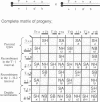
Abstract
We describe a meiotic fine-structure mapping strategy for achieving molecular access to developmental mutations in the mouse. The induction of lethal point mutations with the potent germ-line mutagen N-ethyl-N-nitrosourea has been reported. One lethal mutation of prime interest is an allele at the quaking locus on chromosome 17. To map this mutation, quaking(lethal-1), we have intercrossed hybrid mice that carry distinct alleles at many classical and DNA marker loci on proximal chromosome 17. From this cross we have obtained 337 animals recombinant in the T to H-2 region. This number of crossovers provides a mapping resolution in the size range of single mammalian genes if recombinational hot spots are absent. DNA samples obtained from these recombinant animals can be used retrospectively to map any restriction fragment length polymorphism in the region. This set of DNA samples has been used to map the molecular marker D17RP17 just distal of quaking(lethal-1). With the nested set of crossover DNA samples and appropriate cloning techniques, this tightly linked marker can be used to clone the quaking locus.
Full text
PDF
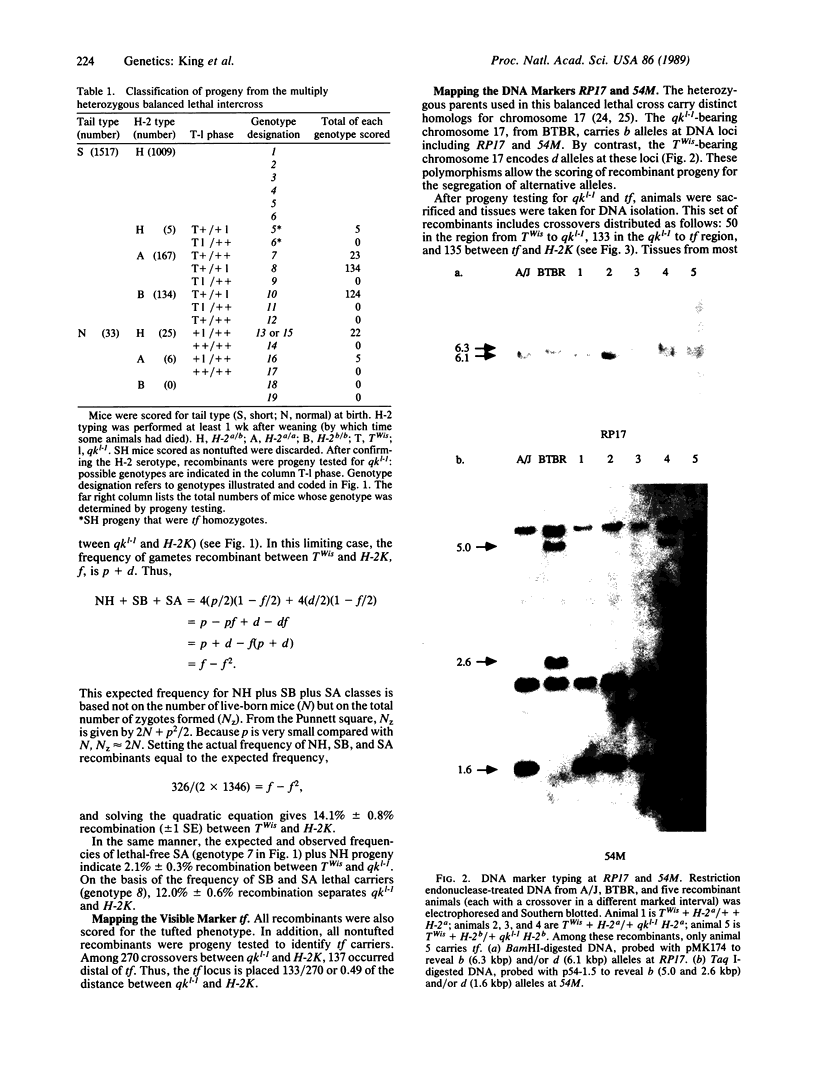
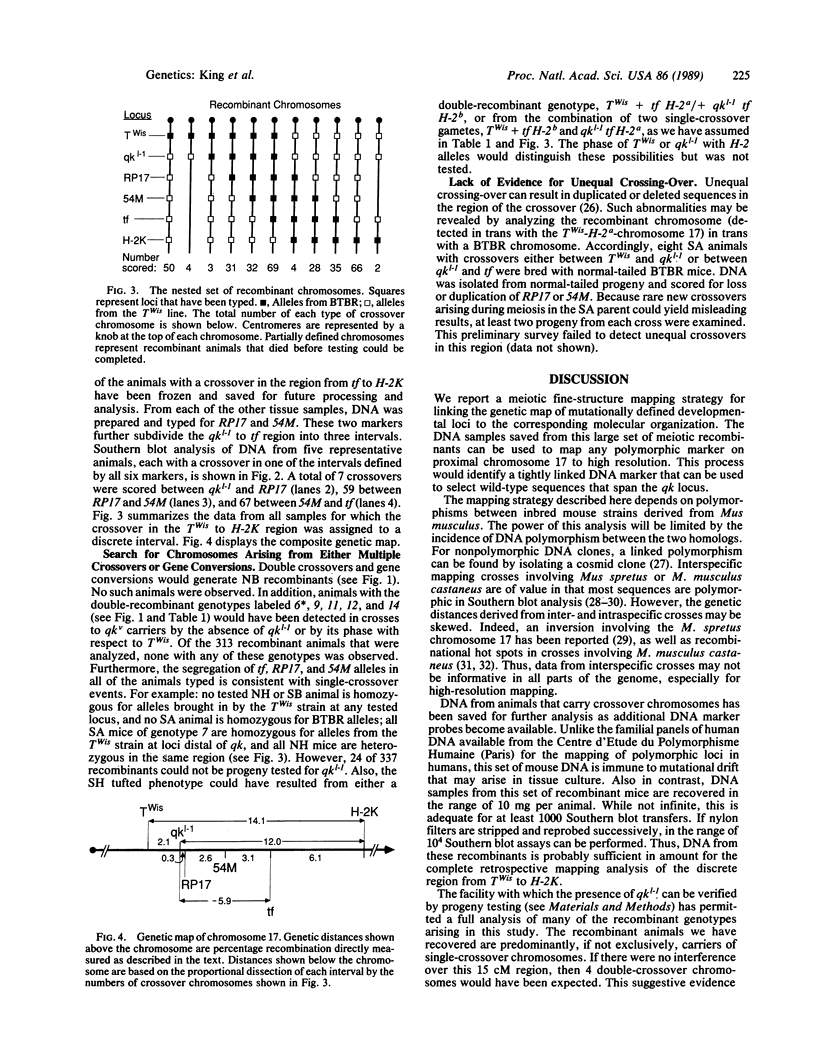

Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Amar L. C., Dandolo L., Hanauer A., Cook A. R., Arnaud D., Mandel J. L., Avner P. Conservation and reorganization of loci on the mammalian X chromosome: a molecular framework for the identification of homologous subchromosomal regions in man and mouse. Genomics. 1988 Apr;2(3):220–230. doi: 10.1016/0888-7543(88)90006-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Avner P., Amar L., Dandolo L., Guénet J. L. Genetic analysis of the mouse using interspecific crosses. Trends Genet. 1988 Jan;4(1):18–23. doi: 10.1016/0168-9525(88)90123-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bird A. P. CpG-rich islands and the function of DNA methylation. Nature. 1986 May 15;321(6067):209–213. doi: 10.1038/321209a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Blin N., Stafford D. W. A general method for isolation of high molecular weight DNA from eukaryotes. Nucleic Acids Res. 1976 Sep;3(9):2303–2308. doi: 10.1093/nar/3.9.2303. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bode V. C. Ethylnitrosourea mutagenesis and the isolation of mutant alleles for specific genes located in the T region of mouse chromosome 17. Genetics. 1984 Oct;108(2):457–470. doi: 10.1093/genetics/108.2.457. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Breindl M., Harbers K., Jaenisch R. Retrovirus-induced lethal mutation in collagen I gene of mice is associated with an altered chromatin structure. Cell. 1984 Aug;38(1):9–16. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(84)90521-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bridges C B, Olbrycht T M. The Multiple Stock "Xple" and Its Use. Genetics. 1926 Jan;11(1):41–56. doi: 10.1093/genetics/11.1.41. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brown W. R., Bird A. P. Long-range restriction site mapping of mammalian genomic DNA. 1986 Jul 31-Aug 6Nature. 322(6078):477–481. doi: 10.1038/322477a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Burke D. T., Carle G. F., Olson M. V. Cloning of large segments of exogenous DNA into yeast by means of artificial chromosome vectors. Science. 