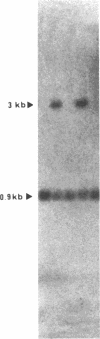
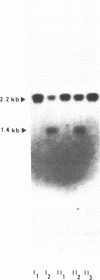
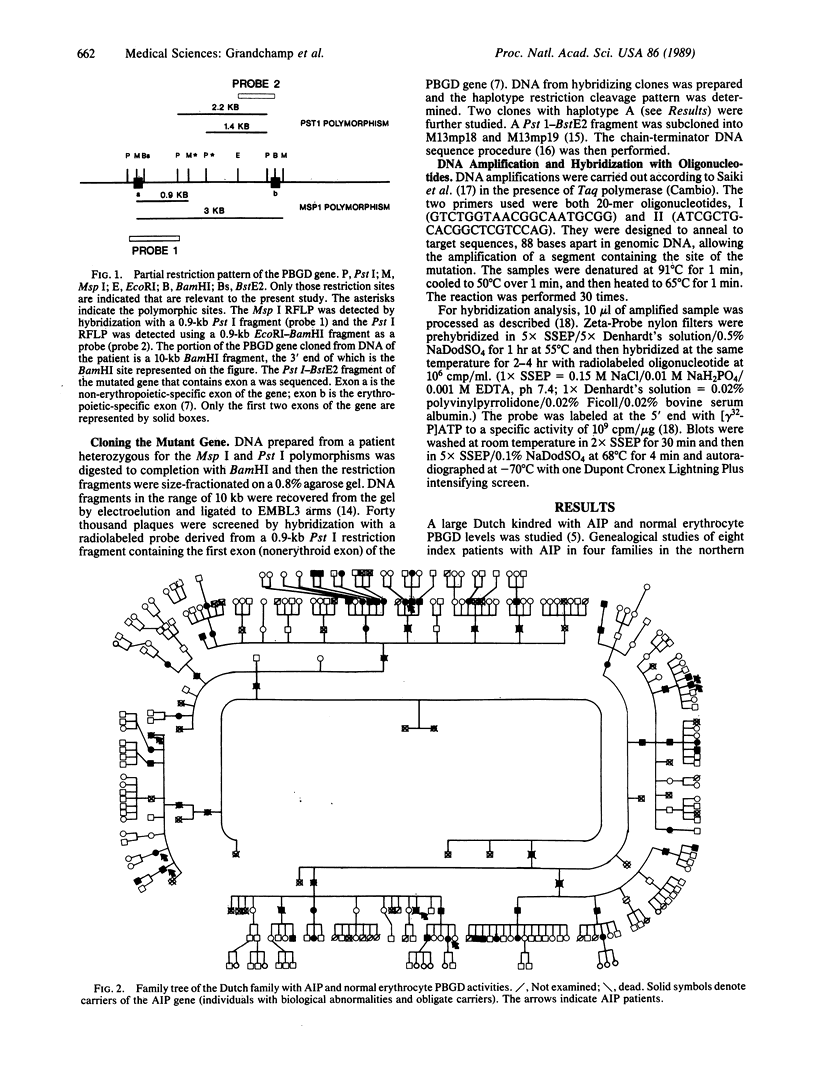
Abstract
An inherited deficiency of porphobilinogen deaminase [porphobilinogen ammonia-lyase (polymerizing), EC 4.3.1.8] in humans is responsible for the autosomal dominant disease acute intermittent porphyria. Different classes of mutations have been described at the protein level suggesting that this is a heterogeneous disease. It was previously demonstrated that porphobilinogen deaminase is encoded by two distinct mRNA species expressed in a tissue-specific manner. Analysis of the genomic sequences indicated that these two mRNAs are transcribed from two promoters and only differ in their first exon. The first mutation identified in the human porphobilinogen deaminase gene is a single-base substitution (G----A) in the canonical 5' splice donor site of intron 1. This mutation leads to a particular subtype of acute intermittent porphyria characterized by the restriction of the enzymatic defect to nonerythropoietic tissues. Hybridization analysis using oligonucleotide probes after in vitro amplification of genomic DNA offers another possibility of detecting asymptomatic carriers of the mutation in affected families.
