Abstract
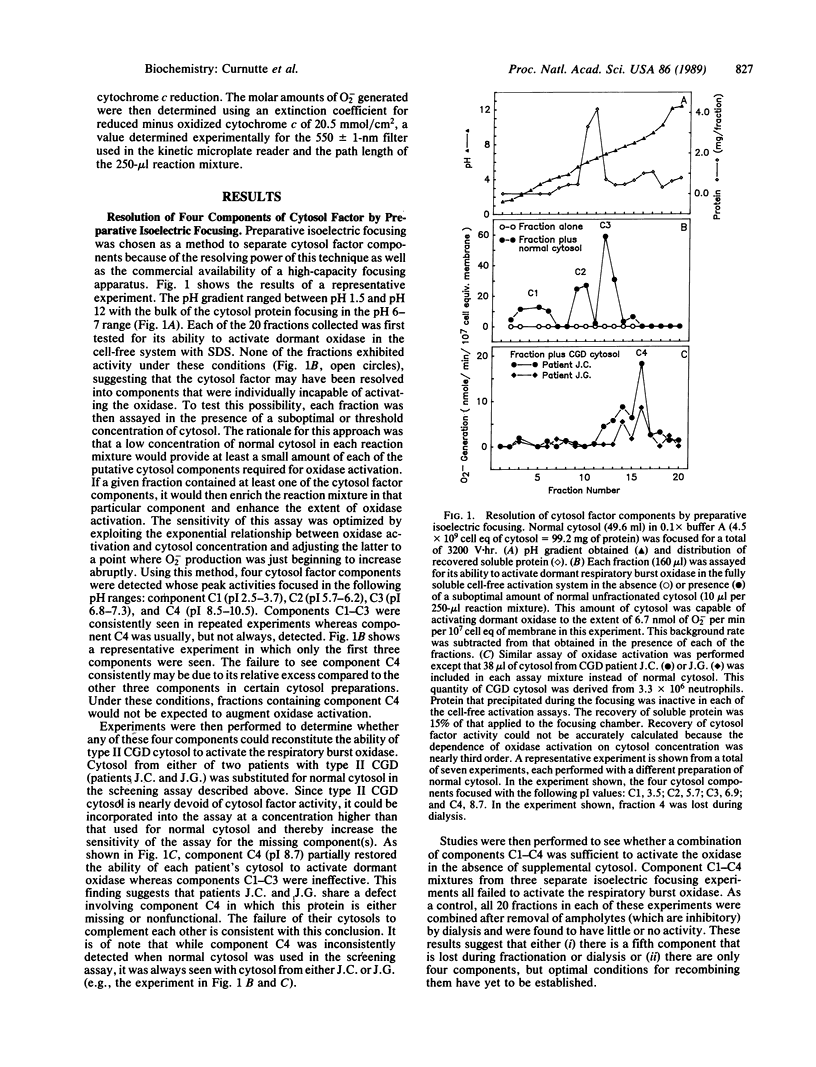
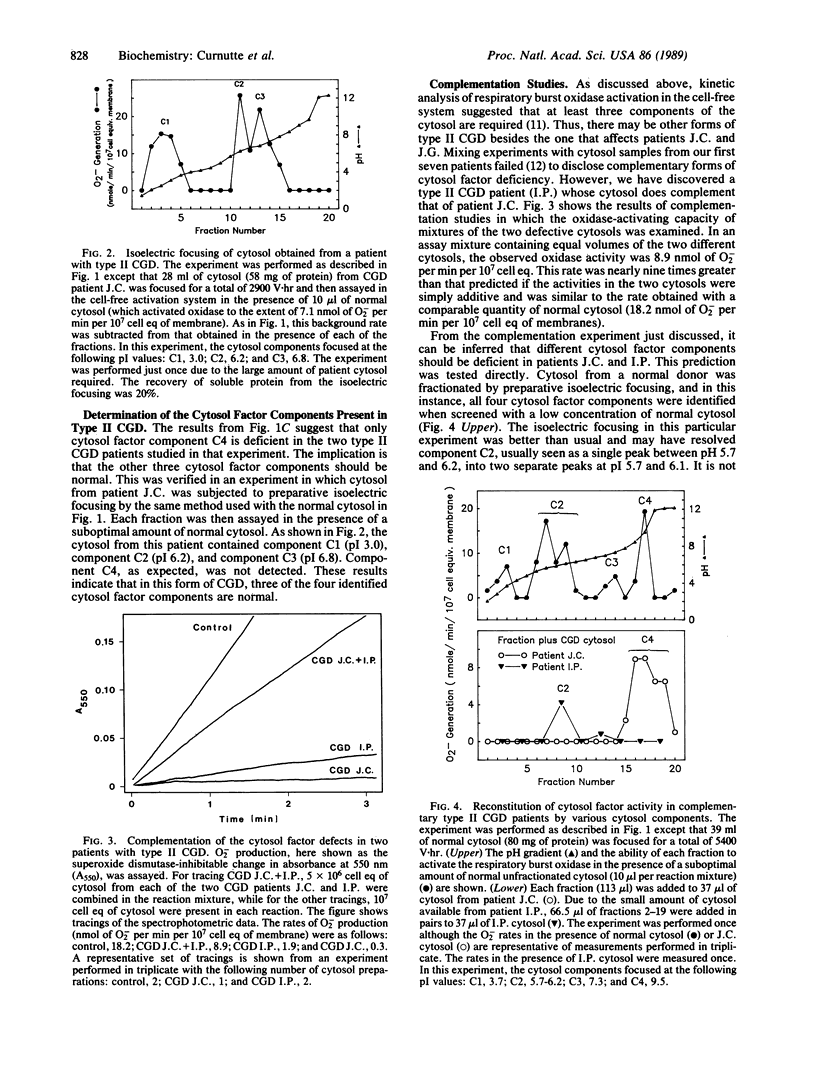
The respiratory burst oxidase of neutrophils can be activated in a cell-free system in which plasma membranes, cytosol, Mg2+, and a membrane-perturbing detergent, such as arachidonate or sodium dodecyl sulfate, are all required. Using the technique of preparative isoelectric focusing, the cytosol factor required for oxidase activation was resolved into four components termed C1-C4 with respective pI values of approximately 3.1, 6.0, 7.0, and 9.5. Individually, these components were incapable of activating the oxidase and could only be detected in the presence of suboptimal amounts of normal cytosol that served to supply at least a limited amount of each of the required components. Attempts to activate the oxidase with a combination of the four components failed, suggesting that there might be a yet undetected fifth cytosolic component. Patients with autosomal recessive cytochrome b-positive chronic granulomatous disease (type II CGD) are severely deficient in cytosol factor activity. When added to cytosol samples from two patients with this form of CGD, component C4 restored the ability of each patient's cytosol to activate dormant oxidase. None of the other three cytosol factor components (C1-C3) was effective in this regard, a finding supported by the direct demonstration that these three components were present in normal amounts in this type of CGD. A different form of type II CGD was identified in a third patient on the basis of complementation studies in which the patient's cytosol was able to activate the oxidase in the cell-free system when mixed with cytosol from one of the first two patients. The defect in this third patient's cytosol could be partially corrected by component C2, but not component C4, obtained from normal cytosol. These findings indicate that the role of cytosol in the activation of the respiratory burst oxidase is more complex than previously appreciated in that at least four cytosolic components appear to be required. Defects in two of these components have now been identified and appear to be responsible for two biochemically distinct forms of CGD.