1987 May 15;236(4803):806–812. doi: 10.1126/science.3033825. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Búcan M., Herrmann B. G., Frischauf A. M., Bautch V. L., Bode V., Silver L. M., Martin G. R., Lehrach H. Deletion and duplication of DNA sequences is associated with the embryonic lethal phenotype of the t9 complementation group of the mouse t complex. Genes Dev. 1987 Jun;1(4):376–385. doi: 10.1101/gad.1.4.376. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dove W. F. Molecular genetics of Mus musculus: point mutagenesis and millimorgans. Genetics. 1987 May;116(1):5–8. doi: 10.1093/genetics/116.1.5. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Helentjaris T., Gesteland R. Evaluation of random cDNA clones as probes for human restriction fragment polymorphisms. J Mol Appl Genet. 1983;2(3):237–247. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Herrmann B. G., Barlow D. P., Lehrach H. A large inverted duplication allows homologous recombination between chromosomes heterozygous for the proximal t complex inversion. Cell. 1987 Mar 13;48(5):813–825. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(87)90078-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Herrmann B., Bućan M., Mains P. E., Frischauf A. M., Silver L. M., Lehrach H. Genetic analysis of the proximal portion of the mouse t complex: evidence for a second inversion within t haplotypes. Cell. 1986 Feb 14;44(3):469–476. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(86)90468-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Justice M. J., Bode V. C. Induction of new mutations in a mouse t-haplotype using ethylnitrosourea mutagenesis. Genet Res. 1986 Jun;47(3):187–192. doi: 10.1017/s0016672300023119. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Justice M. J., Bode V. C. Three ENU-induced alleles of the murine quaking locus are recessive embryonic lethal mutations. Genet Res. 1988 Apr;51(2):95–102. doi: 10.1017/s0016672300024101. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kuehn M. R., Bradley A., Robertson E. J., Evans M. J. A potential animal model for Lesch-Nyhan syndrome through introduction of HPRT mutations into mice. Nature. 1987 Mar 19;326(6110):295–298. doi: 10.1038/326295a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lovett M., Cheng Z. Y., Lamela E. M., Yokoi T., Epstein C. J. Molecular markers for the agouti coat color locus of the mouse. Genetics. 1987 Apr;115(4):747–754. doi: 10.1093/genetics/115.4.747. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mann E. A., Silver L. M., Elliott R. W. Genetic analysis of a mouse t complex locus that is homologous to a kidney cDNA clone. Genetics. 1986 Nov;114(3):993–1006. doi: 10.1093/genetics/114.3.993. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Murphy D. B., Shrefler D. C. Cross-reactivity between H-2K and H-2D products. I. Evidence for extensive and reciprocal serological cross-reactivity. J Exp Med. 1975 Feb 1;141(2):374–391. doi: 10.1084/jem.141.2.374. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Readhead C., Popko B., Takahashi N., Shine H. D., Saavedra R. A., Sidman R. L., Hood L. Expression of a myelin basic protein gene in transgenic shiverer mice: correction of the dysmyelinating phenotype. Cell. 1987 Feb 27;48(4):703–712. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(87)90248-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rigby P. W., Dieckmann M., Rhodes C., Berg P. Labeling deoxyribonucleic acid to high specific activity in vitro by nick translation with DNA polymerase I. J Mol Biol. 1977 Jun 15;113(1):237–251. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(77)90052-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rinchik E. M., Russell L. B., Copeland N. G., Jenkins N. A. Molecular genetic analysis of the dilute-short ear (d-se) region of the mouse. Genetics. 1986 Feb;112(2):321–342. doi: 10.1093/genetics/112.2.321. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Robert B., Barton P., Minty A., Daubas P., Weydert A., Bonhomme F., Catalan J., Chazottes D., Guénet J. L., Buckingham M. Investigation of genetic linkage between myosin and actin genes using an interspecific mouse back-cross. Nature. 1985 Mar 14;314(6007):181–183. doi: 10.1038/314181a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Russell E. S. A history of mouse genetics. Annu Rev Genet. 1985;19:1–28. doi: 10.1146/annurev.ge.19.120185.000245. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Russell W. L., Kelly E. M., Hunsicker P. R., Bangham J. W., Maddux S. C., Phipps E. L. Specific-locus test shows ethylnitrosourea to be the most potent mutagen in the mouse. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1979 Nov;76(11):5818–5819. doi: 10.1073/pnas.76.11.5818. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- SIDMAN R. L., DICKIE M. M., APPEL S. H. MUTANT MICE (QUAKING AND JIMPY) WITH DEFICIENT MYELINATION IN THE CENTRAL NERVOUS SYSTEM. Science. 1964 Apr 17;144(3616):309–311. doi: 10.1126/science.144.3616.309. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schnieke A., Harbers K., Jaenisch R. Embryonic lethal mutation in mice induced by retrovirus insertion into the alpha 1(I) collagen gene. 1983 Jul 28-Aug 3Nature. 304(5924):315–320. doi: 10.1038/304315a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shedlovsky A., Guenet J. L., Johnson L. L., Dove W. F. Induction of recessive lethal mutations in the T/t-H-2 region of the mouse genome by a point mutagen. Genet Res. 1986 Apr;47(2):135–142. doi: 10.1017/s0016672300022977. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shedlovsky A., King T. R., Dove W. F. Saturation germ line mutagenesis of the murine t region including a lethal allele at the quaking locus. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1988 Jan;85(1):180–184. doi: 10.1073/pnas.85.1.180. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shiroishi T., Sagai T., Moriwaki K. Sexual preference of meiotic recombination within the H-2 complex. Immunogenetics. 1987;25(4):258–262. doi: 10.1007/BF00404696. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Silver L. M. Mouse t haplotypes. Annu Rev Genet. 1985;19:179–208. doi: 10.1146/annurev.ge.19.120185.001143. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Steinmetz M., Stephan D., Fischer Lindahl K. Gene organization and recombinational hotspots in the murine major histocompatibility complex. Cell. 1986 Mar 28;44(6):895–904. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(86)90012-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tartof K. D. Unequal crossing over then and now. Genetics. 1988 Sep;120(1):1–6. doi: 10.1093/genetics/120.1.1. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]