Abstract
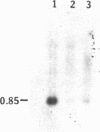
The lymphokine interleukin 2 is an important immune system regulatory glycopolypeptide. It is produced by antigen- or mitogen-stimulated T lymphocytes and is required for the proliferation or clonal expansion of activated T lymphocytes. In this report, it is demonstrated by RNA transfer blot hybridization that the poly(A)+ RNA population of the human placenta contains a 0.85-kilobase RNA transcript that specifically hybridizes to a human interleukin 2 cDNA probe. By using hybridization histochemistry in situ, it is further shown that interleukin 2 RNA transcripts are localized, primarily, to the syncytial (syncytiotrophoblast) layer of the human placenta. Possible roles for syncytiotrophoblast-produced interleukin 2 are suggested and discussed.
Full text
PDF




Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Arya S. K., Gallo R. C. Transcriptional modulation of human T-cell growth factor gene by phorbol ester and interleukin 1. Biochemistry. 1984 Dec 18;23(26):6685–6690. doi: 10.1021/bi00321a062. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Athanassakis I., Bleackley R. C., Paetkau V., Guilbert L., Barr P. J., Wegmann T. G. The immunostimulatory effect of T cells and T cell lymphokines on murine fetally derived placental cells. J Immunol. 1987 Jan 1;138(1):37–44. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Aviv H., Leder P. Purification of biologically active globin messenger RNA by chromatography on oligothymidylic acid-cellulose. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1972 Jun;69(6):1408–1412. doi: 10.1073/pnas.69.6.1408. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bessler H., Sirota L., Dulitzky F., Djaldetti M. Cord serum inhibits allogeneic mixed lymphocyte reaction and stimulates lymphokine production. J Reprod Immunol. 1986 Jul;9(2):103–110. doi: 10.1016/0165-0378(86)90004-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bolton A. E., Pockley A. G., Clough K. J., Mowles E. A., Stoker R. J., Westwood O. M., Chapman M. G. Identification of placental protein 14 as an immunosuppressive factor in human reproduction. Lancet. 1987 Mar 14;1(8533):593–595. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(87)90235-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bulmer J. N., Johnson P. M. The T-lymphocyte population in first-trimester human decidua does not express the interleukin-2 receptor. Immunology. 1986 Aug;58(4):685–687. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Clark D. A., Slapsys R. M., Croy B. A., Rossant J. Suppressor cell activity in uterine decidua correlates with success or failure of murine pregnancies. J Immunol. 1983 Aug;131(2):540–542. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cukrová V., Hrkal Z. Purification and characterization of granulocyte-macrophage colony stimulating factor from human placenta. J Chromatogr. 1987 Jan 23;413:242–246. doi: 10.1016/0378-4347(87)80233-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Daya S., Clark D. A., Devlin C., Jarrell J. Preliminary characterization of two types of suppressor cells in the human uterus. Fertil Steril. 1985 Dec;44(6):778–785. doi: 10.1016/s0015-0282(16)49037-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Daya S., Rosenthal K. L., Clark D. A. Immunosuppressor factor(s) produced by decidua-associated suppressor cells: a proposed mechanism for fetal allograft survival. Am J Obstet Gynecol. 1987 Feb;156(2):344–350. doi: 10.1016/0002-9378(87)90281-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Derynck R., Jarrett J. A., Chen E. Y., Eaton D. H., Bell J. R., Assoian R. K., Roberts A. B., Sporn M. B., Goeddel D. V. Human transforming growth factor-beta complementary DNA sequence and expression in normal and transformed cells. Nature. 1985 Aug 22;316(6030):701–705. doi: 10.1038/316701a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dinarello C. A., Mier J. W. Interleukins. Annu Rev Med. 1986;37:173–178. doi: 10.1146/annurev.me.37.020186.001133. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Domzig W., Stadler B. M., Herberman R. B. Interleukin 2 dependence of human natural killer (NK) cell activity. J Immunol. 1983 Apr;130(4):1970–1973. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dreno B., Jacques Y., Barriere H., Soulillou J. P. Monoclonal anti-interleukin 2 (15-2) antibody binding to granular layer keratinocytes of human skin. J Invest Dermatol. 1986 Apr;86(4):359–362. doi: 10.1111/1523-1747.ep12285581. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Durand D. B., Bush M. R., Morgan J. G., Weiss A., Crabtree G. R. A 275 basepair fragment at the 5' end of the interleukin 2 gene enhances expression from a heterologous promoter in response to signals from the T cell antigen receptor. J Exp Med. 1987 Feb 1;165(2):395–407. doi: 10.1084/jem.165.2.395. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Efrat S., Kaempfer R. Control of biologically active interleukin 2 messenger RNA formation in induced human lymphocytes. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1984 May;81(9):2601–2605. doi: 10.1073/pnas.81.9.2601. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Efrat S., Pilo S., Kaempfer R. Kinetics of induction and molecular size of mRNAs encoding human interleukin-2 and gamma-interferon. Nature. 1982 May 20;297(5863):236–239. doi: 10.1038/297236a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Farrar J. J., Benjamin W. R., Hilfiker M. L., Howard M., Farrar W. L., Fuller-Farrar J. The biochemistry, biology, and role of interleukin 2 in the induction of cytotoxic T cell and antibody-forming B cell responses. Immunol Rev. 1982;63:129–166. doi: 10.1111/j.1600-065x.1982.tb00414.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Farrar W. L., Johnson H. M., Farrar J. J. Regulation of the production of immune interferon and cytotoxic T lymphocytes by interleukin 2. J Immunol. 1981 Mar;126(3):1120–1125. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Flomenberg N., Welte K., Mertelsmann R., O'Reilly R., Dupont B. Interleukin 2-dependent natural killer (NK) cell lines from patients with primary T cell immunodeficiencies. J Immunol. 1983 Jun;130(6):2635–2643. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Flynn A., Finke J. H., Hilfiker M. L. Placental mononuclear phagocytes as a source of interleukin-1. Science. 1982 Oct 29;218(4571):475–477. doi: 10.1126/science.6981846. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Flynn A., Finke J. H., Loftus M. A. Comparison of interleukin 1 production by adherent cells and tissue pieces from human placenta. Immunopharmacology. 1985 Feb;9(1):19–26. doi: 10.1016/0162-3109(85)90042-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Frolik C. A., Dart L. L., Meyers C. A., Smith D. M., Sporn M. B. Purification and initial characterization of a type beta transforming growth factor from human placenta. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1983 Jun;80(12):3676–3680. doi: 10.1073/pnas.80.12.3676. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fujita T., Shibuya H., Ohashi T., Yamanishi K., Taniguchi T. Regulation of human interleukin-2 gene: functional DNA sequences in the 5' flanking region for the gene expression in activated T lymphocytes. Cell. 1986 Aug 1;46(3):401–405. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(86)90660-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gill T. J., 3rd, Repetti C. F. Immunologic and genetic factors influencing reproduction. A review. Am J Pathol. 1979 May;95(2):465–570. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Granelli-Piperno A., Andrus L., Steinman R. M. Lymphokine and nonlymphokine mRNA levels in stimulated human T cells. Kinetics, mitogen requirements, and effects of cyclosporin A. J Exp Med. 1986 Apr 1;163(4):922–937. doi: 10.1084/jem.163.4.922. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Greene W. C., Leonard W. J. The human interleukin-2 receptor. Annu Rev Immunol. 1986;4:69–95. doi: 10.1146/annurev.iy.04.040186.000441. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Grimm E. A., Ramsey K. M., Mazumder A., Wilson D. J., Djeu J. Y., Rosenberg S. A. Lymphokine-activated killer cell phenomenon. II. Precursor phenotype is serologically distinct from peripheral T lymphocytes, memory cytotoxic thymus-derived lymphocytes, and natural killer cells. J Exp Med. 1983 Mar 1;157(3):884–897. doi: 10.1084/jem.157.3.884. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hamblin A. S. Lymphokines and interleukins. Immunol Suppl. 1988;1:39–41. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hefeneider S. H., Conlon P. J., Henney C. S., Gillis S. In vivo interleukin 2 administration augments the generation of alloreactive cytolytic T lymphocytes and resident natural killer cells. J Immunol. 1983 Jan;130(1):222–227. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Henney C. S., Kern D. E., Gillis S. Cytotoxic responses: the regulatory influence of interleukin-2. Transplant Proc. 1982 Sep;14(3):565–569. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Henney C. S., Kuribayashi K., Kern D. E., Gillis S. Interleukin-2 augments natural killer cell activity. Nature. 1981 May 28;291(5813):335–338. doi: 10.1038/291335a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hiraoka A., Ohkubo T., Fukuda M. Production of human hematopoietic survival and growth factor by a myeloid leukemia cell line (KPB-M15) and placenta as detected by a monoclonal antibody. Cancer Res. 1987 Oct 1;47(19):5025–5030. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Imakawa K., Anthony R. V., Kazemi M., Marotti K. R., Polites H. G., Roberts R. M. Interferon-like sequence of ovine trophoblast protein secreted by embryonic trophectoderm. 1987 Nov 26-Dec 2Nature. 330(6146):377–379. doi: 10.1038/330377a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jacoby D. R., Olding L. B., Oldstone M. B. Immunologic regulation of fetal-maternal balance. Adv Immunol. 1984;35:157–208. doi: 10.1016/s0065-2776(08)60576-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kaplan J., Tilton J., Peterson W. D., Jr Identification of T cell lymphoma tumor antigens on human T cell lines. Am J Hematol. 1976;1(2):219–223. doi: 10.1002/ajh.2830010206. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kern D. E., Gillis S., Okada M., Henney C. S. The role of interleukin-2 (IL-2) in the differentiatin of cytotoxic T cells: the effect of monoclonal anti-IL-2 antibody and absorption with IL-2 dependent T cell lines. J Immunol. 1981 Oct;127(4):1323–1328. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Leibson H. J., Marrack P., Kappler J. W. B cell helper factors. I. Requirement for both interleukin 2 and another 40,000 mol wt factor. J Exp Med. 1981 Nov 1;154(5):1681–1693. doi: 10.1084/jem.154.5.1681. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Merluzzi V. J., Savage D. M., Mertelsmann R., Welte K. Generation of nonspecific murine cytotoxic T cells in vitro by purified human interleukin 2. Cell Immunol. 1984 Mar;84(1):74–84. doi: 10.1016/0008-8749(84)90078-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mertelsmann R., Welte K. Human interleukin 2: molecular biology, physiology and clinical possibilities. Immunobiology. 1986 Sep;172(3-5):400–419. doi: 10.1016/S0171-2985(86)80121-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mills N. C., D'Ercole A. J., Underwood L. E., Ilan J. Synthesis of somatomedin C/insulin-like growth factor I by human placenta. Mol Biol Rep. 1986;11(4):231–236. doi: 10.1007/BF00419602. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nabel G. J., Gorka C., Baltimore D. T-cell-specific expression of interleukin 2: evidence for a negative regulatory site. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1988 May;85(9):2934–2938. doi: 10.1073/pnas.85.9.2934. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nakagawa T., Nakagawa N., Goldstein H., Volkman D. J., Fauci A. S. Demonstration that human B cells respond differently to interleukin 2 and B cell differentiation factor based on their stages of maturation. J Immunol. 1986 Nov 15;137(10):3175–3182. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nelson J., Leong J. A., Levy J. A. Normal human placentas contain RNA-directed DNA polymerase activity like that in viruses. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1978 Dec;75(12):6263–6267. doi: 10.1073/pnas.75.12.6263. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pollard J. W., Bartocci A., Arceci R., Orlofsky A., Ladner M. B., Stanley E. R. Apparent role of the macrophage growth factor, CSF-1, in placental development. Nature. 