Abstract
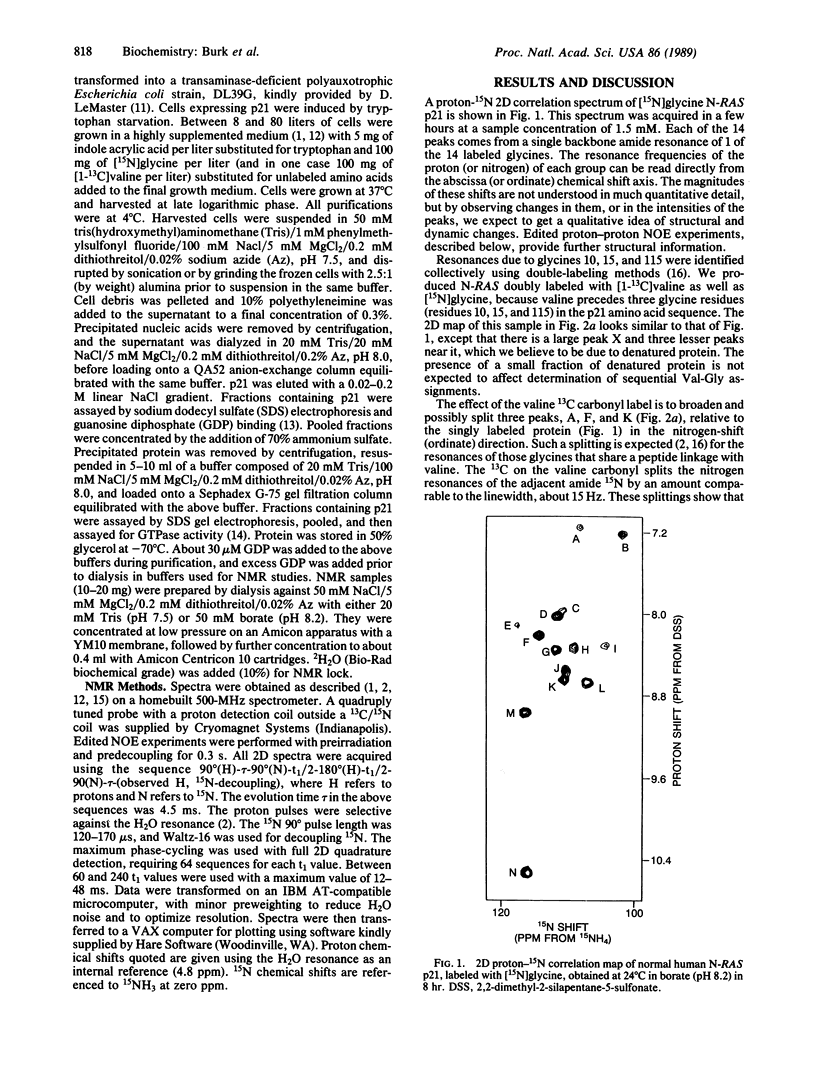
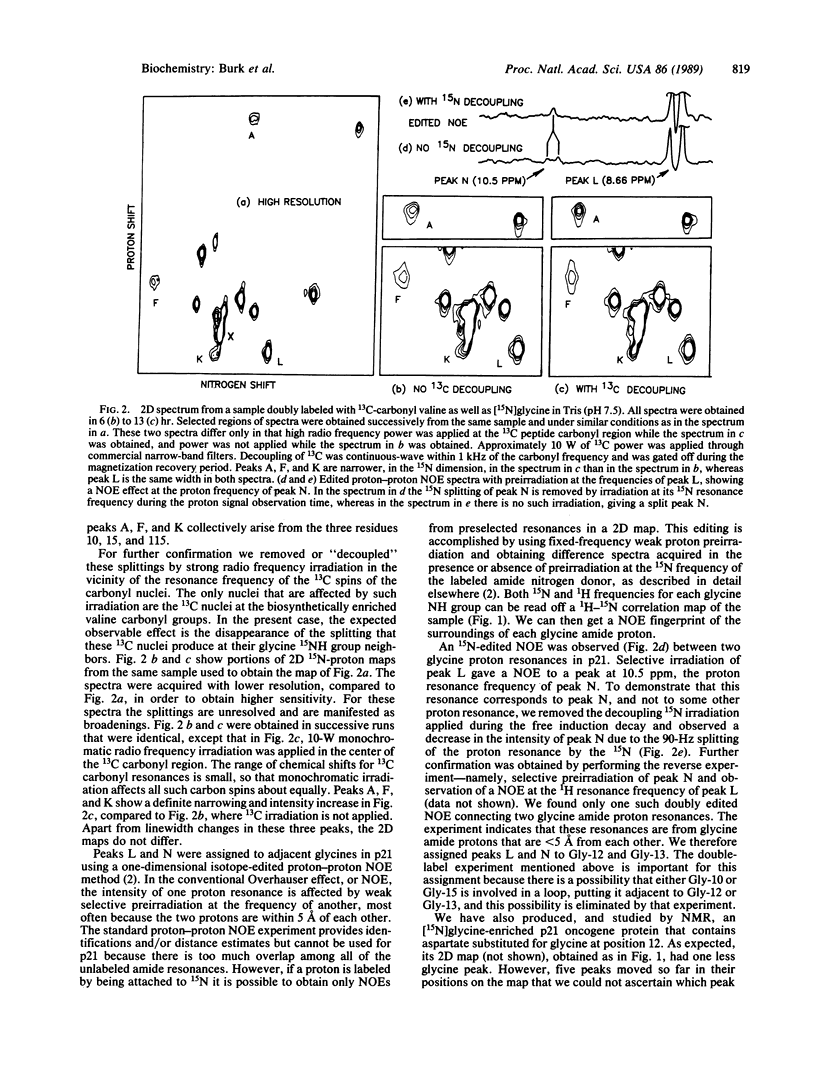
A sample of Escherichia coli-expressed human N-RAS-encoded p21, a 21-kDa protein, was selectively labeled with 15N at each of the 14 glycine amide positions. Two-dimensional proton-observe 15N correlation spectra showed one peak for each glycine residue. Five glycine resonances were identified with residues near the nucleotide binding site and provide useful reporters of several oncogene-activating positions. Three of these resonances were assigned to residues 10, 15, and 115 from the spectrum of a sample that was also labeled with [13C]valine. These resonances showed extra splitting or broadening due to the 13C label, which could be eliminated by 13C decoupling. Two other peaks were unambiguously identified as Gly-12 and Gly-13 using a one-dimensional edited nuclear Overhauser experiment and by spectral comparison with an Asp-12 mutant. These assignments have provided several site-specific probes of critical domains in p21.
