Abstract
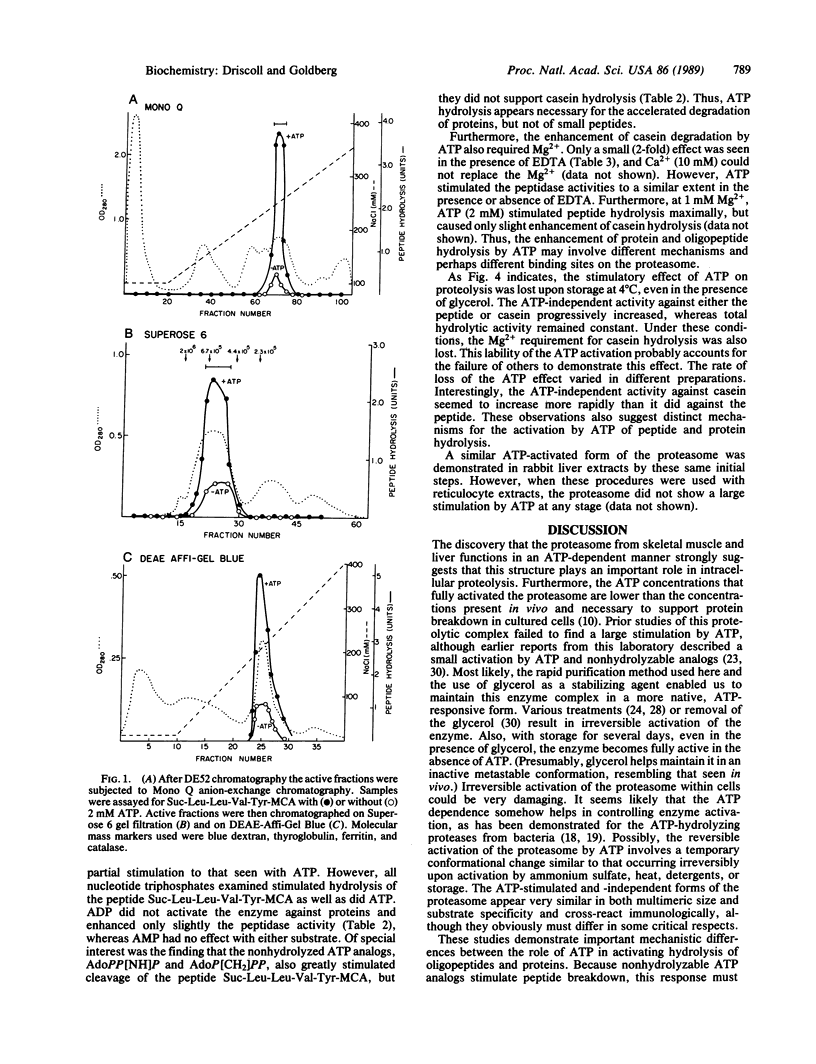
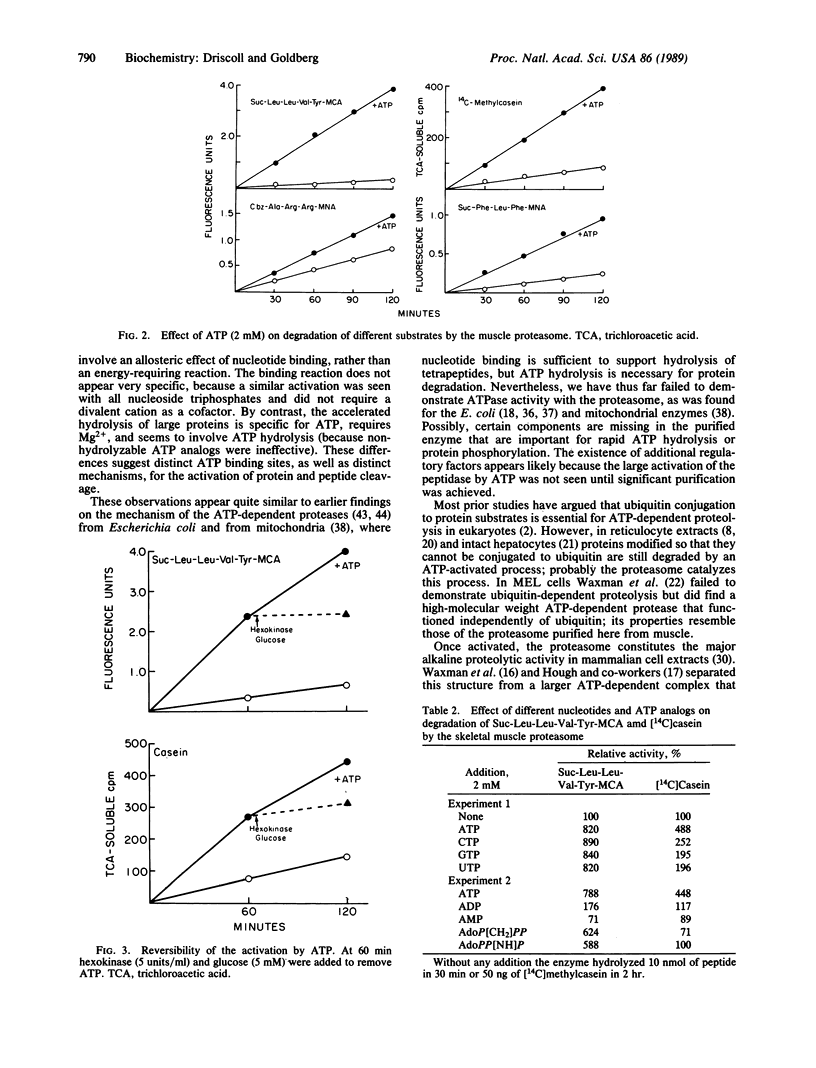
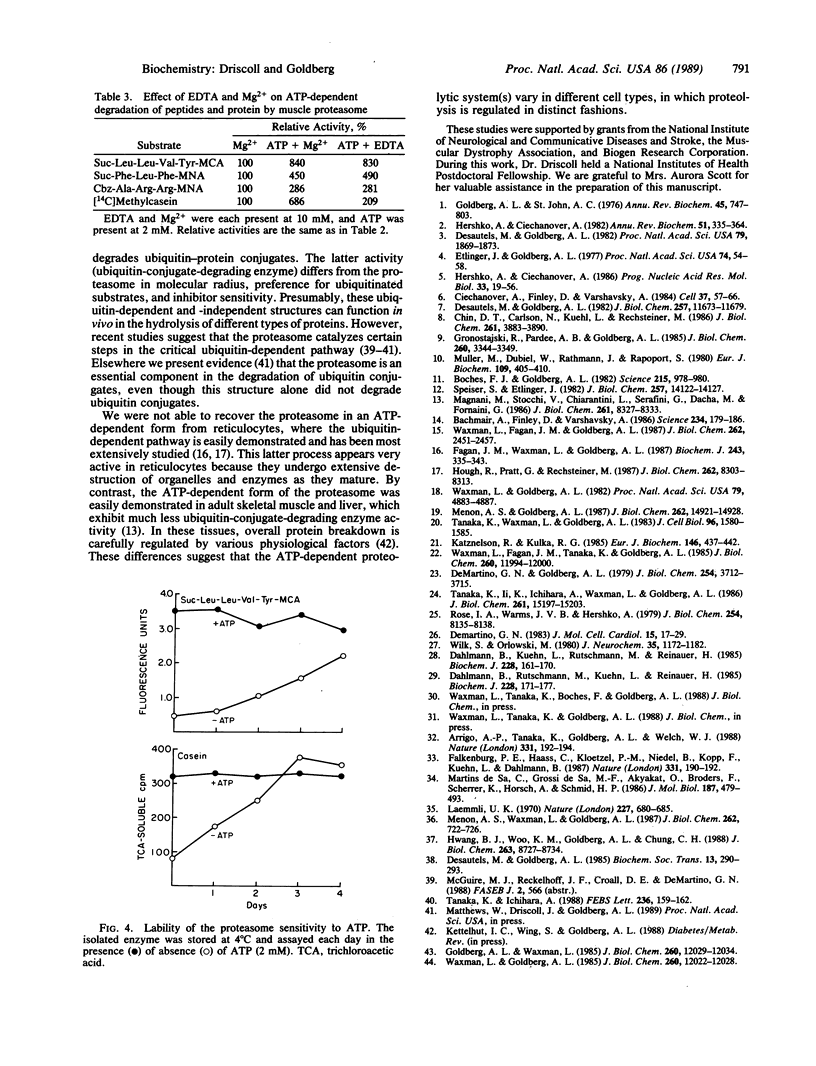
The proteasome (the multicatalytic endoproteinase complex) in mammalian tissues hydrolyzes proteins and several types of peptides. When this structure was isolated rapidly from rabbit skeletal muscle in the presence of glycerol, its various peptidase and protease activities showed a large reversible activation by physiological concentrations of ATP (Ka = 0.3-0.5 mM). Hydrolysis of succinyl-Leu-Leu-Val-Tyr-(4-methylcoumaryl-7-amide) was stimulated up to 12-fold by ATP, whereas degradation of casein and bovine serum albumin increased 4- to 7-fold. Neither ADP nor AMP had any effect. CTP, GTP, UTP, and the nonhydrolyzable analogs adenosine 5'-[beta,gamma-imino]triphosphate (AMPP[NH]P) and adenosine 5'-[alpha,beta-methylene]triphosphate (AMP[CH2]PP) increased peptide hydrolysis as well as ATP did. However, only ATP stimulated casein breakdown and only in the presence of Mg2+. Thus, nucleotide binding allows activation of the peptidase functions, but ATP hydrolysis seems necessary for enhanced degradation of proteins. The ATP effect on proteolysis was reversible and did not require ubiquitin. Sensitivity to ATP was labile, and with storage at 4 degrees C the enzyme became fully active in the absence of ATP or Mg2+. The ATP-activated form closely resembles the proteasome complex described previously, which did not show ATP dependence: both have molecular masses of 650 kDa, contain the same 8-10 subunits, and are precipitated by the same antibodies. A similar ATP-activated form was found in rabbit liver but not in rabbit reticulocytes. The proteasome seems to represent a ubiquitin-independent, ATP-stimulated proteolytic activity within nucleated mammalian cells.
Full text
PDF

Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Arrigo A. P., Tanaka K., Goldberg A. L., Welch W. J. Identity of the 19S 'prosome' particle with the large multifunctional protease complex of mammalian cells (the proteasome). Nature. 1988 Jan 14;331(6152):192–194. doi: 10.1038/331192a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bachmair A., Finley D., Varshavsky A. In vivo half-life of a protein is a function of its amino-terminal residue. Science. 1986 Oct 10;234(4773):179–186. doi: 10.1126/science.3018930. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Boches F. S., Goldberg A. L. Role for the adenosine triphosphate-dependent proteolytic pathway in reticulocyte maturation. Science. 1982 Feb 19;215(4535):978–980. doi: 10.1126/science.7156977. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chin D. T., Carlson N., Kuehl L., Rechsteiner M. The degradation of guanidinated lysozyme in reticulocyte lysate. J Biol Chem. 1986 Mar 15;261(8):3883–3890. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ciechanover A., Finley D., Varshavsky A. Ubiquitin dependence of selective protein degradation demonstrated in the mammalian cell cycle mutant ts85. Cell. 1984 May;37(1):57–66. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(84)90300-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dahlmann B., Kuehn L., Rutschmann M., Reinauer H. Purification and characterization of a multicatalytic high-molecular-mass proteinase from rat skeletal muscle. Biochem J. 1985 May 15;228(1):161–170. doi: 10.1042/bj2280161. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dahlmann B., Rutschmann M., Kuehn L., Reinauer H. Activation of the multicatalytic proteinase from rat skeletal muscle by fatty acids or sodium dodecyl sulphate. Biochem J. 1985 May 15;228(1):171–177. doi: 10.1042/bj2280171. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- DeMartino G. N., Goldberg A. L. Identification and partial purification of an ATP-stimulated alkaline protease in rat liver. J Biol Chem. 1979 May 25;254(10):3712–3715. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- DeMartino G. N. Identification of a high molecular weight alkaline protease in rat heart. J Mol Cell Cardiol. 1983 Jan;15(1):17–29. doi: 10.1016/0022-2828(83)90304-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Desautels M., Goldberg A. L. Demonstration of an ATP-dependent, vanadate-sensitive endoprotease in the matrix of rat liver mitochondria. J Biol Chem. 1982 Oct 10;257(19):11673–11679. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Desautels M., Goldberg A. L. Liver mitochondria contain an ATP-dependent, vanadate-sensitive pathway for the degradation of proteins. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1982 Mar;79(6):1869–1873. doi: 10.1073/pnas.79.6.1869. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Desautels M., Goldberg A. L. The ATP-dependent breakdown of proteins in mammalian mitochondria. Biochem Soc Trans. 