Abstract
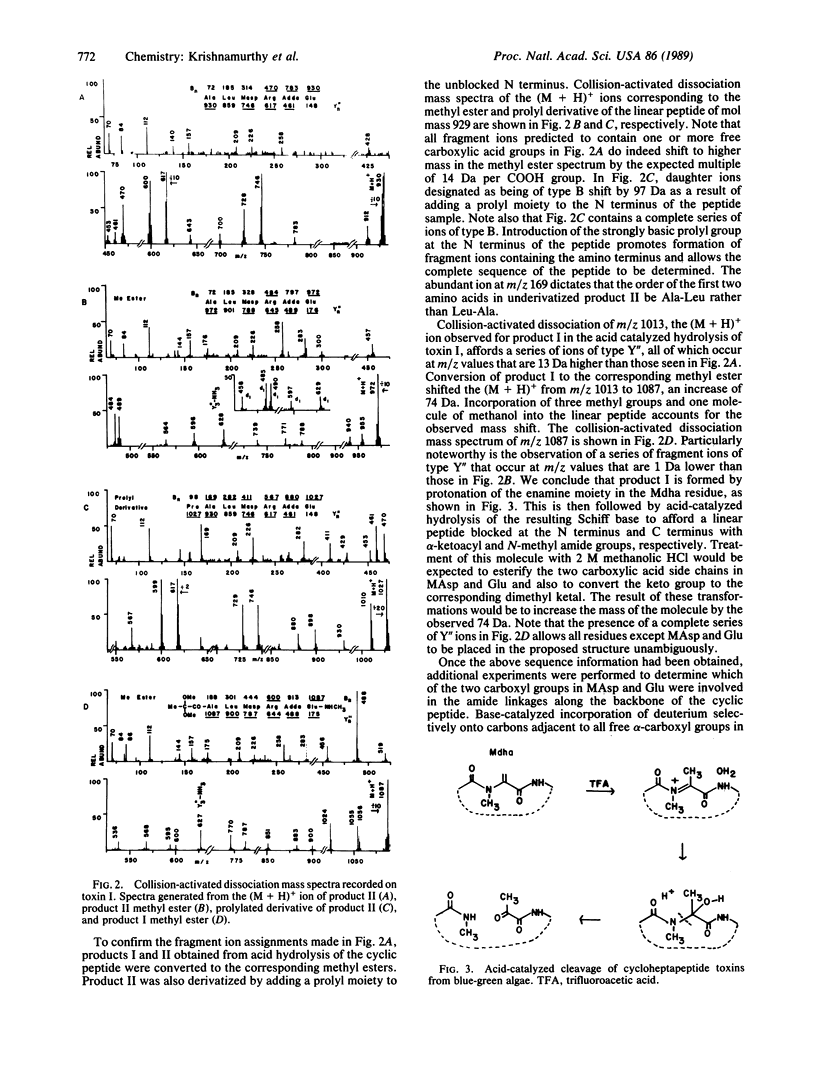
Combined use of chemical degradation, derivatization, and tandem mass spectrometry for rapid structural characterization of toxic cyclic peptides from blue-green algae at the nanomole level is described. Previously, all blue-green algal toxins were thought to belong to a family of seven-residue cyclic peptides, having the general structure cyclo-D-Ala-L-Xaa-erythro-beta-methyl-D-isoaspartic acid-L-Yaa-Adda-D-isoglutamic acid-N-methyldehydroalanine, where Xaa and Yaa represent variable amino acids of the L configuration and Adda is 3-amino-9-methoxy-2,6,8-trimethyl-10-phenyl-deca-4,6-dienoic acid. Structural characterization of two additional toxins indicates that further variability can exist within this family of naturally occurring toxic cyclic peptides. Isoaspartic acid and dehydroalanine can substitute for beta-methylisoaspartic acid and N-methyldehydroalanine, respectively.
Full text
PDF



Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Botes D. P., Kruger H., Viljoen C. C. Isolation and characterization of four toxins from the blue-green alga, Microcystis aeruginosa. Toxicon. 1982;20(6):945–954. doi: 10.1016/0041-0101(82)90097-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Botes D. P., Viljoen C. C., Kruger H., Wessels P. L., Williams D. H. Configuration assignments of the amino acid residues and the presence of N-methyldehydroalanine in toxins from the blue-green alga, Microcystis aeruginosa. Toxicon. 1982;20(6):1037–1042. doi: 10.1016/0041-0101(82)90105-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Holcomb G. N., James S. A., Ward D. N. A critical evaluation of the selective tritiation method of determining C-terminal amino acids and its application to luteinizing hormone. Biochemistry. 1968 Apr;7(4):1291–1296. doi: 10.1021/bi00844a007. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hunt D. F., Giordani A. B., Rhodes G., Herold D. A. Mixture analysis by triple-quadrupole mass spectrometry: metabolic profiling of urinary carboxylic acids. Clin Chem. 1982 Dec;28(12):2387–2392. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hunt D. F., Shabanowitz J., Yates J. R., 3rd, Zhu N. Z., Russell D. H., Castro M. E. Tandem quadrupole Fourier-transform mass spectrometry of oligopeptides and small proteins. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1987 Feb;84(3):620–623. doi: 10.1073/pnas.84.3.620. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hunt D. F., Yates J. R., 3rd, Shabanowitz J., Winston S., Hauer C. R. Protein sequencing by tandem mass spectrometry. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1986 Sep;83(17):6233–6237. doi: 10.1073/pnas.83.17.6233. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Roepstorff P., Fohlman J. Proposal for a common nomenclature for sequence ions in mass spectra of peptides. Biomed Mass Spectrom. 1984 Nov;11(11):601–601. doi: 10.1002/bms.1200111109. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Steffens J. C., Hunt D. F., Williams B. G. Accumulation of non-protein metal-binding polypeptides (gamma-glutamyl-cysteinyl)n-glycine in selected cadmium-resistant tomato cells. J Biol Chem. 1986 Oct 25;261(30):13879–13882. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tomer K. B., Crow F. W., Gross M. L., Kopple K. D. Fast atom bombardment combined with tandem mass spectrometry for the determination of cyclic peptides. Anal Chem. 1984 May;56(6):880–886. doi: 10.1021/ac00270a006. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]