Full text
PDF

Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Barbacid M. ras genes. Annu Rev Biochem. 1987;56:779–827. doi: 10.1146/annurev.bi.56.070187.004023. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Griffey R. H., Redfield A. G., Loomis R. E., Dahlquist F. W. Nuclear magnetic resonance observation and dynamics of specific amide protons in T4 lysozyme. Biochemistry. 1985 Feb 12;24(4):817–822. doi: 10.1021/bi00325a001. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Griffey R. H., Redfield A. G. Proton-detected heteronuclear edited and correlated nuclear magnetic resonance and nuclear Overhauser effect in solution. Q Rev Biophys. 1987 Feb;19(1-2):51–82. doi: 10.1017/s0033583500004029. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hattori S., Ulsh L. S., Halliday K., Shih T. Y. Biochemical properties of a highly purified v-rasH p21 protein overproduced in Escherichia coli and inhibition of its activities by a monoclonal antibody. Mol Cell Biol. 1985 Jun;5(6):1449–1455. doi: 10.1128/mcb.5.6.1449. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jurnak F. Structure of the GDP domain of EF-Tu and location of the amino acids homologous to ras oncogene proteins. Science. 1985 Oct 4;230(4721):32–36. doi: 10.1126/science.3898365. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kainosho M., Tsuji T. Assignment of the three methionyl carbonyl carbon resonances in Streptomyces subtilisin inhibitor by a carbon-13 and nitrogen-15 double-labeling technique. A new strategy for structural studies of proteins in solution. Biochemistry. 1982 Nov 23;21(24):6273–6279. doi: 10.1021/bi00267a036. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- LeMaster D. M., Richards F. M. NMR sequential assignment of Escherichia coli thioredoxin utilizing random fractional deuteriation. Biochemistry. 1988 Jan 12;27(1):142–150. doi: 10.1021/bi00401a022. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Manne V., Bekesi E., Kung H. F. Ha-ras proteins exhibit GTPase activity: point mutations that activate Ha-ras gene products result in decreased GTPase activity. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1985 Jan;82(2):376–380. doi: 10.1073/pnas.82.2.376. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McCormick F., Clark B. F., la Cour T. F., Kjeldgaard M., Norskov-Lauritsen L., Nyborg J. A model for the tertiary structure of p21, the product of the ras oncogene. Science. 1985 Oct 4;230(4721):78–82. doi: 10.1126/science.3898366. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McIntosh L. P., Griffey R. H., Muchmore D. C., Nielson C. P., Redfield A. G., Dahlquist F. W. Proton NMR measurements of bacteriophage T4 lysozyme aided by 15N isotopic labeling: structural and dynamic studies of larger proteins. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1987 Mar;84(5):1244–1248. doi: 10.1073/pnas.84.5.1244. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Torchia D. A., Sparks S. W., Bax A. NMR signal assignments of amide protons in the alpha-helical domains of staphylococcal nuclease. Biochemistry. 1988 Jul 12;27(14):5135–5141. doi: 10.1021/bi00414a028. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Trahey M., Milley R. J., Cole G. E., Innis M., Paterson H., Marshall C. J., Hall A., McCormick F. Biochemical and biological properties of the human N-ras p21 protein. Mol Cell Biol. 1987 Jan;7(1):541–544. doi: 10.1128/mcb.7.1.541. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- de Vos A. M., Tong L., Milburn M. V., Matias P. M., Jancarik J., Noguchi S., Nishimura S., Miura K., Ohtsuka E., Kim S. H. Three-dimensional structure of an oncogene protein: catalytic domain of human c-H-ras p21. Science. 1988 Feb 19;239(4842):888–893. doi: 10.1126/science.2448879. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]