1985 Apr;13(2):290–293. doi: 10.1042/bst0130290. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Etlinger J. D., Goldberg A. L. A soluble ATP-dependent proteolytic system responsible for the degradation of abnormal proteins in reticulocytes. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1977 Jan;74(1):54–58. doi: 10.1073/pnas.74.1.54. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fagan J. M., Waxman L., Goldberg A. L. Skeletal muscle and liver contain a soluble ATP + ubiquitin-dependent proteolytic system. Biochem J. 1987 Apr 15;243(2):335–343. doi: 10.1042/bj2430335. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Falkenburg P. E., Haass C., Kloetzel P. M., Niedel B., Kopp F., Kuehn L., Dahlmann B. Drosophila small cytoplasmic 19S ribonucleoprotein is homologous to the rat multicatalytic proteinase. Nature. 1988 Jan 14;331(6152):190–192. doi: 10.1038/331190a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Goldberg A. L., St John A. C. Intracellular protein degradation in mammalian and bacterial cells: Part 2. Annu Rev Biochem. 1976;45:747–803. doi: 10.1146/annurev.bi.45.070176.003531. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Goldberg A. L., Waxman L. The role of ATP hydrolysis in the breakdown of proteins and peptides by protease La from Escherichia coli. J Biol Chem. 1985 Oct 5;260(22):12029–12034. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gronostajski R. M., Pardee A. B., Goldberg A. L. The ATP dependence of the degradation of short- and long-lived proteins in growing fibroblasts. J Biol Chem. 1985 Mar 25;260(6):3344–3349. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hershko A., Ciechanover A. Mechanisms of intracellular protein breakdown. Annu Rev Biochem. 1982;51:335–364. doi: 10.1146/annurev.bi.51.070182.002003. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hershko A., Ciechanover A. The ubiquitin pathway for the degradation of intracellular proteins. Prog Nucleic Acid Res Mol Biol. 1986;33:19-56, 301. doi: 10.1016/s0079-6603(08)60019-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hough R., Pratt G., Rechsteiner M. Purification of two high molecular weight proteases from rabbit reticulocyte lysate. J Biol Chem. 1987 Jun 15;262(17):8303–8313. