Abstract
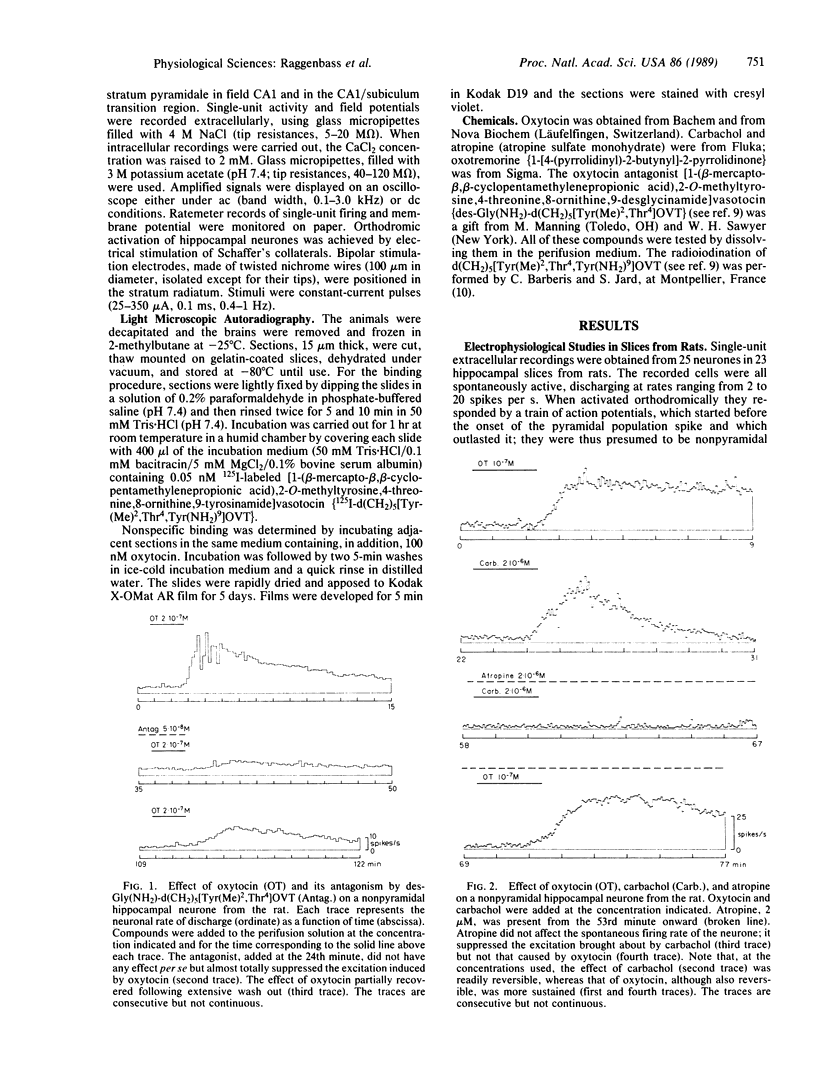
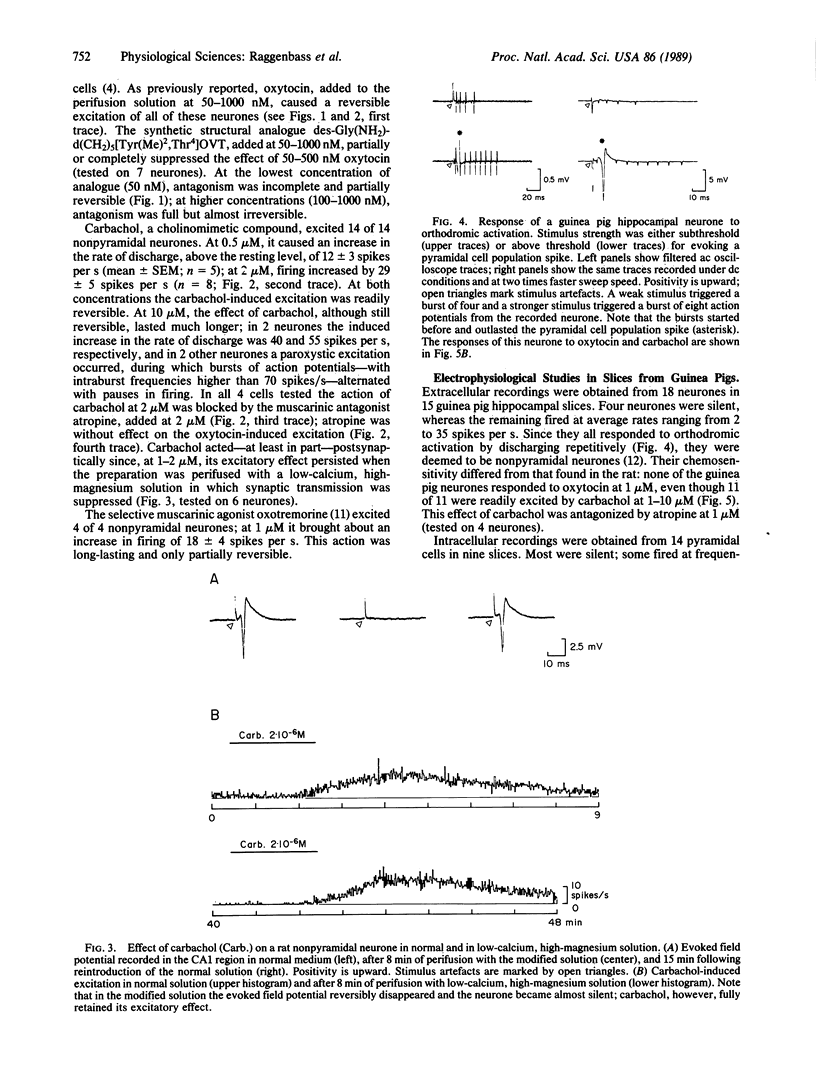
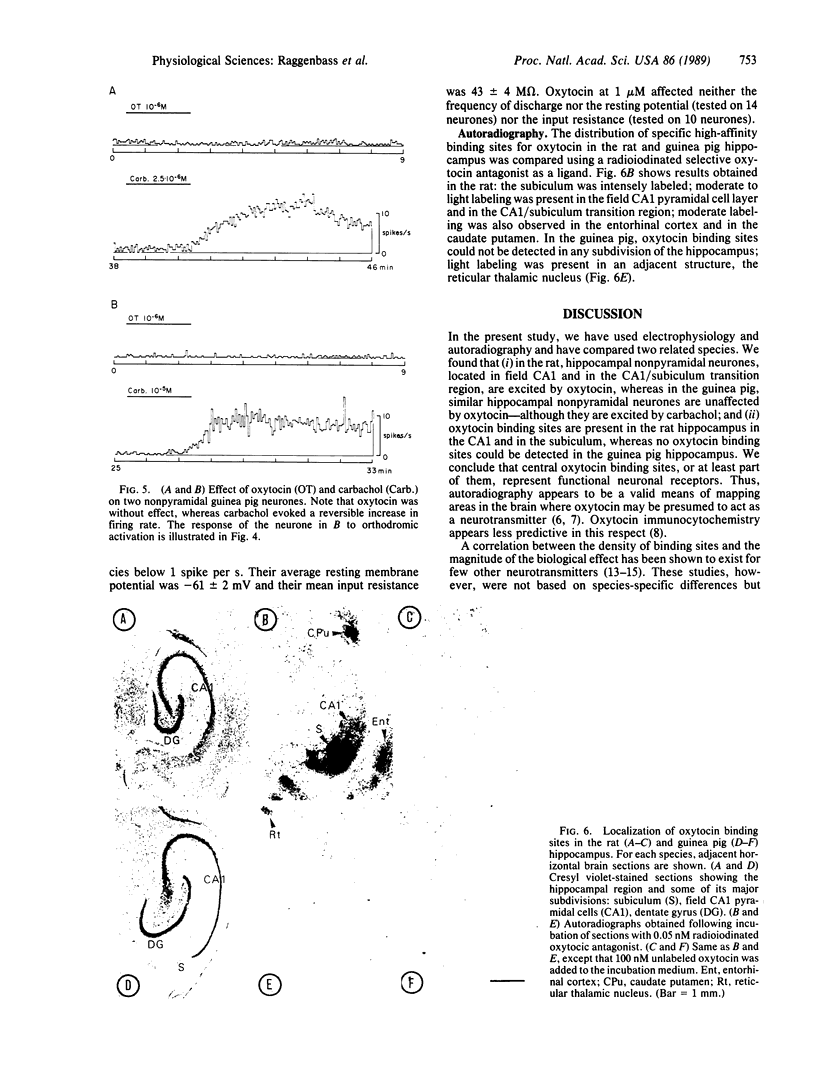
In transverse hippocampal slices from rat and guinea pig brains, we obtained unitary extracellular recordings from nonpyramidal neurones located in or near the stratum pyramidale in the CA1 field and in the transition region between the CA1 and the subiculum. In rats, these neurones responded to oxytocin at 50-1000 nM by a reversible increase in firing rate. The oxytocin-induced excitation was suppressed by a synthetic structural analogue that acts as a potent, selective antioxytocic on peripheral receptors. Nonpyramidal neurones were also excited by carbachol at 0.5-10 microM. The effect of this compound was postsynaptic and was blocked by the muscarinic antagonist atropine. In guinea pigs, by contrast, nonpyramidal neurones were unaffected by oxytocin, although they were excited by carbachol. Light microscopic autoradiography, carried out using a radioiodinated selective antioxytocic as a ligand, revealed labeling in the subiculum and in the CA1 area of the hippocampus of rats, whereas no oxytocin-binding sites were detected in the hippocampus of guinea pigs. Our results indicate (i) that a hippocampal action of oxytocin is species-dependent and (ii) that a positive correlation exists between neuronal responsiveness to oxytocin and the presence in the hippocampus of high-affinity binding sites for this peptide.
Full text
PDF

Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Benardo L. S., Prince D. A. Cholinergic excitation of mammalian hippocampal pyramidal cells. Brain Res. 1982 Oct 14;249(2):315–331. doi: 10.1016/0006-8993(82)90066-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Benardo L. S., Prince D. A. Ionic mechanisms of cholinergic excitation in mammalian hippocampal pyramidal cells. Brain Res. 1982 Oct 14;249(2):333–344. doi: 10.1016/0006-8993(82)90067-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brunner H., Misgeld U. Muscarinic inhibitory effect in the guinea pig dentate gyrus in vitro. Neurosci Lett. 1988 May 16;88(1):63–68. doi: 10.1016/0304-3940(88)90316-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Buzsáki G. Feed-forward inhibition in the hippocampal formation. Prog Neurobiol. 