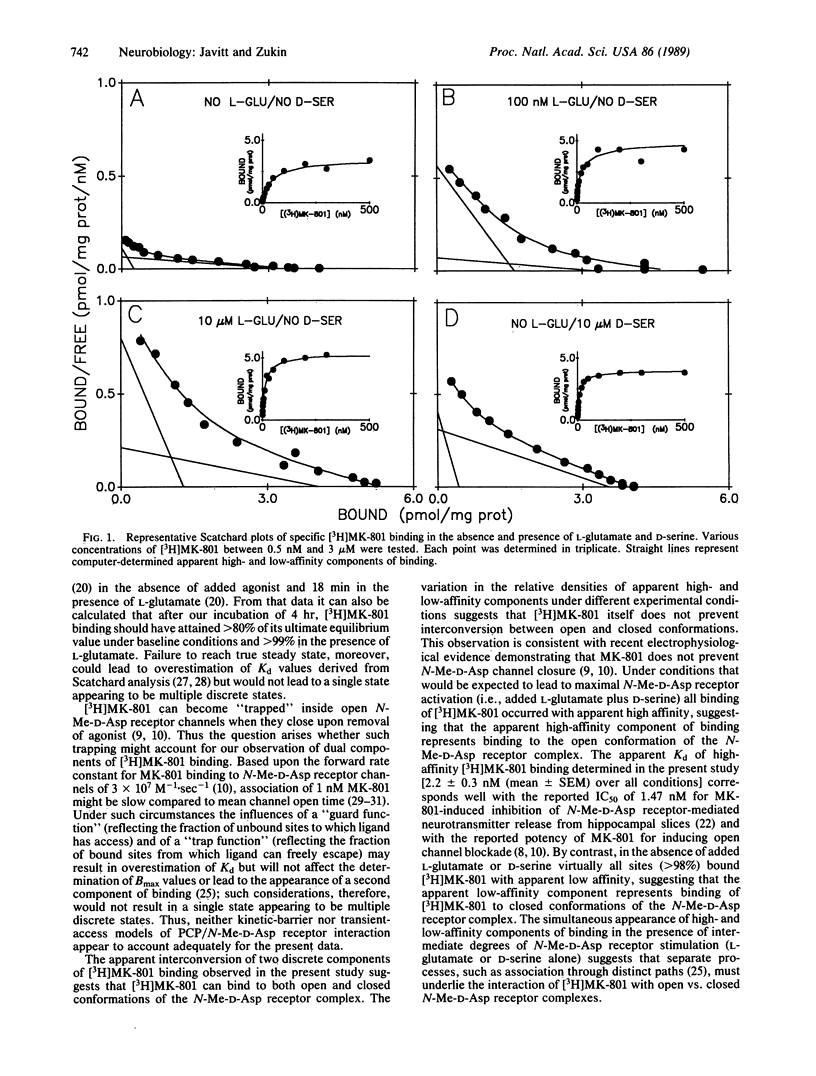
Abstract
N-Methyl-D-aspartate (N-Me-D-Asp) and phencyclidine receptors interactively mediate central nervous system processes including psychotomimetic effects of drugs as well as neurodegenerative, cognitive, and developmental events. To elucidate the mechanism of this interaction, effects of N-Me-D-Asp agonists and antagonists and of glycine-like agents upon binding of the radiolabeled phencyclidine receptor ligand [3H]MK-801 were determined in rat brain. Scatchard analysis revealed two discrete components of [3H]MK-801 binding after 4 hr of incubation. Incubation in the presence of L-glutamate led to an increase in apparent densities but not in affinities of both components of [3H]MK-801 binding as well as conversion of sites from apparent low to high affinity. Incubation in the presence of combined D-serine and L-glutamate led to an increase in the apparent density of high-affinity [3H]MK-801 binding compared with incubation in the presence of either L-glutamate or D-serine alone. These data support a model in which phencyclidine receptor ligands bind differentially to closed as well as open conformations of the N-Me-D-Asp receptor complex and in which glycine-like agents permit or factilitate agonist-induced conversion of N-Me-D-Asp receptors from closed to open conformations.
