Abstract
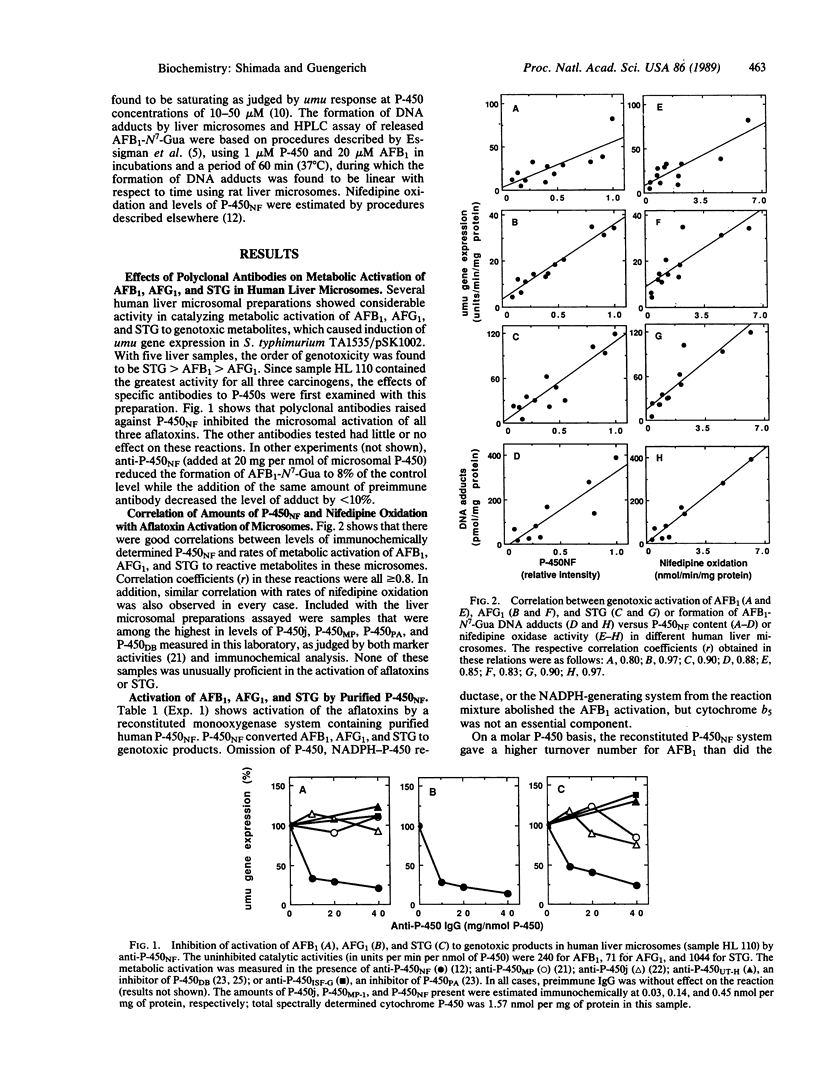
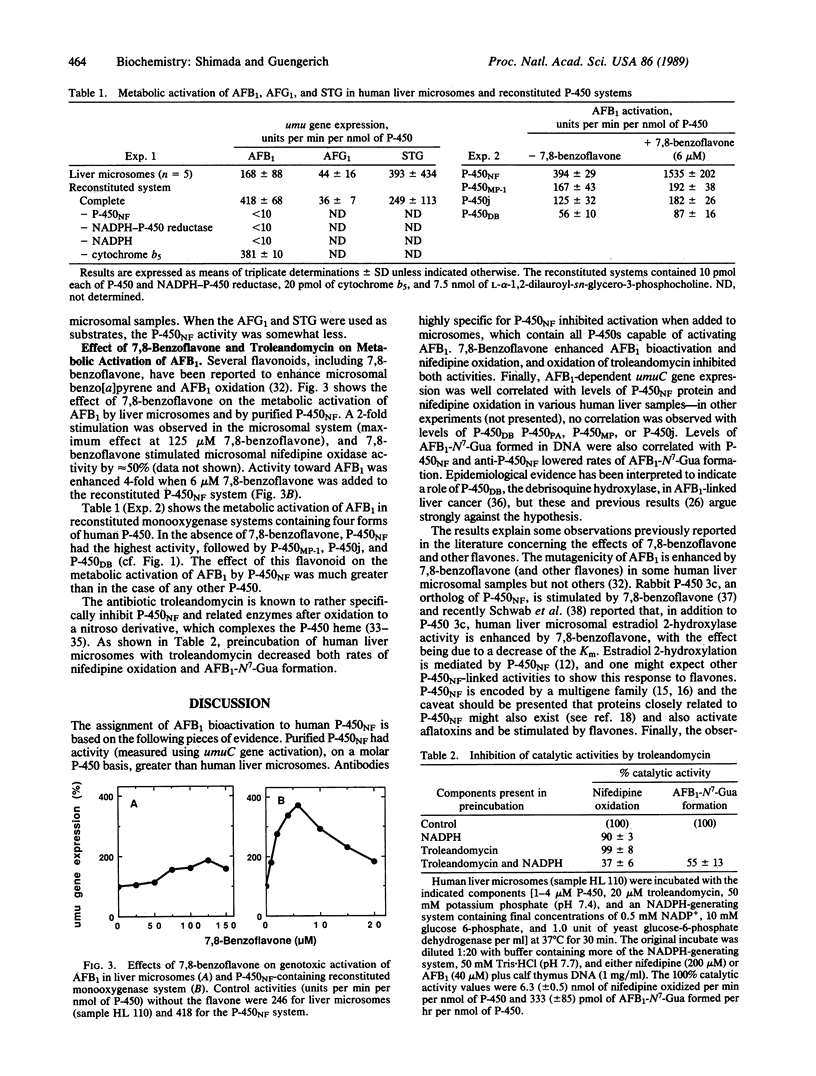
In vitro studies with human liver indicate that the major catalyst involved in the bioactivation of the hepato-carcinogen aflatoxin B1 (AFB1) to its genotoxic 2,3-epoxide derivative is cytochrome P-450NF (P-450NF), a previously characterized protein that also catalyzes the oxidation of nifedipine and other dihydropyridines, quinidine, macrolide antibiotics, various steroids, and other compounds. Evidence was obtained using activation of AFB1 as monitored by umuC gene expression response in Salmonella typhimurium TA1535/pSK1002 and enzyme reconstitution, immunochemical inhibition, correlation of response with levels of P-450NF and nifedipine oxidase activity in different liver samples, stimulation of activity by 7,8-benzoflavone, and inhibition of activity by troleandomycin. Similar results were obtained when levels of 2,3-dihydro-2-(N7-guanyl)-3-hydroxyaflatoxin B1 formed in DNA were measured. P-450NF or a closely related protein also appears to be the major catalyst involved in the activation of aflatoxin G1 and sterigmatocystin, the latter compound being more genotoxic than AFB1 in these systems. Several drugs and conditions are known to influence the levels and activity of P-450NF in human liver, and the activity of the enzyme can be estimated by noninvasive assays. These findings provide a test system for the hypothesis that a specific human disease state (liver cancer) is linked to the level of oxidative metabolism in populations in which aflatoxin ingestion is high.
Full text
PDF

Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Ayesh R., Idle J. R., Ritchie J. C., Crothers M. J., Hetzel M. R. Metabolic oxidation phenotypes as markers for susceptibility to lung cancer. Nature. 1984 Nov 8;312(5990):169–170. doi: 10.1038/312169a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Beaune P. H., Umbenhauer D. R., Bork R. W., Lloyd R. S., Guengerich F. P. Isolation and sequence determination of a cDNA clone related to human cytochrome P-450 nifedipine oxidase. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1986 Nov;83(21):8064–8068. doi: 10.1073/pnas.83.21.8064. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Buening M. K., Chang R. L., Huang M. T., Fortner J. G., Wood A. W., Conney A. H. Activation and inhibition of benzo(a)pyrene and aflatoxin B1 metabolism in human liver microsomes by naturally occurring flavonoids. Cancer Res. 1981 Jan;41(1):67–72. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Distlerath L. M., Reilly P. E., Martin M. V., Davis G. G., Wilkinson G. R., Guengerich F. P. Purification and characterization of the human liver cytochromes P-450 involved in debrisoquine 4-hydroxylation and phenacetin O-deethylation, two prototypes for genetic polymorphism in oxidative drug metabolism. J Biol Chem. 1985 Jul 25;260(15):9057–9067. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Essigmann J. M., Barker L. J., Fowler K. W., Francisco M. A., Reinhold V. N., Wogan G. N. Sterigmatocystin-DNA interactions: identification of a major adduct formed after metabolic activation in vitro. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1979 Jan;76(1):179–183. doi: 10.1073/pnas.76.1.179. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Garner R. C. Microsome-dependent binding of aflatoxin B1 to DNA, RNA, polyribonucleotides and protein in vitro. Chem Biol Interact. 1973 Feb;6(2):125–129. doi: 10.1016/0009-2797(73)90079-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Garner R. C. Reduction in binding of [14C] aflatoxin B1 to rat liver macromolecules by phenobarbitone pretreatment. Biochem Pharmacol. 1975 Aug 15;24(16):1553–1556. doi: 10.1016/0006-2952(75)90039-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Groopman J. D., Donahue P. R., Zhu J. Q., Chen J. S., Wogan G. N. Aflatoxin metabolism in humans: detection of metabolites and nucleic acid adducts in urine by affinity chromatography. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1985 Oct;82(19):6492–6496. doi: 10.1073/pnas.82.19.6492. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Guengerich F. P., Dannan G. A., Wright S. T., Martin M. V., Kaminsky L. S. Purification and characterization of liver microsomal cytochromes p-450: electrophoretic, spectral, catalytic, and immunochemical properties and inducibility of eight isozymes isolated from rats treated with phenobarbital or beta-naphthoflavone. Biochemistry. 1982 Nov 9;21(23):6019–6030. doi: 10.1021/bi00266a045. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Guengerich F. P., Martin M. V., Beaune P. H., Kremers P., Wolff T., Waxman D. J. Characterization of rat and human liver microsomal cytochrome P-450 forms involved in nifedipine oxidation, a prototype for genetic polymorphism in oxidative drug metabolism. J Biol Chem. 1986 Apr 15;261(11):5051–5060. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Guengerich F. P., Müller-Enoch D., Blair I. A. Oxidation of quinidine by human liver cytochrome P-450. Mol Pharmacol. 1986 Sep;30(3):287–295. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Guengerich F. P. Oxidation of 17 alpha-ethynylestradiol by human liver cytochrome P-450. Mol Pharmacol. 1988 May;33(5):500–508. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Guengerich F. P. Roles of cytochrome P-450 enzymes in chemical carcinogenesis and cancer chemotherapy. Cancer Res. 1988 Jun 1;48(11):2946–2954. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Huang M. T., Johnson E. F., Muller-Eberhard U., Koop D. R., Coon M. J., Conney A. H. Specificity in the activation and inhibition by flavonoids of benzo[a]pyrene hydroxylation by cytochrome P-450 isozymes from rabbit liver microsomes. J Biol Chem. 1981 Nov 10;256(21):10897–10901. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Idle J. R., Mahgoub A., Sloan T. P., Smith R. L., Mbanefo C. O., Bababunmi E. A. Some observations on the oxidation phenotype status of Nigerian patients presenting with cancer. Cancer Lett. 1981 Feb;11(4):331–338. doi: 10.1016/0304-3835(81)90099-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kaisary A., Smith P., Jaczq E., McAllister C. B., Wilkinson G. R., Ray W. A., Branch R. A. Genetic predisposition to bladder cancer: ability to hydroxylate debrisoquine and mephenytoin as risk factors. Cancer Res. 1987 Oct 15;47(20):5488–5493. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kitada M., Kamataki T., Itahashi K., Rikihisa T., Kanakubo Y. P-450 HFLa, a form of cytochrome P-450 purified from human fetal livers, is the 16 alpha-hydroxylase of dehydroepiandrosterone 3-sulfate. J Biol Chem. 1987 Oct 5;262(28):13534–13537. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kleinbloesem C. H., van Brummelen P., Faber H., Danhof M., Vermeulen N. P., Breimer D. D. Variability in nifedipine pharmacokinetics and dynamics: a new oxidation polymorphism in man. Biochem Pharmacol. 1984 Nov 15;33(22):3721–3724. doi: 10.1016/0006-2952(84)90165-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McCann J., Choi E., Yamasaki E., Ames B. N. Detection of carcinogens as mutagens in the Salmonella/microsome test: assay of 300 chemicals. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1975 Dec;72(12):5135–5139. doi: 10.1073/pnas.72.12.5135. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mori H., Sugie S., Yoshimi N., Kitamura J., Niwa M., Hamasaki T., Kawai K. Genotoxic effects of a variety of sterigmatocystin-related compounds in the hepatocyte/DNA-repair test and the Salmonella microsome assay. Mutat Res. 1986 Mar;173(3):217–222. doi: 10.1016/0165-7992(86)90039-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nakamura S. I., Oda Y., Shimada T., Oki I., Sugimoto K. SOS-inducing activity of chemical carcinogens and mutagens in Salmonella typhimurium TA1535/pSK1002: examination with 151 chemicals. Mutat Res. 1987 Dec;192(4):239–246. doi: 10.1016/0165-7992(87)90063-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nebert D. W., Adesnik M., Coon M. J., Estabrook R. W., Gonzalez F. J., Guengerich F. P., Gunsalus I. C., Johnson E. F., Kemper B., Levin W. The P450 gene superfamily: recommended nomenclature. DNA. 1987 Feb;6(1):1–11. doi: 10.1089/dna.1987.6.1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Oda Y., Nakamura S., Oki I., Kato T., Shinagawa H. Evaluation of the new system (umu-test) for the detection of environmental mutagens and carcinogens. Mutat Res. 1985 Oct;147(5):219–229. doi: 10.1016/0165-1161(85)90062-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ohnhaus E. E., Park B. K. Measurement of urinary 6-beta-hydroxycortisol excretion as an in vivo parameter in the clinical assessment of the microsomal enzyme-inducing capacity of antipyrine, phenobarbitone and rifampicin. Eur J Clin Pharmacol. 1979 Mar 26;15(2):139–145. doi: 10.1007/BF00609878. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pessayre D., Descatoire V., Konstantinova-Mitcheva M., Wandscheer J. C., Cobert B., Level R., Benhamou P. J., Jaouen M., Mansuy D. Self-induction by triacetyloleandomycin of its own transformation into a metabolite forming a stable 456 nm-absorbing complex with cytochrome P-450. Biochem Pharmacol. 1981 Mar 15;30(6):553–558. doi: 10.1016/0006-2952(81)90125-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Purchase I. F., Van Der Watt J. J. Carcinogenicity of sterigmatocystin. Food Cosmet Toxicol. 1970 Jun;8(3):289–295. doi: 10.1016/s0015-6264(70)80004-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schellens J. H., Soons P. A., Breimer D. D. Lack of bimodality in nifedipine plasma kinetics in a large population of healthy subjects. Biochem Pharmacol. 1988 Jul 1;37(13):2507–2510. doi: 10.1016/0006-2952(88)90238-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schwab G. E., Raucy J. L., Johnson E. F. Modulation of rabbit and human hepatic cytochrome P-450-catalyzed steroid hydroxylations by alpha-naphthoflavone. Mol Pharmacol. 1988 May;33(5):493–499. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shimada T., Misono K. S., Guengerich F. P. Human liver microsomal cytochrome P-450 mephenytoin 4-hydroxylase, a prototype of genetic polymorphism in oxidative drug metabolism. Purification and characterization of two similar forms involved in the reaction. J Biol Chem. 1986 Jan 15;261(2):909–921. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shimada T., Nakamura S. Cytochrome P-450-mediated activation of procarcinogens and promutagens to DNA-damaging products by measuring expression of umu gene in Salmonella typhimurium TA1535/pSK1002. Biochem Pharmacol. 1987 Jun 15;36(12):1979–1987. doi: 10.1016/0006-2952(87)90497-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shimada T., Nakamura S., Imaoka S., Funae Y. Genotoxic and mutagenic activation of aflatoxin B1 by constitutive forms of cytochrome P-450 in rat liver microsomes. Toxicol Appl Pharmacol. 1987 Oct;91(1):13–21. doi: 10.1016/0041-008x(87)90189-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shimada T., Okuda Y. Metabolic activation of environmental carcinogens and mutagens by human liver microsomes. Role of cytochrome P-450 homologous to a 3-methylcholanthrene-inducible isozyme in rat liver. Biochem Pharmacol. 1988 Feb 1;37(3):459–465. doi: 10.1016/0006-2952(88)90215-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Swenson D. H., Lin J. K., Miller E. C., Miller J. A. Aflatoxin B1-2,3-oxide as a probable intermediate in the covalent binding of aflatoxins B1 and B2 to rat liver DNA and ribosomal RNA in vivo. Cancer Res. 1977 Jan;37(1):172–181. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Swenson D. H., Miller E. C., Miller J. A. Aflatoxin B1-2,3-oxide: evidence for its formation in rat liver in vivo and by human liver microsomes in vitro. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1974 Oct 8;60(3):1036–1043. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(74)90417-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Watkins P. B., Wrighton S. A., Maurel P., Schuetz E. G., Mendez-Picon G., Parker G. A., Guzelian P. S. Identification of an inducible form of cytochrome P-450 in human liver. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1985 Sep;82(18):6310–6314. doi: 10.1073/pnas.82.18.6310. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Waxman D. J., Attisano C., Guengerich F. P., Lapenson D. P. Human liver microsomal steroid metabolism: identification of the major microsomal steroid hormone 6 beta-hydroxylase cytochrome P-450 enzyme. Arch Biochem Biophys. 1988 Jun;263(2):424–436. doi: 10.1016/0003-9861(88)90655-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wolff T., Distlerath L. M., Worthington M. T., Groopman J. D., Hammons G. J., Kadlubar F. F., Prough R. A., Martin M. V., Guengerich F. P. Substrate specificity of human liver cytochrome P-450 debrisoquine 4-hydroxylase probed using immunochemical inhibition and chemical modeling. Cancer Res. 1985 May;45(5):2116–2122. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wrighton S. A., Thomas P. E., Ryan D. E., Levin W. Purification and characterization of ethanol-inducible human hepatic cytochrome P-450HLj. Arch Biochem Biophys. 1987 Oct;258(1):292–297. doi: 10.1016/0003-9861(87)90347-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]



