fragments of 50 kb to 2 Mb. Forty percent or more of the individuals screened revealed a unique hybridization pattern with these enzymes and at least one of the three chromosome-specific alphoid probes. Five individuals differed from one another in hybridization pattern for each of the three enzymes HindIII, HpaI, and SstI and for each of the three centromeric probes. All 24 individuals could be distinguished on the basis of unique hybridization patterns with only two enzymes and one chromosome-specific alphoid probe. Family studies showed that these polymorphisms are inherited. The high frequency of these macro restriction fragment length polymorphisms illustrates the high degree of variability of the centromeric region among normal individuals and demonstrates its usefulness for DNA fingerprinting and pericentromeric mapping by linkage analysis.
Full text
PDF

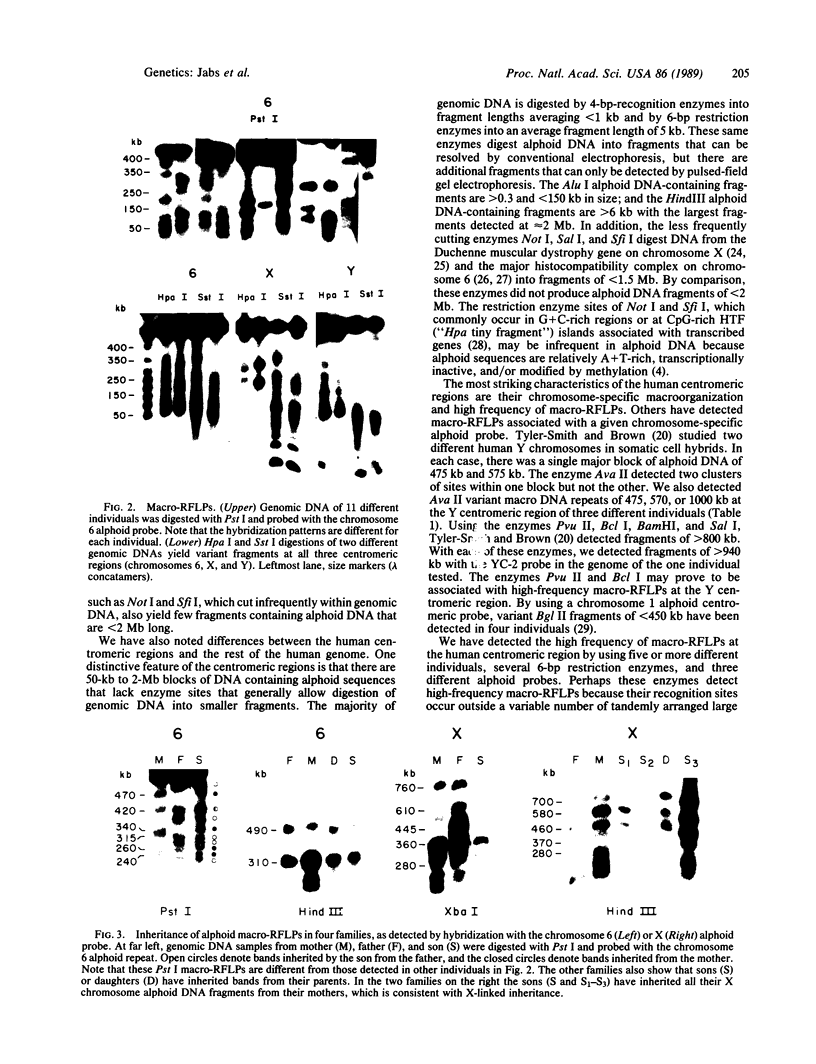

Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Barker D., Wright E., Nguyen K., Cannon L., Fain P., Goldgar D., Bishop D. T., Carey J., Baty B., Kivlin J. Gene for von Recklinghausen neurofibromatosis is in the pericentromeric region of chromosome 17. Science. 1987 May 29;236(4805):1100–1102. doi: 10.1126/science.3107130. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brown W. R., Bird A. P. Long-range restriction site mapping of mammalian genomic DNA. 1986 Jul 31-Aug 6Nature. 322(6078):477–481. doi: 10.1038/322477a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brutlag D. L. Molecular arrangement and evolution of heterochromatic DNA. Annu Rev Genet. 1980;14:121–144. doi: 10.1146/annurev.ge.14.120180.001005. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Carle G. F., Olson M. V. Separation of chromosomal DNA molecules from yeast by orthogonal-field-alternation gel electrophoresis. Nucleic Acids Res. 1984 Jul 25;12(14):5647–5664. doi: 10.1093/nar/12.14.5647. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Carroll M. C., Katzman P., Alicot E. M., Koller B. H., Geraghty D. E., Orr H. T., Strominger J. L., Spies T. Linkage map of the human major histocompatibility complex including the tumor necrosis factor genes. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1987 Dec;84(23):8535–8539. doi: 10.1073/pnas.84.23.8535. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Devilee P., Slagboom P., Cornelisse C. J., Pearson P. L. Sequence heterogeneity within the human alphoid repetitive DNA family. Nucleic Acids Res. 1986 Mar 11;14(5):2059–2073. doi: 10.1093/nar/14.5.2059. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fuscoe J. C., Clark L. M., Van Dilla M. A. Construction of fifteen human chromosome-specific DNA libraries from flow-purified chromosomes. Cytogenet Cell Genet. 1986;43(1-2):79–86. doi: 10.1159/000132301. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Higgins M. J., Wang H. S., Shtromas I., Haliotis T., Roder J. C., Holden J. J., White B. N. Organization of a repetitive human 1.8 kb KpnI sequence localized in the heterochromatin of chromosome 15. Chromosoma. 1985;93(1):77–86. doi: 10.1007/BF01259449. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jabs E. W., Carpenter N. Molecular cytogenetic evidence for amplification of chromosome-specific alphoid sequences at enlarged C-bands on chromosome 6. Am J Hum Genet. 1988 Jul;43(1):69–74. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jabs E. W., Meyers D. A., Bias W. B. Linkage studies of polymorphic, repeated DNA sequences in centromeric regions of human chromosomes. Am J Hum Genet. 1986 Mar;38(3):297–308. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jabs E. W., Persico M. G. Characterization of human centromeric regions of specific chromosomes by means of alphoid DNA sequences. Am J Hum Genet. 1987 Sep;41(3):374–390. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jabs E. W., Wolf S. F., Migeon B. R. Characterization of a cloned DNA sequence that is present at centromeres of all human autosomes and the X chromosome and shows polymorphic variation. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1984 Aug;81(15):4884–4888. doi: 10.1073/pnas.81.15.4884. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jabs E. W., Wolf S. F., Migeon B. R. Characterization of reiterated human DNA with respect to mammalian X chromosome homology. Somat Cell Mol Genet. 1984 Jan;10(1):93–103. doi: 10.1007/BF01534476. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jeffreys A. J., Wilson V., Thein S. L. Hypervariable 'minisatellite' regions in human DNA. Nature. 1985 Mar 7;314(6006):67–73. doi: 10.1038/314067a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jørgensen A. L., Bostock C. J., Bak A. L. Chromosome-specific subfamilies within human alphoid repetitive DNA. J Mol Biol. 1986 Jan 20;187(2):185–196. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(86)90227-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kenwrick S., Patterson M., Speer A., Fischbeck K., Davies K. Molecular analysis of the Duchenne muscular dystrophy region using pulsed field gel electrophoresis. Cell. 1987 Jan 30;48(2):351–357. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(87)90438-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lawrance S. K., Smith C. L., Srivastava R., Cantor C. R., Weissman S. M. Megabase-scale mapping of the HLA gene complex by pulsed field gel electrophoresis. Science. 1987 Mar 13;235(4794):1387–1390. doi: 10.1126/science.3029868. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Manuelidis L. Complex and simple sequences in human repeated DNAs. Chromosoma. 1978 Mar 22;66(1):1–21. doi: 10.1007/BF00285812. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McCutchan T., Hsu H., Thayer R. E., Singer M. F. Organization of African green monkey DNA at junctions between alpha-satellite and other DNA sequences. J Mol Biol. 1982 May 15;157(2):195–211. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(82)90230-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Moyzis R. K., Albright K. L., Bartholdi M. F., Cram L. S., Deaven L. L., Hildebrand C. E., Joste N. E., Longmire J. L., Meyne J., Schwarzacher-Robinson T. Human chromosome-specific repetitive DNA sequences: novel markers for genetic analysis. Chromosoma. 1987;95(6):375–386. doi: 10.1007/BF00333988. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Potter S. S., Jones R. S. Unusual domains of human alphoid satellite DNA with contiguous non-satellite sequences: sequence analysis of a junction region. Nucleic Acids Res. 1983 May 25;11(10):3137–3153. doi: 10.1093/nar/11.10.3137. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schwartz D. C., Cantor C. R. Separation of yeast chromosome-sized DNAs by pulsed field gradient gel electrophoresis. Cell. 1984 May;37(1):67–75. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(84)90301-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Singer M. F. Highly repeated sequences in mammalian genomes. Int Rev Cytol. 1982;76:67–112. doi: 10.1016/s0074-7696(08)61789-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tyler-Smith C., Brown W. R. Structure of the major block of alphoid satellite DNA on the human Y chromosome. J Mol Biol. 1987 Jun 5;195(3):457–470. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(87)90175-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Waye J. S., Durfy S. J., Pinkel D., Kenwrick S., Patterson M., Davies K. E., Willard H. F. Chromosome-specific alpha satellite DNA from human chromosome 1: hierarchical structure and genomic organization of a polymorphic domain spanning several hundred kilobase pairs of centromeric DNA. Genomics. 1987 Sep;1(1):43–51. doi: 10.1016/0888-7543(87)90103-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Waye J. S., England S. B., Willard H. F. Genomic organization of alpha satellite DNA on human chromosome 7: evidence for two distinct alphoid domains on a single chromosome. Mol Cell Biol. 1987 Jan;7(1):349–356. doi: 10.1128/mcb.7.1.349. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Waye J. S., Willard H. F. Chromosome-specific alpha satellite DNA: nucleotide sequence analysis of the 2.0 kilobasepair repeat from the human X chromosome. Nucleic Acids Res. 1985 Apr 25;13(8):2731–2743. doi: 10.1093/nar/13.8.2731. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Willard H. F., Waye J. S. Chromosome-specific subsets of human alpha satellite DNA: analysis of sequence divergence within and between chromosomal subsets and evidence for an ancestral pentameric repeat. J Mol Evol. 1987;25(3):207–214. doi: 10.1007/BF02100014. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wolfe J., Darling S. M., Erickson R. P., Craig I. W., Buckle V. J., Rigby P. W., Willard H. F., Goodfellow P. N. Isolation and characterization of an alphoid centromeric repeat family from the human Y chromosome. J Mol Biol. 1985 Apr 20;182(4):477–485. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(85)90234-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wu J. C., Manuelidis L. Sequence definition and organization of a human repeated DNA. J Mol Biol. 1980 Sep 25;142(3):363–386. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(80)90277-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- van Ommen G. J., Verkerk J. M., Hofker M. H., Monaco A. P., Kunkel L. M., Ray P., Worton R., Wieringa B., Bakker E., Pearson P. L. A physical map of 4 million bp around the Duchenne muscular dystrophy gene on the human X-chromosome. Cell. 1986 Nov 21;47(4):499–504. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(86)90614-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]