Full text
PDF


Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Anderson K. E., Sassa S., Peterson C. M., Kappas A. Increased erythrocyte uroporphyrinogen-l-synthetase, delta-aminolevulinic acid dehydratase and protoporphyrin in hemolytic anemias. Am J Med. 1977 Sep;63(3):359–364. doi: 10.1016/0002-9343(77)90273-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chretien S., Dubart A., Beaupain D., Raich N., Grandchamp B., Rosa J., Goossens M., Romeo P. H. Alternative transcription and splicing of the human porphobilinogen deaminase gene result either in tissue-specific or in housekeeping expression. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1988 Jan;85(1):6–10. doi: 10.1073/pnas.85.1.6. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- DiLella A. G., Marvit J., Lidsky A. S., Güttler F., Woo S. L. Tight linkage between a splicing mutation and a specific DNA haplotype in phenylketonuria. 1986 Aug 28-Sep 3Nature. 322(6082):799–803. doi: 10.1038/322799a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Feinberg A. P., Vogelstein B. A technique for radiolabeling DNA restriction endonuclease fragments to high specific activity. Anal Biochem. 1983 Jul 1;132(1):6–13. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(83)90418-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Grandchamp B., De Verneuil H., Beaumont C., Chretien S., Walter O., Nordmann Y. Tissue-specific expression of porphobilinogen deaminase. Two isoenzymes from a single gene. Eur J Biochem. 1987 Jan 2;162(1):105–110. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1987.tb10548.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kogan S. C., Doherty M., Gitschier J. An improved method for prenatal diagnosis of genetic diseases by analysis of amplified DNA sequences. Application to hemophilia A. N Engl J Med. 1987 Oct 15;317(16):985–990. doi: 10.1056/NEJM198710153171603. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lee J. S., Anvret M. A PstI polymorphism for the human porphobilinogen deaminase gene (PBG). Nucleic Acids Res. 1987 Aug 11;15(15):6307–6307. doi: 10.1093/nar/15.15.6307. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Llewellyn D. H., Elder G. H., Kalsheker N. A., Marsh O. W., Harrison P. R., Grandchamp B., Picat C., Nordmann Y., Romeo P. H., Goossens M. DNA polymorphism of human porphobilinogen deaminase gene in acute intermittent porphyria. Lancet. 1987 Sep 26;2(8561):706–708. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(87)91073-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- MAUZERALL D., GRANICK S. The occurrence and determination of delta-amino-levulinic acid and porphobilinogen in urine. J Biol Chem. 1956 Mar;219(1):435–446. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Messing J., Vieira J. A new pair of M13 vectors for selecting either DNA strand of double-digest restriction fragments. Gene. 1982 Oct;19(3):269–276. doi: 10.1016/0378-1119(82)90016-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mustajoki P. Normal erythrocyte uroporphyrinogen I synthase in a kindred with acute intermittent porphyria. Ann Intern Med. 1981 Aug;95(2):162–166. doi: 10.7326/0003-4819-95-2-162. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Saiki R. K., Gelfand D. H., Stoffel S., Scharf S. J., Higuchi R., Horn G. T., Mullis K. B., Erlich H. A. Primer-directed enzymatic amplification of DNA with a thermostable DNA polymerase. Science. 1988 Jan 29;239(4839):487–491. doi: 10.1126/science.2448875. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sanger F., Nicklen S., Coulson A. R. DNA sequencing with chain-terminating inhibitors. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1977 Dec;74(12):5463–5467. doi: 10.1073/pnas.74.12.5463. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Strand L. J., Meyer U. A., Felsher B. F., Redeker A. G., Marver H. S. Decreased red cell uroporphyrinogen I synthetase activity in intermittent acute porphyria. J Clin Invest. 1972 Oct;51(10):2530–2536. doi: 10.1172/JCI107068. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Treisman R., Orkin S. H., Maniatis T. Specific transcription and RNA splicing defects in five cloned beta-thalassaemia genes. Nature. 1983 Apr 14;302(5909):591–596. doi: 10.1038/302591a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wilson J. H., De Rooy F. W., Te Velde K. Acute intermittent porphyria in The Netherlands. Heterogeneity of the enzyme porphobilinogen deaminase. Neth J Med. 1986;29(11):393–399. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- de Martinville B., Wyman A. R., White R., Francke U. Assignment of first random restriction fragment length polymorphism (RFLP) locus ((D14S1) to a region of human chromosome 14. Am J Hum Genet. 1982 Mar;34(2):216–226. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]