Full text
PDF


Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Babior B. M., Kuver R., Curnutte J. T. Kinetics of activation of the respiratory burst oxidase in a fully soluble system from human neutrophils. J Biol Chem. 1988 Feb 5;263(4):1713–1718. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Babior B. M. Oxygen-dependent microbial killing by phagocytes (first of two parts). N Engl J Med. 1978 Mar 23;298(12):659–668. doi: 10.1056/NEJM197803232981205. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bromberg Y., Pick E. Activation of NADPH-dependent superoxide production in a cell-free system by sodium dodecyl sulfate. J Biol Chem. 1985 Nov 5;260(25):13539–13545. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bromberg Y., Pick E. Unsaturated fatty acids stimulate NADPH-dependent superoxide production by cell-free system derived from macrophages. Cell Immunol. 1984 Oct 1;88(1):213–221. doi: 10.1016/0008-8749(84)90066-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Caldwell S. E., McCall C. E., Hendricks C. L., Leone P. A., Bass D. A., McPhail L. C. Coregulation of NADPH oxidase activation and phosphorylation of a 48-kD protein(s) by a cytosolic factor defective in autosomal recessive chronic granulomatous disease. J Clin Invest. 1988 May;81(5):1485–1496. doi: 10.1172/JCI113480. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Curnutte J. T. Activation of human neutrophil nicotinamide adenine dinucleotide phosphate, reduced (triphosphopyridine nucleotide, reduced) oxidase by arachidonic acid in a cell-free system. J Clin Invest. 1985 May;75(5):1740–1743. doi: 10.1172/JCI111885. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Curnutte J. T., Babior B. M. Chronic granulomatous disease. Adv Hum Genet. 1987;16:229–297. doi: 10.1007/978-1-4757-0620-8_4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Curnutte J. T., Berkow R. L., Roberts R. L., Shurin S. B., Scott P. J. Chronic granulomatous disease due to a defect in the cytosolic factor required for nicotinamide adenine dinucleotide phosphate oxidase activation. J Clin Invest. 1988 Feb;81(2):606–610. doi: 10.1172/JCI113360. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Curnutte J. T., Kuver R., Babior B. M. Activation of the respiratory burst oxidase in a fully soluble system from human neutrophils. J Biol Chem. 1987 May 15;262(14):6450–6452. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Curnutte J. T., Kuver R., Scott P. J. Activation of neutrophil NADPH oxidase in a cell-free system. Partial purification of components and characterization of the activation process. J Biol Chem. 1987 Apr 25;262(12):5563–5569. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dinauer M. C., Orkin S. H., Brown R., Jesaitis A. J., Parkos C. A. The glycoprotein encoded by the X-linked chronic granulomatous disease locus is a component of the neutrophil cytochrome b complex. 1987 Jun 25-Jul 1Nature. 327(6124):717–720. doi: 10.1038/327717a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Glass G. A., DeLisle D. M., DeTogni P., Gabig T. G., Magee B. H., Markert M., Babior B. M. The respiratory burst oxidase of human neutrophils. Further studies of the purified enzyme. J Biol Chem. 1986 Oct 5;261(28):13247–13251. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hayakawa T., Suzuki K., Suzuki S., Andrews P. C., Babior B. M. A possible role for protein phosphorylation in the activation of the respiratory burst in human neutrophils. Evidence from studies with cells from patients with chronic granulomatous disease. J Biol Chem. 1986 Jul 15;261(20):9109–9115. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Heyneman R. A., Vercauteren R. E. Activation of a NADPH oxidase from horse polymorphonuclear leukocytes in a cell-free system. J Leukoc Biol. 1984 Dec;36(6):751–759. doi: 10.1002/jlb.36.6.751. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Heyworth P. G., Segal A. W. Further evidence for the involvement of a phosphoprotein in the respiratory burst oxidase of human neutrophils. Biochem J. 1986 Nov 1;239(3):723–731. doi: 10.1042/bj2390723. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McPhail L. C., Shirley P. S., Clayton C. C., Snyderman R. Activation of the respiratory burst enzyme from human neutrophils in a cell-free system. Evidence for a soluble cofactor. J Clin Invest. 1985 May;75(5):1735–1739. doi: 10.1172/JCI111884. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Okamura N., Curnutte J. T., Roberts R. L., Babior B. M. Relationship of protein phosphorylation to the activation of the respiratory burst in human neutrophils. Defects in the phosphorylation of a group of closely related 48-kDa proteins in two forms of chronic granulomatous disease. J Biol Chem. 1988 May 15;263(14):6777–6782. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Okamura N., Malawista S. E., Roberts R. L., Rosen H., Ochs H. D., Babior B. M., Curnutte J. T. Phosphorylation of the oxidase-related 48K phosphoprotein family in the unusual autosomal cytochrome-negative and X-linked cytochrome-positive types of chronic granulomatous disease. Blood. 1988 Aug;72(2):811–816. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Peerless A. G., Liebhaber M., Anderson S., Lehrer R. I., Stiehm E. R. Legionella pneumonia in chronic granulomatous disease. J Pediatr. 1985 May;106(5):783–785. doi: 10.1016/s0022-3476(85)80355-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Weening R. S., Corbeel L., de Boer M., Lutter R., van Zwieten R., Hamers M. N., Roos D. Cytochrome b deficiency in an autosomal form of chronic granulomatous disease. A third form of chronic granulomatous disease recognized by monocyte hybridization. J Clin Invest. 1985 Mar;75(3):915–920. doi: 10.1172/JCI111792. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]