Full text
PDF



Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Anis N. A., Berry S. C., Burton N. R., Lodge D. The dissociative anaesthetics, ketamine and phencyclidine, selectively reduce excitation of central mammalian neurones by N-methyl-aspartate. Br J Pharmacol. 1983 Jun;79(2):565–575. doi: 10.1111/j.1476-5381.1983.tb11031.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Aoshima H., Anan M., Ishii H., Iio H., Kobayashi S. Minimal model to account for the membrane conductance increase and desensitization of gamma-aminobutyric acid receptors synthesized in the Xenopus oocytes injected with rat brain mRNA. Biochemistry. 1987 Jul 28;26(15):4811–4816. doi: 10.1021/bi00389a031. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Berry S. C., Dawkins S. L., Lodge D. Comparison of sigma- and kappa-opiate receptor ligands as excitatory amino acid antagonists. Br J Pharmacol. 1984 Sep;83(1):179–185. doi: 10.1111/j.1476-5381.1984.tb10133.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bertolino M., Vicini S., Mazzetta J., Costa E. Phencyclidine and glycine modulate NMDA-activated high conductance cationic channels by acting at different sites. Neurosci Lett. 1988 Feb 3;84(3):351–355. doi: 10.1016/0304-3940(88)90534-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bonhaus D. W., Burge B. C., McNamara J. O. Biochemical evidence that glycine allosterically regulates an NMDA receptor-coupled ion channel. Eur J Pharmacol. 1987 Oct 27;142(3):489–490. doi: 10.1016/0014-2999(87)90096-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- FURCHGOTT R. F. The pharmacology of vascular smooth muscle. Pharmacol Rev. 1955 Jun;7(2):183–265. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fagg G. E. Phencyclidine and related drugs bind to the activated N-methyl-D-aspartate receptor-channel complex in rat brain membranes. Neurosci Lett. 1987 May 6;76(2):221–227. doi: 10.1016/0304-3940(87)90719-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Foster A. C., Wong E. H. The novel anticonvulsant MK-801 binds to the activated state of the N-methyl-D-aspartate receptor in rat brain. Br J Pharmacol. 1987 Jun;91(2):403–409. doi: 10.1111/j.1476-5381.1987.tb10295.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hess G. P., Cash D. J., Aoshima H. Acetylcholine receptor-controlled ion translocation: chemical kinetic investigations of the mechanism. Annu Rev Biophys Bioeng. 1983;12:443–473. doi: 10.1146/annurev.bb.12.060183.002303. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hucho F. The nicotinic acetylcholine receptor and its ion channel. Eur J Biochem. 1986 Jul 15;158(2):211–226. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1986.tb09740.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Huettner J. E., Bean B. P. Block of N-methyl-D-aspartate-activated current by the anticonvulsant MK-801: selective binding to open channels. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1988 Feb;85(4):1307–1311. doi: 10.1073/pnas.85.4.1307. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jarvis M. F., Murphy D. E., Williams M. Quantitative autoradiographic localization of NMDA receptors in rat brain using [3H]CPP: comparison with [3H]TCP binding sites. Eur J Pharmacol. 1987 Sep 2;141(1):149–152. doi: 10.1016/0014-2999(87)90423-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Javitt D. C., Jotkowitz A., Sircar R., Zukin S. R. Non-competitive regulation of phencyclidine/sigma-receptors by the N-methyl-D-aspartate receptor antagonist D-(-)-2-amino-5-phosphonovaleric acid. Neurosci Lett. 1987 Jul 22;78(2):193–198. doi: 10.1016/0304-3940(87)90632-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Javitt D. C., Zukin S. R. Modulation of phencyclidine receptors by excitatory amino acid receptor ligands. Psychopharmacol Bull. 1988;24(3):444–449. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Johnson J. W., Ascher P. Glycine potentiates the NMDA response in cultured mouse brain neurons. Nature. 1987 Feb 5;325(6104):529–531. doi: 10.1038/325529a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kishimoto H., Simon J. R., Aprison M. H. Determination of the equilibrium dissociation constants and number of glycine binding sites in several areas of the rat central nervous system, using a sodium-independent system. J Neurochem. 1981 Oct;37(4):1015–1024. doi: 10.1111/j.1471-4159.1981.tb04489.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kleckner N. W., Dingledine R. Requirement for glycine in activation of NMDA-receptors expressed in Xenopus oocytes. Science. 1988 Aug 12;241(4867):835–837. doi: 10.1126/science.2841759. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kloog Y., Haring R., Sokolovsky M. Kinetic characterization of the phencyclidine-N-methyl-D-aspartate receptor interaction: evidence for a steric blockade of the channel. Biochemistry. 