Abstract
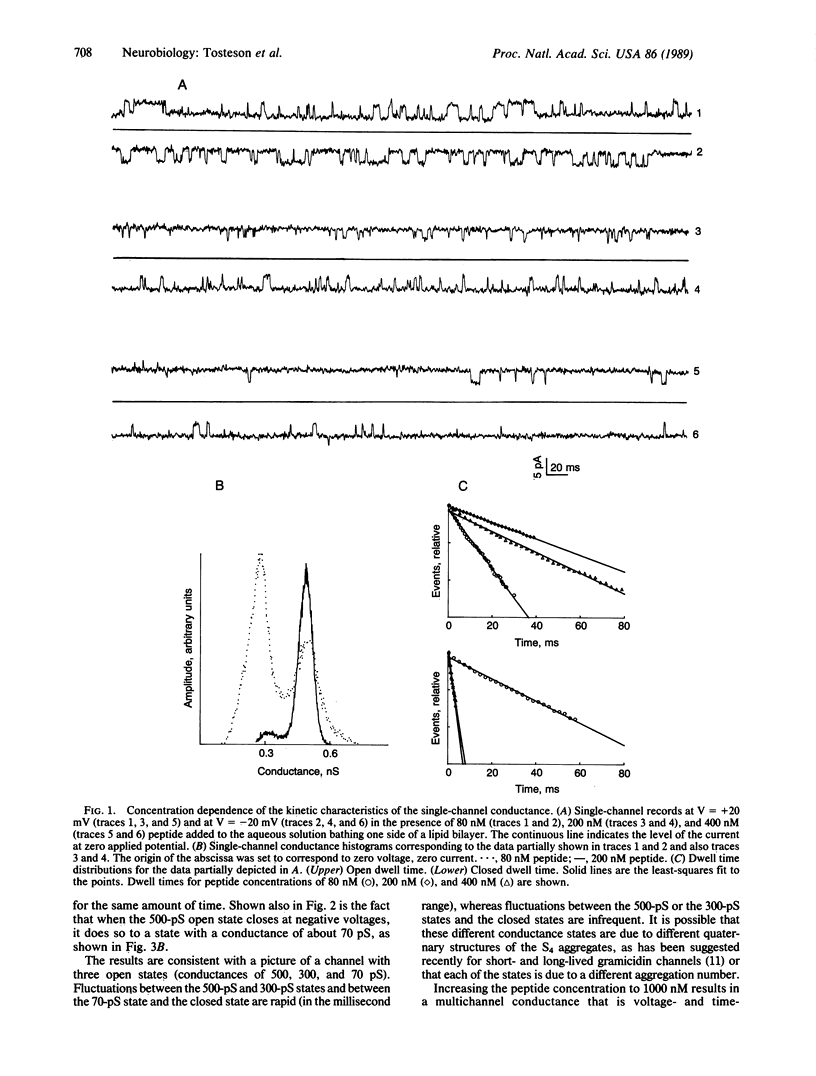
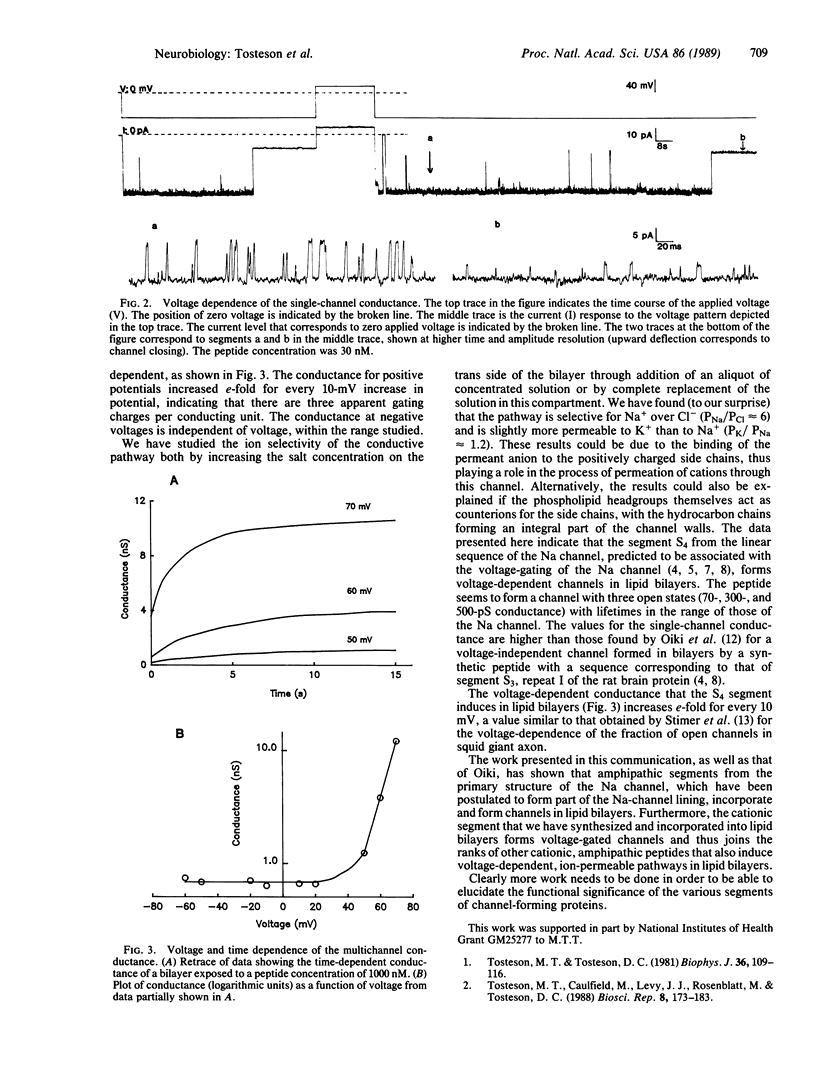
The Na-channel polypeptide is responsible for the voltage-gated and time-dependent ionic permeability changes that give rise to the action potential in the membranes of nerve cells. We have synthesized a 22-amino acid peptide with a sequence identical to that of the segment named S4, repeat IV of the primary structure of the Na channel. We have found that this peptide induces a voltage- and time-dependent conductance in bilayers formed by a mixture of phosphatidyl-ethanolamine and phosphatidylserine. This conductance is activated when the cis side is made positive, with an apparent gating charge of 3. The results are consistent with the idea that this segment plays a role in determining the voltage sensitivity of the Na channel.
Full text
PDF

Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Eisenberg D., Schwarz E., Komaromy M., Wall R. Analysis of membrane and surface protein sequences with the hydrophobic moment plot. J Mol Biol. 1984 Oct 15;179(1):125–142. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(84)90309-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Greenblatt R. E., Blatt Y., Montal M. The structure of the voltage-sensitive sodium channel. Inferences derived from computer-aided analysis of the Electrophorus electricus channel primary structure. FEBS Lett. 1985 Dec 2;193(2):125–134. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(85)80136-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Guy H. R. A structural model of the acetylcholine receptor channel based on partition energy and helix packing calculations. Biophys J. 1984 Jan;45(1):249–261. doi: 10.1016/S0006-3495(84)84152-1. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Guy H. R., Seetharamulu P. Molecular model of the action potential sodium channel. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1986 Jan;83(2):508–512. doi: 10.1073/pnas.83.2.508. