Abstract
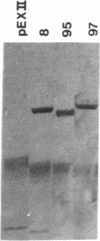
The nucleotide sequence coding for the cytotoxic T-lymphocyte (CTL) protein perforin 1 (P1) has been determined and the corresponding protein sequence has been derived. Murine CTL cDNA libraries contained in the vector lambda gt11 were screened by using a monospecific antiserum to purified P1. Three recombinant phages were isolated and their cDNA inserts were sequenced. The derived protein sequence contains 554 amino acids and displays, as expected, considerable homology with certain functional domains in the complement components C9, C8 alpha, C8 beta, and C7. The identity of P1 cDNA clones was verified by prokaryotic expression and the reactivities of antisera produced to the expressed proteins. In addition, antisera were produced to two synthetic peptides located in the center and C-terminal portions of P1. All antisera reacted with purified P1. In Northern blot analyses, P1 cDNA probes recognized a 2.9-kilobase mRNA only in CTL. Perforin mRNA was found in all cloned CTL and in all mixed lymphocyte reactions that gave rise to cytotoxic cells. Perforin mRNA was also detected in virus-specific CTL that had been generated in vivo and isolated from liver tissue of mice infected with lymphocytic choriomeningitis virus. The cell-specific expression of perforin is consistent with its postulated role in cytolysis.
Full text
PDF




Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Berke G., Rosen D. Are lytic granules and perforin 1 involved in lysis induced by in vivo-primed peritoneal exudate cytolytic T lymphocytes? Transplant Proc. 1987 Feb;19(1 Pt 1):412–416. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chomczynski P., Sacchi N. Single-step method of RNA isolation by acid guanidinium thiocyanate-phenol-chloroform extraction. Anal Biochem. 1987 Apr;162(1):156–159. doi: 10.1006/abio.1987.9999. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dennert G., Anderson C. G., Warner J. T killer cells play a role in allogeneic bone marrow graft rejection but not in hybrid resistance. J Immunol. 1985 Dec;135(6):3729–3734. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dennert G., Podack E. R. Cytolysis by H-2-specific T killer cells. Assembly of tubular complexes on target membranes. J Exp Med. 1983 May 1;157(5):1483–1495. doi: 10.1084/jem.157.5.1483. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- DiScipio R. G., Chakravarti D. N., Muller-Eberhard H. J., Fey G. H. The structure of human complement component C7 and the C5b-7 complex. J Biol Chem. 1988 Jan 5;263(1):549–560. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- DiScipio R. G., Gehring M. R., Podack E. R., Kan C. C., Hugli T. E., Fey G. H. Nucleotide sequence of cDNA and derived amino acid sequence of human complement component C9. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1984 Dec;81(23):7298–7302. doi: 10.1073/pnas.81.23.7298. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Duke R. C., Chervenak R., Cohen J. J. Endogenous endonuclease-induced DNA fragmentation: an early event in cell-mediated cytolysis. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1983 Oct;80(20):6361–6365. doi: 10.1073/pnas.80.20.6361. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Geiger B., Rosen D., Berke G. Spatial relationships of microtubule-organizing centers and the contact area of cytotoxic T lymphocytes and target cells. J Cell Biol. 1982 Oct;95(1):137–143. doi: 10.1083/jcb.95.1.137. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gershenfeld H. K., Weissman I. L. Cloning of a cDNA for a T cell-specific serine protease from a cytotoxic T lymphocyte. Science. 1986 May 16;232(4752):854–858. doi: 10.1126/science.2422755. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Haefliger J. A., Tschopp J., Nardelli D., Wahli W., Kocher H. P., Tosi M., Stanley K. K. Complementary DNA cloning of complement C8 beta and its sequence homology to C9. Biochemistry. 1987 Jun 16;26(12):3551–3556. doi: 10.1021/bi00386a045. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Herberman R. B., Ortaldo J. R. Natural killer cells: their roles in defenses against disease. Science. 1981 Oct 2;214(4516):24–30. doi: 10.1126/science.7025208. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Iwamoto A., Ohashi P. S., Pircher H., Walker C. L., Michalopoulos E. E., Rupp F., Hengartner H., Mak T. W. T cell receptor variable gene usage in a specific cytotoxic T cell response. Primary structure of the antigen-MHC receptor of four hapten-specific cytotoxic T cell clones. J Exp Med. 1987 Mar 1;165(3):591–600. doi: 10.1084/jem.165.3.591. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kupfer A., Dennert G., Singer S. J. Polarization of the Golgi apparatus and the microtubule-organizing center within cloned natural killer cells bound to their targets. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1983 Dec;80(23):7224–7228. doi: 10.1073/pnas.80.23.7224. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Liu C. C., Steffen M., King F., Young J. D. Identification, isolation, and characterization of a novel cytotoxin in murine cytolytic lymphocytes. Cell. 1987 Nov 6;51(3):393–403. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(87)90635-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lobe C. G., Finlay B. B., Paranchych W., Paetkau V. H., Bleackley R. C. Novel serine proteases encoded by two cytotoxic T lymphocyte-specific genes. Science. 1986 May 16;232(4752):858–861. doi: 10.1126/science.3518058. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- MacDermott R. P., Schmidt R. E., Caulfield J. P., Hein A., Bartley G. T., Ritz J., Schlossman S. F., Austen K. F., Stevens R. L. Proteoglycans in cell-mediated cytotoxicity. Identification, localization, and exocytosis of a chondroitin sulfate proteoglycan from human cloned natural killer cells during target cell lysis. J Exp Med. 1985 Dec 1;162(6):1771–1787. doi: 10.1084/jem.162.6.1771. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Masson D., Tschopp J. A family of serine esterases in lytic granules of cytolytic T lymphocytes. Cell. 1987 Jun 5;49(5):679–685. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(87)90544-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Masson D., Tschopp J. Isolation of a lytic, pore-forming protein (perforin) from cytolytic T-lymphocytes. J Biol Chem. 1985 Aug 5;260(16):9069–9072. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McChesney M. B., Oldstone M. B. Viruses perturb lymphocyte functions: selected principles characterizing virus-induced immunosuppression. Annu Rev Immunol. 1987;5:279–304. doi: 10.1146/annurev.iy.05.040187.001431. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mueller C., Gershenfeld H. K., Lobe C. G., Okada C. Y., Bleackley R. C., Weissman I. L. A high proportion of T lymphocytes that infiltrate H-2-incompatible heart allografts in vivo express genes encoding cytotoxic cell-specific serine proteases, but do not express the MEL-14-defined lymph node homing receptor. J Exp Med. 1988 Mar 1;167(3):1124–1136. doi: 10.1084/jem.167.3.1124. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ostergaard H. L., Kane K. P., Mescher M. F., Clark W. R. Cytotoxic T lymphocyte mediated lysis without release of serine esterase. Nature. 1987 Nov 5;330(6143):71–72. doi: 10.1038/330071a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pasternack M. S., Eisen H. N. A novel serine esterase expressed by cytotoxic T lymphocytes. 1985 Apr 25-May 1Nature. 314(6013):743–745. doi: 10.1038/314743a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pasternack M. S., Verret C. R., Liu M. A., Eisen H. N. Serine esterase in cytolytic T lymphocytes. Nature. 1986 Aug 21;322(6081):740–743. doi: 10.1038/322740a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Podack E. R., Dennert G. Assembly of two types of tubules with putative cytolytic function by cloned natural killer cells. 1983 Mar 31-Apr 6Nature. 302(5907):442–445. doi: 10.1038/302442a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Podack E. R., Young J. D., Cohn Z. A. Isolation and biochemical and functional characterization of perforin 1 from cytolytic T-cell granules. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1985 Dec;82(24):8629–8633. doi: 10.1073/pnas.82.24.8629. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Queen C., Korn L. J. A comprehensive sequence analysis program for the IBM personal computer. Nucleic Acids Res. 1984 Jan 11;12(1 Pt 2):581–599. doi: 10.1093/nar/12.1part2.581. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rao A. G., Howard O. M., Ng S. C., Whitehead A. S., Colten H. R., Sodetz J. M. Complementary DNA and derived amino acid sequence of the alpha subunit of human complement protein C8: evidence for the existence of a separate alpha subunit messenger RNA. Biochemistry. 1987 Jun 16;26(12):3556–3564. doi: 10.1021/bi00386a046. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rupp F., Acha-Orbea H., Hengartner H., Zinkernagel R., Joho R. Identical V beta T-cell receptor genes used in alloreactive cytotoxic and antigen plus I-A specific helper T cells. 1985 May 30-Jun 5Nature. 315(6018):425–427. doi: 10.1038/315425a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Russell J. H., Masakowski V., Rucinsky T., Phillips G. Mechanisms of immune lysis. III. Characterization of the nature and kinetics of the cytotoxic T lymphocyte-induced nuclear lesion in the target. J Immunol. 1982 May;128(5):2087–2094. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schmid D. S., Tite J. P., Ruddle N. H. DNA fragmentation: manifestation of target cell destruction mediated by cytotoxic T-cell lines, lymphotoxin-secreting helper T-cell clones, and cell-free lymphotoxin-containing supernatant. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1986 Mar;83(6):1881–1885. doi: 10.1073/pnas.83.6.1881. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stanley K. K., Luzio J. P. Construction of a new family of high efficiency bacterial expression vectors: identification of cDNA clones coding for human liver proteins. EMBO J. 1984 Jun;3(6):1429–1434. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1984.tb01988.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stanley K. K., Page M., Campbell A. K., Luzio J. P. A mechanism for the insertion of complement component C9 into target membranes. Mol Immunol. 1986 May;23(5):451–458. doi: 10.1016/0161-5890(86)90108-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tschopp J., Masson D., Stanley K. K. Structural/functional similarity between proteins involved in complement- and cytotoxic T-lymphocyte-mediated cytolysis. 1986 Aug 28-Sep 3Nature. 322(6082):831–834. doi: 10.1038/322831a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Young J. D., Cohn Z. A., Podack E. R. The ninth component of complement and the pore-forming protein (perforin 1) from cytotoxic T cells: structural, immunological, and functional similarities. Science. 1986 Jul 11;233(4760):184–190. doi: 10.1126/science.2425429. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Young R. A., Davis R. W. Yeast RNA polymerase II genes: isolation with antibody probes. Science. 1983 Nov 18;222(4625):778–782. doi: 10.1126/science.6356359. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zinkernagel R. M., Doherty P. C. H-2 compatability requirement for T-cell-mediated lysis of target cells infected with lymphocytic choriomeningitis virus. Different cytotoxic T-cell specificities are associated with structures coded for in H-2K or H-2D;. J Exp Med. 1975 Jun 1;141(6):1427–1436. doi: 10.1084/jem.141.6.1427. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zinkernagel R. M., Haenseler E., Leist T., Cerny A., Hengartner H., Althage A. T cell-mediated hepatitis in mice infected with lymphocytic choriomeningitis virus. Liver cell destruction by H-2 class I-restricted virus-specific cytotoxic T cells as a physiological correlate of the 51Cr-release assay? J Exp Med. 1986 Oct 1;164(4):1075–1092. doi: 10.1084/jem.164.4.1075. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]