1988 Feb 9;27(3):843–848. doi: 10.1021/bi00403a001. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kloog Y., Nadler V., Sokolovsky M. Mode of binding of [3H]dibenzocycloalkenimine (MK-801) to the N-methyl-D-aspartate (NMDA) receptor and its therapeutic implication. FEBS Lett. 1988 Mar 28;230(1-2):167–170. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(88)80664-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kushner L., Lerma J., Zukin R. S., Bennett M. V. Coexpression of N-methyl-D-aspartate and phencyclidine receptors in Xenopus oocytes injected with rat brain mRNA. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1988 May;85(9):3250–3254. doi: 10.1073/pnas.85.9.3250. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Loo P. S., Braunwalder A. F., Lehmann J., Williams M., Sills M. A. Interaction of L-glutamate and magnesium with phencyclidine recognition sites in rat brain: evidence for multiple affinity states of the phencyclidine/N-methyl-D-aspartate receptor complex. Mol Pharmacol. 1987 Dec;32(6):820–830. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Loo P., Braunwalder A., Lehmann J., Williams M. Radioligand binding to central phencyclidine recognition sites is dependent on excitatory amino acid receptor agonists. Eur J Pharmacol. 1986 Apr 29;123(3):467–468. doi: 10.1016/0014-2999(86)90726-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- MacDonald J. F., Miljkovic Z., Pennefather P. Use-dependent block of excitatory amino acid currents in cultured neurons by ketamine. J Neurophysiol. 1987 Aug;58(2):251–266. doi: 10.1152/jn.1987.58.2.251. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Maragos W. F., Chu D. C., Greenamyre J. T., Penney J. B., Young A. B. High correlation between the localization of [3H]TCP binding and NMDA receptors. Eur J Pharmacol. 1986 Apr 9;123(1):173–174. doi: 10.1016/0014-2999(86)90703-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Monaghan D. T., Cotman C. W. Identification and properties of N-methyl-D-aspartate receptors in rat brain synaptic plasma membranes. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1986 Oct;83(19):7532–7536. doi: 10.1073/pnas.83.19.7532. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Reynolds I. J., Miller R. J. Multiple sites for the regulation of the N-methyl-D-aspartate receptor. Mol Pharmacol. 1988 Jun;33(6):581–584. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Reynolds I. J., Murphy S. N., Miller R. J. 3H-labeled MK-801 binding to the excitatory amino acid receptor complex from rat brain is enhanced by glycine. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1987 Nov;84(21):7744–7748. doi: 10.1073/pnas.84.21.7744. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sircar R., Rappaport M., Nichtenhauser R., Zukin S. R. The novel anticonvulsant MK-801: a potent and specific ligand of the brain phencyclidine/sigma-receptor. Brain Res. 1987 Dec 1;435(1-2):235–240. doi: 10.1016/0006-8993(87)91606-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Snell L. D., Morter R. S., Johnson K. M. Glycine potentiates N-methyl-D-aspartate-induced [3H]TCP binding to rat cortical membranes. Neurosci Lett. 1987 Dec 29;83(3):313–317. doi: 10.1016/0304-3940(87)90106-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Starmer C. F., Grant A. O. Phasic ion channel blockade. A kinetic model and parameter estimation procedure. Mol Pharmacol. 1985 Oct;28(4):348–356. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Verdoorn T. A., Kleckner N. W., Dingledine R. Rat brain N-methyl-D-aspartate receptors expressed in Xenopus oocytes. Science. 1987 Nov 20;238(4830):1114–1116. doi: 10.1126/science.2825347. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wong E. H., Kemp J. A., Priestley T., Knight A. R., Woodruff G. N., Iversen L. L. The anticonvulsant MK-801 is a potent N-methyl-D-aspartate antagonist. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1986 Sep;83(18):7104–7108. doi: 10.1073/pnas.83.18.7104. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Woodruff G. N., Foster A. C., Gill R., Kemp J. A., Wong E. H., Iversen L. L. The interaction between MK-801 and receptors for N-methyl-D-aspartate: functional consequences. Neuropharmacology. 1987 Jul;26(7B):903–909. doi: 10.1016/0028-3908(87)90068-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zukin S. R., Young A. B., Snyder S. H. Gamma-aminobutyric acid binding to receptor sites in the rat central nervous system. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1974 Dec;71(12):4802–4807. doi: 10.1073/pnas.71.12.4802. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]