1987 Dec 3;330(6147):484–486. doi: 10.1038/330484a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pontzer C. H., Torres B. A., Vallet J. L., Bazer F. W., Johnson H. M. Antiviral activity of the pregnancy recognition hormone ovine trophoblast protein-1. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1988 Apr 29;152(2):801–807. doi: 10.1016/s0006-291x(88)80109-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ruscetti F. W., Chou J. Y., Gallo R. C. Human trophoblasts: cellular source of colony-stimulating activity in placental tissue. Blood. 1982 Jan;59(1):86–90. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shen S. J., Wang C. Y., Nelson K. K., Jansen M., Ilan J. Expression of insulin-like growth factor II in human placentas from normal and diabetic pregnancies. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1986 Dec;83(23):9179–9182. doi: 10.1073/pnas.83.23.9179. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Siebenlist U., Durand D. B., Bressler P., Holbrook N. J., Norris C. A., Kamoun M., Kant J. A., Crabtree G. R. Promoter region of interleukin-2 gene undergoes chromatin structure changes and confers inducibility on chloramphenicol acetyltransferase gene during activation of T cells. Mol Cell Biol. 1986 Sep;6(9):3042–3049. doi: 10.1128/mcb.6.9.3042. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Smith K. A. Interleukin 2. Annu Rev Immunol. 1984;2:319–333. doi: 10.1146/annurev.iy.02.040184.001535. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Smith K. A. Interleukin-2: inception, impact, and implications. Science. 1988 May 27;240(4856):1169–1176. doi: 10.1126/science.3131876. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Smith K. A. T-cell growth factor. Immunol Rev. 1980;51:337–357. doi: 10.1111/j.1600-065x.1980.tb00327.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Smith K. A. The interleukin 2 receptor. Adv Immunol. 1988;42:165–179. doi: 10.1016/s0065-2776(08)60844-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Soubiran P., Zapitelli J. P., Schaffar L. IL2-like material is present in human placenta and amnion. J Reprod Immunol. 1987 Nov;12(3):225–234. doi: 10.1016/0165-0378(87)90026-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Swain S. L., Dennert G., Warner J. F., Dutton R. W. Culture supernatants of a stimulated T-cell line have helper activity that acts synergistically with interleukin 2 in the response of B cells to antigen. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1981 Apr;78(4):2517–2521. doi: 10.1073/pnas.78.4.2517. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Taniguchi T., Matsui H., Fujita T., Takaoka C., Kashima N., Yoshimoto R., Hamuro J. Structure and expression of a cloned cDNA for human interleukin-2. Nature. 1983 Mar 24;302(5906):305–310. doi: 10.1038/302305a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ting C. C., Yang S. S., Hargrove M. E. Induction of suppressor T cells by interleukin 2. J Immunol. 1984 Jul;133(1):261–266. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Waldmann T. A. The structure, function, and expression of interleukin-2 receptors on normal and malignant lymphocytes. Science. 1986 May 9;232(4751):727–732. doi: 10.1126/science.3008337. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Walker E., Leemhuis T., Roeder W. Murine B lymphoma cell lines release functionally active interleukin 2 after stimulation with Staphylococcus aureus. J Immunol. 1988 Feb 1;140(3):859–865. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Weiss A., Shields R., Newton M., Manger B., Imboden J. Ligand-receptor interactions required for commitment to the activation of the interleukin 2 gene. J Immunol. 1987 Apr 1;138(7):2169–2176. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Williams T. M., Eisenberg L., Burlein J. E., Norris C. A., Pancer S., Yao D., Burger S., Kamoun M., Kant J. A. Two regions within the human IL-2 gene promoter are important for inducible IL-2 expression. J Immunol. 1988 Jul 15;141(2):662–666. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wolf R. L. Human placental cells that regulate lymphocyte function. Pediatr Res. 1988 Feb;23(2):212–218. doi: 10.1203/00006450-198802000-00017. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]