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Montal M., Mueller P. Formation of bimolecular membranes from lipid monolayers and a study of their electrical properties. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1972 Dec;69(12):3561–3566. doi: 10.1073/pnas.69.12.3561. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Noda M., Shimizu S., Tanabe T., Takai T., Kayano T., Ikeda T., Takahashi H., Nakayama H., Kanaoka Y., Minamino N. Primary structure of Electrophorus electricus sodium channel deduced from cDNA sequence. Nature. 1984 Nov 8;312(5990):121–127. doi: 10.1038/312121a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Oiki S., Danho W., Madison V., Montal M. M2 delta, a candidate for the structure lining the ionic channel of the nicotinic cholinergic receptor. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1988 Nov;85(22):8703–8707. doi: 10.1073/pnas.85.22.8703. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stimers J. R., Bezanilla F., Taylor R. E. Sodium channel activation in the squid giant axon. Steady state properties. J Gen Physiol. 1985 Jan;85(1):65–82. doi: 10.1085/jgp.85.1.65. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tosteson M. T., Caulfield M. P., Levy J. J., Rosenblatt M., Tosteson D. C. The synthetic precursor specific region of pre-pro-parathyroid hormone forms ion channels in lipid bilayers. Biosci Rep. 1988 Apr;8(2):173–183. doi: 10.1007/BF01116462. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tosteson M. T., Tosteson D. C. The sting. Melittin forms channels in lipid bilayers. Biophys J. 1981 Oct;36(1):109–116. doi: 10.1016/S0006-3495(81)84719-4. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wallace B. A., Ravikumar K. The gramicidin pore: crystal structure of a cesium complex. Science. 1988 Jul 8;241(4862):182–187. doi: 10.1126/science.2455344. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]