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hwang B. J., Woo K. M., Goldberg A. L., Chung C. H. Protease Ti, a new ATP-dependent protease in Escherichia coli, contains protein-activated ATPase and proteolytic functions in distinct subunits. J Biol Chem. 1988 Jun 25;263(18):8727–8734. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Katznelson R., Kulka R. G. Effects of denaturation and methylation on the degradation of proteins in cultured hepatoma cells and in reticulocyte cell-free systems. Eur J Biochem. 1985 Jan 15;146(2):437–442. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1985.tb08670.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Laemmli U. K. Cleavage of structural proteins during the assembly of the head of bacteriophage T4. Nature. 1970 Aug 15;227(5259):680–685. doi: 10.1038/227680a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Magnani M., Stocchi V., Chiarantini L., Serafini G., Dachà M., Fornaini G. Rabbit red blood cell hexokinase. Decay mechanism during reticulocyte maturation. J Biol Chem. 1986 Jun 25;261(18):8327–8333. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Martins de Sa C., Grossi de Sa M. F., Akhayat O., Broders F., Scherrer K., Horsch A., Schmid H. P. Prosomes. Ubiquity and inter-species structural variation. J Mol Biol. 1986 Feb 20;187(4):479–493. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(86)90328-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Menon A. S., Goldberg A. L. Binding of nucleotides to the ATP-dependent protease La from Escherichia coli. J Biol Chem. 1987 Nov 5;262(31):14921–14928. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Menon A. S., Waxman L., Goldberg A. L. The energy utilized in protein breakdown by the ATP-dependent protease (La) from Escherichia coli. J Biol Chem. 1987 Jan 15;262(2):722–726. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Müller M., Dubiel W., Rathmann J., Rapoport S. Determination and characteristics of energy-dependent proteolysis in rabbit reticulocytes. Eur J Biochem. 1980 Aug;109(2):405–410. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1980.tb04808.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rose I. A., Warms J. V., Hershko A. A high molecular weight protease in liver cytosol. J Biol Chem. 1979 Sep 10;254(17):8135–8138. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Speiser S., Etlinger J. D. Loss of ATP-dependent proteolysis with maturation of reticulocytes and erythrocytes. J Biol Chem. 1982 Dec 10;257(23):14122–14127. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tanaka K., Ichihara A. Involvement of proteasomes (multicatalytic proteinase) in ATP-dependent proteolysis in rat reticulocyte extracts. FEBS Lett. 1988 Aug 15;236(1):159–162. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(88)80306-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tanaka K., Ii K., Ichihara A., Waxman L., Goldberg A. L. A high molecular weight protease in the cytosol of rat liver. I. Purification, enzymological properties, and tissue distribution. J Biol Chem. 1986 Nov 15;261(32):15197–15203. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tanaka K., Waxman L., Goldberg A. L. ATP serves two distinct roles in protein degradation in reticulocytes, one requiring and one independent of ubiquitin. J Cell Biol. 1983 Jun;96(6):1580–1585. doi: 10.1083/jcb.96.6.1580. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Waxman L., Fagan J. M., Goldberg A. L. Demonstration of two distinct high molecular weight proteases in rabbit reticulocytes, one of which degrades ubiquitin conjugates. J Biol Chem. 1987 Feb 25;262(6):2451–2457. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Waxman L., Fagan J. M., Tanaka K., Goldberg A. L. A soluble ATP-dependent system for protein degradation from murine erythroleukemia cells. Evidence for a protease which requires ATP hydrolysis but not ubiquitin. J Biol Chem. 1985 Oct 5;260(22):11994–12000. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Waxman L., Goldberg A. L. Protease La from Escherichia coli hydrolyzes ATP and proteins in a linked fashion. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1982 Aug;79(16):4883–4887. doi: 10.1073/pnas.79.16.4883. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Waxman L., Goldberg A. L. Protease La, the lon gene product, cleaves specific fluorogenic peptides in an ATP-dependent reaction. J Biol Chem. 1985 Oct 5;260(22):12022–12028. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wilk S., Orlowski M. Cation-sensitive neutral endopeptidase: isolation and specificity of the bovine pituitary enzyme. J Neurochem. 1980 Nov;35(5):1172–1182. doi: 10.1111/j.1471-4159.1980.tb07873.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]