1984;22(2):131–153. doi: 10.1016/0301-0082(84)90023-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- CHO A. K., HASLETT W. L., JENDEN D. J. The peripheral actions of oxotremorine, a metabolite of tremorine. J Pharmacol Exp Ther. 1962 Nov;138:249–257. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chandler J. P., Crutcher K. A. The septohippocampal projection in the rat: an electron microscopic horseradish peroxidase study. Neuroscience. 1983 Nov;10(3):685–696. doi: 10.1016/0306-4522(83)90210-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Charpak S., Armstrong W. E., Mühlethaler M., Dreifuss J. J. Stimulatory action of oxytocin on neurones of the dorsal motor nucleus of the vagus nerve. Brain Res. 1984 May 21;300(1):83–89. doi: 10.1016/0006-8993(84)91342-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cole A. E., Nicoll R. A. Characterization of a slow cholinergic post-synaptic potential recorded in vitro from rat hippocampal pyramidal cells. J Physiol. 1984 Jul;352:173–188. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1984.sp015285. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dreifuss J. J., Raggenbass M. Tachykinins and bombesin excite non-pyramidal neurones in rat hippocampus. J Physiol. 1986 Oct;379:417–428. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1986.sp016261. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Elands J., Barberis C., Jard S., Tribollet E., Dreifuss J. J., Bankowski K., Manning M., Sawyer W. H. 125I-labelled d(CH2)5[Tyr(Me)2,Thr4,Tyr-NH2(9)]OVT: a selective oxytocin receptor ligand. Eur J Pharmacol. 1988 Mar 1;147(2):197–207. doi: 10.1016/0014-2999(88)90778-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Elands J., Barberis C., Jard S. [3H]-[Thr4,Gly7]OT: a highly selective ligand for central and peripheral OT receptors. Am J Physiol. 1988 Jan;254(1 Pt 1):E31–E38. doi: 10.1152/ajpendo.1988.254.1.E31. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Freund-Mercier M. J., Stoeckel M. E., Palacios J. M., Pazos A., Reichhart J. M., Porte A., Richard P. Pharmacological characteristics and anatomical distribution of [3H]oxytocin-binding sites in the Wistar rat brain studied by autoradiography. Neuroscience. 1987 Feb;20(2):599–614. doi: 10.1016/0306-4522(87)90113-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gahwiler B. H., Brown D. A. Functional innervation of cultured hippocampal neurones by cholinergic afferents from co-cultured septal explants. Nature. 1985 Feb 14;313(6003):577–579. doi: 10.1038/313577a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Haas H. L. Cholinergic disinhibition in hippocampal slices of the rat. Brain Res. 1982 Feb 4;233(1):200–204. doi: 10.1016/0006-8993(82)90942-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Johnson R. D., Minneman K. P. Alpha 1-adrenergic receptors and stimulation of [3H]inositol metabolism in rat brain: regional distribution and parallel inactivation. Brain Res. 1985 Aug 19;341(1):7–15. doi: 10.1016/0006-8993(85)91466-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kimura H., McGeer P. L., Peng J. H., McGeer E. G. The central cholinergic system studied by choline acetyltransferase immunohistochemistry in the cat. J Comp Neurol. 1981 Aug 1;200(2):151–201. doi: 10.1002/cne.902000202. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lee K. S., Schubert P., Reddington M., Kreutzberg G. W. Adenosine receptor density and the depression of evoked neuronal activity in the rat hippocampus in vitro. Neurosci Lett. 1983 May 27;37(1):81–85. doi: 10.1016/0304-3940(83)90508-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lewis P. R., Shute C. C. The cholinergic limbic system: projections to hippocampal formation, medial cortex, nuclei of the ascending cholinergic reticular system, and the subfornical organ and supra-optic crest. Brain. 1967 Sep;90(3):521–540. doi: 10.1093/brain/90.3.521. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Madison D. V., Lancaster B., Nicoll R. A. Voltage clamp analysis of cholinergic action in the hippocampus. J Neurosci. 1987 Mar;7(3):733–741. doi: 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.07-03-00733.1987. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mantyh P. W., Pinnock R. D., Downes C. P., Goedert M., Hunt S. P. Correlation between inositol phospholipid hydrolysis and substance P receptors in rat CNS. 1984 Jun 28-Jul 4Nature. 309(5971):795–797. doi: 10.1038/309795a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mühlethaler M., Charpak S., Dreifuss J. J. Contrasting effects of neurohypophysial peptides on pyramidal and non-pyramidal neurones in the rat hippocampus. Brain Res. 1984 Aug 6;308(1):97–107. doi: 10.1016/0006-8993(84)90921-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mühlethaler M., Sawyer W. H., Manning M. M., Dreifuss J. J. Characterization of a uterine-type oxytocin receptor in the rat hippocampus. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1983 Nov;80(21):6713–6717. doi: 10.1073/pnas.80.21.6713. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Raggenbass M., Dubois-Dauphin M., Charpak S., Dreifuss J. J. Neurons in the dorsal motor nucleus of the vagus nerve are excited by oxytocin in the rat but not in the guinea pig. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1987 Jun;84(11):3926–3930. doi: 10.1073/pnas.84.11.3926. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Raggenbass M., Wuarin J. P., Gähwiler B. H., Dreifuss J. J. Opposing effects of oxytocin and of a mu-receptor agonistic opioid peptide on the same class of non-pyramidal neurones in rat hippocampus. Brain Res. 1985 Oct 7;344(2):392–396. doi: 10.1016/0006-8993(85)90822-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schwartzkroin P. A., Mathers L. H. Physiological and morphological identification of a nonpyramidal hippocampal cell type. Brain Res. 1978 Nov 17;157(1):1–10. doi: 10.1016/0006-8993(78)90991-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tribollet E., Barberis C., Jard S., Dubois-Dauphin M., Dreifuss J. J. Localization and pharmacological characterization of high affinity binding sites for vasopressin and oxytocin in the rat brain by light microscopic autoradiography. Brain Res. 1988 Feb 23;442(1):105–118. doi: 10.1016/0006-8993(88)91437-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]